Why is grass green? The familiar green landscapes we see owe their color to chlorophyll, a pigment vital for photosynthesis. WHY.EDU.VN delves into the science behind this vibrant hue, offering insights into how plants use light to create energy. Explore with us to discover the underlying principles of light absorption, energy conversion, and the remarkable adaptation of plant life, unveiling the magic behind the color of grass. Understand the biological mechanisms and environmental adaptations that contribute to this widespread phenomenon, and appreciate the delicate balance of nature’s processes.
1. The Role of Chlorophyll in Grass’s Green Color
The green color of grass is primarily due to the presence of chlorophyll, a pigment crucial for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll molecules absorb specific wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum, particularly red and blue light. According to research published in “Plant Physiology” by the American Society of Plant Biologists, chlorophyll’s molecular structure is optimized to capture these wavelengths efficiently. This selective absorption leaves green light largely unabsorbed, causing it to be reflected back, which is why grass appears green to our eyes. Chlorophyll’s effectiveness in light absorption plays a significant role in the overall health and productivity of plant ecosystems.
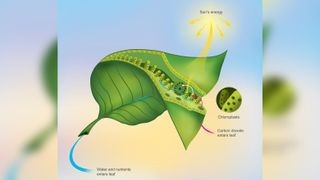 Chloroplasts inside a leaf where photosynthesis occurs
Chloroplasts inside a leaf where photosynthesis occurs
2. Understanding Light Absorption and Reflection in Plants
Plants exhibit a fascinating interaction with light, absorbing certain wavelengths while reflecting others. Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color in grass, primarily absorbs red and blue light from the visible spectrum. A study in “Photosynthesis Research” highlights that the specific molecular structure of chlorophyll allows it to efficiently capture energy from these wavelengths, converting them into chemical energy through photosynthesis. The green light, however, is not as readily absorbed and is instead reflected, which is why grass appears green to the human eye. This process of selective light absorption and reflection is essential for plant survival and energy production.
3. Photosynthesis: How Chlorophyll Converts Light into Energy
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process by which plants, including grass, convert light energy into chemical energy. Chlorophyll, located in chloroplasts within plant cells, plays a central role in this process. According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, chlorophyll captures light energy, which then drives a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a type of sugar that serves as the plant’s primary source of energy. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of this reaction. This conversion of light energy into chemical energy is vital for plant growth, development, and survival.
4. The Science Behind Visible Light and Color Perception
Visible light, a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, is essential for our perception of color, including the greenness of grass. Visible light consists of different wavelengths, each corresponding to a specific color. When light strikes an object, such as grass, certain wavelengths are absorbed, while others are reflected. A study published in the “Journal of Optics” explains that the color we perceive is determined by the wavelengths that are reflected. In the case of grass, chlorophyll absorbs most colors except green, which is reflected, leading us to see grass as green. Understanding the science of visible light and color perception provides insights into how we experience the world around us.
5. Exploring the Electromagnetic Spectrum and Wavelengths
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of radiation types, including visible light, which plays a key role in determining the color of grass. Visible light consists of different wavelengths, each associated with a specific color. According to NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, these wavelengths range from shorter, higher-energy blue and violet light to longer, lower-energy red light. Chlorophyll, the pigment in grass, absorbs red and blue light most efficiently, while reflecting green light. This reflection of green light is why grass appears green to the human eye. Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum and the properties of different wavelengths is crucial for comprehending the science behind color perception in nature.
6. The Significance of Chloroplasts in Plant Cells
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles within plant cells where photosynthesis takes place, making them essential for the green color of grass. These structures contain chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing light energy. Research from the University of Cambridge highlights that chloroplasts have a complex internal structure, including thylakoid membranes where chlorophyll molecules are arranged to maximize light capture. The light energy absorbed by chlorophyll is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, providing the plant with energy. The efficiency of chloroplasts in capturing and converting light energy is critical for the plant’s survival and growth.
7. Why Are There Different Types of Chlorophyll?
There are several types of chlorophyll, each with slightly different light absorption properties, which optimize photosynthesis in various environments. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are the most common types in land plants, with chlorophyll a being the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis. According to a study in “Biochemistry,” chlorophyll a absorbs blue-violet and red light most effectively, while chlorophyll b absorbs blue and orange light. This difference in absorption spectra allows plants to capture a broader range of light energy. Other types, like chlorophyll c and d, are found in algae and cyanobacteria, adapted to absorb light in aquatic environments.
8. The Evolutionary Advantage of Green Pigmentation in Plants
The green pigmentation in plants, due to chlorophyll, offers a significant evolutionary advantage by optimizing photosynthesis. The abundance of green plants on Earth suggests that this coloration is highly successful for energy production. A paper published in “Evolutionary Biology” notes that chlorophyll’s ability to efficiently absorb red and blue light aligns with the wavelengths most available from the sun, maximizing energy capture. Additionally, the reflection of green light may protect plants from excessive energy absorption, preventing damage to their photosynthetic machinery.
9. How Do Other Pigments Affect Plant Color?
While chlorophyll is the primary pigment responsible for the green color of grass, other pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins can influence plant color under certain conditions. Carotenoids, which produce yellow, orange, and red hues, are typically masked by chlorophyll but become visible in the fall when chlorophyll breaks down. A study in “Plant Physiology and Biochemistry” explains that anthocyanins, which produce red, purple, and blue colors, are often synthesized in response to environmental stresses such as cold, drought, or high light intensity. These pigments can provide protection against these stresses and contribute to the vibrant colors seen in leaves and flowers.
10. Exploring the Role of Accessory Pigments in Photosynthesis
Accessory pigments play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of photosynthesis by capturing a broader spectrum of light. These pigments, such as carotenoids and phycobilins, absorb light wavelengths that chlorophyll does not absorb effectively. According to research in “Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,” carotenoids absorb blue-green light, while phycobilins, found in cyanobacteria and red algae, absorb green and yellow light. The energy absorbed by these accessory pigments is then transferred to chlorophyll, increasing the overall amount of light energy available for photosynthesis. This allows plants and other photosynthetic organisms to thrive in diverse light environments.
11. What Happens to Chlorophyll in the Fall?
In the fall, as temperatures drop and daylight hours decrease, many trees and plants stop producing chlorophyll, leading to a change in leaf color. As chlorophyll breaks down, the green color fades, revealing other pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins that were previously masked. A study in “Tree Physiology” indicates that the breakdown of chlorophyll is an active process, allowing plants to recover valuable nutrients such as nitrogen and magnesium before the leaves are shed. The changing colors of leaves in the fall are a visual reminder of the seasonal changes in plant physiology.
12. The Impact of Environmental Factors on Grass Color
Environmental factors such as sunlight, water availability, and nutrient levels significantly impact the color of grass. Adequate sunlight is essential for photosynthesis and chlorophyll production, so shaded areas may result in paler grass. Water stress can reduce chlorophyll levels, leading to a yellowish or brownish tint. According to the “Agronomy Journal,” nutrient deficiencies, particularly nitrogen, can also cause grass to lose its green color. Proper lawn care practices, including adequate watering, fertilization, and sunlight exposure, are essential for maintaining healthy, green grass.
13. How Does Nitrogen Deficiency Affect Grass Color?
Nitrogen deficiency is a common issue that can significantly affect the color of grass. Nitrogen is a crucial component of chlorophyll, and when it is lacking, plants cannot produce enough chlorophyll to maintain their vibrant green color. Research published in “Crop Science” shows that nitrogen-deficient grass often appears pale green or yellow, and growth may be stunted. Correcting nitrogen deficiency through fertilization can restore the grass’s green color and promote healthy growth. Regular soil testing can help identify and address nutrient imbalances in lawns.
14. The Effects of Sunlight Exposure on Chlorophyll Production
Sunlight exposure plays a vital role in chlorophyll production and, consequently, the green color of grass. Adequate sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. According to studies in “Plant, Cell & Environment,” sufficient sunlight stimulates the synthesis of chlorophyll, resulting in a deep green color. Conversely, grass growing in shaded areas may produce less chlorophyll and appear paler. Managing sunlight exposure, through pruning trees or selecting shade-tolerant grass varieties, can help maintain healthy chlorophyll levels and vibrant green color.
15. Understanding the Role of Water in Maintaining Green Grass
Water is crucial for maintaining the green color of grass by supporting photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. Adequate water ensures that plants can efficiently transport nutrients from the soil to the leaves, where chlorophyll production takes place. Research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln indicates that water stress can reduce chlorophyll levels, leading to a yellowish or brownish appearance. Proper irrigation practices are essential for preventing water stress and maintaining healthy, green grass. Mulching and selecting drought-tolerant grass varieties can also help conserve water and maintain lawn color.
16. How Do Herbicides Affect Grass Color?
Herbicides can significantly affect grass color, depending on their mode of action and the type of grass. Selective herbicides are designed to target weeds without harming desirable grasses, while non-selective herbicides kill all vegetation. A study in “Weed Science” found that some herbicides can cause temporary yellowing or browning of grass due to disruption of photosynthesis or other metabolic processes. It’s essential to use herbicides carefully, following label instructions, to minimize potential damage to grass and maintain its healthy green color.
17. The Science of Lawn Care: Maintaining Green Grass
Maintaining green grass requires a science-based approach that considers soil health, nutrient levels, and environmental conditions. Regular soil testing can identify nutrient deficiencies and pH imbalances that may affect grass color and growth. Proper fertilization, irrigation, and mowing practices are essential for promoting healthy chlorophyll production. According to lawn care experts at Penn State University, selecting grass varieties suited to the local climate and soil conditions can also improve lawn health and maintain a vibrant green color.
18. The Importance of Soil pH for Grass Color
Soil pH plays a critical role in the availability of nutrients to grass, thereby affecting its color and overall health. Grass thrives in a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH, typically between 6.0 and 7.0. According to the Soil Science Society of America, soil pH affects the solubility of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron. When the pH is too high or too low, these nutrients become less available, leading to nutrient deficiencies and reduced chlorophyll production. Regular soil testing and amendments such as lime or sulfur can help maintain optimal soil pH for healthy, green grass.
19. Understanding Grass Species and Their Color Variations
Different grass species exhibit variations in color due to genetic differences and adaptation to specific environmental conditions. For instance, Kentucky bluegrass is known for its deep green color, while fescue grasses may have a lighter green hue. Research from the University of Wisconsin-Madison indicates that these color variations are influenced by the concentration and types of pigments in the grass leaves. Selecting grass species that are well-suited to the local climate, soil type, and sunlight exposure can help ensure a healthy and vibrant lawn.
20. The Role of Iron in Maintaining Green Grass Color
Iron is an essential micronutrient for maintaining the green color of grass, as it is required for chlorophyll synthesis. Iron deficiency, often referred to as iron chlorosis, can result in yellowing leaves, a condition known as chlorosis. A study in the “Journal of Plant Nutrition” found that iron plays a crucial role in various enzymatic processes involved in chlorophyll production. Soil pH, waterlogging, and high levels of other nutrients can affect iron availability in the soil. Applying chelated iron or adjusting soil pH can help correct iron deficiencies and restore the green color of grass.
21. Exploring the Connection Between Grass Color and Plant Health
The color of grass is a reliable indicator of its overall health and vigor. Healthy, vibrant green grass indicates adequate nutrient levels, sufficient water, and appropriate sunlight exposure. Conversely, yellowing, browning, or patchy grass may indicate nutrient deficiencies, water stress, disease, or pest infestations. According to plant pathology experts at Cornell University, regular monitoring of grass color can help identify and address potential problems early, preventing more serious damage. Proper lawn care practices, including fertilization, irrigation, and pest control, can maintain healthy grass color and overall plant health.
22. How Do Lawn Diseases Affect Grass Color?
Lawn diseases can significantly impact grass color, often causing yellowing, browning, or discoloration of the leaves. Fungal diseases, such as brown patch, dollar spot, and rust, can disrupt chlorophyll production and damage plant tissues. Research from the University of Minnesota Extension indicates that disease severity depends on environmental conditions, grass species, and lawn management practices. Proper identification of lawn diseases and timely application of appropriate fungicides can help control the spread of infection and restore healthy grass color.
23. The Impact of Pests on Grass Color and Health
Pests can have a significant impact on grass color and overall health. Insects such as grubs, sod webworms, and chinch bugs feed on grass roots and leaves, causing damage that can lead to yellowing, browning, and thinning of the lawn. According to entomologists at the University of Kentucky, pest infestations can weaken grass plants, making them more susceptible to disease and environmental stresses. Regular monitoring for pests and timely application of appropriate insecticides can help prevent damage and maintain healthy grass color.
24. The Effects of Mowing Practices on Grass Color
Mowing practices play a critical role in maintaining the green color and overall health of grass. Proper mowing height, frequency, and blade sharpness can promote healthy growth and prevent stress on grass plants. According to turfgrass experts at Purdue University, mowing grass too short can reduce its ability to photosynthesize and increase its susceptibility to drought and disease. Sharp mower blades ensure clean cuts, reducing the risk of disease transmission. Regular mowing at the appropriate height encourages dense, green growth and a healthy lawn.
25. Understanding the Role of Aeration in Maintaining Green Grass
Aeration is an essential lawn care practice that improves soil health and promotes green grass by alleviating soil compaction. Compacted soil restricts the movement of air, water, and nutrients to grass roots, leading to reduced growth and discoloration. Research from the University of Georgia Extension indicates that aeration creates small holes in the soil, allowing these essential elements to penetrate more effectively. This promotes deeper root growth, improves nutrient uptake, and enhances chlorophyll production, resulting in healthier, greener grass.
26. Exploring the Use of Grass Dyes and Paints for Green Lawns
Grass dyes and paints offer a temporary solution for achieving a green lawn, particularly in cases of drought, disease, or dormancy. These products contain non-toxic pigments that coat the grass blades, providing an instant green appearance. According to studies in “HortScience,” grass dyes and paints do not harm the grass and can last for several weeks, depending on weather conditions and mowing frequency. While they do not improve the underlying health of the grass, they provide an aesthetic enhancement for homeowners looking to maintain a green lawn appearance.
27. The Future of Grass Color Research and Technology
Research and technology continue to advance our understanding of grass color and develop innovative solutions for maintaining green lawns. Scientists are exploring new grass varieties with enhanced chlorophyll production, improved stress tolerance, and reduced nutrient requirements. According to the American Society of Agronomy, advancements in precision agriculture and sensor technology are enabling more targeted and efficient lawn care practices. These innovations promise to improve lawn health, reduce environmental impacts, and maintain the vibrant green color of grass.
28. Can Genetic Engineering Enhance Grass Color?
Genetic engineering holds potential for enhancing grass color by manipulating genes involved in chlorophyll production and pigment synthesis. Scientists are exploring ways to increase chlorophyll content, improve photosynthetic efficiency, and enhance stress tolerance through genetic modification. A review in “Frontiers in Plant Science” highlights that genetic engineering can also be used to introduce novel pigments that enhance the aesthetic appeal of grass. While genetically modified grasses are not yet widely available, research in this area is ongoing and may lead to new solutions for achieving greener and more resilient lawns.
29. The Importance of Green Spaces for Mental Health
Green spaces, including lawns and parks, play a significant role in promoting mental health and well-being. Studies have shown that exposure to green environments can reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance cognitive function. According to research published in “Environmental Science & Technology,” spending time in nature can lower levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, and increase feelings of relaxation. Maintaining green grass and creating accessible green spaces are important for supporting the mental and emotional health of communities.
30. Exploring the Cultural Significance of Green Lawns
Green lawns hold cultural significance in many societies, often symbolizing prosperity, order, and community pride. In suburban landscapes, well-maintained lawns are often seen as a reflection of responsible homeownership and community values. According to cultural studies scholars at Yale University, the emphasis on green lawns has evolved over time, influenced by factors such as social norms, advertising, and environmental awareness. Understanding the cultural significance of green lawns can inform more sustainable lawn care practices and promote a balanced approach to landscaping.
31. How Does Altitude Affect the Green Color of Grass?
Altitude can subtly influence the green color of grass due to changes in sunlight intensity and atmospheric conditions. At higher altitudes, there is less atmosphere to filter sunlight, resulting in increased exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. According to a study published in “Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research,” this increased UV exposure can stimulate the production of protective pigments, such as anthocyanins, which may slightly alter the green hue of grass. Additionally, lower temperatures at higher altitudes can slow down chlorophyll production, potentially leading to a less intense green color.
32. Does Artificial Light Affect the Greenness of Grass?
Artificial light can influence the greenness of grass, depending on the light spectrum and intensity. Grass requires specific wavelengths of light for photosynthesis, primarily red and blue light. A study in “Environmental and Experimental Botany” found that grass grown under artificial lights with a balanced spectrum, including red and blue wavelengths, can maintain a healthy green color. However, if the artificial light lacks these essential wavelengths, grass may become pale or yellow due to reduced chlorophyll production. Proper lighting systems can help maintain the greenness of grass in indoor or shaded environments.
33. How Does Snow Cover Affect Grass Color in Winter?
Snow cover can have both positive and negative effects on the color of grass during winter. A layer of snow can insulate the soil, protecting grass from extreme temperature fluctuations and desiccation. Research from the University of Alaska Fairbanks indicates that snow cover can also reduce light penetration, which may slow down photosynthesis and chlorophyll production. When the snow melts, grass may temporarily appear less green due to reduced photosynthetic activity. However, the insulation provided by snow cover can ultimately help grass survive harsh winter conditions and maintain better color in the long run.
34. Can Climate Change Affect the Green Color of Grass?
Climate change can significantly affect the green color of grass through various mechanisms, including altered temperature and precipitation patterns. Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts can lead to water stress, reducing chlorophyll production and causing grass to turn brown or yellow. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events can also damage grass and disrupt its growth cycle. Adopting climate-resilient lawn care practices, such as selecting drought-tolerant grass varieties and implementing water conservation measures, can help mitigate these effects.
35. How Do Organic Lawn Care Practices Affect Grass Color?
Organic lawn care practices can positively influence the green color of grass by promoting soil health and nutrient availability. Organic methods such as compost application, natural fertilizers, and biological pest control enhance soil fertility and microbial activity. Research from the Rodale Institute shows that healthy soil supports robust root growth and improves nutrient uptake, resulting in greener and more resilient grass. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, organic lawn care practices also reduce the risk of harming beneficial organisms and disrupting the ecosystem, contributing to long-term lawn health and vibrant color.
36. Exploring the Use of Remote Sensing to Monitor Grass Color
Remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery and drone-based sensors, are increasingly used to monitor grass color and assess lawn health over large areas. These technologies can detect subtle changes in vegetation indices, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), which correlates with chlorophyll content and greenness. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), remote sensing data can provide valuable insights into lawn health, identify areas of stress or disease, and guide targeted management practices. This allows for more efficient and sustainable lawn care management.
37. How Do Urban Environments Affect the Greenness of Grass?
Urban environments can pose unique challenges to maintaining the greenness of grass due to factors such as air pollution, soil compaction, and limited sunlight. Air pollutants can damage plant tissues and reduce photosynthetic efficiency, leading to discoloration. Soil compaction restricts root growth and nutrient uptake, while buildings and other structures can create shaded areas that limit sunlight exposure. A study in “Urban Ecosystems” suggests that selecting pollution-tolerant grass varieties, improving soil drainage, and managing shade can help mitigate these effects and promote healthier, greener lawns in urban settings.
38. The Role of Mycorrhizae in Enhancing Grass Color
Mycorrhizae, symbiotic fungi that form associations with plant roots, can enhance grass color by improving nutrient and water uptake. These fungi extend the root system’s reach, accessing nutrients and water that would otherwise be unavailable to the plant. Research from Oregon State University indicates that mycorrhizal associations can increase chlorophyll production and improve the overall health and vigor of grass. Inoculating lawns with mycorrhizal fungi can be a beneficial organic lawn care practice, particularly in nutrient-poor soils.
39. How Do Invasive Plant Species Affect the Green Color of Grass?
Invasive plant species can negatively affect the green color of grass by competing for resources such as sunlight, water, and nutrients. Weeds such as crabgrass, dandelions, and creeping Charlie can quickly spread and crowd out desirable grass species, leading to patchy and uneven lawns. According to the Invasive Plant Atlas of the United States, these invasive plants often have different growth habits and nutrient requirements than grass, disrupting the ecosystem and affecting the overall color and health of the lawn. Effective weed control measures are essential for maintaining a healthy, green lawn.
40. The Impact of Soil Microorganisms on Grass Color and Health
Soil microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, play a crucial role in maintaining grass color and overall health. These organisms contribute to nutrient cycling, organic matter decomposition, and disease suppression. Research from the University of California, Davis, indicates that beneficial soil microorganisms can enhance root growth, improve nutrient uptake, and protect grass from pathogens. Promoting a diverse and thriving soil microbiome through organic lawn care practices can lead to healthier, greener, and more resilient lawns.
FAQ: Unlocking the Secrets of Green Grass
1. Why is grass green and not another color?
Grass is green because of chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs red and blue light while reflecting green light. This reflected green light is what we perceive as the color of grass.
2. What role does chlorophyll play in the color of grass?
Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. It absorbs specific wavelengths of light, enabling plants to produce glucose for energy.
3. How does sunlight affect the greenness of grass?
Sunlight is crucial for chlorophyll production. Adequate sunlight stimulates the synthesis of chlorophyll, resulting in a deep green color. Insufficient sunlight can lead to paler grass.
4. Can water affect the color of grass?
Yes, water is vital for maintaining green grass. Adequate water ensures efficient nutrient transport to the leaves for chlorophyll production. Water stress can reduce chlorophyll levels, causing a yellowish appearance.
5. What nutrients are essential for maintaining green grass?
Nitrogen, iron, and magnesium are essential for maintaining green grass. Nitrogen is a key component of chlorophyll, while iron and magnesium are involved in chlorophyll synthesis.
6. How do herbicides affect grass color?
Herbicides can affect grass color depending on their mode of action. Some herbicides may cause temporary yellowing or browning due to disruption of photosynthesis, while others can kill the grass outright.
7. How does soil pH impact grass color?
Soil pH affects the availability of nutrients to grass. A slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0-7.0) is optimal for nutrient uptake. Extreme pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies and reduced chlorophyll production.
8. What are some natural ways to maintain green grass?
Organic lawn care practices, such as compost application, natural fertilizers, and biological pest control, can enhance soil health and promote green grass naturally.
9. How do lawn diseases affect grass color?
Lawn diseases can disrupt chlorophyll production and damage plant tissues, leading to yellowing, browning, or discoloration of the leaves.
10. Can grass dyes and paints improve the color of my lawn?
Grass dyes and paints offer a temporary solution for achieving a green lawn. They contain non-toxic pigments that coat the grass blades, providing an instant green appearance without harming the grass.
Do you have more questions about why grass is green or other fascinating topics? Visit WHY.EDU.VN, where our team of experts is ready to provide clear, reliable answers. Whether you’re curious about science, nature, or any subject under the sun, we’re here to help you explore and understand the world around you. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Discover the answers you’ve been searching for at why.edu.vn today!
