Why Does My Lung Hurt? Exploring the reasons behind lung discomfort, WHY.EDU.VN provides insights into potential causes, related health conditions, and effective relief strategies. Delve into lung pain analysis, chest discomfort etiologies, and pulmonary ache solutions.
1. Decoding Lung Pain: Common Causes
Experiencing pain in your lung area can be alarming, and understanding the possible reasons is the first step toward finding relief. Lung discomfort can arise from a variety of factors, ranging from minor muscle strains to more serious underlying health conditions. Identifying the root cause of the pain is crucial for receiving appropriate medical attention and implementing effective management strategies. Below are some of the potential reasons why you might be experiencing lung pain.
1.1. Musculoskeletal Issues
 Person touching their chest in pain
Person touching their chest in pain
Musculoskeletal issues are a frequent source of chest discomfort that can mimic lung pain. These conditions involve the muscles, bones, and connective tissues in the chest area.
1.1.1. Muscle Strain
Straining the muscles in your chest wall can lead to localized pain that may feel like it’s coming from your lungs. This can result from activities such as heavy lifting, intense exercise, or even forceful coughing. The pain is typically sharp and worsens with movement or deep breathing.
1.1.2. Costochondritis
Costochondritis is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects your ribs to your breastbone (sternum). This inflammation can cause sharp, aching pain in the chest, often on one side. The pain may worsen with movement, deep breathing, or pressing on the affected area. According to the Mayo Clinic, costochondritis is a common cause of chest pain, accounting for a significant number of emergency room visits.
1.1.3. Rib Fractures
Rib fractures, whether from trauma or underlying conditions like osteoporosis, can cause intense pain that radiates through the chest. The pain is usually sharp and increases with breathing, coughing, or movement. Rib fractures require medical evaluation and treatment to ensure proper healing.
1.2. Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia, can directly affect the lungs and lead to chest pain. These infections cause inflammation and irritation of the airways, resulting in discomfort.
1.2.1. Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from your lungs. It can cause a persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. The pain is often described as a burning or aching sensation in the chest. According to the American Lung Association, bronchitis affects millions of people each year and is often caused by viral infections.
1.2.2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of one or both lungs, causing inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli). Symptoms include cough, fever, chills, shortness of breath, and chest pain. The pain is typically sharp and worsens with breathing or coughing. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and requires prompt medical treatment.
1.2.3. Pleurisy
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, the lining of the lungs and chest wall. When the pleura becomes inflamed, it can cause sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing. Pleurisy often occurs as a complication of respiratory infections like pneumonia or bronchitis. The pain can be quite severe and may require pain management strategies.
1.3. Lung Conditions
Various lung conditions can directly contribute to chest pain, ranging from asthma to more serious illnesses like lung cancer. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms associated with these conditions and seek appropriate medical care.
1.3.1. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. While asthma primarily affects the airways, the resulting inflammation and muscle constriction can cause chest discomfort that feels like lung pain. The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America reports that asthma affects millions of people in the United States.
1.3.2. Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious condition where a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow. Symptoms include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, and rapid heart rate. The chest pain associated with PE is often sharp and worsens with breathing. PE is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.
1.3.3. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the lungs. Symptoms may include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing up blood. The chest pain associated with lung cancer can be dull, aching, or sharp and may worsen with breathing or coughing. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in lung cancer.
1.3.4. Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax, also known as a collapsed lung, occurs when air leaks into the space between the lung and chest wall. This can cause sudden chest pain and shortness of breath. Pneumothorax can happen spontaneously or as a result of trauma or underlying lung disease. Treatment may involve inserting a chest tube to remove the air and allow the lung to re-expand.
1.4. Cardiovascular Issues
While not directly related to the lungs, certain cardiovascular conditions can cause chest pain that mimics lung pain. It’s important to consider these possibilities and seek medical evaluation to rule out any heart-related issues.
1.4.1. Angina
Angina is chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen-rich blood. It’s often described as a squeezing, pressure, or tightness in the chest. Angina is usually triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience angina, as it may be a sign of underlying heart disease.
1.4.2. Pericarditis
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, the sac-like structure that surrounds the heart. Symptoms include sharp, stabbing chest pain that may worsen with breathing or lying down. Pericarditis can be caused by viral infections, autoimmune disorders, or other medical conditions. Treatment typically involves medications to reduce inflammation and pain.
2. Dissecting the Discomfort: Understanding Lung Pain Symptoms
Understanding the specific symptoms associated with lung pain is crucial for identifying the underlying cause and seeking appropriate medical attention. Lung pain can manifest in various ways, ranging from sharp, localized pain to dull, aching discomfort. Recognizing the characteristics of your pain can help your healthcare provider make an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most effective treatment plan. Below are some of the common symptoms associated with lung pain.
2.1. Types of Pain
Lung pain can present in various forms, each potentially indicating a different underlying cause. Sharp, stabbing pain may suggest conditions like pleurisy or pneumothorax, while dull, aching pain could be related to muscle strain or chronic lung conditions. Understanding the specific type of pain you’re experiencing is an important first step in determining the cause.
- Sharp Pain: Often associated with inflammation or irritation of the pleura, the lining of the lungs and chest wall.
- Dull Ache: May indicate muscle strain, chronic lung conditions, or underlying inflammation.
- Burning Sensation: Can occur with respiratory infections like bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Pressure or Tightness: Often associated with asthma or cardiovascular issues like angina.
2.2. Accompanying Symptoms
Lung pain rarely occurs in isolation. It’s often accompanied by other symptoms that can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause. These accompanying symptoms may include cough, shortness of breath, fever, wheezing, or coughing up blood. Paying attention to these additional symptoms can help your healthcare provider narrow down the possible diagnoses.
| Symptom | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Cough | Respiratory infections (bronchitis, pneumonia), asthma, lung cancer |
| Shortness of Breath | Asthma, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, pneumothorax, lung cancer |
| Fever | Respiratory infections (bronchitis, pneumonia) |
| Wheezing | Asthma, bronchitis |
| Coughing Up Blood | Lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, severe respiratory infections |
| Dizziness | Hyperventilation, Pulmonary embolism |
2.3. Location of Pain
The location of your lung pain can also provide important clues about the underlying cause. Pain that is localized to one side of the chest may suggest conditions like pleurisy, pneumonia, or pneumothorax affecting that particular lung. Pain that is more generalized throughout the chest may be related to musculoskeletal issues, asthma, or cardiovascular conditions.
- Left Lung Pain: May indicate conditions affecting the left lung, such as pneumonia, pleurisy, or lung cancer.
- Right Lung Pain: May indicate conditions affecting the right lung, such as pneumonia, pleurisy, or lung cancer.
- Central Chest Pain: May be related to musculoskeletal issues, asthma, or cardiovascular conditions.
- Pain Radiating to the Back or Shoulder: Can occur with lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, or musculoskeletal issues.
2.4. When to Seek Medical Attention
While some cases of lung pain may be minor and self-limiting, it’s important to know when to seek medical attention. Seek immediate medical care if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe chest pain
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Rapid heart rate
- Fever
These symptoms may indicate a serious underlying condition that requires prompt medical evaluation and treatment.
3. Navigating Diagnosis: How to Identify the Cause
Diagnosing the cause of lung pain involves a comprehensive evaluation that includes a review of your medical history, a physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider will use this information to determine the underlying cause of your pain and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan. Below are some of the common diagnostic methods used to identify the cause of lung pain.
3.1. Medical History and Physical Exam
Your healthcare provider will start by asking about your medical history, including any previous illnesses, injuries, or chronic conditions. They will also inquire about your symptoms, including the type, location, and duration of your pain, as well as any accompanying symptoms. During the physical exam, your healthcare provider will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds, such as wheezing or crackling. They will also examine your chest for tenderness or signs of inflammation.
3.2. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests play a crucial role in diagnosing lung conditions and identifying the cause of chest pain. These tests provide detailed images of your lungs and surrounding structures, allowing your healthcare provider to visualize any abnormalities.
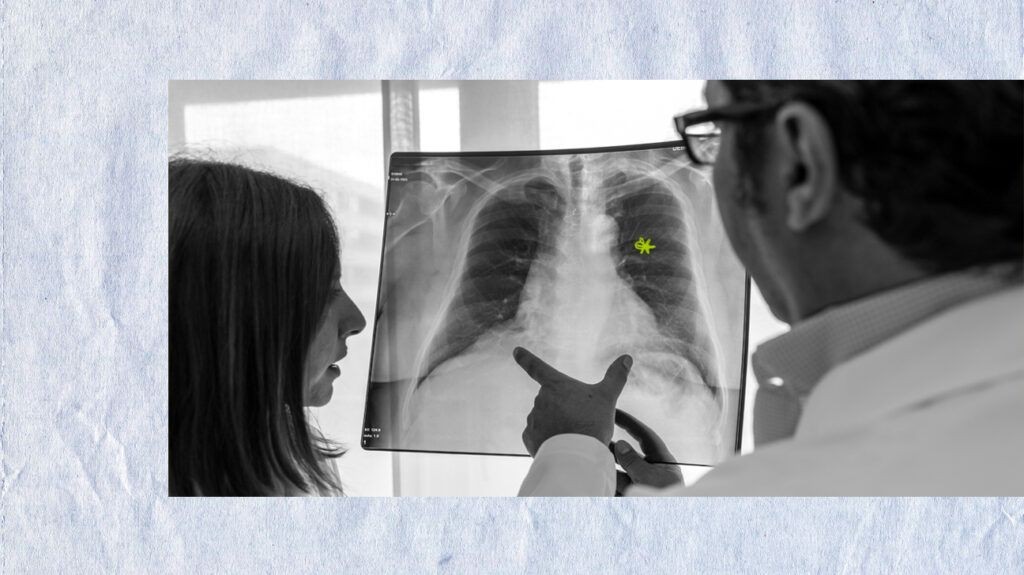
3.2.1. Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray is a common imaging test that uses small amounts of radiation to create images of your lungs, heart, and blood vessels. It can help identify conditions such as pneumonia, lung cancer, pneumothorax, and pleural effusion. Chest X-rays are relatively quick and painless, making them a valuable tool for initial evaluation.
3.2.2. CT Scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of your lungs and chest. CT scans provide more detailed information than chest X-rays and can help identify smaller abnormalities, such as lung nodules, blood clots, and tumors. CT scans may involve the injection of a contrast dye to enhance the images.
3.2.3. MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of your lungs and chest. MRI is particularly useful for evaluating soft tissues, such as the pleura and chest wall. It can help identify conditions such as lung cancer, pleural effusion, and musculoskeletal abnormalities.
3.3. Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are non-invasive tests that measure how well your lungs are working. These tests assess lung volume, airflow, and gas exchange. PFTs can help diagnose conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and restrictive lung diseases.
3.4. Blood Tests
Blood tests can provide valuable information about your overall health and help identify potential causes of lung pain.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Can help detect signs of infection or inflammation.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG): Measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood, helping to assess lung function.
- D-dimer Test: Can help detect blood clots in the lungs, which may indicate pulmonary embolism.
3.5. Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached is inserted into your airways to visualize the lungs. It allows your healthcare provider to examine the airways for abnormalities, such as tumors, inflammation, or foreign objects. Bronchoscopy can also be used to collect tissue samples for biopsy.
4. Tailoring Treatment: Effective Relief Strategies
The treatment for lung pain depends on the underlying cause. Once a diagnosis has been made, your healthcare provider will recommend the most appropriate treatment plan to alleviate your pain and address the underlying condition. Below are some of the common treatment strategies for lung pain.
4.1. Medications
Medications can play a crucial role in managing lung pain and addressing the underlying cause.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) can help alleviate mild to moderate pain. Prescription pain medications may be necessary for more severe pain.
- Antibiotics: Used to treat bacterial infections like pneumonia.
- Bronchodilators: Used to open up the airways in conditions like asthma and COPD.
- Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation in conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and pleurisy.
- Anticoagulants: Used to prevent and treat blood clots in conditions like pulmonary embolism.
4.2. Respiratory Therapies
Respiratory therapies can help improve lung function and alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath and wheezing.
- Oxygen Therapy: Provides supplemental oxygen to increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A program of exercise, education, and support for people with chronic lung conditions.
- Chest Physiotherapy: Techniques to help clear mucus from the airways.
4.3. Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help improve lung health and reduce the risk of lung pain.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for lung disease and should be avoided.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimize exposure to pollutants, allergens, and other irritants that can trigger lung inflammation.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can improve lung function and overall health.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet can help support lung health and boost the immune system.
4.4. Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat the underlying cause of lung pain.
- Thoracentesis: A procedure to remove fluid from the pleural space.
- Chest Tube Insertion: Used to drain air or fluid from the chest cavity in conditions like pneumothorax or pleural effusion.
- Lung Resection: Surgical removal of a portion of the lung in cases of lung cancer or severe lung disease.
4.5. Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can help alleviate lung pain and promote healing.
- Rest: Getting plenty of rest can help your body recover from illness or injury.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids can help thin mucus and make it easier to cough up.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the chest can help relieve muscle pain and inflammation.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam can help loosen mucus and relieve congestion.
- Humidifier: Using a humidifier can help keep the air moist and prevent dryness in the airways.
5. Seeking Expert Advice: Leveraging WHY.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of lung pain and its potential causes can be overwhelming. Knowing where to turn for reliable information and expert guidance is essential for making informed decisions about your health. WHY.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive platform for individuals seeking answers to their health-related questions, providing access to a wealth of information and expert insights.
5.1. Comprehensive Q&A Platform
WHY.EDU.VN is designed to be your go-to resource for finding answers to your health-related questions. Our platform features a vast library of articles, FAQs, and expert insights covering a wide range of topics, including lung health and chest pain. Whether you’re curious about the potential causes of your symptoms or seeking advice on managing a specific condition, WHY.EDU.VN has you covered.
5.2. Expert Insights and Guidance
One of the key features of WHY.EDU.VN is our commitment to providing expert insights and guidance. Our team of healthcare professionals and medical experts carefully curates and reviews all content to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date information. You can trust that the information you find on WHY.EDU.VN is based on the latest scientific evidence and best practices.
5.3. Personalized Support and Recommendations
In addition to our comprehensive library of resources, WHY.EDU.VN also offers personalized support and recommendations. Our platform allows you to submit your specific questions and concerns, which will be reviewed by our team of experts. We strive to provide tailored advice and guidance to help you make informed decisions about your health.
5.4. Interactive Community Forum
WHY.EDU.VN also features an interactive community forum where you can connect with other individuals who are experiencing similar health challenges. This forum provides a supportive and collaborative environment where you can share your experiences, ask questions, and exchange information with others.
5.5. Access to Telehealth Services
For those seeking more immediate medical attention, WHY.EDU.VN offers access to telehealth services. Through our telehealth platform, you can connect with licensed healthcare providers for virtual consultations, diagnoses, and treatment recommendations. Telehealth services provide a convenient and accessible way to receive medical care from the comfort of your own home.
6. Prevention is Key: Maintaining Optimal Lung Health
While it’s important to address lung pain and related symptoms when they arise, prevention is always the best approach. Taking proactive steps to maintain optimal lung health can significantly reduce your risk of developing lung conditions and experiencing chest discomfort. Below are some of the key strategies for preventing lung problems and promoting overall respiratory wellness.
6.1. Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer and a major contributor to other lung diseases, such as COPD and bronchitis. Quitting smoking is one of the most important things you can do to protect your lung health. Additionally, avoiding secondhand smoke is crucial, as it can also damage your lungs and increase your risk of respiratory problems.
6.2. Protect Yourself from Environmental Pollutants
Exposure to air pollution, chemicals, and other environmental irritants can damage your lungs and increase your risk of respiratory problems. Minimize your exposure to these pollutants by:
- Avoiding outdoor activities on days with high air pollution levels
- Using air purifiers in your home and office
- Wearing a mask when working with chemicals or other irritants
6.3. Practice Good Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene is essential for preventing respiratory infections like the flu and pneumonia. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after being in public places or around sick individuals. Avoid touching your face, and cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
6.4. Get Vaccinated
Vaccinations can help protect you from respiratory infections that can cause lung pain and other complications. Get vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
6.5. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity can improve lung function and overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, running, swimming, and cycling can help strengthen your respiratory muscles and improve your lung capacity.
6.6. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support lung health and boost your immune system. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of unhealthy fats.
6.7. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids can help keep your airways moist and prevent dryness, which can irritate your lungs. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
6.8. Get Regular Checkups
Regular checkups with your healthcare provider can help detect lung problems early, when they are most treatable. If you have a history of lung disease or risk factors for lung cancer, your healthcare provider may recommend regular lung cancer screenings.
7. Real-World Scenarios: Case Studies on Lung Pain
Understanding how lung pain presents in real-world scenarios can provide valuable insights into the diagnostic and treatment process. Reviewing case studies allows you to see how healthcare professionals approach different types of lung pain and the strategies they use to identify the underlying cause and provide relief.
7.1. Case Study 1: The Athlete with Chest Pain
A 25-year-old male athlete presents to the clinic with sharp chest pain that worsens with deep breathing. He reports no recent injuries or illnesses, but he has been training intensely for an upcoming marathon. Physical examination reveals tenderness over his ribs on the left side. A chest X-ray is normal.
Diagnosis: Costochondritis, likely caused by overuse and strain from intense training.
Treatment: Rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers. The athlete is advised to modify his training regimen to avoid further aggravating the condition.
7.2. Case Study 2: The Smoker with Chronic Cough
A 60-year-old female with a history of smoking presents with a chronic cough, shortness of breath, and dull chest pain. She reports feeling fatigued and has noticed some weight loss. A chest X-ray reveals a mass in her right lung.
Diagnosis: Lung cancer.
Treatment: The patient is referred to an oncologist for further evaluation and treatment, which may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
7.3. Case Study 3: The Traveler with Sudden Shortness of Breath
A 45-year-old male presents to the emergency room with sudden shortness of breath and sharp chest pain. He recently returned from a long international flight. A CT scan reveals a blood clot in his lung.
Diagnosis: Pulmonary embolism.
Treatment: The patient is started on anticoagulants to dissolve the blood clot and prevent further complications. He is admitted to the hospital for monitoring.
7.4. Case Study 4: The Child with Wheezing and Chest Tightness
An 8-year-old child presents to the clinic with wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. The symptoms worsen with exposure to allergens like pollen and pet dander. Physical examination reveals wheezing and prolonged expiration.
Diagnosis: Asthma.
Treatment: The child is prescribed an inhaler with a bronchodilator to open up the airways and a corticosteroid to reduce inflammation. The parents are educated on how to manage the child’s asthma and avoid triggers.
7.5. Case Study 5: The Elderly Patient with Fever and Cough
An 80-year-old female presents to the hospital with fever, cough, and chest pain. She reports feeling weak and has difficulty breathing. A chest X-ray reveals consolidation in her left lung.
Diagnosis: Pneumonia.
Treatment: The patient is started on antibiotics to treat the infection. She is admitted to the hospital for supportive care, including oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids.
8. Your Next Steps: Actionable Advice for Lung Health
Understanding the potential causes, symptoms, and treatments for lung pain is just the first step. Now, it’s time to take action and prioritize your lung health. Here’s some actionable advice to help you navigate your next steps.
8.1. Schedule a Medical Evaluation
If you’re experiencing persistent or severe lung pain, don’t hesitate to schedule a medical evaluation with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the underlying cause of your pain and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
8.2. Follow Your Healthcare Provider’s Recommendations
Once you’ve received a diagnosis, be sure to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations carefully. This may include taking medications, undergoing respiratory therapies, or making lifestyle modifications.
8.3. Monitor Your Symptoms
Pay close attention to your symptoms and report any changes or worsening to your healthcare provider. This will help them adjust your treatment plan as needed.
8.4. Seek Support
Living with lung pain or a chronic lung condition can be challenging. Don’t hesitate to seek support from friends, family, or a support group. Sharing your experiences and connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly helpful.
8.5. Continue Learning
Stay informed about lung health and related conditions. WHY.EDU.VN is a valuable resource for finding accurate and up-to-date information. Continue to learn about lung pain, its causes, and its treatments so you can make informed decisions about your health.
9. FAQ: Addressing Your Concerns About Lung Pain
To further assist you in understanding lung pain, here are some frequently asked questions along with their answers.
Q1: What are the most common causes of lung pain?
A: Common causes include musculoskeletal issues, respiratory infections, lung conditions, and cardiovascular issues.
Q2: How can I tell if my chest pain is related to my lungs?
A: Symptoms like shortness of breath, cough, fever, or wheezing along with chest pain may indicate a lung-related issue.
Q3: When should I seek medical attention for lung pain?
A: Seek immediate medical care for severe chest pain, sudden shortness of breath, coughing up blood, or dizziness.
Q4: What tests are used to diagnose the cause of lung pain?
A: Tests may include chest X-rays, CT scans, pulmonary function tests, and blood tests.
Q5: What are some home remedies for lung pain?
A: Home remedies include rest, hydration, warm compresses, and steam inhalation.
Q6: Can lung pain be a sign of lung cancer?
A: Yes, lung pain can be a symptom of lung cancer, especially if accompanied by chronic cough, weight loss, and fatigue.
Q7: How can I prevent lung pain?
A: Avoid smoking, protect yourself from pollutants, practice good hygiene, and get vaccinated.
Q8: What lifestyle changes can improve lung health?
A: Quit smoking, exercise regularly, maintain a healthy diet, and stay hydrated.
Q9: Are there specific exercises that can help with lung pain?
A: Breathing exercises and light physical activity can help improve lung function, but consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
Q10: How does WHY.EDU.VN help with lung pain-related questions?
A: WHY.EDU.VN provides comprehensive information, expert insights, personalized support, and access to telehealth services for lung pain-related queries.
10. Call to Action: Get Your Questions Answered at WHY.EDU.VN
Experiencing lung pain can be concerning, but you don’t have to navigate it alone. At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges and uncertainties that come with lung-related discomfort. Our mission is to provide you with the knowledge, resources, and support you need to make informed decisions about your health.
Are you struggling to find reliable answers to your questions about lung pain? Do you need expert guidance on managing your symptoms and improving your lung health? Look no further than WHY.EDU.VN. Our comprehensive platform offers a wealth of information, including articles, FAQs, and expert insights, all carefully curated and reviewed by healthcare professionals.
Whether you’re curious about the potential causes of your lung pain, seeking advice on managing a specific condition, or looking for personalized support, WHY.EDU.VN has you covered. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the most accurate, up-to-date, and trustworthy information available.
Don’t let lung pain hold you back from living your life to the fullest. Take control of your health and get the answers you deserve. Visit WHY.EDU.VN today to explore our resources, connect with our community, and access expert guidance.
If you have specific questions or concerns, we encourage you to submit them through our platform. Our team of experts will review your questions and provide tailored advice and recommendations to help you on your journey to better lung health.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we believe that everyone deserves access to reliable and accessible health information. That’s why we’ve created a platform that is easy to use, informative, and empowering. Join our community today and take the first step towards a healthier, happier you.
Contact us:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let why.edu.vn be your trusted partner in navigating the complexities of lung pain and achieving optimal respiratory wellness.