Is your hand suddenly burning? It can be alarming and uncomfortable, but don’t worry. At WHY.EDU.VN, we’ll explore the potential reasons behind this sensation, from simple irritations to more complex conditions, and offer practical solutions to alleviate your discomfort, leveraging our expertise. This guide will cover conditions, treatments, and related symptoms, so you can take action toward relief with the correct diagnosis of nerve damage and skin conditions.
1. Decoding the Burning Sensation: What’s Causing Your Hand to Burn?
Burning sensations in your hand can stem from various underlying causes, each requiring a different approach to diagnosis and treatment. Here are some of the most common culprits, categorized for clarity:
1.1. Localized Skin Reactions:
- Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when your skin comes into direct contact with an irritant or allergen.
- Sunburn: Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can damage the skin and cause inflammation, leading to a burning sensation.
1.2. Nerve-Related Issues:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS): Compression of the median nerve in the wrist can cause burning, tingling, numbness, and pain in the hand and fingers.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Damage to the peripheral nerves can result in a variety of sensations, including burning, stabbing, or electric-like pain in the hands and feet.
1.3. Circulatory Problems:
- Erythromelalgia: This rare condition affects the blood vessels, causing intense burning pain, redness, and warmth in the extremities, particularly the hands and feet.
1.4. Systemic Conditions:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over time can damage nerves, leading to peripheral neuropathy.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins, such as B12, can contribute to nerve damage and burning sensations.
1.5. Infections and Inflammatory Conditions:
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles): This viral infection can cause a painful rash with burning sensations, typically on one side of the body.
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): This chronic pain condition can develop after an injury or surgery, causing burning pain, swelling, and changes in skin color and temperature.
Understanding these potential causes is the first step toward finding relief. Keep reading to delve deeper into each condition, its symptoms, and available treatment options.
2. Infections, Allergies, and Drug Reactions: Immediate Culprits
Sometimes, the reason for your hand burning is quite straightforward, stemming from an immediate reaction to an external factor.
2.1. Infection: When a Wound Becomes a Worry
If you have an inflamed wound on your hand, infection is a likely culprit. Bacteria can enter through cuts or abrasions, leading to inflammation, pain, and a burning sensation. According to the National Institutes of Health, prompt treatment with topical or oral antibiotics is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, pain, pus or drainage, warmth, and a burning sensation around the wound.
- Treatment: Clean the wound thoroughly with soap and water. Apply a topical antibiotic ointment. If the infection is severe or doesn’t improve, see a doctor for oral antibiotics.
2.2. Drug Reaction: The Unintended Side Effect
If you’ve recently started a new medication or changed dosages, a drug reaction could be the cause of your burning hands. Some medications can trigger nerve damage or allergic reactions that manifest as a burning sensation.
According to the Mayo Clinic, drug-induced neuropathy is a known side effect of certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, and medications for high blood pressure.
- Symptoms: Burning, tingling, numbness, or pain in the hands or feet, often accompanied by other side effects of the medication.
- Treatment: Contact your doctor immediately to discuss your symptoms. They may recommend adjusting the dosage, switching to a different medication, or discontinuing the drug altogether.
2.3. Allergies: An Unexpected Trigger
Allergies can also cause burning hands or fingers. Allergic reactions can trigger inflammation and irritation, leading to a burning sensation. Common allergens include certain foods, insect bites, and plants.
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, food allergies can cause a variety of symptoms, including skin rashes, itching, and burning sensations.
- Symptoms: Burning, itching, redness, swelling, or hives on the hands or fingers after exposure to an allergen.
- Treatment: Identify and avoid the allergen. Apply a topical corticosteroid cream to relieve inflammation and itching. Take an antihistamine to reduce allergic symptoms.
3. Unraveling Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Common Cause of Burning Hands
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a prevalent condition that affects millions worldwide. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. This compression can lead to a variety of symptoms, including burning hands, numbness, tingling, and pain.
3.1. The Mechanics of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist formed by bones and ligaments. The median nerve, along with tendons that control finger movement, passes through this tunnel. When the tissues surrounding the tendons become inflamed, they can compress the median nerve, leading to CTS.
Repetitive hand and wrist movements, such as typing, assembly line work, or playing musical instruments, are common risk factors for CTS. Other factors that can contribute to CTS include:
- Anatomy: Some people have smaller carpal tunnels than others, making them more susceptible to nerve compression.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disorders can increase the risk of CTS.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause fluid retention, which can compress the median nerve.
- Wrist Injuries: Sprains or fractures of the wrist can narrow the carpal tunnel and compress the median nerve.
3.2. Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The symptoms of CTS typically develop gradually over time. Common symptoms include:
- Burning Hands: A burning sensation in the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger, and part of the ring finger.
- Numbness: Numbness in the same fingers as the burning sensation.
- Tingling: A pins-and-needles sensation in the same fingers.
- Pain: Pain in the wrist, hand, or forearm, which may radiate up the arm.
- Weakness: Weakness in the hand, making it difficult to grip objects or perform fine motor tasks.
- Nighttime Symptoms: Symptoms are often worse at night, due to sleeping positions that compress the wrist.
3.3. Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A doctor can diagnose CTS based on a physical exam and nerve conduction studies. During the physical exam, the doctor will assess your symptoms, examine your wrist and hand, and perform tests to evaluate nerve function.
Nerve conduction studies measure the speed at which electrical signals travel along the median nerve. Slowed conduction velocity indicates nerve compression.
3.4. Treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment for CTS depends on the severity of the symptoms. Mild cases may respond to conservative treatments, while more severe cases may require surgery.
3.4.1. Conservative Treatments
- Wrist Bracing: Wearing a wrist brace, especially at night, can help to keep the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve.
- Stretching Exercises: Performing stretching exercises can help to improve flexibility and reduce inflammation in the wrist.
- Ergonomics: Making changes to your workstation or activities to reduce repetitive hand and wrist movements can help to prevent further nerve compression.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the carpal tunnel can help to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
3.4.2. Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be necessary to release the pressure on the median nerve. Carpal tunnel release surgery involves cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, which widens the tunnel and relieves pressure on the nerve.
Surgery can be performed using an open or endoscopic technique. Open surgery involves making a larger incision in the wrist, while endoscopic surgery involves making smaller incisions and using a camera to guide the procedure.
3.5. Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
You can take several steps to prevent CTS, including:
- Taking frequent breaks: When performing repetitive hand and wrist movements, take frequent breaks to rest your hands and wrists.
- Using proper posture: Maintain good posture and keep your wrists straight when working.
- Using ergonomic equipment: Use ergonomic keyboards, mice, and other equipment to reduce strain on your hands and wrists.
- Performing stretching exercises: Perform stretching exercises regularly to improve flexibility and reduce inflammation in the wrist.
4. Neuropathy: When Nerves Misbehave
Neuropathy refers to nerve damage that can cause a range of symptoms, including burning hands. Peripheral neuropathy, in particular, affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, often leading to sensations like burning, tingling, or numbness in the hands and feet.
4.1. Understanding Neuropathy: A Network Gone Awry
Neuropathy arises from damage to the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. When these nerves are damaged, they can misfire, sending abnormal signals that result in various sensory disturbances.
4.2. Causes of Neuropathy
Neuropathy can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over time can damage nerves, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as shingles, Lyme disease, and HIV, can damage nerves.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, can cause inflammation that damages nerves.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins, such as B12, can contribute to nerve damage.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can cause neuropathy as a side effect.
- Trauma: Injuries to the nerves can cause neuropathy.
- Alcohol Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage nerves.
- Genetic Disorders: Some genetic disorders can cause neuropathy.
4.3. Symptoms of Neuropathy
The symptoms of neuropathy can vary depending on the type of nerves affected and the extent of the damage. Common symptoms include:
- Burning Hands and Feet: A burning sensation in the hands and feet is a hallmark symptom of neuropathy.
- Numbness: Numbness in the hands and feet.
- Tingling: A pins-and-needles sensation in the hands and feet.
- Sharp, Stabbing Pain: Sharp, stabbing pain in the hands and feet.
- Sensitivity to Touch: Increased sensitivity to touch, making even light touch painful.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the hands and feet.
- Loss of Coordination: Difficulty with coordination and balance.
4.4. Diagnosing Neuropathy
A doctor can diagnose neuropathy based on a physical exam, a review of your medical history, and nerve conduction studies. Nerve conduction studies measure the speed at which electrical signals travel along the nerves. Slowed conduction velocity indicates nerve damage.
4.5. Treating Neuropathy
Treatment for neuropathy depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Medications, such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, can help to relieve pain and other symptoms of neuropathy.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve muscle strength, coordination, and balance.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy diet, can help to improve nerve health.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: Treating underlying conditions, such as diabetes, can help to prevent further nerve damage.
4.6. Managing Neuropathy
In addition to medical treatment, several self-care strategies can help to manage neuropathy symptoms:
- Protect Your Hands and Feet: Wear gloves and socks to protect your hands and feet from injury.
- Inspect Your Hands and Feet Regularly: Check your hands and feet regularly for cuts, blisters, or other signs of injury.
- Maintain Good Blood Sugar Control: If you have diabetes, maintain good blood sugar control to prevent further nerve damage.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can help to improve blood flow and nerve health.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Eat a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support nerve health.
- Avoid Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol can damage nerves.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the nerves.
5. Erythromelalgia: A Rare Vascular Condition
Erythromelalgia is a rare condition that affects the blood vessels, causing intense burning pain, redness, and warmth in the extremities, particularly the hands and feet.
5.1. Understanding Erythromelalgia: A Vascular Disorder
Erythromelalgia is characterized by episodes of intense burning pain, redness, and warmth in the extremities. These episodes, known as flares, can be triggered by heat, exercise, or prolonged standing.
5.2. Causes of Erythromelalgia
Erythromelalgia can be primary or secondary. Primary erythromelalgia is caused by a genetic mutation that affects the function of the sodium channels in the nerve cells. Secondary erythromelalgia is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as:
- Myeloproliferative Disorders: These disorders, such as polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, cause an overproduction of blood cells, which can lead to blood vessel abnormalities.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can cause inflammation that damages blood vessels.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels.
- Multiple Sclerosis: This neurological disorder can affect blood vessel function.
5.3. Symptoms of Erythromelalgia
The symptoms of erythromelalgia can vary in severity and frequency. Common symptoms include:
- Burning Pain: Intense burning pain in the hands and feet.
- Redness: Redness of the skin in the affected areas.
- Warmth: Increased warmth in the affected areas.
- Swelling: Swelling of the hands and feet.
- Triggered by Heat: Symptoms are often triggered by heat, exercise, or prolonged standing.
- Relieved by Cooling: Symptoms are often relieved by cooling the affected areas.
5.4. Diagnosing Erythromelalgia
A doctor can diagnose erythromelalgia based on a physical exam and a review of your medical history. The doctor may also order blood tests to rule out underlying medical conditions.
5.5. Treating Erythromelalgia
There is no cure for erythromelalgia, but treatments are available to manage the symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers, cooling the affected areas, and elevating the hands and feet, can help to relieve symptoms.
- Medications: Medications, such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, can help to relieve pain and other symptoms.
- Topical Creams: Topical creams containing capsaicin or lidocaine can help to relieve pain.
- Nerve Blocks: Nerve blocks can be used to block pain signals from the affected nerves.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to remove or bypass damaged blood vessels.
5.6. Managing Erythromelalgia
In addition to medical treatment, several self-care strategies can help to manage erythromelalgia symptoms:
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that worsen your symptoms.
- Cool the Affected Areas: Cool the affected areas with cold water or ice packs.
- Elevate Your Hands and Feet: Elevate your hands and feet to reduce swelling.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing to avoid constricting blood flow.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Avoid Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption, as alcohol can worsen symptoms.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking constricts blood vessels, worsening symptoms.
6. Seeking Relief: Practical Solutions for Burning Hands
Regardless of the underlying cause, there are several practical steps you can take to alleviate the burning sensation in your hands.
6.1. Home Remedies
- Cooling: Apply a cool compress or soak your hands in cool water for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Elevation: Elevate your hands to reduce swelling and improve circulation.
- Moisturizing: Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer to soothe dry, irritated skin.
- Avoiding Irritants: Avoid contact with harsh chemicals, soaps, and other irritants.
- Gentle Massage: Gently massage your hands to improve circulation and relieve muscle tension.
6.2. Over-the-Counter Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Topical Creams: Topical creams containing capsaicin or lidocaine can help to relieve pain.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines can help to relieve itching and other allergic symptoms.
- Corticosteroid Creams: Topical corticosteroid creams can help to reduce inflammation.
6.3. Medical Treatments
If home remedies and over-the-counter medications are not effective, your doctor may recommend medical treatments, such as:
- Prescription Medications: Prescription medications, such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, can help to relieve pain and other symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve muscle strength, coordination, and balance.
- Nerve Blocks: Nerve blocks can be used to block pain signals from the affected nerves.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to remove or bypass damaged blood vessels.
7. Unveiling the Expert’s Insight
Let’s hear from Dr. Maik Zannakis (Dr. Z), the Medical Director at CarpalRx, a renowned expert in carpal tunnel syndrome and soft tissue disorders, shares insights on the burning sensations of hands.
Dr. Maik Zannakis (Dr. Z)
Medical Director at the CarpalRx
“Burning hands can be a perplexing and uncomfortable symptom, often indicative of an underlying issue that requires careful attention. It’s essential not to dismiss this sensation, as it can be a sign of various conditions, ranging from carpal tunnel syndrome to peripheral neuropathy. Understanding the potential causes is the first step toward finding effective relief.
At CarpalRx, we often encounter patients experiencing burning hands due to carpal tunnel syndrome. This condition arises when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. The compression can lead to burning, tingling, numbness, and pain in the hand and fingers.
However, carpal tunnel syndrome is not the only culprit behind burning hands. Peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage outside the brain and spinal cord, can also cause a burning sensation in the hands and feet. This nerve damage can result from various factors, including diabetes, infections, autoimmune diseases, and vitamin deficiencies.
In addition, erythromelalgia, a rare vascular condition, can manifest as intense burning pain, redness, and warmth in the extremities, particularly the hands and feet. This condition affects the blood vessels and can be triggered by heat, exercise, or prolonged standing.
To accurately diagnose the cause of burning hands, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. A thorough examination and nerve conduction studies can help determine the underlying condition and guide appropriate treatment.
Fortunately, various treatment options are available to alleviate the symptoms of burning hands. For carpal tunnel syndrome, wrist bracing, stretching exercises, and ergonomic adjustments can provide relief. In more severe cases, carpal tunnel release surgery may be necessary.
For peripheral neuropathy, treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms. Medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes can help to improve nerve health and reduce pain.
In erythromelalgia, lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers, cooling the affected areas, and elevating the hands and feet, can help to manage symptoms. Medications and topical creams may also provide relief.
Ultimately, finding relief from burning hands requires a comprehensive approach that involves identifying the underlying cause, implementing appropriate treatments, and adopting self-care strategies. By working closely with a healthcare professional, you can develop a personalized plan to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Remember, burning hands can be a symptom of a more significant health issue, so don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. With proper diagnosis and treatment, you can find relief and regain control over your hand health.”
8. FAQ: Addressing Your Burning Hand Concerns
Here are some frequently asked questions about burning hands, along with expert answers:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What does a burning sensation in my hand usually mean? | A burning sensation can stem from various causes like nerve compression (carpal tunnel), nerve damage (neuropathy), skin irritation (contact dermatitis), or vascular issues (erythromelalgia). |
| Can stress cause my hands to burn? | Yes, indirectly. Stress can exacerbate conditions like neuropathy or cause muscle tension that aggravates carpal tunnel, both leading to burning sensations. |
| Are burning hands a sign of diabetes? | Possibly. Diabetic neuropathy, a complication of diabetes, often causes burning sensations in the hands and feet due to nerve damage from prolonged high blood sugar. |
| When should I see a doctor about burning hands? | If the sensation is severe, persistent, accompanied by other symptoms like numbness or weakness, or if home remedies provide no relief, consult a doctor. Early diagnosis can prevent long-term damage. |
| How is carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosed? | Typically through a physical examination involving symptom assessment and tests like the Tinel’s sign or Phalen’s maneuver, along with nerve conduction studies to measure nerve function. |
| What are the first steps to relieve burning hands at home? | Try cooling the hands with cold water or ice packs, gently massaging the area, elevating your hands, and avoiding activities that seem to trigger or worsen the burning. |
| Can vitamin deficiencies cause burning hands? | Yes, deficiencies in certain vitamins like B12, B6, or folate can lead to peripheral neuropathy, which may cause burning sensations in the hands. |
| Is burning hands always a serious condition? | Not always, sometimes it is due to minor skin irritations. However, because it can also indicate more severe underlying conditions, it’s important to monitor and seek medical advice if it persists or worsens. |
| Are there specific exercises that can help burning hands? | Yes, especially if the cause is carpal tunnel syndrome. Exercises that stretch and strengthen the wrist and hand can help relieve pressure on the median nerve. Consult a physical therapist for tailored exercises. |
| What if my hands burn only at night? | This could be related to carpal tunnel syndrome or peripheral neuropathy, where symptoms often worsen at night due to sleeping positions. Elevating your hands and wearing a wrist splint can help manage nighttime symptoms. Additionally, neuropathy symptoms often increase in the evening. |
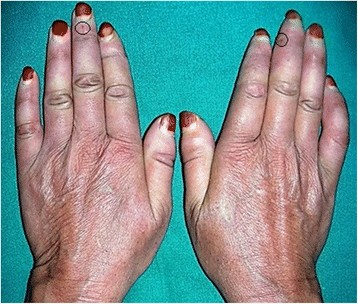

9. Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Hand Health
Experiencing a burning sensation in your hands can be unsettling, but understanding the potential causes and available solutions is the first step toward finding relief. From localized skin reactions to nerve-related issues, circulatory problems, and systemic conditions, the range of possibilities is wide. By seeking professional medical advice, exploring home remedies, and considering medical treatments, you can take control of your hand health and improve your quality of life.
Remember, WHY.EDU.VN is here to provide you with accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Are you still searching for answers? Do you need expert guidance to understand the cause of your burning hands?
Visit WHY.EDU.VN today! Our platform connects you with qualified professionals who can provide personalized answers to your health questions.
Contact Us:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let why.edu.vn be your trusted partner in finding the answers you need to live a healthier, happier life. We’re here to provide expert insights and support to guide you on your wellness journey.
