Why Do You Get The Hiccups? At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand your curiosity and offer a comprehensive guide to understanding the causes of hiccups and how to effectively manage them, providing insights into potential underlying conditions and practical remedies. Uncover relief for diaphragm spasms, vocal cord closure, and explore remedies with the help of our health tips, medical advice, and professional healthcare guidance.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Hiccups: A Comprehensive Overview
- Decoding the Symptoms of Hiccups
- When Should You Consult a Doctor for Hiccups?
- Unveiling the Common Causes of Short-Term Hiccups
- Exploring Nerve-Related Causes of Prolonged Hiccups
- Central Nervous System Disorders Linked to Chronic Hiccups
- Metabolic Issues That Can Trigger Long-Term Hiccups
- The Role of Drugs and Alcohol in Persistent Hiccups
- Identifying the Risk Factors for Developing Hiccups
- Potential Complications of Ongoing Hiccups
- Effective Home Remedies to Stop Hiccups Quickly
- Medical Treatments for Severe or Persistent Hiccups
- Preventive Measures to Reduce the Occurrence of Hiccups
- Expert Insights on Managing Hiccups from WHY.EDU.VN
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Hiccups
1. Understanding Hiccups: A Comprehensive Overview
Hiccups are those involuntary contractions of the diaphragm that can strike at any time, often seemingly without reason. The diaphragm, a large muscle located at the base of the chest, plays a vital role in breathing, contracting to draw air into the lungs and relaxing to expel it. A hiccup occurs when the diaphragm experiences a sudden, uncontrolled spasm. This spasm forces the vocal cords to close abruptly, producing the characteristic “hic” sound. While usually harmless and short-lived, understanding what triggers these spasms can help in managing and potentially preventing them. Causes range from simple lifestyle factors to more complex underlying medical conditions. For more comprehensive insights, visit WHY.EDU.VN.
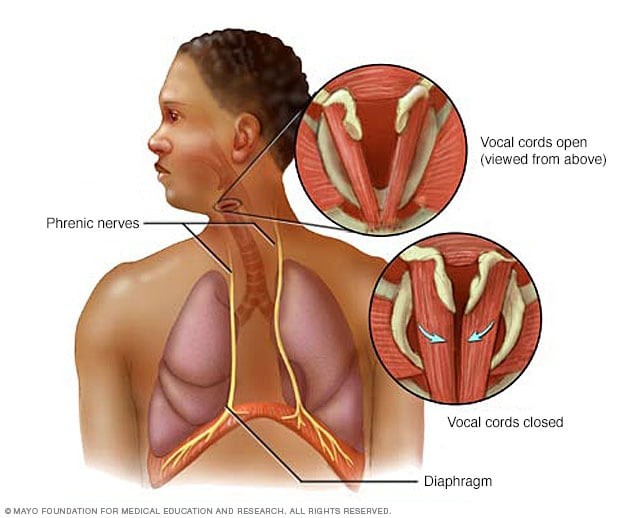 Illustration of diaphragm spasms causing hiccups
Illustration of diaphragm spasms causing hiccups
2. Decoding the Symptoms of Hiccups
The primary symptom of hiccups is the unmistakable “hic” sound, a result of the vocal cords snapping shut after a diaphragm spasm. However, the experience can also involve other sensations. Some individuals may feel a slight tightening in the chest, abdomen, or throat just before the hiccup occurs. These sensations are due to the involuntary contraction of the diaphragm and the subsequent reaction of surrounding muscles. Understanding these associated symptoms can help individuals recognize the onset of hiccups and potentially take steps to alleviate them.
3. When Should You Consult a Doctor for Hiccups?
While most episodes of hiccups resolve within a few minutes, persistent hiccups may indicate an underlying medical issue that requires professional attention. According to the Mayo Clinic, if hiccups last longer than 48 hours or are severe enough to interfere with eating, sleeping, or breathing, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Prolonged hiccups can lead to exhaustion, weight loss, and significant discomfort, impacting overall quality of life. Doctors can evaluate the potential causes and recommend appropriate treatment strategies. You can always find reliable information at WHY.EDU.VN.
4. Unveiling the Common Causes of Short-Term Hiccups
Short-term hiccups, those that last less than 48 hours, are often triggered by lifestyle and environmental factors. Common causes include:
- Carbonated Beverages: The excess gas can irritate the diaphragm.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can disrupt normal nerve function.
- Overeating: A full stomach can put pressure on the diaphragm.
- Emotional Stress: Excitement or stress can trigger spasms.
- Sudden Temperature Changes: These can shock the body and cause involuntary reactions.
- Swallowing Air: Chewing gum or smoking can lead to increased air intake.
| Trigger | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Carbonated Beverages | Excess gas irritates the diaphragm. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Disrupts normal nerve function. |
| Overeating | Puts pressure on the diaphragm. |
| Emotional Stress | Excitement or stress can trigger spasms. |
| Sudden Temperature Changes | Can shock the body and cause involuntary reactions. |
| Swallowing Air | Chewing gum or smoking can lead to increased air intake, irritating diaphragm |
These triggers are generally benign and easily addressed, but understanding them can help in preventing future episodes.
5. Exploring Nerve-Related Causes of Prolonged Hiccups
Long-term hiccups, lasting more than 48 hours, can sometimes stem from nerve damage or irritation affecting the vagus or phrenic nerves. These nerves are crucial as they control the diaphragm. Factors that can cause nerve irritation or damage include:
- Ear Irritation: A foreign object in the ear touching the eardrum.
- Thyroid Issues: Tumors, cysts, or growths on the thyroid gland.
- Acid Reflux: Stomach acid backing up into the esophagus.
- Throat Infections: Sore throat or laryngitis.
Addressing these underlying nerve issues can often resolve the persistent hiccups.
6. Central Nervous System Disorders Linked to Chronic Hiccups
Disruptions in the central nervous system (CNS) can also lead to chronic hiccups. Tumors, infections, or injuries affecting the brain and spinal cord can interfere with the body’s control over the hiccup reflex. Examples of such conditions include:
- Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain.
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Hardening of tissue in the brain or spinal cord.
- Stroke: Disruption of blood supply to the brain.
- Brain Injury: Trauma to the brain affecting normal function.
Identifying and treating these CNS disorders is essential to alleviating the related hiccup symptoms.
7. Metabolic Issues That Can Trigger Long-Term Hiccups
Metabolic imbalances can sometimes manifest as persistent hiccups. When the body’s metabolism isn’t functioning correctly, it can disrupt normal bodily processes, leading to involuntary diaphragm spasms. Common metabolic issues associated with hiccups include:
- Diabetes: Issues with blood sugar regulation.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Abnormal levels of potassium, sodium, or other electrolytes.
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function affecting electrolyte balance.
Correcting these metabolic imbalances through appropriate medical treatment can help resolve chronic hiccups.
8. The Role of Drugs and Alcohol in Persistent Hiccups
Certain substances, including drugs and alcohol, can contribute to long-term hiccups. Some medications can affect nerve function or alter brain activity, triggering involuntary spasms. Alcohol, particularly in excessive amounts, can also disrupt normal physiological processes. Examples include:
- Sedatives: Medications that cause relaxation and sleepiness.
- Steroids: Such as dexamethasone, used to relieve inflammation.
- Alcohol Use Disorder: Chronic alcohol abuse.
If you suspect that a medication or alcohol use is contributing to your hiccups, consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable.
9. Identifying the Risk Factors for Developing Hiccups
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing hiccups. These include:
- Gender: Males are more prone to long-term hiccups than females.
- Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, stress, and excitement.
- Surgery: General anesthesia or procedures involving abdominal organs.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek timely medical attention if hiccups become persistent.
10. Potential Complications of Ongoing Hiccups
Persistent hiccups can lead to several complications that affect daily life. These include:
- Interference with Eating and Drinking: Making it difficult to consume adequate nutrients.
- Sleep Disruption: Leading to fatigue and reduced quality of life.
- Speech Difficulties: Affecting communication.
- Increased Pain: Worsening existing pain conditions.
Addressing hiccups promptly is crucial to prevent these complications.
11. Effective Home Remedies to Stop Hiccups Quickly
Many simple home remedies can help stop hiccups quickly. These methods often work by stimulating the vagus or phrenic nerve, disrupting the hiccup reflex. Common remedies include:
- Holding Your Breath: Increases carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
- Drinking Water Rapidly: Can stimulate the vagus nerve.
- Gargling with Water: Another way to stimulate the vagus nerve.
- Eating a Spoonful of Sugar: May help reset nerve function.
- Breathing into a Paper Bag: Increases carbon dioxide levels.
| Remedy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Holding Your Breath | Increases carbon dioxide levels. |
| Drinking Water Rapidly | Stimulates the vagus nerve. |
| Gargling with Water | Stimulates the vagus nerve. |
| Eating a Spoonful of Sugar | May help reset nerve function. |
| Breathing into Paper Bag | Increases carbon dioxide levels in the blood. |
These remedies are generally safe and can provide immediate relief for most people.
12. Medical Treatments for Severe or Persistent Hiccups
For severe or persistent hiccups, medical treatments may be necessary. These can include:
- Medications: Such as chlorpromazine, baclofen, or metoclopramide.
- Acupuncture: May help stimulate nerve function.
- Hypnosis: Can alter brain activity related to hiccups.
- Nerve Blocks: Injections to block the phrenic nerve.
Medical interventions are usually reserved for cases where home remedies are ineffective and the hiccups significantly impact the individual’s quality of life.
13. Preventive Measures to Reduce the Occurrence of Hiccups
Preventing hiccups involves avoiding known triggers and adopting healthy lifestyle habits. Key preventive measures include:
- Eating Slowly: To avoid swallowing excess air.
- Avoiding Carbonated Beverages: Which can irritate the diaphragm.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: As it can disrupt nerve function.
- Managing Stress: Through relaxation techniques.
- Avoiding Sudden Temperature Changes: Which can shock the body.
By being mindful of these factors, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of hiccup episodes.
14. Expert Insights on Managing Hiccups from WHY.EDU.VN
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the frustration and discomfort that hiccups can cause. Our team is dedicated to providing you with reliable, expert-backed information to help you manage and understand your health concerns. We offer detailed guides, articles, and expert opinions on various health topics, including effective strategies for dealing with persistent hiccups. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and resources you need to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. For personalized advice and further information, visit our website at WHY.EDU.VN or contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. You can also reach us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let us help you find the answers you’re looking for.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Hiccups
1. What exactly causes hiccups?
Hiccups are caused by involuntary spasms of the diaphragm, a large muscle at the base of the chest that plays a crucial role in breathing. These spasms cause the vocal cords to close suddenly, producing the characteristic “hic” sound.
2. Are hiccups ever a sign of a serious medical condition?
While most hiccups are harmless and short-lived, persistent hiccups (lasting more than 48 hours) can sometimes indicate an underlying medical condition. These can include nerve damage, central nervous system disorders, metabolic issues, or side effects from certain drugs or alcohol.
3. How can I stop hiccups quickly using home remedies?
Several home remedies can help stop hiccups, including holding your breath, drinking water rapidly, gargling with water, eating a spoonful of sugar, or breathing into a paper bag. These methods often work by stimulating the vagus or phrenic nerve.
4. What should I do if my hiccups last for more than 48 hours?
If your hiccups last for more than 48 hours, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Persistent hiccups may indicate an underlying medical issue that requires professional evaluation and treatment.
5. Can stress or anxiety cause hiccups?
Yes, stress and anxiety can be triggers for hiccups. Emotional stress can lead to involuntary muscle spasms, including those in the diaphragm that cause hiccups.
6. Are there any medications that can help with chronic hiccups?
Yes, several medications can be prescribed for chronic hiccups, including chlorpromazine, baclofen, and metoclopramide. These medications work by affecting nerve function or reducing muscle spasms.
7. How does drinking carbonated beverages trigger hiccups?
Carbonated beverages can cause hiccups by irritating the diaphragm. The excess gas in these drinks can lead to distension in the stomach, putting pressure on the diaphragm and triggering spasms.
8. Is there a link between acid reflux and hiccups?
Yes, there is a link between acid reflux and hiccups. Stomach acid that backs up into the esophagus can irritate the vagus nerve, which controls the diaphragm, leading to hiccups.
9. Can surgery cause hiccups?
Yes, surgery, particularly procedures involving general anesthesia or abdominal organs, can sometimes cause hiccups. This may be due to nerve irritation or changes in the body’s physiological balance.
10. What can I do to prevent hiccups from recurring?
To prevent hiccups from recurring, try to avoid known triggers such as carbonated beverages, overeating, and sudden temperature changes. Practicing stress management techniques and eating slowly can also help reduce the likelihood of hiccups.
Remember, for any health concerns, always consult with a qualified healthcare professional. Visit why.edu.vn for more information and expert advice.