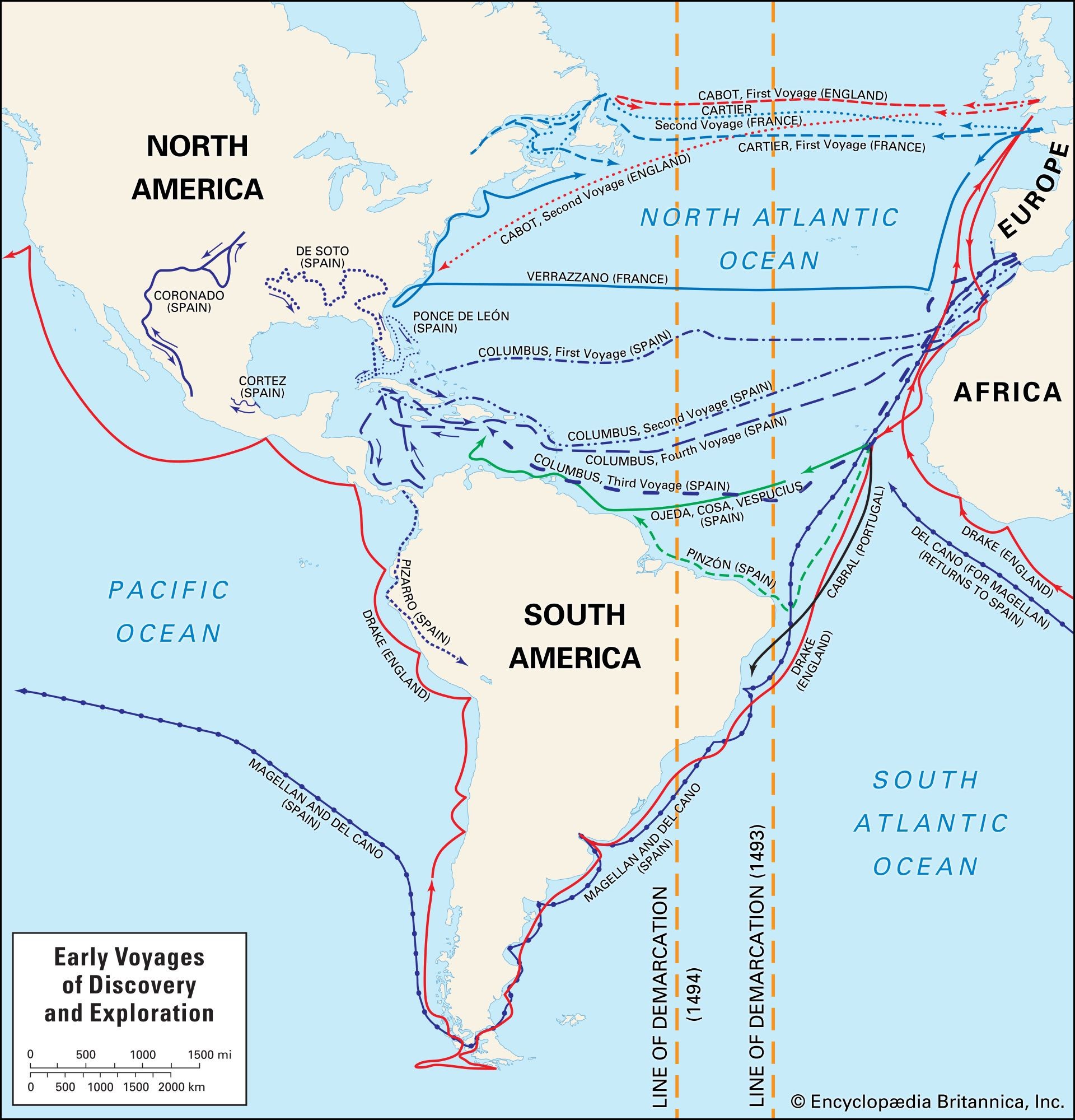
Giovanni da Verrazzano, though often less celebrated than some of his contemporaries, played a pivotal role in the European exploration of North America. Born in Tuscany in 1485, this Italian navigator sailed under the French flag and became the first European to chart significant portions of the eastern coast of what is now the United States and Canada. While he wasn’t directly involved in English exploration, understanding his voyages is crucial to grasping the broader context of European expansion and its impact on the New World, which inevitably influenced later English endeavors.
Verrazzano’s early life saw him educated in Florence before he entered maritime service in Dieppe, France. His experience in voyages to the Levant positioned him well for a more ambitious undertaking. By 1523, he had gained the backing of King Francis I of France to find a westward passage to Asia. This was a common goal among European powers at the time, driven by the desire to find quicker trade routes to the East and to expand their territories and influence.
 European exploration: early voyages
European exploration: early voyages
Verrazzano embarked on his most famous voyage in January 1524 with the ship La Dauphine. Reaching Cape Fear around early March, he began his exploration northward along the Atlantic coast. This voyage was groundbreaking for several reasons. He meticulously charted the coastline, providing Europe with its first detailed understanding of this part of North America. He explored and named areas including present-day New York Harbor, which he called “Santa Margarita” (though this name did not stick), Block Island, and Narragansett Bay. His descriptions of these locations, while sometimes debated for their accuracy in hindsight, were the first European accounts of these significant geographical features.
One of Verrazzano’s key contributions was being the first European explorer to assign European names to North American locations. This act of naming was not merely descriptive; it was an assertion of European presence and a symbolic claiming of territory. Although sailing for France, his actions and the information he gathered had implications for all European powers, including England, who were vying for influence in the New World.
Verrazzano’s interactions with the indigenous populations he encountered are also noteworthy, though his accounts must be viewed with a critical eye, considering the biases of the time. He described the inhabitants and the lands, contributing to the growing European understanding – and often misunderstanding – of the New World and its peoples. His voyage extended as far north as Newfoundland before he returned to France in July 1524.
Upon his return, Verrazzano’s reports provided King Francis I with France’s initial claim to territories in the New World. This French claim, based on Verrazzano’s explorations, became a significant factor in the unfolding European competition for North America. While England would later establish its own strong presence along the eastern coast, the groundwork laid by explorers like Verrazzano shaped the geopolitical landscape of the continent. His voyage demonstrated the potential of the region and spurred further exploration and colonization efforts by various European nations.
Verrazzano undertook further voyages, including one to Brazil in 1527 and his final voyage in 1528 to the Lesser Antilles, where he tragically met his end. Despite his death and the fact that he sailed for France, Giovanni da Verrazzano’s explorations were fundamentally important to the broader narrative of European exploration. He expanded European geographical knowledge, initiated French claims in North America, and his detailed coastal charting provided invaluable information that would influence subsequent voyages and colonial endeavors, indirectly impacting even English strategies in the New World. His legacy lies in his pioneering role in unveiling the eastern coast of North America to Europe and setting the stage for the complex interactions that would follow.