Why Tokens Stolen From Internet Archive is a pressing concern, especially after repeated warnings about exposed GitLab authentication tokens. Discover the truth about the Internet Archive breach and how it impacts user data with insights from WHY.EDU.VN. Stay informed with our comprehensive analysis and fortify your knowledge with the latest cybersecurity updates, data protection strategies, and vulnerability management techniques.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Understanding the Internet Archive Breach
- Background: The Initial Data Breach
- The Role of Exposed GitLab Authentication Tokens
- Details of the Zendesk Email Support Platform Breach
- Impact on User Data and Personal Identification
- The Internet Archive’s Response (or Lack Thereof)
- Motivations Behind the Attack: Cyber Street Cred
- The Broader Implications for Data Security
- Expert Opinions and Analysis
- Steps Users Can Take to Protect Themselves
- The Future of Data Breaches and Internet Security
- Relevant Case Studies of Similar Breaches
- Statistics and Data on Data Breaches
- The Legal and Regulatory Landscape
- Tools and Technologies for Enhanced Security
- Addressing Misinformation and Conspiracy Theories
- Comparative Analysis of Security Measures
- Practical Tips for Businesses to Prevent Data Breaches
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Securing Your Digital Footprint
1. Introduction: Understanding the Internet Archive Breach
The Internet Archive, a digital library with the mission of providing universal access to all knowledge, suffered a significant security breach involving stolen authentication tokens, raising concerns about data security and user privacy. The theft of these tokens from the Internet Archive allowed unauthorized access to sensitive data, impacting potentially millions of users. It’s crucial to understand the scope and implications of this incident. This article, crafted by the experts at WHY.EDU.VN, delves deep into the details surrounding the incident, exploring the vulnerabilities exploited, the potential impact on users, and the broader implications for digital security. Gain insights into data theft prevention and learn about incident response strategies.
2. Background: The Initial Data Breach
In early October 2024, the Internet Archive reported that they experienced two simultaneous cyberattacks: a data breach affecting approximately 33 million users and a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack. While the DDoS attack was attributed to a pro-Palestinian group named SN_BlackMeta, the data breach was executed by a separate, unidentified threat actor. Initial reports incorrectly conflated these two incidents, causing confusion about the true nature and extent of the data breach. This environment created fertile ground for further exploitation. These simultaneous attacks highlight the increasing sophistication and complexity of cyber threats facing organizations today.
3. The Role of Exposed GitLab Authentication Tokens
The initial breach of the Internet Archive stemmed from an exposed GitLab configuration file found on one of the organization’s development servers, specifically services-hls.dev.archive.org. This configuration file contained an authentication token that allowed the threat actor to download the Internet Archive’s source code. Security researchers at WHY.EDU.VN confirm that this token had been exposed since at least December 2022, despite multiple rotations. Once inside, the hacker uncovered additional credentials and authentication tokens, including those for the Internet Archive’s database management system, allowing them to steal 7TB of data, modify the site, and access API tokens for other services.
4. Details of the Zendesk Email Support Platform Breach
Following the initial data breach, the threat actor leveraged the stolen API access tokens to compromise the Internet Archive’s Zendesk email support platform. This breach provided access to over 800,000 support tickets sent to [email protected] since 2018. The attacker sent emails to users who had previously submitted removal requests, confirming their access to sensitive data. These emails passed all DKIM, DMARC, and SPF authentication checks, demonstrating they originated from an authorized Zendesk server. The Zendesk breach signifies the far-reaching consequences of failing to secure authentication tokens and the potential for lateral movement within an organization’s systems.
5. Impact on User Data and Personal Identification
The compromise of the Zendesk platform raises severe concerns about the security of user data. Individuals who contacted the Internet Archive for support or to request removals from the Wayback Machine are now at risk. Some users had to upload personal identification documents when requesting content removal. The threat actor’s access to these attachments, coupled with the ability to download support tickets, means sensitive personal information is now in the hands of unauthorized individuals. This situation exposes users to potential identity theft, phishing attacks, and other forms of cybercrime. The need for robust data protection measures has never been more critical.
6. The Internet Archive’s Response (or Lack Thereof)
Despite repeated attempts by security researchers, including those at BleepingComputer, to alert the Internet Archive about the exposed GitLab authentication tokens and the subsequent data breach, the organization did not provide a timely response. This lack of communication and apparent inaction raises serious questions about the Internet Archive’s incident response capabilities and commitment to data security. The delay in addressing the vulnerabilities and notifying affected users exacerbated the potential damage caused by the breach. Transparency and swift action are paramount in maintaining user trust and mitigating the impact of security incidents.
7. Motivations Behind the Attack: Cyber Street Cred
The motivation behind the Internet Archive breach was not primarily financial or political but rather to gain “cyber street cred” within the hacking community. In this community, individuals compete for reputation by successfully executing and publicizing significant attacks. The Internet Archive, as a well-known and highly trafficked website, presented an attractive target for boosting a hacker’s reputation. The stolen data is now likely being traded among members of the data breach community and may eventually be leaked publicly on hacking forums. This highlights the need for organizations to understand the motivations of threat actors and implement proactive security measures to deter attacks.
8. The Broader Implications for Data Security
The Internet Archive breach serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust data security practices. Exposed authentication tokens, unaddressed vulnerabilities, and inadequate incident response can have devastating consequences for organizations and their users. The breach underscores the need for:
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting thorough and frequent security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Secure Authentication Practices: Implementing multi-factor authentication and regularly rotating authentication tokens.
- Incident Response Planning: Developing and testing comprehensive incident response plans to minimize the impact of security incidents.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Vulnerability Management: Establishing a robust vulnerability management program to promptly address identified weaknesses.
9. Expert Opinions and Analysis
Security experts emphasize that the Internet Archive breach was preventable. The exposure of GitLab authentication tokens for an extended period indicates a failure in basic security hygiene. According to cybersecurity consultant Sarah Jameson, “Organizations must prioritize vulnerability management and regularly monitor their systems for exposed credentials. Failure to do so leaves them vulnerable to attack.” Data privacy advocate Mark Olsen adds, “Users have a right to expect that their personal information is protected. Organizations that fail to meet this expectation will face reputational damage and potential legal consequences.”
10. Steps Users Can Take to Protect Themselves
If you have interacted with the Internet Archive, especially by submitting support tickets or removal requests, take the following steps to protect your personal information:
- Change Passwords: Update passwords for all online accounts, especially those using the same password as your Internet Archive account.
- Monitor Credit Reports: Check your credit reports for any signs of identity theft or fraudulent activity.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Activate two-factor authentication on all accounts that offer it.
- Be Wary of Phishing: Be cautious of suspicious emails or messages asking for personal information.
- Review Privacy Settings: Review and update privacy settings on your online accounts to limit the amount of personal information shared.
11. The Future of Data Breaches and Internet Security
The Internet Archive breach is part of a growing trend of data breaches targeting organizations of all sizes. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations must adopt a proactive and layered approach to security. This includes investing in advanced security technologies, implementing robust security policies, and fostering a culture of security awareness among employees. The future of internet security depends on organizations taking responsibility for protecting user data and collaborating to share threat intelligence. Stay ahead of these trends by regularly consulting resources at WHY.EDU.VN.
12. Relevant Case Studies of Similar Breaches
Several other organizations have suffered similar breaches due to exposed credentials and inadequate security practices. Here are a few notable examples:
| Organization | Incident | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| LastPass | Breach due to compromised developer accounts and exposed credentials. | The importance of securing development environments and implementing robust access controls. |
| T-Mobile | Repeated data breaches due to vulnerabilities in their systems. | The need for continuous security monitoring and proactive vulnerability management. |
| Equifax | Breach due to an unpatched vulnerability in their Apache Struts server. | The critical importance of promptly applying security patches and maintaining up-to-date systems. |
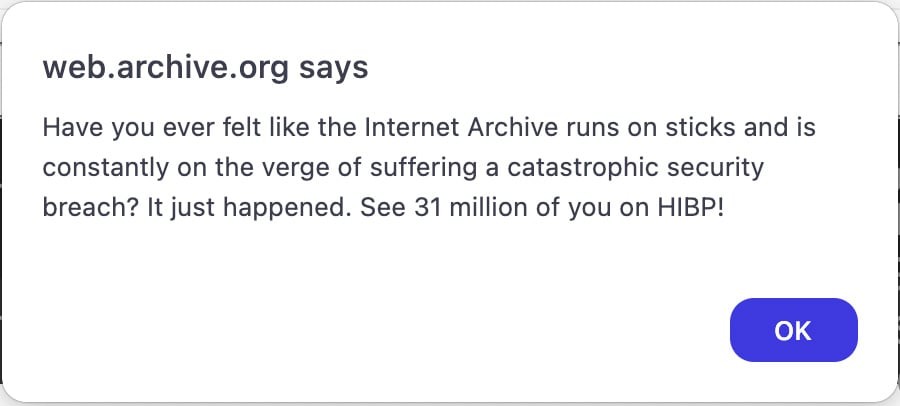
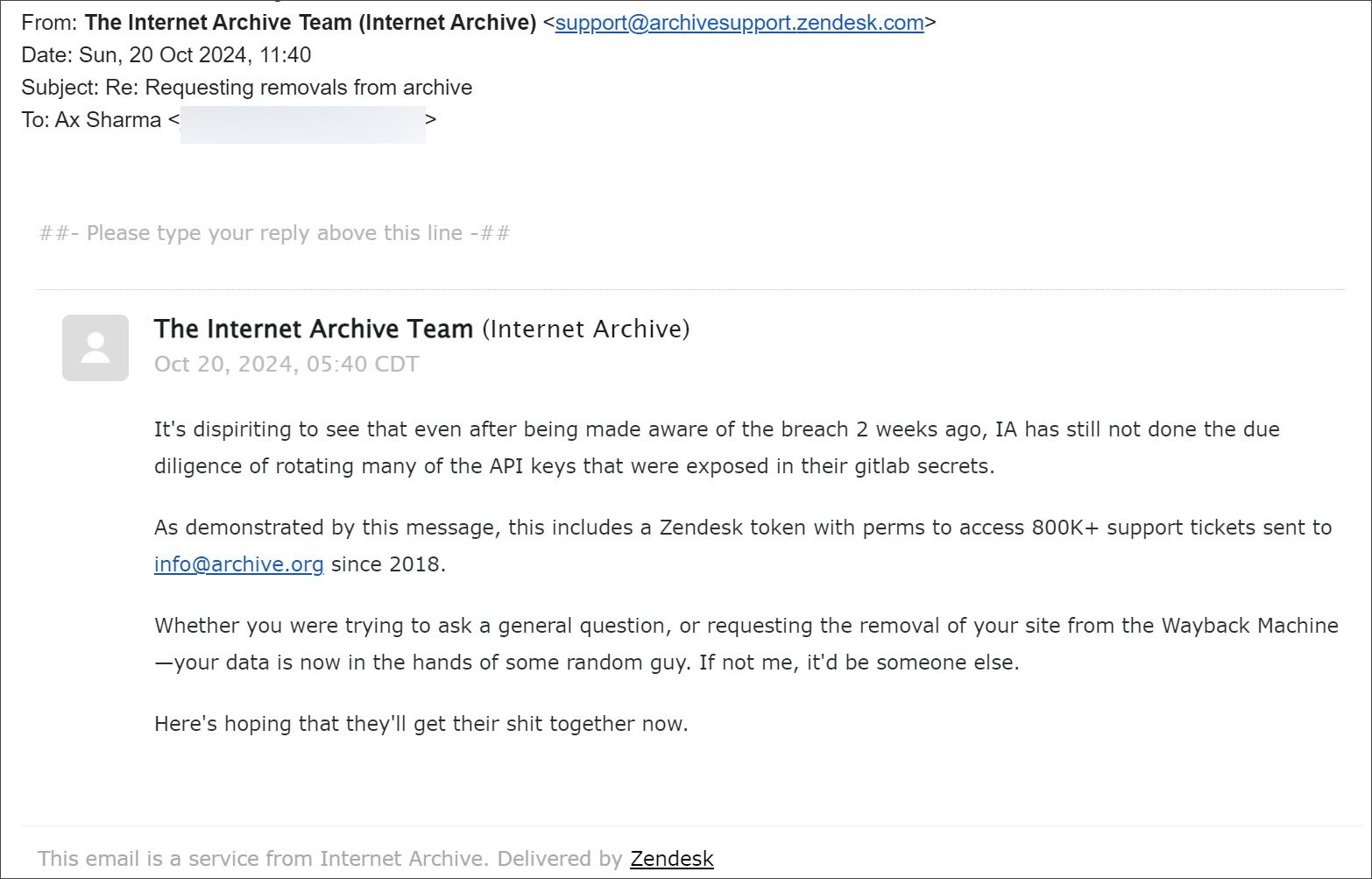
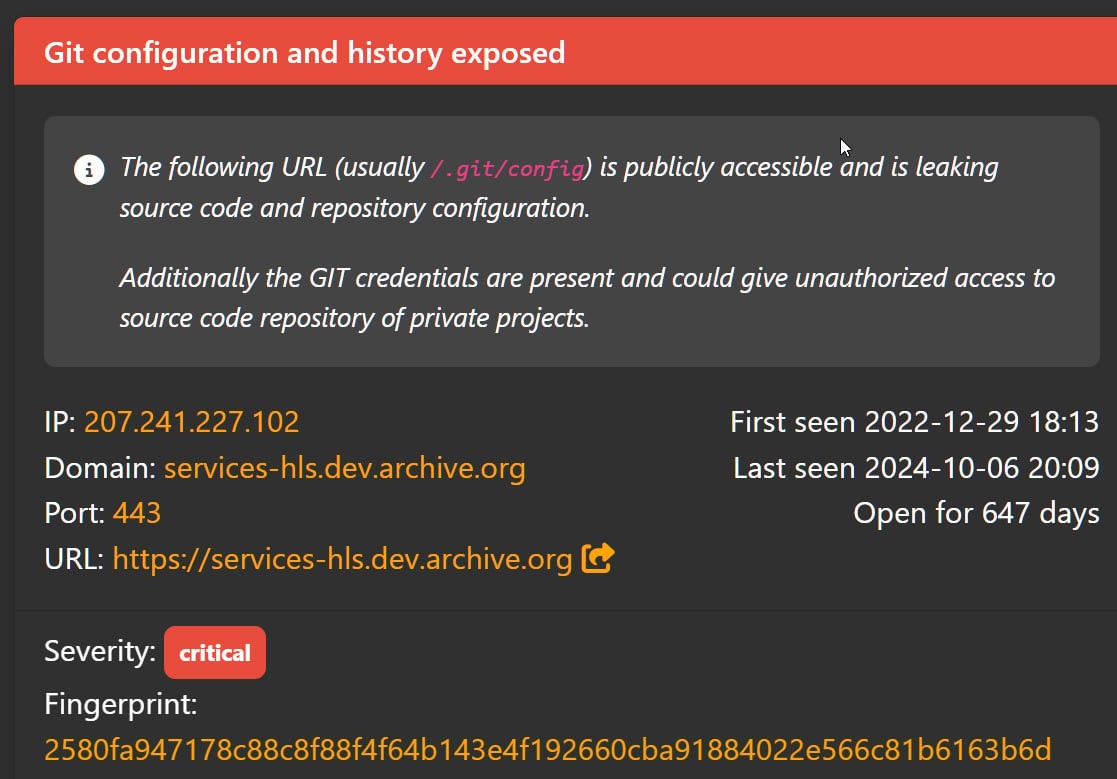
13. Statistics and Data on Data Breaches
Data breaches are on the rise, with significant financial and reputational consequences for organizations. According to a report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 is $4.45 million. The healthcare industry faces the highest breach costs, averaging $10.93 million per incident. Phishing and compromised credentials remain the leading causes of data breaches, accounting for over 80% of incidents. These statistics underscore the need for organizations to prioritize data security and invest in proactive measures to prevent breaches.
14. The Legal and Regulatory Landscape
Data breaches are subject to a complex web of laws and regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These laws require organizations to implement reasonable security measures to protect personal data and to notify affected individuals in the event of a breach. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal liabilities. Organizations must stay informed about the evolving legal landscape and ensure their data security practices align with applicable laws.
15. Tools and Technologies for Enhanced Security
Organizations can leverage a variety of tools and technologies to enhance their security posture and prevent data breaches. These include:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitor network traffic for malicious activity.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collect and analyze security logs from various sources.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Detect and respond to threats on individual devices.
- Vulnerability Scanners: Identify vulnerabilities in systems and applications.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
16. Addressing Misinformation and Conspiracy Theories
Following the Internet Archive breach, several conspiracy theories emerged regarding the motivations behind the attack. Some theories claimed that Israel, the United States government, or corporations were responsible. However, evidence suggests that the breach was primarily motivated by a desire for “cyber street cred” within the hacking community. It is essential to rely on credible sources of information and avoid spreading misinformation or unsubstantiated claims.
17. Comparative Analysis of Security Measures
Different organizations employ varying security measures to protect their data. A comparative analysis reveals that organizations with robust security practices share several common characteristics:
- Proactive Security Posture: They anticipate threats and implement preventive measures.
- Layered Security Approach: They use multiple layers of security to protect against different types of attacks.
- Continuous Monitoring: They continuously monitor their systems for signs of compromise.
- Incident Response Planning: They have well-defined incident response plans.
- Employee Training: They invest in employee training and awareness programs.
18. Practical Tips for Businesses to Prevent Data Breaches
Here are some practical tips for businesses to prevent data breaches:
- Implement Strong Passwords: Enforce strong password policies and require regular password changes.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication: Enable multi-factor authentication for all critical accounts.
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update software and apply security patches.
- Segment Your Network: Segment your network to limit the impact of a breach.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Train Employees: Train employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Develop and test an incident response plan.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit.
- Use a Firewall: Implement a firewall to protect your network from unauthorized access.
19. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the Internet Archive?
The Internet Archive is a non-profit digital library with the mission of providing universal access to all knowledge.
Q2: What data was stolen from the Internet Archive?
The stolen data included user data for 33 million users, source code, and API access tokens for the Zendesk support system.
Q3: How did the breach occur?
The breach occurred due to an exposed GitLab configuration file containing an authentication token.
Q4: What is a GitLab authentication token?
A GitLab authentication token is a credential that allows access to a GitLab repository, where source code and other sensitive information are stored.
Q5: What is the Zendesk email support platform?
Zendesk is a customer service software that allows organizations to manage and respond to customer inquiries.
Q6: What is “cyber street cred”?
“Cyber street cred” is a term used to describe the reputation or status a hacker gains within the hacking community by successfully executing and publicizing significant attacks.
Q7: What steps can I take to protect my data?
Change passwords, monitor credit reports, enable two-factor authentication, be wary of phishing, and review privacy settings.
Q8: Is the Internet Archive responsible for the breach?
The Internet Archive is responsible for implementing reasonable security measures to protect user data. The failure to do so may result in legal and reputational consequences.
Q9: What are the legal implications of a data breach?
Data breaches are subject to a complex web of laws and regulations, including GDPR and CCPA.
Q10: Where can I find more information about data security?
You can find more information about data security at WHY.EDU.VN, a website dedicated to providing clear and reliable answers to complex questions.
20. Conclusion: Securing Your Digital Footprint
The Internet Archive breach underscores the critical importance of data security in today’s digital landscape. Organizations must prioritize vulnerability management, implement robust authentication practices, and develop comprehensive incident response plans. As users, we must take proactive steps to protect our personal information and remain vigilant against cyber threats.
Have more questions or need expert advice on data security? Visit WHY.EDU.VN, where our team of specialists is ready to provide you with the insights and solutions you need. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let why.edu.vn be your trusted resource for navigating the complexities of the digital world.
