Why Honey Is Good For Health? Honey, a natural sweetener revered for centuries, offers far more than just a delightful taste; WHY.EDU.VN reveals its remarkable health benefits backed by scientific research. From its potent antioxidant and antimicrobial properties to its potential in managing various health conditions, we’ll explore why incorporating honey into your diet can be a sweet and healthy choice. Discover the advantages, nutritional facts and health boosting potential of this golden elixir and similar health boosting foods.
1. Understanding Honey: A Natural Elixir
Honey, produced by bees from the nectar of flowers, is a complex mixture of sugars, enzymes, minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants. Its unique composition contributes to its diverse range of health benefits.
- Source: Nectar of flowers, collected and processed by bees (Apis mellifera).
- Historical Use: Used for nutritional and medicinal purposes for over 5500 years by various ancient civilizations.
- Composition: Primarily carbohydrates (95-97% of dry weight), including fructose and glucose, along with proteins, vitamins, amino acids, minerals, and organic acids.
- Unique Properties: High fructose content (25% sweeter than table sugar), low water activity (0.56-0.62), acidic pH (around 3.9).
- Storage: Does not require refrigeration, never spoils when stored properly in a dry place at room temperature.
- Types: Over 300 recognized types, each with varying characteristics based on the nectar source.
2. Key Nutritional Components of Honey
Honey’s nutritional profile extends beyond simple sugars, providing a range of essential and beneficial compounds.
- Carbohydrates: Predominantly fructose and glucose, providing energy.
- Minerals: Includes phosphorus, sodium, calcium, potassium, sulfur, magnesium, and chlorine. Essential trace elements like silicon, rubidium, and lithium are also present.
- Vitamins: Contains water-soluble vitamins, with Vitamin C being the most prevalent.
- Amino Acids: Includes all nine essential amino acids and nonessential amino acids (except asparagine and glutamine), with proline being the primary amino acid.
- Enzymes: Diastase, invertases, glucose oxidase, catalase, and acid phosphatase.
- Organic Acids: Gluconic acid (product of glucose oxidation) along with small amounts of acetic, formic, and citric acids.
- Antioxidants: Flavonoids and polyphenols (e.g., gallic acid, caffeic acid, quercetin, kaempferol).
3. The Power of Antioxidants in Honey
Honey is rich in antioxidants, primarily flavonoids and polyphenols, which play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and protecting the body from oxidative stress.
- Role of Antioxidants: Protect the body by neutralizing free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and disease.
- Types of Antioxidants:
- Flavonoids: Including quercetin, kaempferol, and pinobanksin.
- Phenolic Acids: Such as gallic acid, caffeic acid, and ellagic acid.
- Benefits: Reduce the risk of chronic diseases, support immune function, and promote overall health.
- Darker Honey: Generally contains higher levels of antioxidants compared to lighter varieties.
- Mechanism: Antioxidants in honey intercept free radicals, preventing them from damaging cellular components like lipids, proteins, and DNA.
4. Honey’s Antimicrobial Properties: A Natural Defense
Honey exhibits potent antimicrobial activity, inhibiting the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- Factors Contributing to Antimicrobial Activity:
- Enzymatic Glucose Oxidation: Production of hydrogen peroxide.
- Low Water Activity: Inhibits microbial growth by reducing available moisture.
- Acidity: Low pH (3.2-4.5) creates an unfavorable environment for many microbes.
- Phytochemicals: Presence of compounds like terpenes, pinocembrin, and syringic acid.
- Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC): The lowest concentration of honey required to inhibit microbial growth.
- Manuka Honey: Known for its high non-peroxide antibacterial activity, effective against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Applications: Effective against various bacterial pathogens and fungi, making it useful in wound care and infection control.
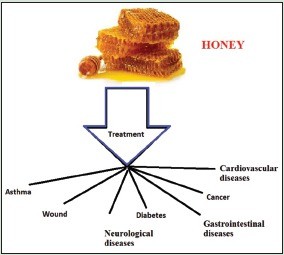
5. Honey and Wound Healing: A Traditional Remedy
Honey has been used for centuries to promote wound healing, and modern research supports its effectiveness in treating burns, ulcers, and other skin injuries.
- Historical Use: One of the oldest known wound-healing agents.
- Mechanisms of Action:
- Antibacterial Activity: Prevents infection and promotes a clean wound environment.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Reduces swelling and pain.
- Antioxidant Activity: Protects tissue from damage and promotes healing.
- Cytokine Release: Stimulates leukocytes to release cytokines, initiating tissue repair.
- Immune Response Activation: Enhances immune function to fight infection.
- Types of Wounds Treated: Acute wounds, mild to moderate superficial and partial thickness burns.
6. Honey and Diabetes: A Sweet Alternative?
While honey is a sugar-rich food, studies suggest it may have beneficial effects on blood sugar control and lipid profiles compared to other sweeteners.
- Glycemic Index (GI): Honey may have a lower GI compared to sucrose or glucose in some individuals with type 1 diabetes.
- Blood Glucose Reduction: Studies indicate that honey can reduce plasma glucose levels compared to dextran in diabetic patients.
- Lipid Profile Improvement: Honey may reduce blood lipids, homocysteine, and C-reactive protein levels in normal and hyperlipidemic patients.
- Antioxidant Benefits: Honey’s antioxidants may help mitigate oxidative stress associated with diabetes.
- Important Note: Individuals with diabetes should consume honey in moderation and monitor their blood sugar levels closely. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential before making significant dietary changes.
7. Honey and Cancer: Exploring the Potential
Emerging research suggests that honey may possess anticancer properties, interfering with multiple cell-signaling pathways and inhibiting cancer cell growth.
- Mechanisms of Action:
- Apoptosis Induction: Promotes programmed cell death in cancer cells.
- Antimutagenic Properties: Reduces the risk of DNA mutations.
- Antiproliferative Effects: Inhibits cancer cell growth and spread.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Reduces inflammation that can promote cancer development.
- Immune Response Modulation: Enhances the body’s natural defenses against cancer.
- Types of Cancer Cells Affected: Skin cancer (melanoma), cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, liver cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and others.
- Animal Studies: Honey has shown potential in inhibiting tumor growth in animal models of breast cancer, colon carcinoma, hepatic cancer, and bladder cancer.
- Current research: While promising, further studies are needed to fully understand honey’s role in cancer prevention and treatment.
8. Honey and Asthma: Soothing the Airways
Honey has been used traditionally to treat coughs and respiratory ailments, and some studies suggest it may help alleviate asthma symptoms.
- Traditional Use: Used in folk medicine for inflammation, cough, and fever.
- Potential Benefits:
- Symptom Reduction: May reduce asthma-related symptoms.
- Airway Inflammation Inhibition: Studies suggest honey can inhibit ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation.
- Mucus Reduction: Inhalation of honey may help remove mucus-secreting goblet cell hyperplasia.
- Research Needs: More studies are required to fully understand the mechanisms by which honey reduces asthma symptoms.
9. Honey and Cardiovascular Health: Protecting the Heart
The antioxidants in honey may contribute to cardiovascular health by improving blood vessel function and reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Antioxidant Protection: Flavonoids, polyphenolics, Vitamin C, and monophenolics in honey may reduce the risk of cardiovascular failures.
- Mechanisms of Action:
- Improved Coronary Vasodilation: Enhances blood flow to the heart.
- Reduced Platelet Clotting: Decreases the risk of blood clots.
- Inhibition of LDL Oxidation: Prevents the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (bad cholesterol).
- Key Antioxidants: Caffeic acid, quercetin, phenethyl ester, kaempferol, galangin, and acacetin.
- Further Research: More research is needed to validate these compounds in medical applications.
10. Honey and Neurological Health: Nourishing the Brain
Honey’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may offer neuroprotective benefits, potentially reducing the risk of neurological diseases.
- Nutraceutical Properties: Honey is considered a promising nutraceutical antioxidant.
- Potential Benefits:
- Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects: May reduce anxiety and depression.
- Anticonvulsant and Antinociceptive Effects: May help control seizures and reduce pain.
- Oxidative Stress Reduction: Ameliorates oxidative content in the central nervous system.
- Polyphenol Benefits:
- Neuroprotection: Protects against neurotoxicity.
- Memory Improvement: Enhances memory production at the molecular level.
- Neuroinflammation Reduction: Counters neuroinflammation in the hippocampus, a brain structure involved in memory.
- Future Research: Further studies are needed to determine the biochemical impact of honey on neurological function.
11. Honey and Gastrointestinal Health: Soothing the Gut
Honey has been suggested as potentially useful for various gastrointestinal conditions, including oral disorders, dyspepsia, and diarrhea.
- Potential Benefits:
- Oral Health: May help with periodontal and other oral disorders.
- Dyspepsia Relief: May alleviate symptoms of indigestion.
- Oral Rehydration Therapy: Can be part of oral rehydration therapy.
- Helicobacter pylori: In vitro studies suggest honey has bactericidal activity against Helicobacter pylori, though clinical trial results have been mixed.
- Diarrhea Treatment: Clinical trials show honey may reduce the duration of diarrhea in infants and children with gastroenteritis.
12. Incorporating Honey into Your Diet: A Sweet and Healthy Choice
Honey can be a delicious and nutritious addition to your diet, offering a range of health benefits when consumed in moderation.
- As a Natural Sweetener: Use honey as a substitute for refined sugar in beverages, baked goods, and other foods.
- In Tea and Drinks: Add a spoonful of honey to tea or other beverages for sweetness and flavor.
- On Toast and Oatmeal: Drizzle honey over toast, oatmeal, or yogurt for a healthy breakfast or snack.
- In Salad Dressings and Marinades: Incorporate honey into homemade salad dressings and marinades for added sweetness and flavor.
- As a Cough Remedy: Take a spoonful of honey to soothe a sore throat and relieve cough symptoms.
- Skin Care: Apply honey topically to minor burns, cuts, and skin irritations to promote healing.
13. Potential Risks and Considerations
While honey offers numerous health benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and considerations.
- Infant Botulism: Honey should not be given to infants under one year old due to the risk of botulism.
- Allergies: Individuals with allergies to bee pollen or other bee products may experience allergic reactions to honey.
- High Sugar Content: Honey is high in sugar and should be consumed in moderation, especially by individuals with diabetes or those watching their weight.
- Dental Health: Honey can contribute to tooth decay if oral hygiene is not maintained.
- Quality and Purity: Choose high-quality, pure honey from reputable sources to ensure you are getting the full benefits.
14. Choosing the Right Honey: Quality Matters
Selecting high-quality honey is crucial to ensure you reap its full benefits.
- Pure Honey: Look for honey that is labeled as “pure” and has not been processed or adulterated with added sugars or syrups.
- Raw Honey: Raw honey retains more of its natural enzymes, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds.
- Local Honey: Local honey may offer additional benefits, such as helping to reduce seasonal allergies.
- Color and Texture: The color and texture of honey can vary depending on the floral source, but generally, darker honey tends to have higher antioxidant levels.
- Reputable Sources: Purchase honey from reputable beekeepers or retailers who prioritize quality and purity.
15. Scientific Evidence Supporting Honey’s Benefits
Numerous studies have investigated the health benefits of honey, providing evidence for its various medicinal properties.
- Antioxidant Activity: Studies have shown that honey’s phenolic compounds are responsible for its antioxidant activity.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Research indicates that honey is effective against various bacterial pathogens and fungi.
- Wound Healing: Clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of honey in treating burns, ulcers, and other skin injuries.
- Diabetes Management: Some studies suggest that honey may have beneficial effects on blood sugar control and lipid profiles in individuals with diabetes.
- Cancer Research: Emerging research indicates that honey may possess anticancer properties, interfering with multiple cell-signaling pathways.
- Asthma Relief: Studies have shown that honey may help alleviate asthma symptoms.
- Cardiovascular Health: Research suggests that the antioxidants in honey may contribute to cardiovascular health.
- Neurological Benefits: Studies propose that honey polyphenols have nootropic and neuroprotective properties.
- Gastrointestinal Health: In vitro studies suggest honey has bactericidal activity against Helicobacter pylori.
16. Honey in Traditional Medicine: A Time-Tested Remedy
Honey has a long history of use in traditional medicine systems around the world, including Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine, and ancient Egyptian medicine.
- Ayurveda: Honey is used to balance the three doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and is believed to have warming, drying, and scraping properties.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine: Honey is used to tonify the Qi, moisten the lungs, and relieve coughs.
- Ancient Egyptian Medicine: Honey was used to treat wounds, burns, and other skin conditions.
- Other Traditional Uses: Honey has been used to treat eye diseases, bronchial asthma, throat infections, tuberculosis, fatigue, dizziness, hepatitis, constipation, and worm infestations.
17. Honey vs. Other Sweeteners: A Healthier Choice?
When compared to other sweeteners like refined sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, and artificial sweeteners, honey offers several advantages.
- Nutritional Value: Honey contains vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are not found in refined sugar and artificial sweeteners.
- Lower Glycemic Index: Honey may have a lower glycemic index compared to refined sugar, resulting in a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
- Natural Source: Honey is a natural product made by bees, while refined sugar and artificial sweeteners are processed.
- Flavor and Aroma: Honey has a unique flavor and aroma that can enhance the taste of foods and beverages.
- Potential Health Benefits: Honey offers a range of potential health benefits, including antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
18. The Future of Honey Research: Exploring New Frontiers
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the health benefits of honey, paving the way for innovative applications in medicine and healthcare.
- Cancer Therapy: Further research is needed to explore honey’s potential as an adjunct therapy for cancer treatment.
- Wound Care: Studies are investigating the use of honey-based dressings for chronic wounds and infections.
- Diabetes Management: Research is exploring the effects of honey on blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity in individuals with diabetes.
- Neurological Disorders: Studies are investigating the potential of honey to protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Immune Function: Research is examining the effects of honey on immune function and its potential to enhance the body’s defenses against infection.
- Product Development: Honey is being incorporated into various health and wellness products, including cough syrups, skin creams, and dietary supplements.
19. Expert Opinions on Honey’s Health Benefits
Experts in nutrition, medicine, and beekeeping recognize the diverse health benefits of honey and advocate for its responsible use in a balanced diet and healthcare practices.
- Nutritionists: Emphasize the importance of consuming honey in moderation as part of a healthy diet, highlighting its antioxidant and nutritional value.
- Medical Professionals: Acknowledge the potential of honey as a natural remedy for wound healing, cough relief, and other ailments, while stressing the need for further research.
- Beekeepers: Advocate for sustainable beekeeping practices to ensure the availability of high-quality honey and protect bee populations.
- Researchers: Continue to explore the mechanisms of action behind honey’s health benefits and identify new applications in medicine and healthcare.
20. Honey and Sustainable Beekeeping: A Vital Connection
The health benefits of honey are intrinsically linked to the health and sustainability of bee populations and beekeeping practices.
- Importance of Bees: Bees play a crucial role in pollination, which is essential for agriculture and food production.
- Threats to Bee Populations: Bee populations are facing threats from habitat loss, pesticide use, climate change, and diseases.
- Sustainable Beekeeping Practices:
- Habitat Preservation: Protecting and restoring natural habitats for bees.
- Pesticide Reduction: Minimizing the use of pesticides that can harm bees.
- Disease Management: Implementing strategies to prevent and control bee diseases.
- Supporting Local Beekeepers: Purchasing honey from local beekeepers who prioritize sustainable practices.
- Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about the importance of supporting sustainable beekeeping and choosing honey from responsible sources.
Honey, with its rich history and diverse health benefits, offers a compelling case for its inclusion in a healthy lifestyle. From its potent antioxidant and antimicrobial properties to its potential in managing various health conditions, honey stands as a testament to nature’s healing power.
FAQ About Honey and Health
Q1: Is honey a healthy substitute for sugar?
A: Yes, honey can be a healthier substitute for refined sugar due to its nutritional value, lower glycemic index, and potential health benefits.
Q2: Can honey help with coughs and colds?
A: Yes, honey has been shown to soothe sore throats and relieve cough symptoms due to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Q3: Is honey safe for diabetics?
A: Individuals with diabetes should consume honey in moderation and monitor their blood sugar levels closely. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential.
Q4: Can honey be used to treat wounds?
A: Yes, honey has been used for centuries to promote wound healing due to its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
Q5: Is honey safe for infants?
A: No, honey should not be given to infants under one year old due to the risk of botulism.
Q6: What are the best types of honey to buy?
A: Look for pure, raw, and local honey from reputable sources to ensure quality and purity.
Q7: Can honey help with allergies?
A: Local honey may help reduce seasonal allergies by exposing you to local pollens.
Q8: Does honey have any side effects?
A: Potential side effects include allergic reactions, high sugar content, and dental issues if oral hygiene is not maintained.
Q9: What is Manuka honey, and why is it special?
A: Manuka honey is known for its high non-peroxide antibacterial activity and is effective against various bacteria.
Q10: How much honey should I consume daily?
A: Consume honey in moderation, typically 1-2 tablespoons per day, as part of a balanced diet.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with accurate and insightful answers to all your burning questions. We understand the challenges of finding reliable information online and the desire for expert perspectives. That’s why we encourage you to visit our website, WHY.EDU.VN, to explore a wealth of knowledge and connect with specialists in various fields.
Do you have more questions about honey or other health-related topics? Don’t hesitate to reach out! Our team of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you need. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or connect with us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Visit our website, why.edu.vn, today and unlock a world of knowledge!