Is the Lutheran Church really facing a decline? Yes, the Lutheran Church is experiencing a decline due to cultural shifts, unclear Christian distinctiveness, and difficulties in providing meaning, however, why.edu.vn will provide comprehensive insights, explore the underlying causes, and propose potential solutions to address this issue. Discover the reasons behind the decline and explore strategies for revitalization. Uncover the current trends, theological identity, and spiritual habits.
1. What Factors Are Contributing to The Decline of The Lutheran Church?
The decline of the Lutheran Church is a multifaceted issue stemming from various interconnected factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for addressing the challenges and seeking revitalization. Here’s a detailed look at the key contributors:
1.1. Cultural Shifts
Modern Western culture presents significant challenges to religious organizations. God is often perceived as unnecessary for a fulfilling life, and divine agency seems implausible to many. Individuals are encouraged to discover their own meaning, purpose, identity, and community, making faith an optional choice among numerous alternatives.
1.1.1. Secularization
Secularization, the decline in religious belief and practice in modern societies, has significantly impacted church attendance and membership. As societies become more secular, traditional religious institutions like the Lutheran Church struggle to maintain their relevance.
1.1.2. Individualism
The emphasis on individualism, where personal autonomy and self-discovery are prioritized, can conflict with the communal and doctrinal aspects of religious life. People are increasingly seeking individualized spiritual paths rather than adhering to traditional religious structures.
1.1.3. Pluralism
The proliferation of diverse beliefs and lifestyles creates a competitive environment for religious institutions. People have more options than ever for finding meaning and community, reducing the appeal of traditional churches.
1.2. Unclear Christian Distinctiveness
Many churches struggle to differentiate themselves from other social, cultural, or community service organizations. If the primary purpose of a church is perceived as merely providing social or community services, people can easily find more accessible alternatives. The core theological identity and unique practices of the church must be clearly articulated and demonstrated.
1.2.1. Lack of Clear Identity
Without a clear and compelling theological identity, the church risks becoming indistinguishable from secular organizations. This lack of distinctiveness makes it difficult to attract and retain members who are looking for something unique and meaningful.
1.2.2. Ineffective Communication
Churches often struggle to effectively communicate their core values and beliefs to both members and the wider community. This can lead to misunderstandings and a perception that the church is out of touch with contemporary issues.
1.2.3. Failure to Adapt
The inability to adapt to changing cultural norms and preferences can alienate potential members. Churches that cling rigidly to tradition without addressing modern concerns may find themselves increasingly irrelevant.
1.3. Difficulty in Providing Meaning
For many, faith is no longer the central source of meaning in life. Studies show that people are increasingly turning to family, career, and money for purpose and identity. Faith is often seen as a helpful addition but not a necessity.
1.3.1. Shifting Priorities
As societal values shift, people prioritize different aspects of life. Career success, financial stability, and personal fulfillment often take precedence over religious engagement.
1.3.2. Meaning Crisis
Many individuals experience a sense of meaninglessness or existential angst, which traditional religious institutions may fail to address adequately. The church needs to offer compelling answers to the deeper questions of life.
1.3.3. Disconnect from Daily Life
The church’s teachings and practices may seem disconnected from the realities of daily life. People need to see how their faith can provide practical guidance and support in navigating the challenges they face.
1.4. Institutional Challenges
Beyond cultural and spiritual factors, the Lutheran Church faces internal challenges that contribute to its decline.
1.4.1. Aging Membership
Many Lutheran congregations have an aging membership base, with fewer young people joining. This demographic imbalance threatens the long-term sustainability of the church.
1.4.2. Declining Attendance
Regular church attendance is declining across many denominations, including the Lutheran Church. This decrease in participation weakens the sense of community and reduces financial support.
1.4.3. Financial Constraints
Declining membership and attendance lead to financial challenges for many congregations. Limited resources can hinder the church’s ability to invest in programs, outreach, and infrastructure.
1.4.4. Leadership Issues
Effective leadership is crucial for guiding a church through challenging times. Some congregations may struggle with leadership issues, such as a lack of vision, ineffective communication, or internal conflicts.
1.5. Societal Trends
Broader societal trends also play a role in the decline of the Lutheran Church.
1.5.1. Rise of the “Nones”
The growing number of people who identify as “nones” (having no religious affiliation) is a significant trend. This group includes atheists, agnostics, and those who are spiritual but not religious.
1.5.2. Distrust of Institutions
There is a growing distrust of institutions in general, including religious organizations. Scandals, controversies, and perceived hypocrisy can erode public trust.
1.5.3. Digital Age
The digital age presents both opportunities and challenges for the church. While technology can be used to reach new audiences, it also provides alternative sources of information, entertainment, and community.
By addressing these multifaceted factors, the Lutheran Church can begin to revitalize its mission and relevance in the 21st century. It requires a willingness to adapt, innovate, and engage with the world in meaningful ways.
 lutheran church members
lutheran church members
2. What Does The Data Say About The Lutheran Church’s Decline?
Examining statistical trends provides a clear picture of the challenges facing the Lutheran Church. These figures highlight the urgency of addressing the factors contributing to its decline.
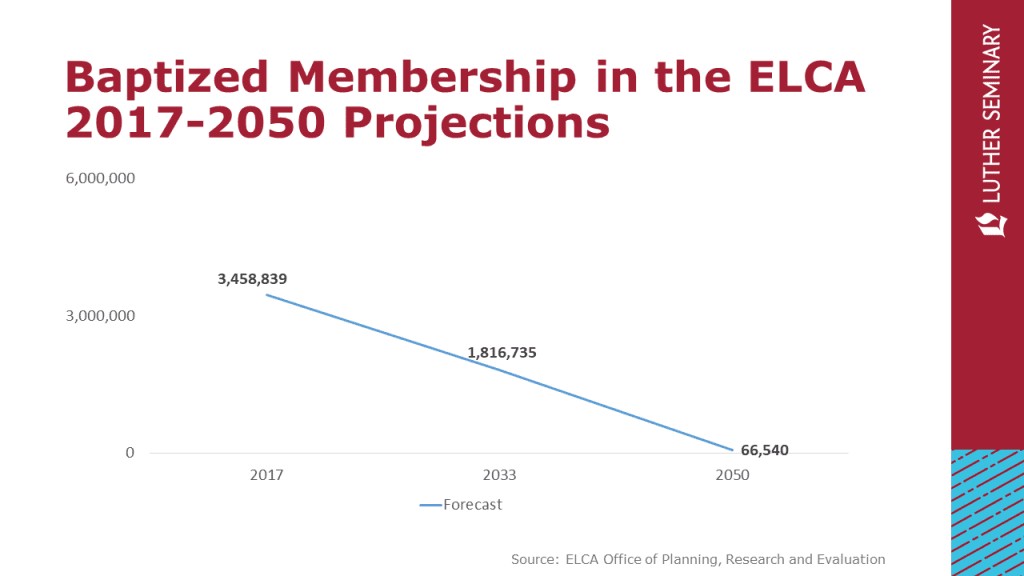
2.1. Evangelical Lutheran Church in America (ELCA) Projections
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America (ELCA) has released projections indicating a significant decline in membership and attendance. According to the ELCA’s Office of Research and Evaluation:
- Membership Decline: By 2050, the ELCA is projected to have fewer than 67,000 members.
- Attendance Decline: By 2041, average Sunday worship attendance is expected to fall below 16,000.
These projections suggest that the ELCA could effectively cease to exist within the next generation if current trends continue.
2.2. Historical Membership Trends
The ELCA was formed in 1988 with over five million members. Since then, it has experienced a consistent decline in membership. This decline has not only continued but has also accelerated over time.
| Year | Membership |
|---|---|
| 1988 | 5,000,000 |
| 2024 | Significant Decline |
| 2050 | < 67,000 |
2.3. Mainline Protestant Decline
The decline of the Lutheran Church is part of a broader trend affecting mainline Protestant denominations in the United States. These denominations have been experiencing membership losses for over half a century.
2.3.1. Pew Research Center Studies
Pew Research Center has conducted numerous studies on religious affiliation and trends in the U.S. These studies consistently show a decline in the percentage of Americans who identify as Christian, particularly within mainline Protestant denominations.
2.3.2. Causes of Decline
Pew Research Center studies identify several factors contributing to the decline of mainline Protestant denominations, including:
- Generational Shifts: Younger generations are less likely to identify with a particular religious denomination than older generations.
- Rise of the “Nones”: The increasing number of Americans who do not identify with any religion is a significant factor.
- Changing Social Norms: Shifts in social norms and values have led some people to distance themselves from traditional religious institutions.
2.4. Comparison with Other Denominations
Comparing the Lutheran Church’s trends with those of other denominations provides additional context. While many denominations are facing challenges, some are experiencing growth or stability.
2.4.1. Growing Denominations
Evangelical Protestant denominations, for example, have generally fared better than mainline Protestant denominations. Some have even experienced growth in recent years.
2.4.2. Factors in Growth
Factors contributing to the growth of some denominations include:
- Emphasis on Personal Experience: These denominations often emphasize personal religious experiences and emotional engagement.
- Conservative Theology: A more conservative theological stance can appeal to some individuals seeking traditional values.
- Community Focus: Strong community-building efforts can help attract and retain members.
2.5. Impact of Cultural Factors
Cultural shifts play a significant role in the decline of the Lutheran Church. The increasing secularization of society, the emphasis on individualism, and the rise of pluralism all contribute to the challenges faced by the church.
2.5.1. Secularization
As societies become more secular, traditional religious institutions lose their influence. People are less likely to prioritize religious participation and may view religion as irrelevant to their daily lives.
2.5.2. Individualism
The emphasis on individual autonomy and self-discovery can conflict with the communal and doctrinal aspects of religious life. People may prefer to explore their own spiritual paths rather than adhere to traditional religious structures.
2.5.3. Pluralism
The proliferation of diverse beliefs and lifestyles creates a competitive environment for religious institutions. People have more options than ever for finding meaning and community, reducing the appeal of traditional churches.
2.6. Addressing the Decline
To address the decline, the Lutheran Church needs to adapt to changing cultural norms, strengthen its theological identity, and find new ways to provide meaning and purpose in people’s lives. This may involve:
- Re-evaluating traditional practices: Identifying practices that are no longer effective and adapting them to meet the needs of contemporary society.
- Emphasizing core values: Clearly articulating and promoting the core values of the Lutheran tradition.
- Building community: Creating strong, supportive communities that foster a sense of belonging and purpose.
- Engaging with contemporary issues: Addressing relevant social and ethical issues in a thoughtful and engaging way.
By understanding the statistical trends and the underlying factors contributing to the decline, the Lutheran Church can develop strategies to revitalize its mission and relevance in the 21st century.
3. What Are The Key Theological And Doctrinal Challenges?
The Lutheran Church faces significant theological and doctrinal challenges that contribute to its decline. Addressing these issues requires a deep understanding of Lutheran theology and a willingness to engage with contemporary questions.
3.1. Relevance of Traditional Doctrines
One of the main challenges is ensuring the relevance of traditional Lutheran doctrines in a modern context. Many people struggle to see how these doctrines relate to their daily lives.
3.1.1. Justification by Faith
The doctrine of justification by faith alone (sola fide) is central to Lutheran theology. However, it can be misunderstood or perceived as irrelevant in a society that emphasizes works and achievements. The challenge is to explain how this doctrine provides comfort, hope, and meaning in the face of life’s challenges.
3.1.2. The Authority of Scripture
Lutherans traditionally hold a high view of Scripture as the inspired Word of God. However, in an age of skepticism and scientific inquiry, some people question the Bible’s authority and accuracy. The challenge is to engage with these questions in a thoughtful and respectful way, while still affirming the Bible’s central role in Christian faith and practice.
3.1.3. The Sacraments
Lutheran theology emphasizes the importance of the sacraments of baptism and Holy Communion as means of grace. However, many people do not understand the significance of these rituals or their connection to daily life. The challenge is to make the sacraments more accessible and meaningful to contemporary believers.
3.2. Interpreting Scripture in a Modern Context
The Lutheran Church must grapple with how to interpret Scripture in a way that is both faithful to tradition and relevant to contemporary issues.
3.2.1. Historical-Critical Method
The historical-critical method of biblical interpretation, which examines the historical and cultural context of the biblical texts, has become widely accepted in theological circles. However, it can also raise questions about the Bible’s literal accuracy and authority. The challenge is to use this method responsibly, while still affirming the Bible’s unique status as the Word of God.
3.2.2. Addressing Social Issues
The Bible addresses a wide range of social and ethical issues, but its teachings can be complex and open to interpretation. The Lutheran Church must engage with these issues in a way that is both faithful to Scripture and sensitive to the needs of contemporary society.
3.2.3. Hermeneutics
The study of hermeneutics, or the principles of biblical interpretation, is essential for addressing these challenges. By developing sound hermeneutical principles, the Lutheran Church can ensure that its interpretation of Scripture is both faithful and relevant.
3.3. Engaging with Contemporary Ethical Issues
The Lutheran Church must address contemporary ethical issues such as environmentalism, social justice, and sexuality in a way that is both faithful to its theological tradition and relevant to the needs of contemporary society.
3.3.1. Environmental Stewardship
The Bible teaches that humans have a responsibility to care for the earth and its resources. The Lutheran Church must develop a theology of environmental stewardship that addresses the urgent challenges of climate change and environmental degradation.
3.3.2. Social Justice
The Bible calls on Christians to advocate for justice and equality for all people. The Lutheran Church must address issues such as poverty, racism, and discrimination in a way that is both compassionate and effective.
3.3.3. Sexuality
Issues related to sexuality, such as same-sex marriage and LGBTQ+ inclusion, have become increasingly divisive in many Christian denominations. The Lutheran Church must engage with these issues in a way that is both faithful to Scripture and respectful of the diversity of human experience.
3.4. Maintaining Doctrinal Integrity
The Lutheran Church must balance the need to adapt to changing cultural norms with the importance of maintaining doctrinal integrity.
3.4.1. Confessional Identity
The Lutheran Church has a rich confessional tradition, rooted in the Augsburg Confession and other Lutheran confessions of faith. These confessions provide a framework for understanding Lutheran theology and identity. The challenge is to uphold these confessions while still being open to new insights and perspectives.
3.4.2. Avoiding Doctrinal Drift
Doctrinal drift, or the gradual erosion of traditional beliefs, can occur when a church becomes too accommodating to contemporary culture. The Lutheran Church must be vigilant in safeguarding its core doctrines and ensuring that its teachings remain faithful to Scripture and the Lutheran tradition.
3.4.3. Theological Education
Strong theological education is essential for maintaining doctrinal integrity. The Lutheran Church must invest in the training of pastors and theologians who are well-versed in Lutheran theology and capable of engaging with contemporary challenges.
By addressing these theological and doctrinal challenges, the Lutheran Church can strengthen its identity, revitalize its mission, and remain a vibrant force for good in the world.
4. How Can The Lutheran Church Adapt To Modern Culture?
Adapting to modern culture is crucial for the Lutheran Church to remain relevant and attract new members. This involves embracing innovation while staying true to its core values and theological identity.
4.1. Embracing Technology
Technology offers numerous opportunities for the Lutheran Church to reach new audiences and enhance its ministry.
4.1.1. Online Presence
Creating a strong online presence is essential for connecting with people in the digital age. This includes having a user-friendly website, active social media accounts, and engaging online content.
4.1.2. Virtual Worship
Offering virtual worship services and online Bible studies can reach people who are unable to attend church in person. This can be particularly beneficial for those who are homebound, have mobility issues, or live in remote areas.
4.1.3. Digital Communication
Using digital communication tools such as email, text messaging, and social media can help keep members informed about church events and activities. It can also facilitate communication and connection within the congregation.
4.2. Rethinking Worship
Rethinking traditional worship practices can make services more engaging and relevant to contemporary audiences.
4.2.1. Contemporary Music
Incorporating contemporary music into worship services can attract younger generations and create a more vibrant atmosphere. This may involve using contemporary hymns, praise songs, or original compositions.
4.2.2. Interactive Services
Making worship services more interactive can help keep people engaged. This may involve incorporating multimedia presentations, group discussions, or opportunities for personal reflection.
4.2.3. Casual Atmosphere
Creating a more casual and welcoming atmosphere can make people feel more comfortable attending church. This may involve relaxing dress codes, offering refreshments, or creating a more informal seating arrangement.
4.3. Community Engagement
Engaging with the local community is essential for demonstrating the church’s relevance and commitment to serving others.
4.3.1. Outreach Programs
Developing outreach programs that address local needs can help the church build relationships with the community. This may involve providing food, clothing, or shelter to the homeless, tutoring children, or volunteering at local organizations.
4.3.2. Partnerships
Partnering with other organizations, such as schools, hospitals, and community centers, can help the church expand its reach and impact. This may involve co-sponsoring events, sharing resources, or collaborating on community projects.
4.3.3. Social Justice Advocacy
Advocating for social justice issues can demonstrate the church’s commitment to making a positive difference in the world. This may involve lobbying for legislation, organizing protests, or raising awareness about important social issues.
4.4. Focusing on Young People
Attracting and retaining young people is crucial for the long-term health of the Lutheran Church.
4.4.1. Youth Programs
Developing youth programs that are engaging, relevant, and fun can help young people connect with their faith and build relationships with one another. This may involve offering youth groups, mission trips, or retreats.
4.4.2. Mentorship
Providing mentorship opportunities can help young people connect with adult role models who can guide and support them. This may involve pairing young people with mentors who share their interests or who can offer advice on career and life choices.
4.4.3. Leadership Opportunities
Providing leadership opportunities can help young people develop their skills and confidence. This may involve inviting young people to serve on church committees, lead worship services, or organize community events.
4.5. Interfaith Dialogue
Engaging in interfaith dialogue can help the Lutheran Church build bridges with other religious communities and promote understanding and cooperation.
4.5.1. Building Relationships
Building relationships with leaders and members of other religious communities can foster mutual respect and understanding. This may involve attending interfaith events, participating in joint service projects, or engaging in theological discussions.
4.5.2. Common Ground
Identifying areas of common ground can help build bridges between different religious traditions. This may involve focusing on shared values such as compassion, justice, and peace.
4.5.3. Addressing Differences
Addressing differences in a respectful and open-minded way can help promote understanding and avoid conflict. This may involve engaging in theological discussions, asking questions, and listening to different perspectives.
By embracing these strategies, the Lutheran Church can adapt to modern culture, attract new members, and remain a vibrant force for good in the world.
5. What Role Does Leadership Play In The Church’s Future?
Effective leadership is crucial for the future of the Lutheran Church. Leaders must guide the church through challenges and inspire congregations to embrace change while staying true to their faith.
5.1. Visionary Leadership
Visionary leaders can articulate a clear and compelling vision for the future of the church.
5.1.1. Strategic Planning
Developing a strategic plan that outlines the church’s goals and objectives can help guide its efforts and ensure that resources are used effectively. This may involve conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and setting measurable goals.
5.1.2. Innovation
Encouraging innovation and experimentation can help the church adapt to changing circumstances and find new ways to reach people. This may involve creating a culture of creativity and risk-taking, and providing resources for new initiatives.
5.1.3. Communication
Communicating the church’s vision effectively can inspire and motivate members. This may involve using a variety of communication channels, such as sermons, newsletters, and social media.
5.2. Servant Leadership
Servant leaders prioritize the needs of others and lead by example.
5.2.1. Empathy
Demonstrating empathy and compassion can help leaders connect with members and understand their needs. This may involve listening actively, asking questions, and showing genuine concern.
5.2.2. Humility
Practicing humility and admitting mistakes can build trust and credibility. This may involve being open to feedback, acknowledging limitations, and seeking forgiveness when necessary.
5.2.3. Empowerment
Empowering others to take on leadership roles can help build a stronger and more resilient church. This may involve delegating tasks, providing training and support, and recognizing achievements.
5.3. Collaborative Leadership
Collaborative leaders work with others to achieve common goals.
5.3.1. Team Building
Building strong teams can help the church accomplish its mission more effectively. This may involve identifying and recruiting talented individuals, providing team-building activities, and fostering a sense of camaraderie.
5.3.2. Conflict Resolution
Resolving conflicts constructively can help maintain harmony and unity within the church. This may involve using mediation techniques, facilitating dialogue, and seeking common ground.
5.3.3. Networking
Networking with other churches and organizations can help the church expand its reach and impact. This may involve attending conferences, joining professional associations, and partnering on community projects.
5.4. Spiritual Leadership
Spiritual leaders provide guidance and inspiration based on their faith.
5.4.1. Prayer
Prioritizing prayer and spiritual reflection can help leaders stay grounded and focused on God’s will. This may involve setting aside time for personal prayer, participating in group prayer meetings, and seeking guidance from spiritual mentors.
5.4.2. Bible Study
Studying the Bible regularly can help leaders deepen their understanding of God’s Word and apply it to their lives and ministry. This may involve reading the Bible daily, participating in Bible study groups, and attending theological conferences.
5.4.3. Discernment
Exercising discernment can help leaders make wise decisions that align with God’s will. This may involve seeking counsel from trusted advisors, weighing different options carefully, and trusting in God’s guidance.
5.5. Adaptive Leadership
Adaptive leaders can navigate complex and uncertain situations.
5.5.1. Flexibility
Being flexible and adaptable can help leaders respond effectively to changing circumstances. This may involve being open to new ideas, adjusting plans as needed, and embracing innovation.
5.5.2. Resilience
Demonstrating resilience in the face of adversity can inspire others and help the church overcome challenges. This may involve maintaining a positive attitude, learning from mistakes, and persevering through difficult times.
5.5.3. Change Management
Managing change effectively can help the church adapt to new realities and avoid resistance. This may involve communicating clearly, involving members in the decision-making process, and providing support and resources.
By embodying these leadership qualities, leaders can guide the Lutheran Church towards a vibrant and sustainable future.
6. Case Studies Of Successful Church Revitalization
Examining case studies of successful church revitalization can provide valuable insights and inspiration for the Lutheran Church.
6.1. Example 1: The “Innovative” Church
- Background: A struggling Lutheran church in a suburban community.
- Challenges: Declining membership, aging congregation, lack of engagement with young people.
- Strategies:
- Revamped Worship: Introduced contemporary music, multimedia presentations, and interactive services.
- Community Outreach: Partnered with local schools and organizations to provide after-school programs, food drives, and community events.
- Youth Ministry: Developed a dynamic youth program that included mission trips, retreats, and service projects.
- Online Presence: Created a user-friendly website, active social media accounts, and online worship services.
- Results: Increased membership, younger congregation, stronger community engagement, and improved financial stability.
6.2. Example 2: The “Traditional” Church
- Background: A historic Lutheran church in a rural area.
- Challenges: Declining attendance, outdated facilities, lack of relevance to modern life.
- Strategies:
- Restored Facilities: Renovated the church building to create a more welcoming and functional space.
- Preserved Traditions: Maintained traditional worship practices, hymns, and liturgy.
- Community Service: Focused on serving the local community through food banks, clothing drives, and support for local farmers.
- Intergenerational Programs: Developed programs that brought together people of all ages, such as family dinners, Bible studies, and service projects.
- Results: Increased attendance, stronger sense of community, renewed appreciation for tradition, and improved financial support.
6.3. Example 3: The “Social Justice” Church
- Background: A Lutheran church in an urban neighborhood.
- Challenges: Social inequality, poverty, and racial tension.
- Strategies:
- Advocacy: Advocated for social justice issues, such as affordable housing, fair wages, and racial equality.
- Community Organizing: Organized community members to address local issues and advocate for change.
- Partnerships: Partnered with other churches and organizations to provide social services, such as job training, legal aid, and healthcare.
- Education: Educated members about social justice issues through Bible studies, workshops, and guest speakers.
- Results: Increased engagement with social justice issues, stronger community partnerships, greater awareness of inequality, and a more diverse congregation.
6.4. Key Success Factors
These case studies highlight several key success factors for church revitalization:
- Visionary Leadership: Strong leadership is essential for guiding the church through change and inspiring members to embrace new ideas.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with the local community is crucial for demonstrating the church’s relevance and commitment to serving others.
- Adaptability: Being willing to adapt to changing circumstances and embrace innovation is essential for staying relevant.
- Authenticity: Staying true to the church’s core values and theological identity is important for maintaining its integrity.
- Collaboration: Working with others, such as other churches, organizations, and community members, can help the church expand its reach and impact.
By learning from these case studies and implementing these success factors, the Lutheran Church can overcome its challenges and create a vibrant and sustainable future.
7. How Can Lutherans Reclaim Their Identity?
Reclaiming their identity involves rediscovering the core values and beliefs that define Lutheranism and expressing them in ways that are relevant to contemporary society.
7.1. Rediscovering Core Values
Lutherans can start by revisiting the core values and beliefs that define their tradition.
7.1.1. Justification by Faith
Re-emphasizing the doctrine of justification by faith alone can provide comfort, hope, and meaning in a world that often feels overwhelming. This involves teaching that salvation is a gift from God, not something that can be earned through good works.
7.1.2. The Authority of Scripture
Reaffirming the authority of Scripture as the inspired Word of God can provide guidance and direction in a complex and uncertain world. This involves studying the Bible regularly, interpreting it responsibly, and applying its teachings to daily life.
7.1.3. The Sacraments
Re-emphasizing the importance of the sacraments of baptism and Holy Communion as means of grace can provide spiritual nourishment and connection with God. This involves understanding the significance of these rituals and participating in them regularly.
7.2. Engaging with Contemporary Issues
Lutherans can reclaim their identity by engaging with contemporary issues in a way that is both faithful to their theological tradition and relevant to the needs of contemporary society.
7.2.1. Social Justice
Advocating for social justice issues can demonstrate the church’s commitment to making a positive difference in the world. This involves addressing issues such as poverty, racism, and discrimination in a way that is both compassionate and effective.
7.2.2. Environmental Stewardship
Developing a theology of environmental stewardship can address the urgent challenges of climate change and environmental degradation. This involves promoting sustainable practices, advocating for environmental policies, and educating members about environmental issues.
7.2.3. Interfaith Dialogue
Engaging in interfaith dialogue can build bridges with other religious communities and promote understanding and cooperation. This involves building relationships with leaders and members of other religious communities, identifying areas of common ground, and addressing differences in a respectful and open-minded way.
7.3. Creating Meaningful Experiences
Lutherans can reclaim their identity by creating meaningful experiences that connect people with their faith and with one another.
7.3.1. Worship
Rethinking traditional worship practices can make services more engaging and relevant to contemporary audiences. This involves incorporating contemporary music, multimedia presentations, and interactive services.
7.3.2. Community
Building strong communities can provide a sense of belonging and purpose. This involves creating opportunities for people to connect with one another, such as small groups, social events, and service projects.
7.3.3. Service
Engaging in service to others can help people experience the love of God and make a positive difference in the world. This involves providing opportunities for people to volunteer their time, donate to charitable causes, and advocate for social justice issues.
7.4. Promoting Lutheran Heritage
Lutherans can reclaim their identity by promoting their heritage and sharing their story with others.
7.4.1. Education
Educating members and the wider community about Lutheran history, theology, and culture can help people understand the unique contributions of Lutheranism. This involves offering classes, workshops, and lectures on Lutheran topics, and promoting Lutheran books, music, and art.
7.4.2. Storytelling
Sharing stories about Lutheran heroes, events, and traditions can help people connect with their heritage and feel a sense of pride in their identity. This involves collecting and preserving Lutheran stories, sharing them in sermons, newsletters, and social media, and celebrating Lutheran holidays and anniversaries.
7.4.3. Outreach
Reaching out to others and inviting them to learn more about Lutheranism can help grow the church and expand its influence. This involves creating welcoming and inclusive environments, offering introductory classes and tours, and promoting Lutheran events and activities.
By reclaiming their identity in these ways, Lutherans can strengthen their church, revitalize their faith, and make a positive difference in the world.
8. What Innovative Ministry Models Can Be Adopted?
Adopting innovative ministry models can help the Lutheran Church reach new audiences and address contemporary challenges.
8.1. Missional Communities
Missional communities are small groups of people who gather together to live out their faith in a specific context, such as a neighborhood, workplace, or social network.
8.1.1. Focus on Relationships
Missional communities prioritize building authentic relationships with one another and with people in their community. This involves spending time together, sharing meals, and supporting one another through life’s challenges.
8.1.2. Contextualization
Missional communities adapt their practices and programs to fit the specific needs and context of their community. This involves listening to the needs of the community, partnering with local organizations, and developing creative solutions to local problems.
8.1.3. Multiplication
Missional communities are designed to multiply and spread throughout a community. This involves training leaders, empowering members, and encouraging new communities to form.
8.2. Fresh Expressions
Fresh expressions are new forms of church that are designed to reach people who are not currently connected to traditional churches.
8.2.1. Innovation
Fresh expressions are innovative and experimental, often taking place in unconventional settings such as coffee shops, pubs, or community centers.
8.2.2. Relevance
Fresh expressions are designed to be relevant to the needs and interests of the people they are trying to reach. This involves listening to their stories, understanding their culture, and adapting their practices accordingly.
8.2.3. Collaboration
Fresh expressions often involve collaboration between different churches and organizations. This can help share resources, expand reach, and create a stronger sense of community.
8.3. Online Ministry
Online ministry uses technology to reach people who are not able to attend church in person.
8.3.1. Virtual Worship
Virtual worship services can reach people who are homebound, have mobility issues, or live in remote areas. This involves streaming services online, creating interactive elements, and offering opportunities for online fellowship.
8.3.2. Digital Content
Digital content, such as podcasts, blogs, and social media posts, can provide information, inspiration, and community for people who are interested in exploring their faith online.
8.3.3. Online Courses
Online courses can provide opportunities for people to learn about Lutheran theology, history, and culture. This involves creating engaging and interactive courses, offering opportunities for online discussion, and providing feedback and support.
8.4. Social Enterprise
Social enterprise uses business principles to address social problems.
8.4.1. Mission-Driven
Social enterprises are driven by a social mission, such as providing job training for the unemployed, offering affordable housing for the homeless, or supporting sustainable agriculture.
8.4.2. Revenue Generation
Social enterprises generate revenue through the sale of goods or services. This revenue is used to support the social mission of the enterprise.
8.4.3. Community Impact
Social enterprises create a positive impact in the community by addressing social problems and creating opportunities for people in need.
8.5. Multi-Site Churches
Multi-site churches have multiple locations, each with its own worship service and community.
8.5.1. Expanded Reach
Multi-site churches can reach a wider audience by establishing locations in different neighborhoods or communities.
8.5.2. Shared Resources
Multi-site churches can share resources, such as staff, technology, and curriculum, across multiple locations.
8.5.3. Local Autonomy
Multi-site churches allow each location to have its own unique identity and culture, while still maintaining a connection to the larger church.
By adopting these innovative ministry models, the Lutheran Church can reach new audiences, address contemporary challenges, and create a vibrant and sustainable future.
9. How Can The Church Foster A Sense Of Community?
Fostering a strong sense of community is essential for the health and vitality of the Lutheran Church.
9.1. Small Groups
Small groups provide opportunities for people to connect with one another on a deeper level.
9.1.1. Shared Interests
Small groups can be based on shared interests, such as Bible study, book clubs, or hobby groups.
9.1.2. Support
Small groups can provide support and encouragement during times of need.
9.1.3. Accountability
Small groups can provide accountability for members to live out their faith in their daily lives.
9.2. Social Events
Social events provide opportunities for people to connect with one another in a casual and fun environment.
9.2.1. Church Picnics
Church picnics can be a great way to bring people together for food, games, and fellowship.
9.2.2. Holiday Parties
Holiday parties can celebrate special occasions and provide opportunities for people to connect with one another.
9.2.3. Game Nights
Game nights can be a fun and engaging way for people to spend time together.
9.3. Service Projects
Service projects provide opportunities for people to work together to make a positive impact in the community.
9.3.1. Food Banks
Volunteering at a local food bank can help provide food for people in need.
9.3.2. Homeless Shelters
Volunteering at a local homeless shelter can help provide