Experiencing ache in your left testicle can be concerning, and it’s natural to seek answers. WHY.EDU.VN is here to provide insights into the potential causes and treatment options, like varicocele. Understanding the anatomy and available treatments can help you make informed decisions about your health, improving your reproductive health and addressing potential pain or discomfort.
1. What Causes Left Testicle Pain?
Left testicle pain can arise from various causes, with varicocele being a common culprit. Varicocele involves the enlargement of veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs. These enlarged veins can cause discomfort, pain, and a feeling of heaviness in the testicle, especially during physical activity or prolonged standing.
- Varicocele: Enlargement of veins in the scrotum, affecting blood flow.
- Epididymitis: Inflammation of the epididymis, often due to infection.
- Testicular Torsion: Twisting of the spermatic cord, cutting off blood supply.
- Hydrocele: Fluid accumulation around the testicle.
- Trauma: Injury to the testicle or scrotum.
- Inguinal Hernia: Protrusion of tissue through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles.
- Testicular Cancer: Although less common, pain can be a symptom.
The exact cause can only be determined through a medical evaluation by a healthcare professional.
2. Why is Varicocele More Common on the Left Side?
Varicoceles predominantly occur on the left side due to anatomical differences. The left testicular vein drains into the left renal vein at a 90-degree angle, while the right testicular vein drains directly into the inferior vena cava. This anatomical asymmetry creates higher pressure in the left testicular vein, making it more susceptible to varicocele formation.
| Side | Venous Drainage | Angle of Drainage | Pressure | Varicocele Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Drains into the left renal vein | 90 degrees | Higher | Higher |
| Right | Drains directly into the inferior vena cava | Straight | Lower | Lower |
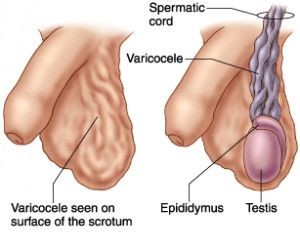


3. What are the Symptoms of Varicocele?
Varicocele symptoms can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain. Some men may not experience any symptoms at all. Common symptoms include:
- Dull ache or pain: Usually described as a heavy or dragging sensation in the scrotum.
- Visible enlarged veins: Veins in the scrotum may appear enlarged and twisted, often described as a “bag of worms.”
- Swelling: The affected testicle may be swollen.
- Pain that worsens with standing or exertion: Pain may increase after prolonged standing or physical activity and improve when lying down.
- Infertility: Varicocele can affect sperm production and quality, leading to infertility issues.
- Testicular atrophy: In some cases, the affected testicle may shrink.
4. How is Varicocele Diagnosed?
Diagnosing varicocele typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests. A healthcare provider will examine the scrotum while the patient is standing and lying down to assess the presence and size of enlarged veins.
- Physical Exam: Palpation of the scrotum to identify enlarged veins.
- Ultrasound: Imaging test to visualize the veins and assess blood flow. A Doppler ultrasound can detect reversed blood flow, confirming the diagnosis.
- Semen Analysis: To evaluate sperm count and quality, especially if infertility is a concern.
- Thermography: Detects temperature differences, which can indicate abnormal blood flow.
- Venography: X-ray of the veins after injecting a contrast dye.
5. What are the Treatment Options for Varicocele?
Several treatment options are available for varicocele, ranging from conservative management to surgical intervention. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, the presence of infertility, and the patient’s overall health.
- Observation: For mild cases with no symptoms, observation may be recommended.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
- Supportive Underwear: Wearing supportive underwear can provide comfort and reduce pressure on the scrotum.
- Varicocelectomy: Surgical removal of the affected veins. This can be done through open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or microsurgery.
- Varicocele Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the vein, and coils or sclerosing agents are used to block blood flow to the enlarged veins.
6. What is Varicocele Embolization?
Varicocele embolization is a minimally invasive procedure performed by an interventional radiologist. A small catheter is inserted, typically through the groin or neck, into the affected vein. Coils or a liquid embolic agent is then used to block the vein, redirecting blood flow to healthy veins.
| Feature | Varicocele Embolization | Varicocelectomy (Surgery) |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Minimally Invasive | Invasive |
| Anesthesia | Local Anesthesia | General or Local Anesthesia |
| Incision | Small Puncture | Surgical Incision |
| Recovery Time | 1-2 Days | 2-3 Weeks |
| Pain | Minimal | Moderate to Severe |
| Recurrence Rate | Lower | Higher |
| Bilateral Treatment | Can Treat Both Sides Simultaneously Through One Puncture | Requires Separate Incisions for Each Side |
7. What are the Advantages of Varicocele Embolization?
Varicocele embolization offers several advantages over traditional surgery, including:
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions, leading to less pain and scarring.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Most patients can return to normal activities within a day or two.
- Outpatient Procedure: Typically performed on an outpatient basis.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Reduced risk of infection and other surgical complications.
- Bilateral Treatment: Both sides can be treated during the same procedure through a single puncture site.
8. What are the Risks of Varicocele Embolization?
As with any medical procedure, varicocele embolization carries some risks, although they are generally low. Potential risks include:
- Infection: Risk of infection at the puncture site.
- Bleeding: Bleeding or hematoma formation at the puncture site.
- Allergic Reaction: Allergic reaction to the contrast dye used during the procedure.
- Coil Migration: Movement of the coils to other veins.
- Recurrence: Varicocele may recur in some cases.
- Post-Embolization Syndrome: Mild pain, fever, and nausea that usually resolve within a few days.
9. How Does Varicocele Affect Fertility?
Varicocele can affect fertility by increasing the temperature around the testicles, which can impair sperm production and function. The enlarged veins can also cause a buildup of toxic substances, leading to oxidative stress and DNA damage in sperm cells.
- Increased Testicular Temperature: Elevated temperature impairs sperm production.
- Oxidative Stress: Buildup of toxic substances damages sperm cells.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Disrupts hormone production necessary for sperm development.
- Sperm DNA Fragmentation: Damage to sperm DNA reduces fertilization potential.
Addressing varicocele can improve sperm parameters and increase the chances of natural conception or success with assisted reproductive technologies.
10. What Can I Expect After Varicocele Treatment?
After varicocele treatment, whether through surgery or embolization, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
- Pain Management: Pain medication may be prescribed to manage post-procedure discomfort.
- Wound Care: Keep the incision site clean and dry.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for a specified period.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress and assess sperm parameters.
- Fertility Improvement: Sperm quality may improve within a few months after treatment.
11. Could Testicular Cancer Be the Reason for My Left Testicle Ache?
While pain in the testicle is not a common symptom of testicular cancer, it is important to rule out this possibility. Testicular cancer often presents as a painless lump or swelling in the testicle. However, some men may experience a dull ache or discomfort. If you notice any changes in your testicles, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
| Symptom | Testicular Cancer | Varicocele |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Possible, but less common | Common, often described as a dull ache or heavy sensation |
| Lump or Swelling | Common | Less Common |
| Scrotal Enlargement | Possible | Common, especially when standing |
| Heaviness in the Scrotum | Possible | Common |
12. What is Epididymitis and How is it Related to Testicle Ache?
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, a coiled tube located at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm. This condition can cause significant pain and discomfort in the testicle.
- Causes: Bacterial infections (often sexually transmitted), viral infections, or non-infectious causes like trauma.
- Symptoms: Testicle pain, redness, swelling, tenderness, and sometimes fever.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, urine tests, and sometimes ultrasound.
- Treatment: Antibiotics for bacterial infections, pain relievers, and supportive measures like scrotal elevation.
13. What is Testicular Torsion and Why is it an Emergency?
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that occurs when the spermatic cord, which provides blood supply to the testicle, twists. This twisting cuts off blood flow, leading to severe pain and potential loss of the testicle if not treated promptly.
- Symptoms: Sudden, severe testicle pain, swelling, nausea, and vomiting.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination and Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow.
- Treatment: Immediate surgical intervention to untwist the spermatic cord and restore blood flow. The procedure must be performed within hours to save the testicle.
14. How Can Hydrocele Cause Testicle Discomfort?
Hydrocele is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid around the testicle, causing swelling and discomfort.
- Causes: Often congenital, but can also result from inflammation, infection, or injury.
- Symptoms: Painless swelling in the scrotum, feeling of heaviness, and discomfort.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination and ultrasound.
- Treatment: If symptomatic, treatment includes needle aspiration (draining the fluid) or surgical removal of the hydrocele sac.
15. What Role Does Trauma Play in Causing Testicle Ache?
Trauma to the testicle can result in immediate pain, swelling, and bruising. The severity of the pain can vary depending on the extent of the injury.
- Causes: Direct blow to the testicle, sports injuries, accidents.
- Symptoms: Severe pain, swelling, bruising, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination and ultrasound to assess the extent of the injury.
- Treatment: Pain relievers, ice packs, supportive underwear, and in severe cases, surgical intervention to repair the damage.
16. What is Inguinal Hernia and How Does it Cause Testicular Pain?
An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles in the groin area. This can cause pain and discomfort that radiates to the testicle.
- Symptoms: Bulge in the groin area, pain and discomfort, especially when coughing, straining, or lifting heavy objects.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination and sometimes imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scan.
- Treatment: Surgical repair of the hernia to push the protruding tissue back into place and reinforce the abdominal wall.
17. How Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage Testicle Pain?
Lifestyle changes can play a supportive role in managing testicle pain, especially when combined with medical treatment.
- Supportive Underwear: Provides support and reduces pressure on the scrotum.
- Avoidance of Strenuous Activities: Reduces strain on the testicles and groin area.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the groin area.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Using proper techniques when lifting heavy objects can prevent strain.
- Regular Exercise: Promotes overall health and well-being, but avoid overexertion.
18. What Home Remedies Can Help Alleviate Testicle Ache?
While home remedies can provide temporary relief, they should not replace medical evaluation and treatment.
- Ice Packs: Applying ice packs to the scrotum can reduce swelling and pain.
- Warm Baths: Soaking in a warm bath can help relax muscles and ease discomfort.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
- Elevation: Elevating the scrotum can reduce swelling and discomfort.
19. When Should I See a Doctor for Testicle Pain?
It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any of the following:
- Sudden, severe pain: Especially if accompanied by swelling, nausea, or vomiting.
- Lump or swelling in the testicle: Any new or changing lump should be evaluated.
- Pain that doesn’t improve with home remedies: Persistent or worsening pain requires medical attention.
- Fever or signs of infection: Redness, warmth, or discharge from the scrotum.
- History of trauma: Any injury to the testicle should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
20. What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor About Testicle Pain?
When you see a doctor for testicle pain, it’s helpful to have a list of questions to ensure you get the information you need.
- What is the most likely cause of my pain?
- What tests do I need?
- What are my treatment options?
- What are the risks and benefits of each treatment?
- How long will it take to recover?
- Will this affect my fertility?
- Are there any lifestyle changes I should make?
- When should I follow up?
Experiencing ache in the left testicle can be concerning, but understanding the potential causes and available treatments can help alleviate anxiety and guide appropriate action. Varicocele is a common cause and is treatable through minimally invasive procedures like varicocele embolization. Remember, if you have any concerning symptoms or questions, WHY.EDU.VN is here to provide reliable and understandable information.
Do you have more questions about testicle pain or other health concerns? Visit WHY.EDU.VN at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact our experts via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. We’re here to help you find the answers you need.
FAQ: Understanding Left Testicle Pain
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. Why Does My Left Testicle Ache? | There are many potential reasons for a left testicle ache, including varicocele, epididymitis, testicular torsion, hydrocele, trauma, inguinal hernia, or, rarely, testicular cancer. |
| 2. Is left testicle pain always a sign of something serious? | Not always. Many cases of left testicle pain are due to treatable conditions like varicocele or epididymitis. However, it’s essential to get a medical evaluation to rule out serious causes. |
| 3. Can varicocele cause long-term damage if left untreated? | Yes, varicocele can lead to fertility issues, testicular atrophy, and chronic pain if left untreated. |
| 4. How can I tell the difference between varicocele and testicular cancer? | Varicocele typically presents as enlarged veins in the scrotum with a dull ache, while testicular cancer often presents as a painless lump or swelling in the testicle. A medical evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis. |
| 5. What is the recovery time for varicocele embolization? | Recovery time is typically short, with most men returning to normal activities within 1-2 days. |
| 6. Are there any alternative treatments for varicocele besides surgery? | Yes, varicocele embolization is a minimally invasive alternative to surgery. |
| 7. How does epididymitis cause testicle pain? | Epididymitis causes testicle pain due to inflammation of the epididymis, often due to infection or trauma. |
| 8. What should I do if I suspect I have testicular torsion? | Seek immediate medical attention. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that requires prompt surgical intervention. |
| 9. Can wearing tight underwear cause testicle pain? | Tight underwear can contribute to testicle pain by restricting blood flow and increasing pressure on the scrotum. |
| 10. How can WHY.EDU.VN help me with my concerns about testicle pain? | why.edu.vn provides reliable information and connects you with experts who can address your questions and concerns about testicle pain. |
