Why Is My Period Blood Brown On The First Day? It’s a common question, and at WHY.EDU.VN, we understand your concerns about changes in menstrual flow. Discover possible explanations, from oxidation to hormonal shifts, and know when to seek expert advice for your peace of mind. This comprehensive guide also explores light flow, old blood, and potential underlying causes.
1. Understanding Period Blood Color Changes
Typically, period blood is expected to be bright red, but variations in color can occur. Several factors can influence the color of your menstrual flow, ranging from oxidation to hormonal changes. Obstetrician and gynecologist Dr. Renita White explains, “Blood that is older has been oxidized, meaning it has reacted with oxygen. This oxidation leads to red blood turning a browner color.” Understanding these shifts helps in differentiating normal variations from potential health concerns.
2. The Science Behind the Color of Blood
Blood’s red color comes from hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Hemoglobin contains heme, which has iron. When iron binds to oxygen in the lungs, it turns red. But what causes the blood to turn brown? When blood is exposed to air, it oxidizes, changing from bright red to brown. This is similar to how a cut turns darker as it heals.
Reference: Johns Hopkins Medicine – Facts about Blood
3. Why Brown Blood on the First Day?
Brown blood on the first day is often due to a slower flow. A lighter flow gives blood more time to oxidize, resulting in a darker color. Additionally, residual blood from the previous cycle can also appear brown as it is expelled. This is usually normal and nothing to worry about.
4. Common Reasons for Brown Period Blood
It’s crucial to understand the typical reasons behind changes in menstrual blood color, especially if you notice brown blood. While it’s common, it can be linked to various factors, including the speed of your flow and hormonal changes.
The following are some of the causes:
- Slow Flow: A slower flow allows more time for oxidation, which leads to brown blood.
- End of Period: Brown blood is common at the end of a period as the flow slows and the remaining blood oxidizes.
- Old Blood: Blood left over from the previous cycle can also turn brown.
5. Additional Causes of Brown Period Blood
Although brown period blood is usually normal, it can sometimes indicate other underlying conditions. It’s important to monitor your symptoms and consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns.
Here is a list of additional causes:
5.1. Pregnancy
While brown blood isn’t a typical pregnancy symptom, spotting or light bleeding can be a sign of early pregnancy. Implantation bleeding, which is light bleeding that occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining, may appear brown or pink. If you suspect you might be pregnant, take a pregnancy test and consult your healthcare provider.
Reference: Mayo Clinic – Is Implantation Bleeding Common in Early Pregnancy?
5.2. Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the transition period leading up to menopause, during which hormone levels fluctuate. These hormonal changes can cause irregular bleeding or spotting, which may appear brown. Other symptoms of perimenopause include mood changes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Reference: Mayo Clinic – Perimenopause
5.3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. This can cause pelvic pain, painful periods, and spotting between periods, which may appear brown. If you experience these symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for evaluation.
Reference: Mayo Clinic – Endometriosis
5.4. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Certain STIs, such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can cause light irregular bleeding. The blood may appear brown due to the light nature of the bleeding. If you suspect you may have an STI, get tested and treated promptly.
Reference: Mayo Clinic – Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Symptoms
5.5. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths in the uterus. They can cause heavy or painful periods, as well as spotting between periods. Depending on their location, fibroids can lead to light, irregular brown bleeding. Consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns.
Reference: Mayo Clinic – Uterine Fibroids
5.6. Hormonal Birth Control
Starting a new hormonal birth control method can sometimes cause changes in period blood color. Hormonal birth control can lighten a period so much that it can cause brown bleeding. Breakthrough bleeding or spotting may occur as your body adjusts to the new hormone levels.
6. Comprehensive Table of Potential Causes
Here’s a comprehensive table summarizing the potential causes of brown period blood:
| Cause | Description | Additional Symptoms | When to Worry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Flow | Blood oxidizes due to a lighter flow. | None | Generally not a concern. |
| End of Period | Remaining blood from the end of your period oxidizes. | None | Generally not a concern. |
| Old Blood | Blood left over from the previous cycle is expelled. | None | Generally not a concern. |
| Pregnancy | Implantation bleeding may appear brown or pink. | Fatigue, nausea, breast tenderness. | If you suspect you’re pregnant. |
| Perimenopause | Hormonal changes can cause irregular bleeding. | Mood changes, night sweats, vaginal dryness. | If you’re over 40 and experiencing these symptoms. |
| Endometriosis | Tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. | Pelvic pain, painful periods, pain during sex. | If you experience severe pain. |
| STIs | Infections like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis can cause bleeding. | Abnormal discharge, pelvic pain, painful urination. | If you suspect you may have an STI. |
| Uterine Fibroids | Noncancerous growths in the uterus can cause irregular bleeding. | Heavy periods, pelvic pain, frequent urination. | If you experience heavy bleeding or severe pain. |
| Hormonal Birth Control | Starting a new birth control method can cause spotting. | None, or other typical side effects of hormonal birth control. | If the spotting is persistent or accompanied by other concerning symptoms. |
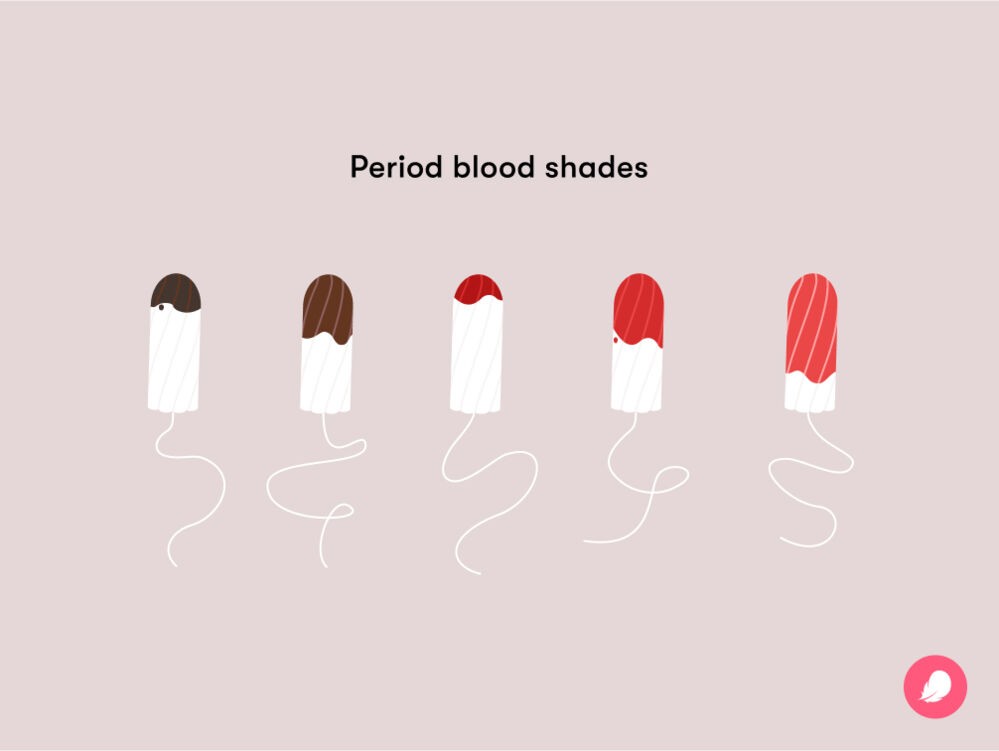

7. Diagnostic Tests for Brown Period Blood
If brown period blood is accompanied by other symptoms or concerns, diagnostic tests can help identify underlying causes. Common tests include:
- Pregnancy Test: Detects the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy.
- STI Screening: Checks for infections like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis using urine or swab samples.
- Hormone Level Testing: Measures hormone levels like estrogen and progesterone to assess hormonal imbalances.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: Visualizes the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes to detect fibroids, cysts, or other abnormalities.
- Endometrial Biopsy: Samples the uterine lining to check for abnormal cells or tissue, often used to diagnose endometriosis.
8. Addressing Concerns About Brown Period Blood
When should you consult a doctor? Generally, brown blood at the beginning or end of your period is not a cause for concern. However, irregular bleeding, severe pain, or other unusual symptoms warrant medical attention. It’s always best to err on the side of caution. If your cycle is usually predictable, there is no need to worry.
9. How Long Should a Brown Period Last?
How long a brown period lasts can vary from person to person. “If it is part of your normal menstrual cycle, it may only last one to two days,” explains Dr. White. There is no one-size-fits-all way to determine how long a brown period should last.
10. Treatment Options
The treatment for brown period blood depends on the underlying cause. For instance, hormonal imbalances may be managed with hormone therapy, while infections require antibiotics. In some cases, lifestyle changes like stress reduction and improved nutrition can also help regulate menstrual cycles.
11. Lifestyle Adjustments for Menstrual Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact menstrual health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can help regulate hormonal levels and reduce menstrual irregularities.
12. Expert Insights on Maintaining a Healthy Cycle
Maintaining a healthy menstrual cycle involves several key strategies. Proper nutrition, stress management, and regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential. Keeping track of your cycle can also help you identify any irregularities early on.
13. Debunking Myths About Period Blood Color
There are several myths surrounding period blood color. For example, some believe that dark blood is always a sign of a serious health issue, which is not necessarily true. Understanding the facts helps to alleviate unnecessary anxiety.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Dark blood is always a sign of illness | Dark blood is often just oxidized blood and may not indicate a problem. |
| The color of period blood is constant | Period blood color can vary from cycle to cycle and even within the same period. |
| Brown blood is always abnormal | Brown blood is fairly common, especially at the beginning or end of your period. |
14. The Role of Diet and Hydration
Diet and hydration play a significant role in menstrual health. Nutrient-rich foods and adequate water intake can help regulate hormones and reduce menstrual symptoms. Including iron-rich foods can also combat anemia, especially if you experience heavy periods.
15. Managing Stress for a Regular Cycle
Stress can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to irregular periods. Incorporating stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help regulate your cycle and improve overall menstrual health.
16. When to See Your Doctor and What to Say
It’s essential to know when to seek medical advice regarding changes in your menstrual cycle. If you experience persistent brown bleeding, severe pain, or other unusual symptoms, consult your doctor. Be prepared to provide a detailed account of your symptoms, menstrual history, and any relevant medical information.
17. Preparing for Your Doctor’s Appointment
Preparing for your doctor’s appointment can help ensure you receive the best possible care. Keep a record of your menstrual cycles, noting any irregularities, symptoms, or concerns. Write down any questions you have for your doctor to make the most of your visit.
18. Additional Tips for Monitoring Your Menstrual Health
Monitoring your menstrual health involves tracking your cycles, noting any symptoms, and paying attention to changes in your flow. Using period tracking apps or journals can help you stay informed about your menstrual patterns and identify potential issues early on.
19. Embracing Open Conversations About Menstrual Health
Open conversations about menstrual health are essential for breaking down stigma and promoting understanding. Sharing experiences and knowledge can empower individuals to take control of their health and seek the care they need.
20. Additional Resources
Here are some additional resources for further reading:
21. More FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about brown period blood:
21.1. Does Brown Discharge Count as a Period?
Brown discharge can count as part of your regular period, either at the end or the beginning. However, it shouldn’t replace your normal period. If you have brown discharge instead of a normal period, or between periods, speak to your healthcare provider.
21.2. How Do You Get Rid of Brown Periods?
You don’t necessarily need to get rid of brown periods. As Dr. White says, “It is normal for some people to have days of brown bleeding.” Unless it is due to a problem (like STI or medical problem), there’s no way to stop it.
21.3. Can Stress Cause Brown Period Blood?
Yes, stress can affect your menstrual cycle and potentially cause brown period blood. Stress can disrupt your hormonal balance, leading to changes in the color and flow of your period. Managing stress through exercise, meditation, or other relaxation techniques can help regulate your cycle.
21.4. Is Brown Period Blood a Sign of Infertility?
Brown period blood is not necessarily a sign of infertility. However, if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as irregular cycles, painful periods, or difficulty conceiving, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can conduct tests to determine if there are any underlying issues affecting your fertility.
21.5. Can Brown Period Blood Indicate a Miscarriage?
Brown period blood can sometimes indicate a miscarriage, especially if you are pregnant and experiencing other symptoms such as cramping or heavy bleeding. If you suspect you may be having a miscarriage, seek immediate medical attention.
21.6. Is Brown Period Blood Common After Giving Birth?
Yes, brown period blood can be common after giving birth. After childbirth, you may experience lochia, which is vaginal discharge containing blood, mucus, and uterine tissue. The color of lochia typically changes over time, starting as bright red and gradually becoming pink, brown, or yellowish.
21.7. How Does Age Affect the Color of Period Blood?
Age can affect the color of period blood due to hormonal changes that occur throughout life. During perimenopause, for example, fluctuating hormone levels can lead to irregular bleeding and changes in the color of period blood.
21.8. Can Medications Affect Period Blood Color?
Yes, certain medications can affect period blood color. For example, blood thinners may cause heavier bleeding, while hormonal birth control can sometimes lighten periods and cause brown spotting.
21.9. Is It Okay to Use Tampons or Menstrual Cups With Brown Period Blood?
Yes, it is generally okay to use tampons or menstrual cups with brown period blood. However, be sure to change tampons regularly to prevent infection.
21.10. What Does Light Brown Period Blood Mean?
Light brown period blood typically means that the blood is older and has had more time to oxidize. It is often seen at the beginning or end of your period when the flow is lighter.
22. Conclusion: Empowering Yourself With Knowledge
Understanding why your period blood might be brown on the first day is key to managing your menstrual health with confidence. It’s often a normal occurrence, but being informed helps you know when to seek further medical advice. Trust your body, stay informed, and prioritize your well-being.
Are you still curious about the color of your period blood or experiencing unusual menstrual symptoms? Don’t hesitate to seek answers and expert advice at WHY.EDU.VN. Our platform provides a trusted space to ask questions and connect with professionals who can address your specific concerns. Visit us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let why.edu.vn be your go-to resource for reliable and comprehensive health information.