Feeling lightheaded everyday can be unsettling and disruptive to your life, but understanding the potential causes is the first step toward finding relief. At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the frustration of searching for reliable health information, so we’ve compiled expert knowledge to explore the reasons behind chronic lightheadedness and provide actionable solutions. Delve into the complexities of orthostatic hypotension, dehydration, and blood sugar fluctuations with insights you can trust, and discover a path towards feeling grounded and stable again.
1. Understanding Daily Lightheadedness: A Comprehensive Overview
Feeling lightheaded daily can stem from a range of underlying factors, varying from minor lifestyle issues to more serious health conditions. It’s important to understand what this sensation means and differentiate it from other forms of dizziness. Lightheadedness is often described as a feeling that you might faint or pass out, a sensation of imbalance, or a floating sensation. Let’s explore this common issue.
1.1. What Does It Mean to Feel Lightheaded?
Lightheadedness is a feeling of unsteadiness or imbalance, as if you are about to faint. It is different from vertigo, which involves a sensation that you or your surroundings are spinning. Lightheadedness can be caused by a temporary drop in blood flow to the brain, dehydration, low blood sugar, or other underlying health issues.
Key Symptoms of Lightheadedness:
- A sensation of nearly fainting
- Unsteadiness
- Blurred vision
- Weakness
- Confusion
- Floating sensation
1.2. Distinguishing Lightheadedness from Vertigo and Dizziness
It’s essential to differentiate lightheadedness from other forms of dizziness, such as vertigo and general imbalance.
- Vertigo: Involves a false sense of movement, either you or your surroundings are spinning or tilting. It often results from inner ear problems.
- Dizziness: A broader term that includes lightheadedness, vertigo, and imbalance. It can be caused by various factors, including inner ear issues, medication side effects, and neurological conditions.
| Symptom | Lightheadedness | Vertigo | Dizziness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensation | Feeling faint or unsteady | Spinning or tilting sensation | General imbalance or unsteadiness |
| Primary Cause | Reduced blood flow to the brain | Inner ear problems | Varies, including inner ear, medication |
| Common Triggers | Dehydration, low blood sugar, standing up quickly | Changes in head position, inner ear infections | Varies widely |
1.3. When Is Daily Lightheadedness a Cause for Concern?
While occasional lightheadedness can be benign, experiencing it daily warrants further investigation. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if lightheadedness is:
- Persistent and doesn’t improve with rest or hydration.
- Accompanied by other symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, severe headache, or neurological changes.
- Occurring after a head injury.
- Affecting your ability to perform daily activities.
For expert insights and reliable health information, visit WHY.EDU.VN, where you can find answers to your health questions and connect with professionals.
2. Potential Causes of Feeling Lightheaded Every Day
The reasons behind daily lightheadedness can be diverse, ranging from dehydration to more serious cardiovascular issues. Understanding the common causes helps in addressing the problem effectively.
2.1. Dehydration and Its Impact on Blood Pressure
Dehydration is a frequent cause of lightheadedness. When your body lacks sufficient fluids, blood volume decreases, leading to lower blood pressure. This can reduce the amount of blood reaching the brain, causing lightheadedness.
- Symptoms of Dehydration: Thirst, dry mouth, dark urine, decreased urination, fatigue, and lightheadedness.
- Solutions: Increase daily fluid intake, especially water. Avoid excessive consumption of caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate dehydration. Consider electrolyte-rich beverages during and after exercise.
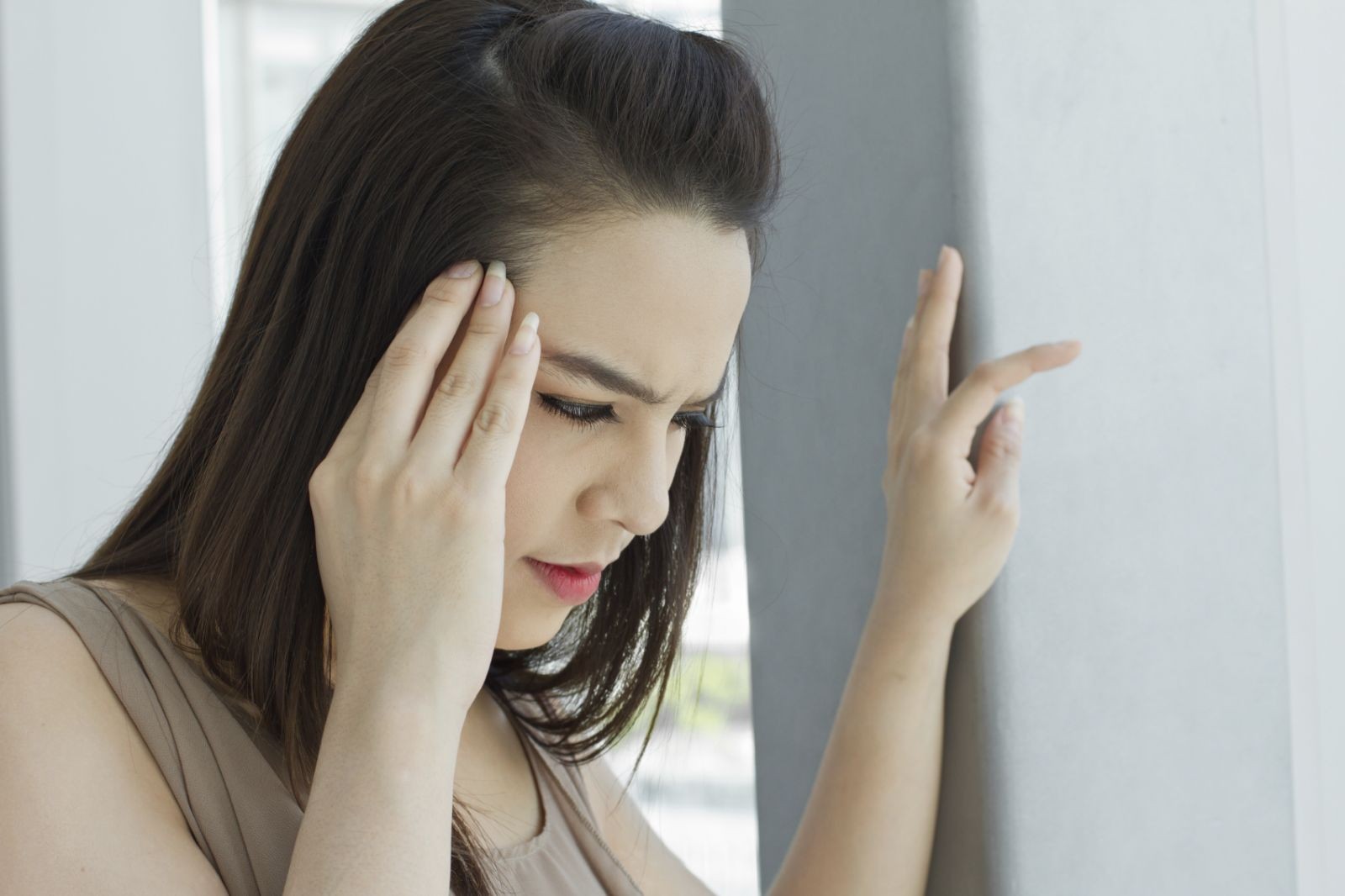 Dehydration and lightheadedness
Dehydration and lightheadedness
Alt text: Illustration depicting a person feeling lightheaded due to dehydration, highlighting the importance of staying hydrated for blood pressure regulation.
2.2. Orthostatic Hypotension (Postural Hypotension)
Orthostatic hypotension, or postural hypotension, is a sudden drop in blood pressure that occurs when you stand up from a sitting or lying position. This condition is common and can cause lightheadedness or fainting.
- Causes: Age-related changes in the autonomic nervous system, dehydration, certain medications (like diuretics or blood pressure drugs), prolonged bed rest, and underlying health conditions like diabetes or heart problems.
- Management:
- Slow Movements: Stand up slowly from a sitting or lying position.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to maintain adequate blood volume.
- Compression Stockings: Wear compression stockings to improve blood circulation in the legs.
- Medication Review: Consult your doctor to review and adjust medications that may contribute to orthostatic hypotension.
2.3. Cardiovascular Issues: Heart Conditions and Blood Flow Problems
Heart conditions and blood flow problems can significantly impact blood supply to the brain, leading to chronic lightheadedness.
- Common Cardiovascular Causes:
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms can reduce the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
- Heart Failure: The heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Valve Problems: Narrowed or leaky heart valves can impede blood flow.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the brain and other organs.
- Symptoms: Lightheadedness, chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue.
- Medical Evaluation: If you suspect a cardiovascular issue, seek immediate medical attention. Diagnostic tests like ECG, echocardiogram, and stress tests can help identify the underlying problem.
2.4. Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, occurs when glucose levels in the blood drop too low. The brain relies on glucose for energy, so when levels are insufficient, it can lead to lightheadedness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
- Causes: Diabetes medications (insulin, sulfonylureas), skipping meals, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions.
- Symptoms: Lightheadedness, shakiness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, and rapid heartbeat.
- Immediate Treatment: Consume a quick source of glucose, such as fruit juice, glucose tablets, or hard candy.
- Prevention: Eat regular, balanced meals and snacks. Monitor blood sugar levels if you have diabetes. Consult your doctor to adjust medications if needed.
2.5. Medication Side Effects
Many medications can cause lightheadedness as a side effect. Common culprits include:
- Blood Pressure Medications: Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers.
- Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs.
- Antihistamines: Diphenhydramine, loratadine.
- Sedatives and Tranquilizers: Benzodiazepines.
- Painkillers: Opioids.
Management:
- Review Medications: Discuss all medications you are taking with your doctor to identify potential culprits.
- Dosage Adjustments: Your doctor may adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative medication.
- Timing: Taking medications at specific times of the day can minimize side effects.
2.6. Inner Ear Problems and Vestibular Disorders
Inner ear problems and vestibular disorders can disrupt your balance, leading to dizziness and lightheadedness.
-
Common Conditions:
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): Dislodged calcium crystals in the inner ear cause brief episodes of vertigo.
- Ménière’s Disease: An inner ear disorder that can cause vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
- Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis: Inflammation of the inner ear or vestibular nerve.
-
Symptoms: Vertigo, lightheadedness, imbalance, nausea, and hearing changes.
-
Treatment:
- BPPV: The Epley maneuver, a series of head movements, can help reposition the calcium crystals.
- Ménière’s Disease: Medications to control symptoms, lifestyle changes (low-sodium diet, stress management), and, in some cases, surgery.
- Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis: Medications to reduce inflammation and nausea, and vestibular rehabilitation therapy.
2.7. Anxiety and Panic Disorders
Anxiety and panic disorders can trigger lightheadedness as part of the body’s stress response. Hyperventilation, a common symptom of anxiety, can lead to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels, causing lightheadedness.
- Symptoms: Lightheadedness, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, sweating, trembling, and a sense of impending doom.
- Management:
- Breathing Exercises: Practice slow, deep breathing to regulate carbon dioxide levels.
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help manage anxiety and panic symptoms.
- Medications: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed.
2.8. Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological conditions can affect balance and coordination, leading to chronic lightheadedness.
-
Common Conditions:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): A chronic autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord.
- Parkinson’s Disease: A progressive neurological disorder that affects movement.
- Migraines: Severe headaches that can cause dizziness and lightheadedness.
- Stroke: Interruption of blood flow to the brain.
-
Symptoms: Lightheadedness, imbalance, coordination problems, muscle weakness, and neurological changes.
-
Medical Evaluation: A thorough neurological examination and diagnostic tests (MRI, CT scan) are essential to identify the underlying condition.
Addressing these potential causes requires a comprehensive approach, often involving medical evaluation, lifestyle adjustments, and targeted treatments. For reliable information and expert advice, turn to WHY.EDU.VN, your trusted source for health-related queries.
3. Diagnosing the Cause of Your Lightheadedness
Pinpointing the exact cause of daily lightheadedness requires a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals. This process typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
3.1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing the cause of lightheadedness is a detailed discussion with your doctor. Be prepared to provide information about:
- Symptoms: Describe the frequency, duration, and intensity of your lightheadedness. Note any triggers or associated symptoms.
- Medical History: Share any pre-existing medical conditions, past surgeries, and hospitalizations.
- Medications: List all medications, including prescription, over-the-counter, and supplements.
- Lifestyle Factors: Discuss your diet, exercise habits, alcohol consumption, and smoking status.
During the physical examination, your doctor will assess:
- Vital Signs: Blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature.
- Neurological Function: Balance, coordination, reflexes, and sensory function.
- Cardiovascular System: Heart and lung sounds.
- Inner Ear: Examination of the ears and assessment of balance.
3.2. Common Diagnostic Tests
Based on your medical history and physical examination, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following diagnostic tests:
-
Blood Tests:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for anemia or infection.
- Electrolyte Levels: To assess for dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
- Blood Sugar Levels: To evaluate for hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Thyroid Function Tests: To check for thyroid disorders.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Records the electrical activity of the heart to detect arrhythmias or signs of heart disease.
-
Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to create images of the heart, assessing its structure and function.
-
Orthostatic Blood Pressure Measurement: Measures blood pressure while lying, sitting, and standing to detect orthostatic hypotension.
-
Tilt Table Test: Monitors blood pressure and heart rate while changing positions to diagnose orthostatic hypotension or other cardiovascular issues.
-
Vestibular Tests:
- Electronystagmography (ENG): Assesses eye movements to evaluate inner ear function.
- Videonystagmography (VNG): Similar to ENG but uses video recording for more precise measurements.
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR): Evaluates hearing and nerve function between the ear and brain.
-
Imaging Studies:
- MRI or CT Scan of the Brain: To detect neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, or tumors.
- CT Angiography: To evaluate blood vessels in the brain and neck.
| Test | Purpose | What It Detects |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Assess overall health, check for anemia or infection | Anemia, infection, blood disorders |
| Electrolyte Levels | Evaluate electrolyte balance | Dehydration, kidney problems, electrolyte imbalances |
| Blood Sugar Levels | Check for hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia | Diabetes, hypoglycemia |
| Thyroid Function Tests | Assess thyroid gland function | Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) | Record electrical activity of the heart | Arrhythmias, heart disease |
| Echocardiogram | Ultrasound imaging of the heart | Heart structure and function abnormalities |
| Orthostatic Blood Pressure | Measure blood pressure in different positions | Orthostatic hypotension |
| Tilt Table Test | Monitor blood pressure and heart rate during position changes | Orthostatic hypotension, vasovagal syncope |
| Electronystagmography (ENG) | Assess eye movements to evaluate inner ear function | Inner ear disorders |
| Videonystagmography (VNG) | Video recording of eye movements for inner ear assessment | Inner ear disorders |
| Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) | Evaluate hearing and nerve function between ear and brain | Hearing loss, nerve disorders |
| MRI or CT Scan of the Brain | Imaging of the brain | Neurological conditions, such as MS, stroke, tumors |
| CT Angiography | Evaluate blood vessels in the brain and neck | Blood vessel abnormalities |
3.3. Importance of Seeking Professional Medical Advice
Self-diagnosing lightheadedness can be risky, as the underlying cause may be serious. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
If you’re seeking reliable information and expert guidance, turn to WHY.EDU.VN. Our platform connects you with professionals who can address your health concerns and provide personalized advice. You can find us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101.
4. Practical Strategies for Managing Daily Lightheadedness
Once the cause of your daily lightheadedness is identified, implementing practical strategies can help manage and alleviate symptoms. These strategies often involve lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments, and supportive therapies.
4.1. Lifestyle Adjustments
Making specific lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of lightheadedness.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain adequate blood volume. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Dietary Modifications:
- Regular Meals: Eat regular, balanced meals to prevent low blood sugar.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can contribute to dehydration and exacerbate lightheadedness.
- Low-Sodium Diet: If you have Ménière’s disease or other inner ear disorders, a low-sodium diet may help reduce fluid retention.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health and balance. Consult your doctor before starting a new exercise program.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: Stand up slowly from a sitting or lying position to prevent orthostatic hypotension.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, to reduce anxiety and stress-related lightheadedness.
4.2. Medical Treatments and Medications
Depending on the underlying cause of your lightheadedness, your doctor may prescribe medications or recommend specific medical treatments.
- Orthostatic Hypotension:
- Fludrocortisone: Helps increase blood volume.
- Midodrine: Helps constrict blood vessels to raise blood pressure.
- Ménière’s Disease:
- Diuretics: Reduce fluid retention in the inner ear.
- Antihistamines and Anti-Nausea Medications: To relieve vertigo and nausea.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation.
- Anxiety and Panic Disorders:
- Antidepressants: SSRIs or SNRIs.
- Anti-Anxiety Medications: Benzodiazepines (use with caution due to potential side effects and dependence).
- Inner Ear Infections:
- Antibiotics: To treat bacterial infections.
- Antiviral Medications: To treat viral infections.
4.3. Supportive Therapies
In addition to lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments, supportive therapies can play a crucial role in managing lightheadedness.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT): A specialized therapy that helps improve balance and reduce dizziness associated with inner ear disorders. VRT involves exercises that retrain the brain to compensate for inner ear dysfunction.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Useful for managing anxiety and panic disorders that contribute to lightheadedness. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Physical Therapy: Can help improve strength, balance, and coordination, particularly for individuals with neurological conditions.
- Assistive Devices: Canes or walkers can provide additional support and stability, reducing the risk of falls.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hydration | Drinking 8-10 glasses of water daily | Maintains blood volume, prevents dehydration-related lightheadedness |
| Regular Meals | Eating balanced meals at consistent intervals | Prevents low blood sugar, stabilizes energy levels |
| Limit Caffeine/Alcohol | Reducing intake of caffeine and alcohol | Prevents dehydration, stabilizes blood pressure |
| Slow Movements | Standing up slowly from sitting or lying positions | Prevents orthostatic hypotension |
| Stress Management | Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation | Reduces anxiety-related lightheadedness |
| Medication Management | Following prescribed medication regimens and consulting with a doctor about side effects | Treats underlying conditions, minimizes medication-induced lightheadedness |
| Vestibular Rehab | Specialized exercises to improve balance and reduce dizziness | Improves balance, reduces dizziness associated with inner ear disorders |
| Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy | Therapy to manage anxiety and change negative thought patterns | Helps manage anxiety-related lightheadedness |
| Physical Therapy | Improving strength, balance, and coordination | Improves stability, reduces fall risk |
| Assistive Devices | Using canes or walkers for additional support | Provides stability, reduces risk of falls |
For personalized advice and expert guidance, visit WHY.EDU.VN. Our team is dedicated to providing reliable health information and connecting you with professionals who can address your specific needs. Find us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101.
5. When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
While many causes of lightheadedness are manageable with lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments, certain symptoms and situations warrant immediate medical attention. Recognizing these warning signs can help prevent serious complications.
5.1. Recognizing Warning Signs
Seek emergency medical care if you experience lightheadedness accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: May indicate a heart attack or other serious cardiovascular issue.
- Shortness of Breath: Can be a sign of heart or lung problems.
- Severe Headache: Especially if sudden and accompanied by stiff neck, fever, or vision changes.
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: Particularly on one side of the body, may indicate a stroke.
- Difficulty Speaking: Slurred speech or inability to find words can be a sign of stroke.
- Vision Changes: Sudden loss of vision, double vision, or blurred vision.
- Loss of Consciousness: Especially if prolonged or associated with injury.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled shaking or convulsions.
- Head Injury: Lightheadedness following a blow to the head.
5.2. Emergency Situations Requiring Immediate Care
Certain situations require immediate medical intervention to prevent life-threatening complications:
- Heart Attack: Characterized by chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and lightheadedness.
- Stroke: Characterized by sudden weakness, numbness, difficulty speaking, and vision changes.
- Severe Head Trauma: Lightheadedness and loss of consciousness following a head injury.
- Severe Dehydration: Characterized by extreme thirst, decreased urination, rapid heartbeat, and confusion.
- Severe Hypoglycemia: Loss of consciousness due to very low blood sugar levels.
5.3. How to Prepare for an Emergency
Being prepared for a medical emergency can help ensure you receive prompt and appropriate care:
- Know Your Medications: Keep a list of all medications, dosages, and allergies.
- Emergency Contact Information: Carry a card with emergency contact information and medical history.
- Medical Alert Bracelet: Wear a medical alert bracelet if you have a chronic condition, such as diabetes or heart disease.
- Emergency Plan: Discuss an emergency plan with family members or caregivers.
- Recognize Symptoms: Educate yourself and loved ones about the warning signs of serious medical conditions.
| Symptom | Potential Condition | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Pain, Shortness of Breath | Heart Attack | Call emergency services immediately |
| Sudden Weakness/Numbness | Stroke | Call emergency services immediately |
| Severe Headache | Stroke, Aneurysm | Call emergency services immediately |
| Vision Changes | Stroke, Eye Condition | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Loss of Consciousness | Various Serious Conditions | Call emergency services immediately |
| Seizures | Neurological Disorder | Call emergency services immediately |
| Head Injury | Concussion, Brain Injury | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Severe Dehydration | Dehydration | Seek medical attention if severe |
| Severe Hypoglycemia | Diabetes | Seek medical attention if unresponsive |
Remember, prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes in emergency situations. For reliable health information and expert guidance, visit WHY.EDU.VN. Our team is dedicated to providing accurate and trustworthy resources to address your health concerns. Find us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101.
6. The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Managing Lightheadedness
Diet and nutrition play a pivotal role in managing daily lightheadedness, particularly in cases related to dehydration, low blood sugar, and cardiovascular health. Making informed dietary choices can help stabilize blood sugar levels, maintain adequate hydration, and support overall well-being.
6.1. Foods to Include in Your Diet
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods can help alleviate lightheadedness and improve overall health.
- Hydrating Foods:
- Water-Rich Fruits and Vegetables: Watermelon, cucumbers, strawberries, and spinach help maintain hydration.
- Soups and Broths: Provide fluids and electrolytes.
- Foods to Stabilize Blood Sugar:
- Complex Carbohydrates: Whole grains, oats, brown rice, and quinoa provide sustained energy.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, beans, and tofu help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil support overall health.
- Foods Rich in Iron and Vitamin B12:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale are rich in iron.
- Lean Meats: Beef and poultry provide iron and vitamin B12.
- Fortified Cereals: Can help meet daily iron and vitamin B12 needs.
- Foods High in Potassium:
- Bananas: Excellent source of potassium.
- Sweet Potatoes: Rich in potassium and fiber.
- Avocados: Provide healthy fats and potassium.
6.2. Foods to Avoid or Limit
Certain foods and beverages can exacerbate lightheadedness and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether.
- Caffeine: Can cause dehydration and fluctuations in blood pressure.
- Alcohol: Can lead to dehydration and low blood sugar.
- High-Sugar Foods: Can cause rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar levels.
- Processed Foods: Often high in sodium, which can contribute to dehydration and fluid retention.
- Excessive Salt: Can increase blood pressure and fluid retention.
6.3. Sample Meal Plans for Managing Lightheadedness
Creating a structured meal plan can help ensure you’re getting the nutrients you need to manage lightheadedness effectively.
- Breakfast:
- Oatmeal with berries and nuts.
- Whole-grain toast with avocado and egg.
- Lunch:
- Salad with grilled chicken or fish.
- Whole-grain wrap with hummus and vegetables.
- Dinner:
- Baked salmon with roasted vegetables.
- Lentil soup with whole-grain bread.
- Snacks:
- Greek yogurt with fruit.
- Handful of almonds or walnuts.
- Banana with peanut butter.
| Meal | Sample Foods | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Provides fiber, antioxidants, and sustained energy |
| Lunch | Salad with grilled chicken or fish | Offers lean protein, vitamins, and hydration |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with roasted vegetables | Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with fruit | Provides protein, calcium, and antioxidants |
| Snack | Handful of almonds or walnuts | Healthy fats, protein, and essential nutrients |
| Snack | Banana with peanut butter | Potassium, fiber, and sustained energy |
6.4. The Importance of Staying Hydrated
Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for managing lightheadedness. Dehydration can lead to decreased blood volume, causing lightheadedness, fatigue, and other symptoms.
- Tips for Staying Hydrated:
- Carry a Water Bottle: Keep a water bottle with you throughout the day.
- Set Reminders: Use phone reminders to drink water regularly.
- Drink Before, During, and After Exercise: Replenish fluids lost through sweat.
- Incorporate Hydrating Foods: Eat water-rich fruits and vegetables.
For personalized dietary recommendations and expert guidance, visit WHY.EDU.VN. Our team is dedicated to providing reliable health information and connecting you with professionals who can address your specific needs. Find us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101.
7. Home Remedies and Over-the-Counter Solutions
In addition to lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments, several home remedies and over-the-counter (OTC) solutions can help alleviate lightheadedness and provide relief from symptoms.
7.1. Simple Home Remedies
Several simple home remedies can help manage lightheadedness:
- Lie Down or Sit Down: If you feel lightheaded, immediately lie down or sit down to prevent falls and increase blood flow to the brain.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practice slow, deep breathing to increase oxygen levels and reduce anxiety.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to maintain adequate blood volume.
- Cool Compress: Apply a cool compress to your forehead or neck to help alleviate dizziness.
- Ginger: Ginger can help reduce nausea and dizziness associated with inner ear problems. Consume ginger tea, ginger candies, or ginger supplements.
7.2. Over-the-Counter Medications
Several OTC medications can help manage symptoms associated with lightheadedness:
- Antihistamines: Such as dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) or meclizine (Bonine), can help reduce motion sickness and dizziness.
- Decongestants: If lightheadedness is due to sinus congestion, decongestants can help relieve symptoms.
- Pain Relievers: OTC pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage headaches or pain that may contribute to lightheadedness.
- Electrolyte Solutions: Such as sports drinks or oral rehydration solutions, can help replenish electrolytes lost due to dehydration.
7.3. Herbal Remedies
Certain herbal remedies have been traditionally used to manage dizziness and lightheadedness:
- Ginkgo Biloba: May improve blood flow to the brain and reduce dizziness.
- Peppermint: Can help alleviate nausea and dizziness. Consume peppermint tea or peppermint candies.
- Lavender: Can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Use lavender essential oil in a diffuser or apply topically (diluted with a carrier oil).
- Chamomile: Can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Consume chamomile tea.
| Remedy | Form | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Lie Down/Sit Down | N/A | Increases blood flow to the brain, prevents falls |
| Deep Breathing | N/A | Increases oxygen levels, reduces anxiety |
| Hydration | Water, Fluids | Maintains blood volume, prevents dehydration |
| Cool Compress | Compress | Alleviates dizziness |
| Ginger | Tea, Candy, Supplement | Reduces nausea and dizziness |
| Antihistamines | OTC Medication | Reduces motion sickness and dizziness |
| Decongestants | OTC Medication | Relieves sinus congestion |
| Pain Relievers | OTC Medication | Manages headaches and pain |
| Electrolyte Solutions | Drinks | Replenishes electrolytes lost due to dehydration |
| Ginkgo Biloba | Supplement | Improves blood flow to the brain, reduces dizziness |
| Peppermint | Tea, Candy | Alleviates nausea and dizziness |
| Lavender | Essential Oil | Reduces anxiety, promotes relaxation |
| Chamomile | Tea | Reduces anxiety, promotes relaxation |
7.4. Precautions and Potential Side Effects
While home remedies and OTC solutions can provide relief, it’s essential to use them with caution and be aware of potential side effects:
- Antihistamines: Can cause drowsiness and dry mouth.
- Decongestants: Can raise blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid if you have high blood pressure or heart problems.
- Herbal Remedies: Can interact with medications. Consult your doctor before using herbal remedies, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
For personalized advice and expert guidance, visit why.edu.vn. Our team is dedicated to providing reliable health information and connecting you with professionals who can address your specific needs. Find us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101.
8. Preventing Future Episodes of Lightheadedness
Preventing future episodes of lightheadedness involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, proactive health management, and awareness of potential triggers. By adopting these strategies, you can reduce the frequency and severity of lightheadedness and improve your overall quality of life.
8.1. Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding specific triggers is crucial for preventing lightheadedness:
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Keep a journal to track when you experience lightheadedness, noting any potential triggers.
- Common Triggers to Avoid:
- Dehydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Skipping Meals: Eat regular, balanced meals.
- Sudden Movements: Stand up slowly from a sitting or lying position.
- Stress: Practice relaxation techniques to manage stress.
- Overheating: Avoid prolonged exposure to heat and stay hydrated during hot weather.
- Alcohol and Caffeine: Consume in moderation or avoid altogether.
8.2. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of lightheadedness:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of nutrient-rich foods to stabilize blood sugar and support overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health and balance.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
8.3. Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring your health and identifying potential problems early:
- Annual Physical Exam: Visit your doctor for an annual physical exam to assess your overall health.
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood pressure to detect and manage hypertension or hypotension.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: If you have diabetes or are at risk, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
- Medication Review: Review your medications with your doctor to identify potential side effects and interactions.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend follow-up appointments as recommended by your doctor.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Monitor Symptoms | Keep a journal to track lightheadedness episodes and potential triggers | Helps identify and avoid specific triggers |
| Stay Hydrated | Drink plenty of water throughout the day | Prevents dehydration-related lightheadedness |
| Regular Meals | Eat regular, balanced meals to stabilize blood sugar | Prevents low blood sugar and stabilizes energy levels |
| Slow Movements | Stand up slowly from sitting or lying positions | Prevents orthostatic hypotension |
| Manage Stress | Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga | Reduces anxiety-related lightheadedness |
| Balanced Diet | Eat a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support overall health | Stabilizes blood sugar, provides essential nutrients |
| Regular Exercise | Engage in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health and balance | Improves cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles, and enhances balance |
| Adequate Sleep | Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night | Supports overall health and well-being |
| Weight Management | Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems | Reduces the risk of heart disease and other health problems |
| Medical Check-Ups | Attend regular check-ups with your doctor for monitoring and early detection of health problems | Early detection and management of potential health issues |
For personalized advice