Are you experiencing a painful or scratchy throat? Why My Throat Hurts is a common question, and at WHY.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the causes, symptoms, and effective remedies for sore throats, ensuring you can find relief and prevent future occurrences. This guide explores various factors, from viral infections to environmental irritants, and offers practical advice for soothing your throat and promoting faster recovery. Discover expert-backed information and personalized solutions to address your specific needs.
1. What Are The Common Causes Of Sore Throat?
The most frequent culprits behind a sore throat include viral infections, bacterial infections, environmental factors, and other underlying medical conditions. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for effective treatment.
1.1. Viral Infections
Viral infections are the most common cause of sore throats. These infections inflame the throat, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Common Cold: A sore throat is often one of the first symptoms of a cold. According to the CDC, adults typically experience two to three colds per year, making this a frequent cause of throat pain.
- Flu (Influenza): The flu can also cause a sore throat, often accompanied by fever, body aches, and fatigue. The severity and duration of symptoms vary depending on the influenza strain.
- Mononucleosis (Mono): This viral infection, often caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), can lead to a severe sore throat, along with fatigue, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Virology highlights the prevalence of EBV and its potential to cause mononucleosis.
- COVID-19: Sore throat has been identified as one of the common symptoms of COVID-19 and its variants.
1.2. Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections can also cause a sore throat. These infections often require treatment with antibiotics to prevent complications.
- Strep Throat: Caused by the Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, strep throat is a common bacterial infection that can lead to severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and fever. The CDC reports that strep throat is most common in children between 5 and 15 years old.
- Tonsillitis: Inflammation of the tonsils, often due to bacterial infection, can cause a sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Recurrent tonsillitis may require surgical removal of the tonsils.
- Epiglottitis: This rare but serious infection involves inflammation of the epiglottis, the flap that covers the trachea. Epiglottitis can cause severe throat pain and breathing difficulties, requiring immediate medical attention.
1.3. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can irritate the throat, leading to soreness and discomfort.
- Dry Air: Dry air can dehydrate the throat, causing irritation and pain. Using a humidifier can help maintain moisture levels and alleviate discomfort.
- Irritants: Exposure to pollutants, smoke, and chemical fumes can irritate the throat lining, resulting in soreness. Avoiding these irritants can help prevent throat pain.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to pollen, dust, and pet dander can cause inflammation in the throat, leading to a sore throat. Antihistamines and allergy management strategies can help reduce symptoms.
- Acid Reflux: Also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), acid reflux can cause stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus and throat, leading to irritation and a sore throat. A study in the American Journal of Gastroenterology discusses the connection between GERD and throat symptoms.
1.4. Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can contribute to a sore throat. Understanding these conditions is important for effective management.
- Postnasal Drip: Excessive mucus production can drip down the back of the throat, causing irritation and soreness. Addressing the underlying cause of postnasal drip can alleviate throat pain.
- Tumors: Although rare, tumors in the throat, tongue, or larynx can cause persistent sore throat. Medical evaluation is necessary to rule out this possibility.
- HIV Infection: HIV can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections that cause sore throat. Early diagnosis and treatment of HIV can improve immune function and reduce the risk of opportunistic infections.
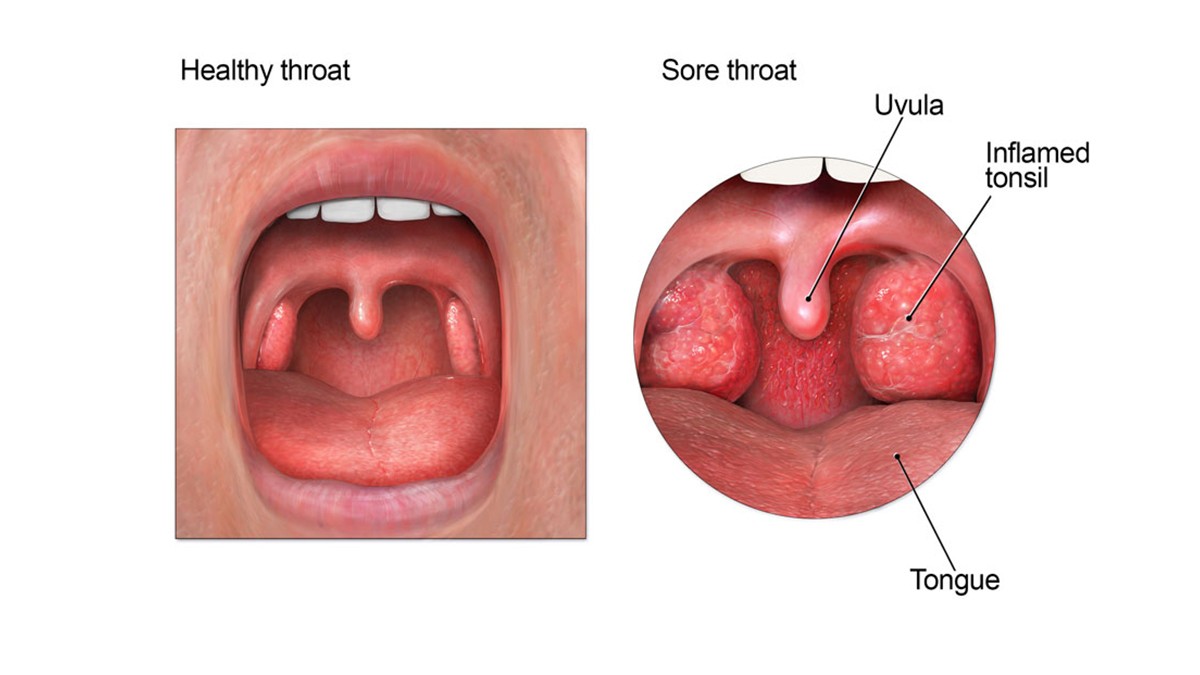 Throat anatomy showing tonsils, uvula, and larynx, highlighting common sore throat locations.
Throat anatomy showing tonsils, uvula, and larynx, highlighting common sore throat locations.
2. What Are The Distinct Symptoms Of A Sore Throat?
Identifying the specific symptoms of a sore throat is essential for determining its cause and seeking appropriate treatment. Common symptoms include pain, difficulty swallowing, a scratchy sensation, and other related signs.
2.1. Pain And Discomfort
The most common symptom of a sore throat is pain, which can range from mild to severe.
- Throat Pain: This can be a constant ache or a sharp pain that worsens when swallowing or talking. The intensity of the pain often correlates with the severity of the underlying cause.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Odynophagia): Swallowing can become painful and difficult, making it challenging to eat and drink. This symptom is particularly common in cases of severe inflammation or infection.
- Pain Radiating To The Ears: Sometimes, throat pain can radiate to the ears, causing additional discomfort. This is due to the shared nerve pathways between the throat and ears.
2.2. Scratchy Sensation
A scratchy or itchy sensation in the throat is another common symptom.
- Irritation: The throat may feel irritated or raw, as if something is constantly scratching it. This sensation can be particularly bothersome and may lead to frequent throat clearing.
- Dryness: The throat may feel dry and parched, especially in dry environments or when dehydrated. Dryness can exacerbate the scratchy sensation and increase discomfort.
2.3. Other Related Symptoms
In addition to pain and a scratchy sensation, other symptoms can accompany a sore throat, providing clues about the underlying cause.
- Fever: A fever often indicates an infection, such as strep throat or the flu. Monitoring body temperature can help track the progression of the illness.
- Cough: A cough may accompany a sore throat, especially if the cause is a viral infection like a cold or the flu. The cough can be dry or productive, depending on the specific infection.
- Runny Nose: A runny nose is a common symptom of viral infections, such as the common cold. Nasal congestion and discharge can contribute to throat irritation.
- Hoarseness: Changes in voice quality, such as hoarseness, can occur if the vocal cords are inflamed. This symptom is common in laryngitis and other throat infections.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged and tender lymph nodes in the neck can indicate an infection. Lymph nodes play a role in the immune response, and swelling is a sign that they are actively fighting off an infection.
- Headache: Headaches can accompany a sore throat, especially if the cause is a viral infection like the flu or mononucleosis. Pain relievers can help alleviate this symptom.
3. How Can I Treat A Sore Throat At Home?
Many sore throats can be effectively managed at home with simple remedies. These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
3.1. Home Remedies
Several home remedies can provide relief from a sore throat.
- Gargling With Salt Water: Gargling with warm salt water can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the throat. A study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that gargling with salt water can reduce the severity of upper respiratory infections. Mix 1/4 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of warm water and gargle for 30 seconds several times a day.
- Honey: Honey has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe a sore throat. A study published in Pediatrics showed that honey is an effective cough suppressant and can help reduce throat irritation. Add a tablespoon of honey to warm water or tea and drink it several times a day. Note: Honey should not be given to children under 1 year of age due to the risk of botulism.
- Warm Liquids: Drinking warm liquids such as herbal tea, broth, or lemon water can help soothe the throat and relieve discomfort. Warm liquids can also help loosen congestion and promote hydration.
- Cool Liquids And Foods: Sucking on ice chips, popsicles, or cold beverages can help numb the throat and reduce pain. Cold foods like yogurt or smoothies can also be soothing.
- Humidifier: Using a humidifier can add moisture to the air, preventing dryness and irritation in the throat. This is especially helpful during the winter months when indoor air tends to be dry.
3.2. Over-The-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide relief from sore throat symptoms.
- Pain Relievers: OTC pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can help reduce pain and fever. Always follow the recommended dosage instructions.
- Throat Lozenges And Sprays: Throat lozenges and sprays containing menthol, benzocaine, or phenol can provide temporary relief from throat pain. These products often work by numbing the throat or providing a cooling sensation.
- Decongestants: If a sore throat is accompanied by nasal congestion, decongestants can help clear the nasal passages and reduce postnasal drip. Decongestants are available in oral and nasal spray forms.
- Antihistamines: If allergies are contributing to the sore throat, antihistamines can help reduce inflammation and other allergy symptoms.
3.3. Rest And Hydration
Rest and hydration are crucial for recovery from a sore throat.
- Adequate Rest: Getting plenty of rest allows the body to focus on healing and fighting off infection. Avoid strenuous activities and prioritize sleep.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps keep the throat moist and prevents dehydration. Water, juice, herbal tea, and broth are all good choices.
4. When Should I Seek Medical Attention For A Sore Throat?
While many sore throats can be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant medical attention. Prompt medical evaluation can help prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
4.1. Severe Symptoms
Severe symptoms that require medical attention include:
- Difficulty Breathing: If you experience difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, seek immediate medical attention. This could indicate a serious condition such as epiglottitis or severe tonsillitis.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Severe difficulty swallowing that prevents you from eating or drinking is a sign of significant inflammation or infection.
- High Fever: A high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C) may indicate a bacterial infection such as strep throat.
- Severe Throat Pain: Intense throat pain that does not improve with home remedies may require medical evaluation.
- Blood In Saliva Or Phlegm: Coughing up blood or noticing blood in your saliva or phlegm is a concerning symptom that requires medical attention.
4.2. Signs Of Bacterial Infection
Signs of a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, include:
- Sudden Onset Of Sore Throat: A sore throat that comes on suddenly and is not accompanied by cold symptoms may be strep throat.
- White Patches On Tonsils: White or yellow patches on the tonsils can indicate a bacterial infection.
- Red And Swollen Tonsils: Red and swollen tonsils are a common sign of tonsillitis or strep throat.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged and tender lymph nodes in the neck can indicate a bacterial infection.
- Rash: A fine, sandpaper-like rash, known as scarlet fever, can accompany strep throat.
4.3. Persistent Symptoms
If a sore throat persists for more than a week or worsens despite home treatment, it’s important to seek medical attention.
- Prolonged Sore Throat: A sore throat that lasts longer than a week may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires diagnosis and treatment.
- Worsening Symptoms: If symptoms worsen despite home remedies, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
- Recurrent Sore Throats: Experiencing frequent sore throats may indicate a chronic condition such as chronic tonsillitis or acid reflux.
5. How Can I Prevent Sore Throats?
Preventing sore throats involves practicing good hygiene and avoiding exposure to irritants and infections.
5.1. Good Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of infections that cause sore throats.
- Wash Hands Frequently: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching surfaces in public places and before eating.
- Use Hand Sanitizer: When soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, as this can transfer germs from your hands to your respiratory system.
- Cover Your Mouth And Nose: Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets.
5.2. Lifestyle Adjustments
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can help reduce the risk of developing a sore throat.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid exposure to smoke, pollutants, and chemical fumes, as these can irritate the throat lining.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep the throat moist and prevent dryness.
- Use A Humidifier: Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air, especially during the winter months.
- Avoid Close Contact With Sick People: Avoid close contact with people who have sore throats, colds, or other respiratory infections.
5.3. Boosting Immune System
A strong immune system can help prevent infections that cause sore throats.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to function properly.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost your immune system.
- Adequate Sleep: Get enough sleep to allow your body to repair and rejuvenate.
- Stress Management: Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Vitamin C and D: Supplements, such as vitamin C and vitamin D, play a crucial role in immune system health.
6. What Is Strep Throat And How Is It Different From A Regular Sore Throat?
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, while a regular sore throat can be caused by various factors, including viruses and environmental irritants. Understanding the differences between these conditions is important for proper diagnosis and treatment.
6.1. Causes
The primary difference between strep throat and a regular sore throat lies in their causes.
- Strep Throat: Strep throat is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. This bacteria is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Regular Sore Throat: A regular sore throat can be caused by various factors, including viral infections (such as the common cold or flu), environmental irritants (such as dry air or pollutants), allergies, and acid reflux.
6.2. Symptoms
While some symptoms overlap, there are distinct differences in the symptoms of strep throat and a regular sore throat.
- Strep Throat: Symptoms of strep throat often include a sudden onset of sore throat, difficulty swallowing, red and swollen tonsils, white patches on the tonsils, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, fever, and sometimes a fine, sandpaper-like rash (scarlet fever).
- Regular Sore Throat: Symptoms of a regular sore throat can vary depending on the cause. Viral sore throats are often accompanied by other cold symptoms, such as a runny nose, cough, and congestion. Sore throats caused by environmental irritants or allergies may include a scratchy sensation, dryness, and mild pain.
6.3. Diagnosis
The diagnosis of strep throat requires a medical evaluation and laboratory testing.
- Strep Throat: Strep throat is typically diagnosed using a rapid strep test or a throat culture. A rapid strep test can provide results within minutes, while a throat culture takes 24-48 hours.
- Regular Sore Throat: A regular sore throat is usually diagnosed based on symptoms and a physical examination. If symptoms are severe or persistent, further testing may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
6.4. Treatment
The treatment for strep throat and a regular sore throat differs significantly.
- Strep Throat: Strep throat is treated with antibiotics, which help kill the bacteria and prevent complications such as rheumatic fever and kidney inflammation. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve.
- Regular Sore Throat: A regular sore throat is typically treated with home remedies and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. Antibiotics are not effective for viral sore throats.
7. How Does A Sore Throat Affect Children Differently Than Adults?
Sore throats can affect children and adults differently due to variations in immune systems and common causes. Understanding these differences is crucial for providing appropriate care and treatment.
7.1. Common Causes
The common causes of sore throats can vary between children and adults.
- Children: Children are more prone to viral and bacterial infections, such as strep throat and tonsillitis. The CDC reports that strep throat is most common in children between 5 and 15 years old.
- Adults: Adults are more likely to experience sore throats due to environmental irritants, allergies, acid reflux, and postnasal drip.
7.2. Symptoms
Symptoms of a sore throat can manifest differently in children and adults.
- Children: Children may have difficulty expressing their symptoms, leading to irritability, decreased appetite, and drooling. They may also experience higher fevers and more severe symptoms with infections like strep throat.
- Adults: Adults may be better able to describe their symptoms and may experience a wider range of symptoms, including hoarseness, cough, and headache.
7.3. Complications
The potential complications of a sore throat can differ between children and adults.
- Children: Children are at a higher risk of developing complications from strep throat, such as rheumatic fever and kidney inflammation. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is crucial to prevent these complications.
- Adults: Adults are less likely to develop complications from strep throat but may experience complications from other causes, such as chronic tonsillitis or acid reflux.
7.4. Treatment Considerations
Treatment considerations for sore throats can vary between children and adults.
- Children: When treating children, it is important to use age-appropriate medications and dosages. Aspirin should be avoided due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Honey should not be given to children under 1 year of age.
- Adults: Adults may have more options for over-the-counter medications and home remedies. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider if symptoms are severe or persistent.
8. What Role Does The Environment Play In Causing A Sore Throat?
The environment can significantly impact the occurrence and severity of sore throats. Factors such as air quality, humidity, and seasonal changes can all play a role.
8.1. Air Quality
Poor air quality can irritate the throat and increase the risk of sore throats.
- Pollution: Exposure to air pollution, such as smog and particulate matter, can irritate the throat lining and make it more susceptible to infections.
- Smoke: Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke can also irritate the throat and increase the risk of sore throats.
- Chemical Fumes: Exposure to chemical fumes and irritants in the workplace or at home can cause throat irritation and soreness.
8.2. Humidity
Humidity levels can impact the moisture content in the throat, affecting its susceptibility to irritation.
- Dry Air: Dry air can dehydrate the throat, causing irritation and pain. This is especially common during the winter months when indoor heating systems reduce humidity levels.
- Humid Air: While humid air can help keep the throat moist, excessively humid environments can promote the growth of mold and allergens, which can also contribute to sore throats.
8.3. Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes can influence the prevalence of infections and allergens that cause sore throats.
- Winter: During the winter months, people spend more time indoors, increasing the risk of viral infections such as the common cold and flu. Dry air from indoor heating systems can also contribute to throat irritation.
- Spring And Fall: During the spring and fall, pollen levels are high, leading to an increase in allergic reactions that can cause sore throats.
8.4. Geographic Location
Geographic location can also influence the risk of sore throats due to variations in climate and environmental factors.
- Urban Areas: People living in urban areas may be exposed to higher levels of air pollution, increasing their risk of sore throats.
- Dry Climates: People living in dry climates may be more prone to throat irritation due to low humidity levels.
- Coastal Areas: People living in coastal areas may be exposed to higher levels of allergens, such as mold and pollen, increasing their risk of sore throats.
9. Are There Any Long-Term Effects Of Untreated Sore Throat?
While most sore throats resolve on their own or with simple treatments, untreated sore throats can lead to various short-term and long-term complications, particularly if the underlying cause is a bacterial infection.
9.1. Short-Term Complications
Short-term complications of an untreated sore throat can include:
- Dehydration: Difficulty swallowing can lead to decreased fluid intake, resulting in dehydration.
- Sleep Disturbances: Throat pain and discomfort can interfere with sleep, leading to fatigue and decreased quality of life.
- Spread Of Infection: Untreated infections can spread to nearby tissues, leading to complications such as ear infections and sinus infections.
9.2. Long-Term Complications Of Strep Throat
If strep throat is left untreated, it can lead to serious long-term complications:
- Rheumatic Fever: Rheumatic fever is a serious inflammatory condition that can affect the heart, joints, brain, and skin. It is caused by an abnormal immune response to strep throat bacteria. Symptoms of rheumatic fever can include fever, joint pain, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
- Kidney Inflammation (Glomerulonephritis): Glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units (glomeruli). It can result from an untreated strep throat infection. Symptoms can include blood in the urine, swelling, and high blood pressure.
- Peritonsillar Abscess: A peritonsillar abscess is a collection of pus behind the tonsils. It can develop as a complication of tonsillitis or strep throat. Symptoms can include severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and fever.
9.3. Chronic Sore Throat
An untreated sore throat can sometimes become chronic, leading to persistent symptoms and reduced quality of life.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Chronic tonsillitis is a persistent inflammation of the tonsils, often caused by recurrent bacterial infections. Symptoms can include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Chronic Laryngitis: Chronic laryngitis is a persistent inflammation of the vocal cords, often caused by overuse, irritants, or acid reflux. Symptoms can include hoarseness, sore throat, and cough.
9.4. Other Potential Long-Term Effects
Other potential long-term effects of an untreated sore throat can include:
- Voice Changes: Chronic inflammation of the vocal cords can lead to permanent voice changes.
- Breathing Difficulties: Severe inflammation of the throat can lead to breathing difficulties.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Difficulty swallowing can lead to decreased food intake, resulting in nutritional deficiencies.
10. How Can WHY.EDU.VN Help Me Understand And Manage My Sore Throat?
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the discomfort and concern that come with a sore throat. That’s why we offer a range of resources and support to help you understand and manage your symptoms effectively.
10.1. Comprehensive Information And Expert Advice
Our website provides a wealth of information on the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for sore throats. We offer expert-backed advice and practical tips to help you find relief and prevent future occurrences.
10.2. Personalized Solutions
We recognize that every individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. That’s why we offer personalized solutions tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
10.3. Expert Consultations
If you have complex or persistent questions about your sore throat, our team of experts is here to help. Our experts can provide personalized guidance and support to help you manage your symptoms effectively.
10.4. Community Support
Connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges and share your experiences, insights, and tips. Our community provides a supportive and welcoming environment where you can learn from others and find encouragement.
10.5. Easy Access To Information
Our website is designed to be user-friendly and accessible, making it easy for you to find the information you need quickly and efficiently. Whether you’re looking for information on home remedies, over-the-counter medications, or when to seek medical attention, you’ll find it all at WHY.EDU.VN.
Why let a sore throat disrupt your life? Visit why.edu.vn today to ask questions, explore our resources, and connect with experts who can provide personalized solutions. Your path to relief starts here. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Sore Throat
1. What is the main cause of sore throat?
The most common cause of sore throat is viral infections, such as the common cold or flu.
2. How can I quickly relieve sore throat pain?
Gargling with warm salt water, drinking warm liquids, and using throat lozenges can provide quick relief.
3. Is strep throat more common in children?
Yes, strep throat is more common in children between the ages of 5 and 15.
4. Can allergies cause a sore throat?
Yes, allergic reactions to pollen, dust, and pet dander can cause inflammation and sore throat.
5. When should I see a doctor for a sore throat?
You should see a doctor if you have difficulty breathing, high fever, severe throat pain, or symptoms that persist for more than a week.
6. What are the symptoms of strep throat?
Symptoms of strep throat include sudden sore throat, difficulty swallowing, red and swollen tonsils, white patches on the tonsils, and fever.
7. How is strep throat treated?
Strep throat is treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria and prevent complications.
8. Can dry air cause a sore throat?
Yes, dry air can dehydrate the throat and cause irritation, leading to a sore throat.
9. Are there any natural remedies for a sore throat?
Yes, honey, lemon juice, and herbal teas are natural remedies that can help soothe a sore throat.
10. How can I prevent sore throats?
You can prevent sore throats by practicing good hygiene, avoiding irritants, and boosting your immune system.

