Why Do People Like The Smell Of Their Own Farts? It may seem strange, but many people find their own flatulence less offensive than that of others, according to WHY.EDU.VN. This tolerance comes from habituation to the unique bacteria and odor of one’s own gas. For a deeper dive, explore the science behind flatulence, odor composition, and the evolutionary reasons for our preferences, including insights on digestive gases and odor perception.
1. What Is A Fart?
A fart, medically known as flatulence, is the body’s way of expelling excess gas from the digestive system through the rectum. This is a natural process that helps to relieve bloating and discomfort caused by the buildup of gases.
Our bodies have two primary ways of expelling excess gas, a byproduct of digestion.
- Belching (Burping): This is the more common method, with the average person burping around 30 times a day.
- Flatulence (Farting): This is the expulsion of gas through the rectum.
When we fart, we release a mixture of gases, including carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. These gases are generally odorless.
2. What Makes Farts Stinky?
The odor of farts is primarily due to trace amounts of sulfur-containing compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol, and dimethyl sulfide. These compounds are produced by bacteria in the gut as they break down food.
Contrary to popular belief, methane is not the primary cause of fart odor; sulfur compounds are to blame.
The Role of Sulfur
Sulfur, found in the oxygen family of elements, is the main culprit behind the unpleasant smell of farts.
- Foods Containing Sulfur: Many foods contain sulfur, including cruciferous vegetables (e.g., Brussels sprouts, cabbage), and beverages like beer and wine.
- Breakdown Process: When sulfur-rich foods are digested, gut bacteria release hydrogen sulfide, contributing to the rotten-egg smell.
Impact of Diet and Lifestyle
A 2021 study indicated that lifestyle factors can also influence flatulence.
- Study Details: A study sampled nearly 6,000 adults from the United States, the United Kingdom, and Mexico.
- Findings: 83.1% of participants experienced gastrointestinal issues related to flatulence.
- Poor Quality of Life: The study found a correlation between gastrointestinal issues and reduced quality of life.
Expert Insight
Professor Olafur Palsson, the lead author of the study, noted the significant impact of flatulence on well-being.
“I think the most remarkable and surprising finding in our study is that almost all adults in the general population experience some daily gas-related symptoms. This is important given the data also clearly reveals that these symptoms affect people’s general wellbeing. Having a high amount of these common intestinal symptoms is associated with higher levels of depression, anxiety and stress, as well as impaired general quality of life,” said Palsson.
3. Why Are Our Farts Less Stinky Than Others?
The perception of fart odor varies depending on whether it is our own or someone else’s. Generally, people find their own farts more tolerable.
Evolution and personal experiences influence our perception of odors.
The Science Behind Self-Recognition
Humans are primed to recognize their own scents, which affects how we perceive them.
- Sense of Self: Our biological sense of self is well-grounded, even on a chemical level.
- Threat Perception: Smells and sounds originating from our own bodies are less threatening than those from others.
University of Pittsburgh Study
A 1976 study by researchers from the University of Pittsburgh examined self-recognition through odors.
- Methodology: 11 male graduate students participated in blind smell tests, rating 12 body odor samples, including their own.
- Findings: While only three students correctly identified their own odor, almost all ranked their own sample as less unpleasant.
Odor Association
The study also found that people associate unpleasant odors with negative social traits.
- Social Traits: Participants expected those with the worst-smelling samples to be unfriendly, dirty, and unpopular.
- Evolutionary Perspective: This association makes sense from an evolutionary standpoint, as we tend to associate terrible smells with danger or unpleasant experiences.
Habituation and Distinctiveness
We become habituated to our own body odors, allowing us to distinguish them from others.
- Distinctive Odors: Our farts are unique to our bodies, and over time, we grow accustomed to their smell.
- Harsh Judgment of Others: We tend to be more critical of others’ farts, possibly due to evolutionary mechanisms that associate negative chemical signals with danger.
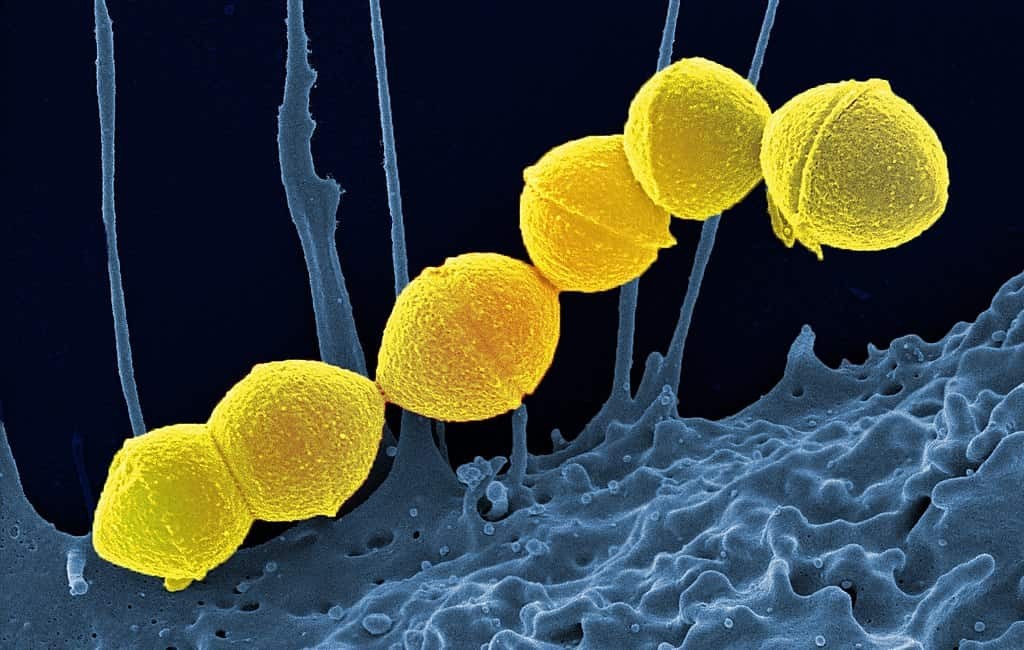
Disease-Causing Pathogens
Farts can contain bacteria, such as Streptococcus pyogenes, which can cause infections like strep throat.
- Bacteria Release: Farts can release bacteria along with gas.
- Health Risks: These bacteria can pose health risks, making us more reactive to others’ farts.
Tolerance and Adventure
Some individuals are less sensitive to flatulence, regardless of the source.
- Sociability and Disgust: Research suggests a correlation between sensitivity to disgust and psychosocial variables like sociability.
- Social Conservatism: People who are more socially conservative tend to be more disgusted by farts, while those who are more amenable are less bothered.
Ultimately, our farts are an extension of ourselves, and our perception of them is influenced by a combination of biological, evolutionary, and psychological factors.
4. Flatulence And Disease
While farting is a natural and healthy bodily function, it’s important to be aware of the potential for disease transmission, albeit rare. Farts can contain bacteria like Streptococcus pyogenes, which may cause strep throat.
Farting is generally a healthy bodily function, serving to expel excess gas.
- Bacteria Transmission: Farts can contain bacteria, such as Streptococcus pyogenes, which may cause strep throat.
- Health Concerns: While the risk of getting sick from smelling someone else’s fart is low, it’s still a good idea to maintain hygiene and avoid prolonged exposure.
Here is a table summarizing the key points discussed above:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Gas Composition | Mixture of carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, and trace amounts of sulfur-containing compounds. |
| Odor Cause | Sulfur-containing compounds (e.g., hydrogen sulfide) produced by gut bacteria. |
| Diet Influence | Sulfur-rich foods (e.g., cruciferous vegetables) increase odor intensity. |
| Self-Recognition | Humans are primed to recognize their own scents, making their own farts more tolerable. |
| Evolutionary Factors | Negative chemical signals (bad smells) from others are associated with danger. |
| Potential Health Risks | Farts can contain bacteria like Streptococcus pyogenes, which may cause strep throat, though transmission risk is low. |
| Psychosocial Factors | Sensitivity to disgust varies with sociability; socially conservative individuals may be more disgusted by farts. |
| Study Findings (2021) | 83.1% of adults experience gas-related gastrointestinal symptoms, which are linked to depression, anxiety, and impaired quality of life. |
| Professor Palsson Quote | “Almost all adults in the general population experience some daily gas-related symptoms… associated with higher levels of depression, anxiety and stress, as well as impaired general quality of life.” |
| University of Pittsburgh Study | Even when individuals cannot recognize their own odors, they rate them as less unpleasant than those of others. |

5. Farting Questions And Answers
Here are some frequently asked questions about farting:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What exactly happens when we fart? | Farting, or flatulence, is the release of intestinal gases through the rectum, produced by bacteria in the large intestine during digestion. These gases include nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, and sometimes oxygen. It is a normal part of digestion. |
| Do all animals fart, and are there any interesting examples? | Many animals fart, including mammals, birds, and some fish. Cows are known for their methane-rich farts, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, not all animals fart; birds have a different digestive system. |
| Is farting a sign of good health? | Generally, yes, farting indicates a healthy digestive system. However, excessive or foul-smelling farts may suggest dietary issues or gastrointestinal disorders, warranting a discussion with a healthcare professional. |
| Why do some farts smell worse than others? | The odor is mainly due to sulfur-containing gases produced by bacteria in the gut. Diets rich in sulfur (garlic, onions, certain vegetables) increase the likelihood of noticeable smells. |
| Does every person fart, and how often is normal? | Yes, every healthy person farts, averaging about 5 to 15 times a day, varying with diet and other factors. |
| What role does diet play in how much we fart? | Diet significantly impacts farting. High-fiber foods like beans and lentils can increase gas production, while reducing certain carbohydrates may decrease gas. |
| How is farting perceived in different cultures? | Attitudes vary widely. Some cultures find it humorous or unimportant, while others consider it rude or embarrassing. |
| How do astronauts deal with farting in space? | In space, farting poses unique challenges due to the lack of gravity affecting gas movement. Astronauts must manage their diet carefully to avoid excessive gas. |
| Can holding in farts be harmful? | Regularly holding in farts can lead to discomfort, bloating, and potentially exacerbate digestive issues. It’s generally healthier to release them when the urge arises. |
| Are there any medical conditions that cause excessive farting? | Yes, conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), lactose intolerance, and certain infections can cause excessive farting. Consulting a doctor can help diagnose and manage these conditions. |
Understanding the science behind flatulence, odor composition, and our evolutionary adaptations can help us appreciate this natural bodily function.
Are you curious about other aspects of human biology or health? Do you have questions that need expert answers? Visit WHY.EDU.VN today, where you can ask questions and receive detailed, reliable information from specialists. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the knowledge you need to understand the world around you.
Contact us at:
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let why.edu.vn be your go-to source for accurate and comprehensive answers!