Vine’s shutdown raises questions about the platform’s decline. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide insights into the factors that led to Vine’s downfall and explore the lessons learned from its journey. This article examines the reasons behind the ban and offers a detailed analysis of its significance in the evolution of social media, focusing on market dynamics and competition strategies.
1. What Was Vine and Why Was It Popular?
Vine was a short-form video hosting service where users could create and share looping video clips that were initially capped at six seconds. Think of it as Twitter, but for videos. The platform attempted to do for YouTube vlogs what Twitter did for traditional blogs, with its character length restrictions encouraging concise content creation. Users loved it for its simplicity and the creative constraint of the six-second limit, which led to innovative and often hilarious content.
Vine’s concept was intriguing enough that Twitter acquired it for $30 million before the app even launched. This acquisition provided Twitter with a way to compete with larger social media platforms like Facebook and Google in the video content space. However, despite its initial success and cultural influence, Vine eventually became a cautionary tale in the tech world. Let’s delve deeper into why Vine was ultimately banned.
2. Why Was Vine Banned? The Core Reasons
Vine’s ban can be attributed to a combination of factors. The platform struggled to adapt to changing market trends and failed to address key issues faced by its content creators. The major reasons behind Vine’s ban include:
- Failure to Meet Market Needs: Vine’s strict six-second limit became restrictive as users sought more versatile content formats.
- Monetization Problems: The platform’s inability to provide adequate revenue opportunities for content creators led to their departure.
- Competition Problems: The emergence of competing platforms, such as Instagram, with similar features, undermined Vine’s market position.
- Parent Company Problems: Vine’s parent company, Twitter, did not prioritize the platform, leading to its neglect.
- Executive Churn and Leadership Problems: Frequent changes in leadership and a lack of clear direction hindered Vine’s ability to innovate and compete.
- Unprofitable Business Model: The platform struggled to generate sustainable revenue, making it financially unsustainable in the long run.
3. Detailed Breakdown: Reasons Behind Vine’s Demise
Let’s explore the various reasons behind Vine’s ban in more detail. Each factor played a crucial role in the platform’s downfall.
3.1. Vine’s Failure to Meet Market Needs
Originally conceived as a microvlogging platform for sharing short video clips with friends, Vine evolved into more of an entertainment hub, similar to YouTube. The majority of users were passive viewers consuming content created by a smaller group of active content creators. This shift meant that Vine’s success relied heavily on retaining these creators. However, the platform failed to meet their needs, which led to their departure.
Rigid Time Constraints: Vine’s strict six-second limit restricted creators’ ability to experiment with different types of short-form video content. Unlike platforms that allowed longer videos, Vine couldn’t accommodate vlogs or more in-depth discussions.
Lack of Monetization: Active content creators invest significant time and effort into producing content. They need a way to monetize their work. Vine excelled at helping creators grow their audience but failed to provide effective monetization tools. As a result, many Viners migrated to platforms that offered better opportunities to earn money.
3.2. Vine’s Monetization Problems
Vine’s monetization issues extended beyond content creators to the platform itself. The company was hesitant to experiment with monetization strategies, which is common in hyper-growth network-effect startups. However, when growth stalled, there was no financial incentive to keep the service alive.
Limited Sponsorship Opportunities: Most of the money flowing into Vine’s ecosystem came from direct sponsorships for top content creators. Vine never integrated sponsorship solutions into the platform. While Twitter attempted to monetize indirectly through a social media talent agency, this approach proved ineffective in incentivizing creators to stay on Vine.
3.3. Vine’s Competition Problems
Competitors with established audiences and resources quickly entered Vine’s market, offering similar short-form video features. Today, short-form video is a standard component of many popular apps, including Instagram, Snapchat, Facebook, and YouTube.
Instagram’s 15-Second Video Feature: The introduction of Instagram’s 15-second video feature was a significant blow to Vine. As one former Vine executive told The Verge, “Instagram video was the beginning of the end.” This feature provided users with a familiar platform to create and share short videos without the limitations of Vine.
3.4. Vine’s Parent Company Problems
Twitter acquired Vine with the strategic goal of using it to enhance Twitter’s brand and business. This meant that Vine was not a top priority for its shareholders as a standalone product.
Conflicting Video Features: Twitter’s decision to launch its own video feature undermined the need for Vine’s existence. Executives considered integrating all of Twitter’s video solutions, which ultimately led to Vine’s demise.
3.5. Vine’s Executive Churn and Leadership Problems
Vine faced significant leadership challenges, which contributed to its downfall. Key executives left the company, creating instability and hindering innovation.
Lack of Innovation: As Ankur Thakkar noted in an interview with The Verge, “Vine didn’t ship anything of consequence for a year.” This lack of progress and innovation signaled deeper issues within the company.
3.6. Unprofitable Business Model
Ultimately, Vine’s inability to generate sustainable revenue made it financially unsustainable. The platform relied heavily on its user base and failed to create a viable business model that could support its operations.
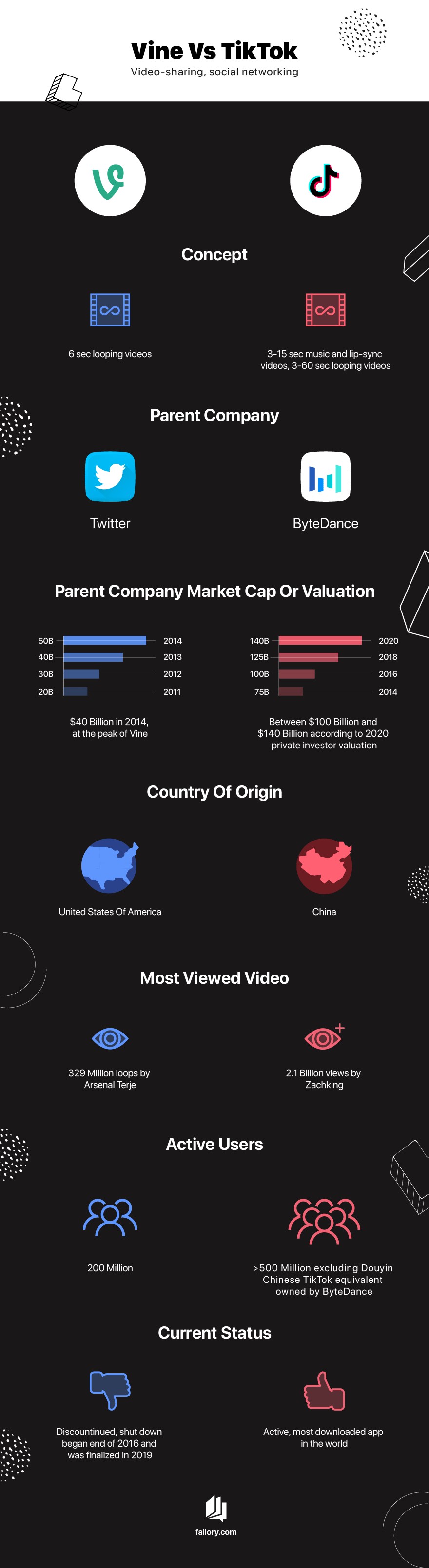
4. Vine vs. TikTok: Lessons Learned
When discussing the ban of Vine, it’s essential to compare it with TikTok, a platform with a similar concept that has achieved immense success. Two key factors make this comparison relevant:
- Both platforms share a similar short-video format.
- Vine failed, while TikTok has become one of the most popular apps globally.
Vine was the first to enter the market, yet TikTok thrived despite facing fiercer competition. This raises the question: How did TikTok succeed where Vine failed?
4.1. Entertainment Media Platform vs. Social Media Platform
Unlike Vine, TikTok recognized that it wasn’t in direct competition with platforms like Instagram. TikTok’s short videos are designed for entertainment, whereas Instagram’s stories focus on sharing moments with friends.
Professional Content Creators: TikTok content creators are more akin to YouTube channel owners. They are professional entertainers who dedicate their time to creating video content and seek to monetize their efforts.
4.2. Addressing Market Needs
TikTok has successfully addressed market needs by offering various video lengths, remix features, and live streaming capabilities. The platform also provides monetization options for both content creators (e.g., donations during live streams) and the platform itself (e.g., TikTok’s ads solution).
4.3. Global Reach and Strategic Importance
TikTok is the first Chinese consumer app to gain widespread popularity in the Western world. Owned by ByteDance, a tech giant based in Beijing, TikTok benefits from strong financial backing and government support.
Commitment to Survival: Unlike Twitter, which quickly abandoned Vine, ByteDance is more likely to fight to ensure TikTok’s survival. The app’s global reach gives it strategic importance, making it unlikely to be scrapped even if it becomes unprofitable.
| Feature | Vine | TikTok |
|---|---|---|
| Video Length | 6 seconds | Varies (15 seconds to 10 minutes) |
| Monetization | Limited | Robust (ads, donations, creator fund) |
| Content Focus | Microvlogging, sharing with friends | Entertainment, performances, trends |
| Parent Company | ByteDance | |
| Global Reach | Limited | Extensive |
| Market Adaptation | Failed to adapt to changing user needs | Successfully adapted to market demands |
| Strategic Support | Low priority, easily abandoned | High priority, strong government backing |

5. Where Are the Top Viners Now?
Many stars who gained popularity on Vine transitioned to other platforms before its shutdown. Their move to competitor platforms was a major factor in Vine’s demise. Popular Viners such as King Bach, Nash Grier, Lele Pons, Brittany Furlan, Rudy Mancuso, Josh Peck, Jerry Purpdrank, Logan Paul, Cameron Dallas, and Alx James have become professional influencers with a presence on multiple platforms, including Instagram, Twitter, YouTube, and TikTok. Building an audience on Vine ultimately paid off for these creators, despite the platform’s limited monetization options. Vine paved the way for a short entertainment video revolution.
6. Expert Opinions on Vine’s Failure
Industry experts have weighed in on the reasons behind Vine’s ban, offering valuable insights into the platform’s shortcomings.
-
Chris Stokel-Walker, author of “TikTok Boom,” notes that Vine’s strict format and lack of monetization options contributed to its downfall. He argues that TikTok’s success lies in its ability to adapt to changing user preferences and provide creators with diverse revenue streams.
-
Rory Cellan-Jones, a technology correspondent for the BBC, suggests that Twitter’s failure to invest in Vine and its decision to focus on its own video features sealed the platform’s fate. He emphasizes the importance of strategic support and resource allocation in the success of social media platforms.
7. The Impact of Vine on Internet Culture
Despite its relatively short lifespan, Vine left an indelible mark on internet culture. The platform popularized short-form video content and introduced new forms of comedy and creative expression.
7.1. Memes and Viral Content
Vine was a breeding ground for memes and viral content. Many popular internet memes originated on Vine, and its influence can still be seen on other social media platforms today.
7.2. Influencer Culture
Vine played a significant role in the rise of influencer culture. The platform gave a platform to aspiring content creators and helped them build a dedicated following. Many of these influencers went on to achieve success on other platforms, demonstrating the lasting impact of Vine.
7.3. Creative Innovation
The six-second limit encouraged creative innovation. Viners developed unique techniques and styles to convey their messages in a concise and engaging way. This innovation influenced the development of short-form video content on other platforms.
8. The Future of Short-Form Video
The rise and fall of Vine provide valuable lessons for the future of short-form video. Platforms that prioritize creator needs, adapt to changing market trends, and offer diverse monetization options are more likely to succeed.
8.1. Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the future of short-form video:
- Personalization: Users expect personalized content recommendations tailored to their interests.
- Interactive Features: Interactive features, such as polls and quizzes, enhance user engagement.
- E-Commerce Integration: The integration of e-commerce capabilities allows creators to sell products directly to their audience.
8.2. Emerging Platforms
New platforms are emerging that aim to build on the success of TikTok and address the shortcomings of Vine. These platforms focus on empowering creators, fostering community, and providing innovative monetization solutions.
| Trend | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Personalization | Content recommendations tailored to user interests | TikTok’s “For You” page |
| Interactive Features | Features that enhance user engagement, such as polls, quizzes, and live Q&A sessions | Instagram Stories’ poll and question stickers |
| E-Commerce | Integration of e-commerce capabilities, allowing creators to sell products directly to their audience | TikTok Shopping |
| Creator Empowerment | Tools and resources that empower creators to build their brand, connect with their audience, and monetize content | Patreon, Substack |
9. FAQ: Common Questions About Vine
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about Vine and its ban.
9.1. Who created Vine?
Vine was founded by Dom Hofmann, Rus Yusupov, and Colin Kroll.
9.2. Who bought Vine?
Twitter acquired Vine in October 2012 for a reported $30 million.
9.3. When did Vine come out?
Vine was founded in June 2012, acquired by Twitter in October 2012, and officially launched on January 24, 2013.
9.4. When was Vine popular?
The app reached its peak popularity in mid-2013, becoming the number one free app in the iOS and Android app stores.
9.5. How long were Vines?
Vine videos were six seconds long, much shorter than TikTok videos.
9.6. What was the first Vine?
Dick Costolo, the then-CEO of Twitter, created the first Vine. It was a video of someone preparing steak tartare at a French restaurant in NYC called Les Halles.
9.7. When was Vine shut down?
Vine was shut down on January 17, 2017.
9.8. How long did Vine last?
Vine lasted almost four years, from January 24, 2013, to January 17, 2017.
9.9. Why was Vine banned?
Vine was banned because it was an unprofitable business that lost popularity to other similar services, most notably Instagram. Burning money while losing market share isn’t sustainable.
10. Conclusion: The Legacy of Vine
Vine’s ban marked the end of an era in social media. While the platform may be gone, its legacy lives on in the form of memes, influencers, and the continued popularity of short-form video content. The lessons learned from Vine’s rise and fall can help inform the development of future social media platforms.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we strive to provide accurate and insightful answers to complex questions. We understand the challenges of finding reliable information in today’s digital landscape. That’s why we offer expert-driven content that is both informative and easy to understand.
Have more questions about social media, technology, or any other topic? Visit WHY.EDU.VN at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Our team of experts is here to help you find the answers you need. Don’t let curiosity go unanswered – explore the world with why.edu.vn.
