Why Do I Have Pain On My Left Side is a common question, and understanding the potential causes is crucial for effective management. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide detailed insights into the various factors that can contribute to this discomfort, offering clarity and guidance for those seeking answers and pain relief solutions. Explore potential diagnoses and find reliable information about left-sided pain.
1. Understanding Pain on Your Left Side: Common Causes
Pain on the left side of your body can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from mild and temporary to more serious underlying conditions. Identifying the precise location and characteristics of the pain, along with any accompanying symptoms, is essential for determining the potential causes and seeking appropriate medical attention. Understanding these factors can provide peace of mind or prompt necessary action.
1.1 The Anatomy of the Left Abdomen
Before diving into the possible causes of left-side pain, it’s helpful to understand the anatomy of the left abdomen. Key organs located in this area include:
- Spleen: Filters blood and helps fight infections.
- Stomach: Digests food.
- Pancreas: Produces enzymes and hormones for digestion and blood sugar regulation.
- Left Kidney: Filters waste from the blood and produces urine.
- Large Intestine (Colon): Processes waste and absorbs water.
- Small Intestine: Absorbs nutrients from food.
Problems within these organs can manifest as pain in the left side of your body.
1.2 Common Culprits: Digestive Issues
Many instances of left-side pain are related to digestive issues. These can range from temporary discomfort to chronic conditions.
- Gas: Trapped gas in the intestines is a frequent cause of abdominal pain. It can result from eating certain foods, swallowing air, or digestive disorders.
- Constipation: Difficulty passing stools can lead to pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, often on the left side.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): This chronic condition affects the large intestine and can cause abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can cause inflammation and pain in the digestive tract, potentially affecting the left side of the abdomen.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon, commonly causing pain in the lower left abdomen.
1.3 Kidney-Related Issues
The left kidney is located in the left side of the abdomen, and problems with this organ can lead to pain in that area.
- Kidney Stones: Mineral deposits that form in the kidneys can cause severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract.
- Kidney Infection: An infection of the kidney can cause pain, fever, and other symptoms.
1.4 Musculoskeletal Problems
Sometimes, pain in the left side is related to muscles, bones, or nerves in the area.
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion or injury can strain the muscles in the abdominal wall, causing pain.
- Rib Injuries: Fractured or bruised ribs can cause pain that radiates to the left side.
- Nerve Entrapment: Compressed or irritated nerves can cause localized pain.
1.5 Gender-Specific Causes
In women, pain in the left side can be related to reproductive organs.
- Menstrual Cramps: Uterine contractions during menstruation can cause pain in the lower abdomen.
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries can cause pain and discomfort.
- Endometriosis: A condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, causing pain and other symptoms.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): An infection of the female reproductive organs can cause pain and fever.
In men, pain can sometimes be related to testicular issues:
- Testicular Torsion: A condition where the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood supply to the testicle, causing severe pain.
- Epididymitis: Inflammation of the epididymis (a tube at the back of the testicle) can cause pain and swelling.
2. Specific Conditions and Their Symptoms
Let’s take a closer look at some specific conditions that can cause pain on your left side.
2.1 Diverticulitis: A Common Cause of Lower Left Abdominal Pain
Diverticulitis is a common condition, especially in people over 40, that involves inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon. It often causes pain in the lower left abdomen.
- Symptoms: Persistent and severe pain in the lower left abdomen, fever, nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, abdominal tenderness.
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, blood tests, CT scan.
- Treatment: Antibiotics, pain relievers, liquid diet, and in severe cases, surgery.
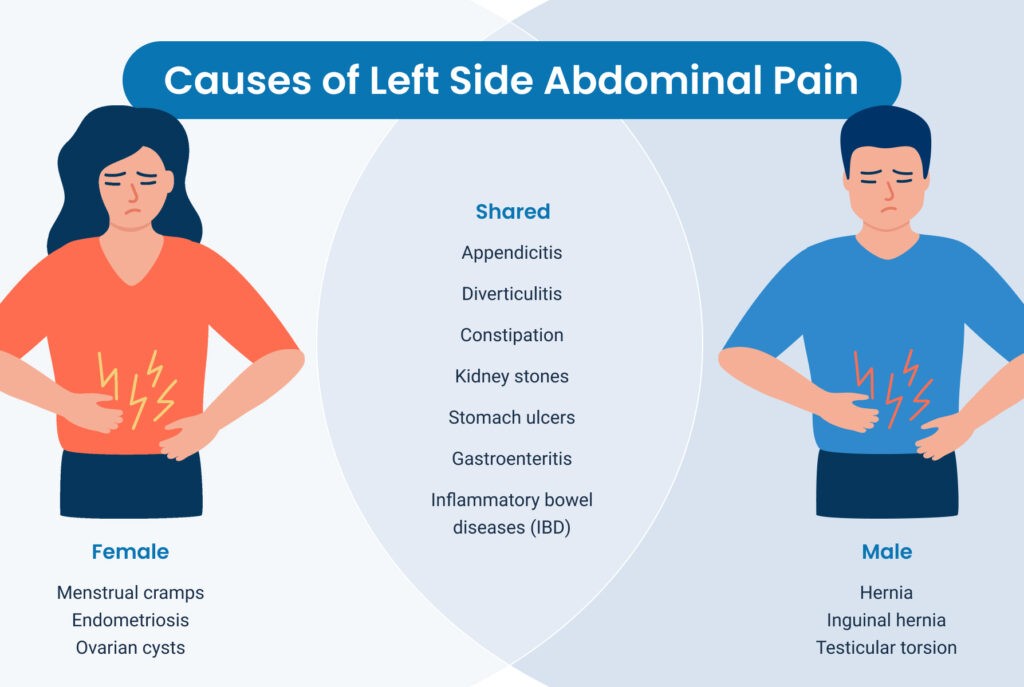 Diagram illustrating the formation of diverticula in the colon, causing diverticulitis.
Diagram illustrating the formation of diverticula in the colon, causing diverticulitis.
2.2 Kidney Stones: Sharp and Intense Pain
Kidney stones are mineral deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause excruciating pain as they pass through the urinary tract.
- Symptoms: Severe pain in the side and back, radiating to the lower abdomen and groin, frequent urination, blood in the urine, nausea, vomiting.
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, urine tests, imaging tests (X-ray, CT scan).
- Treatment: Pain relievers, hydration, medications to help pass the stone, and in some cases, surgery.
2.3 Appendicitis: Pain That Moves
Although appendicitis is typically associated with pain in the lower right abdomen, the initial pain can sometimes start near the belly button and be misinterpreted as coming from the left.
- Symptoms: Pain near the navel or upper abdomen that moves to the lower right abdomen, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal swelling, fever.
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, blood tests, imaging tests (CT scan, ultrasound).
- Treatment: Surgery to remove the appendix (appendectomy).
2.4 Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Chronic Discomfort
IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, can cause chronic inflammation and pain in the digestive tract.
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, diarrhea (often bloody), rectal bleeding, weight loss, fatigue, fever.
- Diagnosis: Physical exam, blood tests, stool tests, colonoscopy, endoscopy.
- Treatment: Medications to reduce inflammation (e.g., corticosteroids, immunomodulators), biologics, surgery.
2.5 Ovarian Cysts: Female-Specific Pain
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the ovaries. Most are harmless, but some can cause pain and other symptoms.
- Symptoms: Pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, abdominal bloating, changes in menstrual cycle, nausea, vomiting.
- Diagnosis: Pelvic exam, ultrasound.
- Treatment: Observation, pain relievers, hormonal birth control, surgery (if the cyst is large or causing severe symptoms).
2.6 Endometriosis: A Complex Condition
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. It can cause chronic pelvic pain and other symptoms.
- Symptoms: Painful periods, lower back pain, abdominal cramps, abnormal bleeding, pain during intercourse, infertility.
- Diagnosis: Pelvic exam, ultrasound, laparoscopy.
- Treatment: Pain relievers, hormonal birth control, surgery to remove endometrial tissue.
3. When to Seek Medical Attention
While many causes of left-side pain are not serious, it’s important to know when to seek medical attention.
3.1 Warning Signs
See a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe and persistent pain
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Bloody stools or vomit
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Rapid breathing
- Cold or clammy skin
- Abdominal tenderness
3.2 Diagnostic Tests
Your doctor may perform various diagnostic tests to determine the cause of your left-side pain. These may include:
- Physical Exam: To assess your overall health and identify any areas of tenderness or swelling.
- Blood Tests: To check for signs of infection, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
- Urine Tests: To look for signs of kidney problems or infection.
- Imaging Tests: Such as X-rays, CT scans, ultrasounds, or MRIs, to visualize the organs and tissues in your abdomen.
- Endoscopy or Colonoscopy: To examine the inside of your digestive tract.
4. Home Remedies and Prevention
In some cases, you can manage mild left-side pain at home with simple remedies.
4.1 Self-Care Tips
- Rest: Avoid strenuous activities and get plenty of rest.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Heat: Apply a warm compress to your abdomen to relieve pain.
- Diet: Avoid foods that trigger gas or bloating.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
4.2 Preventive Measures
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fiber to promote regular bowel movements.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve digestion and overall health.
- Proper Posture: Maintain good posture to prevent muscle strain.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga or meditation.
5. Exploring Treatment Options
Treatment for left-side pain depends on the underlying cause. Your doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on your diagnosis.
5.1 Medical Treatments
- Medications: Antibiotics for infections, pain relievers for pain management, anti-inflammatory drugs for IBD, hormonal therapies for endometriosis.
- Surgery: Appendectomy for appendicitis, surgery to remove kidney stones, surgery to repair hernias.
5.2 Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief from left-side pain through alternative therapies such as:
- Acupuncture: Involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain and promote healing.
- Chiropractic Care: Focuses on adjusting the spine and other joints to improve alignment and reduce pain.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbs have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties.
6. Living with Chronic Left-Side Pain
If you have a chronic condition that causes left-side pain, it’s important to develop strategies for managing your symptoms and improving your quality of life.
6.1 Pain Management Strategies
- Medication Management: Work with your doctor to find the right medications and dosages to manage your pain.
- Physical Therapy: Learn exercises to strengthen your muscles and improve your range of motion.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A type of therapy that helps you change negative thought patterns and behaviors that can contribute to pain.
- Support Groups: Connect with other people who have chronic pain to share experiences and learn coping strategies.
6.2 Lifestyle Adjustments
- Dietary Changes: Identify and avoid foods that trigger your symptoms.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity that you enjoy and that doesn’t worsen your pain.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
7. Left Side Pain During Pregnancy
Experiencing pain on the left side during pregnancy can be concerning. It’s essential to understand the potential causes and when to seek medical attention.
7.1 Common Causes
- Round Ligament Pain: As the uterus grows, the ligaments that support it can stretch and cause pain in the lower abdomen.
- Constipation: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can slow down digestion, leading to constipation and abdominal discomfort.
- Gas: Increased progesterone levels can relax the digestive tract, leading to gas and bloating.
- Braxton Hicks Contractions: These “practice” contractions can cause tightening and discomfort in the abdomen.
7.2 When to Seek Medical Attention
See a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Fever
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Decreased fetal movement
8. Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of the underlying cause of left-side pain is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications.
8.1 Benefits of Prompt Treatment
- Pain Relief: Addressing the underlying cause can relieve pain and improve your quality of life.
- Prevention of Complications: Early treatment can prevent serious complications such as infections, organ damage, or infertility.
- Improved Prognosis: Many conditions that cause left-side pain can be effectively managed with early intervention.
9. Exploring Common Scenarios
To provide a more tailored understanding, let’s explore some common scenarios where individuals might experience pain on their left side.
9.1 Left Side Pain After Eating
Experiencing pain on the left side after eating could be related to several factors. These include:
- Gas and Bloating: Certain foods can cause gas and bloating, leading to discomfort on the left side.
- Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining can cause pain, especially after eating.
- Stomach Ulcers: Sores in the stomach lining can cause pain that worsens after meals.
- Splenic Flexure Syndrome: Trapped gas at the splenic flexure (a bend in the colon) can cause left upper abdominal pain.
9.2 Left Side Pain While Breathing
Pain on the left side that occurs while breathing can be concerning and may indicate several potential issues:
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the lining around the lungs can cause sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing.
- Musculoskeletal Pain: Strained muscles or injured ribs can cause pain that is exacerbated by breathing.
- Costochondritis: Inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone can cause chest pain.
9.3 Left Side Pain and Back Pain
When left-side pain is accompanied by back pain, it may suggest issues involving the kidneys or musculoskeletal system.
- Kidney Stones: Pain from kidney stones can radiate to the back.
- Kidney Infection: Infections can cause both abdominal and back pain.
- Muscle Strain: Strained back muscles can cause pain that radiates to the side.
10. The Role of Technology in Diagnosis and Treatment
Advancements in medical technology have significantly improved the diagnosis and treatment of conditions causing left-side pain.
10.1 Advanced Imaging Techniques
- CT Scans: Provide detailed images of the internal organs and tissues.
- MRI Scans: Offer high-resolution images to detect abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the abdominal organs.
10.2 Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Laparoscopy: A surgical technique that uses small incisions and a camera to visualize and treat abdominal conditions.
- Endoscopy: Involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera to examine the digestive tract.
11. A Holistic Approach to Managing Left-Side Pain
A holistic approach to managing left-side pain involves addressing the physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors that can contribute to pain.
11.1 Mind-Body Techniques
- Meditation: Reduces stress and promotes relaxation.
- Yoga: Improves flexibility, strength, and reduces pain.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Helps to relieve tension and promote relaxation.
11.2 Nutritional Support
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Probiotics: Supports gut health and reduces digestive issues.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water helps to maintain bodily functions.
12. Debunking Myths About Left-Side Pain
There are many misconceptions about the causes and treatments of left-side pain. Here are some common myths debunked:
- Myth: Left-side pain is always due to gas.
- Fact: While gas can cause pain, other conditions like kidney stones, diverticulitis, and ovarian cysts can also be responsible.
- Myth: You should always take pain relievers for left-side pain.
- Fact: While pain relievers can provide temporary relief, it’s important to identify and treat the underlying cause of the pain.
- Myth: Left-side pain is never serious.
- Fact: Severe or persistent left-side pain can be a sign of a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention.
13. Expert Insights on Left-Side Pain
To provide a comprehensive understanding of left-side pain, let’s consider insights from medical experts:
- Gastroenterologist: “Persistent abdominal pain, especially if accompanied by changes in bowel habits, should be evaluated by a gastroenterologist to rule out conditions like IBD or diverticulitis.”
- Urologist: “Severe pain in the side and back that radiates to the groin may indicate kidney stones. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications.”
- Gynecologist: “Pelvic pain in women can be caused by various conditions, including ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and PID. Regular check-ups and prompt evaluation of symptoms are important.”
14. Navigating Healthcare Options
When experiencing left-side pain, it’s important to know where to seek medical care.
14.1 Primary Care Physician
Your primary care physician can evaluate your symptoms, perform a physical exam, and order initial tests. They can also refer you to a specialist if necessary.
14.2 Urgent Care Centers
Urgent care centers can provide prompt medical care for non-life-threatening conditions. They are a good option if you can’t see your primary care physician right away but need medical attention.
14.3 Emergency Rooms
Emergency rooms are for serious medical conditions that require immediate attention. If you experience severe pain, fever, bloody stools or vomit, or other concerning symptoms, go to the emergency room right away.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Left Side Pain
Q1: What are the most common causes of pain on the left side?
A1: Common causes include gas, constipation, diverticulitis, kidney stones, and, in women, ovarian cysts or menstrual cramps.
Q2: When should I be concerned about pain on the left side?
A2: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, bloody stools, or dizziness.
Q3: How is diverticulitis diagnosed?
A3: Diverticulitis is typically diagnosed through a physical exam, blood tests, and a CT scan.
Q4: What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
A4: Symptoms include severe pain in the side and back, frequent urination, blood in the urine, nausea, and vomiting.
Q5: Can stress cause pain on the left side?
A5: Yes, stress can contribute to digestive issues like IBS, which can cause abdominal pain.
Q6: What lifestyle changes can help manage left-side pain?
A6: A healthy diet, regular exercise, proper posture, and stress management techniques can help.
Q7: Is left-side pain during pregnancy normal?
A7: Some pain, like round ligament pain, is common during pregnancy. However, severe pain should be evaluated by a doctor.
Q8: How are ovarian cysts treated?
A8: Treatment options range from observation and pain relievers to hormonal birth control or surgery.
Q9: What is endometriosis?
A9: Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing pain and other symptoms.
Q10: What is the role of technology in diagnosing left-side pain?
A10: Advanced imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs provide detailed images of the internal organs and tissues.
16. Staying Informed and Proactive
Understanding the potential causes of pain on your left side empowers you to take proactive steps to manage your health.
16.1 Regular Check-Ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your health and address any concerns.
16.2 Self-Monitoring
Pay attention to your symptoms and track any changes or patterns.
16.3 Seeking Expert Advice
Don’t hesitate to seek expert advice from healthcare professionals if you have questions or concerns.
By staying informed and proactive, you can effectively manage pain on your left side and maintain your overall well-being.
17. Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
Experiencing pain on your left side can be concerning, but understanding the potential causes and available treatments empowers you to take control of your health. From digestive issues and kidney problems to musculoskeletal conditions and gender-specific concerns, numerous factors can contribute to this discomfort. By recognizing warning signs, seeking timely medical attention, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, you can effectively manage left-side pain and improve your quality of life.
Remember, the information provided here is for educational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
If you are struggling to find answers to your health questions or need expert guidance, visit WHY.EDU.VN. Our platform connects you with experts who can provide accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health. At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of navigating the vast amount of information available online and strive to provide you with trustworthy and easy-to-understand explanations.
Don’t let uncertainty and misinformation keep you from finding the answers you need. Visit WHY.EDU.VN today and take the first step toward better health.
Contact Information:
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Discover reliable insights and expert advice at why.edu.vn, your go-to resource for comprehensive answers and health solutions, addressing abdominal discomfort and promoting well-being.
