Do you wonder Why Do Dogs Need Their Anal Glands Expressed? It’s a common question among dog owners. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive information to help you understand your pet’s health. The anal glands in dogs sometimes require manual expression to prevent impaction, infection, and discomfort. Maintaining your dog’s anal gland health is crucial, and with proper knowledge, including causes, symptoms, and treatments, you can ensure their well-being. Explore pet health topics and access expert advice on our platform, WHY.EDU.VN, to keep your canine companion healthy and happy with reliable content on canine anatomy and pet wellness.
1. What Are Dog Anal Glands and How Do They Work?
Dog anal glands are two small, pea-sized sacs located on either side of the anus. Each gland is connected to a duct that secretes a strong-smelling fluid. During normal bowel movements, the pressure of the stool passing through the anus naturally expresses these glands, releasing the fluid. This fluid serves several purposes, including scent marking and identification.
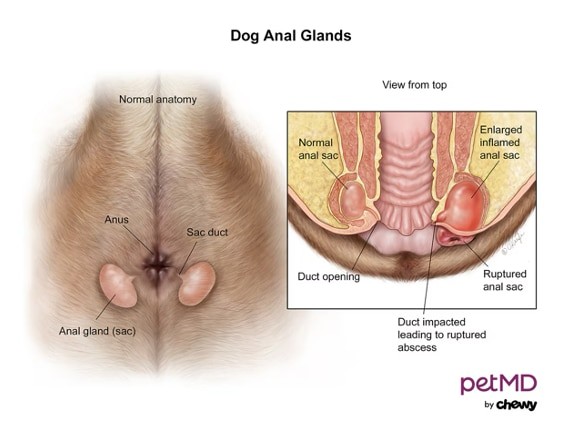 Diagram of dog anal glands
Diagram of dog anal glands
Alt Text: Anatomical diagram illustrating the location and structure of anal glands in dogs, highlighting their position relative to the anus.
1.1. The Purpose of Anal Gland Fluid
The anal gland fluid has a distinct, musky odor that acts as a form of communication between dogs. When dogs greet each other, they often sniff each other’s hindquarters to gather information about the other dog’s identity, hormonal status, and even their health. This fluid essentially serves as a “doggy business card.”
1.2. Natural Expression vs. Impaction
In healthy dogs, the anal glands are expressed naturally during defecation. However, several factors can prevent this natural expression, leading to impaction, infection, or other problems. These factors include:
- Soft stool: If the stool is too soft, it may not exert enough pressure on the glands to express them.
- Obesity: Overweight dogs may have reduced muscle tone in the anal area, making it difficult to express the glands.
- Anatomical issues: Some dogs have narrow ducts or other anatomical abnormalities that prevent proper drainage.
- Allergies: Food or environmental allergies can cause inflammation in the anal area, leading to impaction.
1.3. Location and Anatomy
The anal glands are located internally, just inside the anus, at approximately the 4 o’clock and 8 o’clock positions. Each gland is connected to the anus by a small duct. The fluid produced by the glands is a thick, oily substance that varies in color from yellowish-brown to dark brown.
2. Why Do Anal Glands Need to Be Expressed?
If a dog’s anal glands do not express naturally, the fluid can thicken and become impacted. This impaction can lead to discomfort, pain, and even infection. Regular expression of the anal glands can help prevent these complications.
2.1. Preventing Impaction
When the anal glands become impacted, the thick fluid accumulates and hardens, forming a mass that blocks the duct. This can cause pressure and discomfort for the dog. Regular expression helps remove this accumulated fluid and prevent impaction.
2.2. Avoiding Infections and Abscesses
Impacted anal glands can become infected as bacteria build up in the stagnant fluid. This infection can lead to an abscess, which is a painful, pus-filled pocket. If left untreated, an abscess can rupture, causing severe pain and requiring veterinary intervention.
2.3. Reducing Discomfort and Irritation
Even without infection, impacted anal glands can cause significant discomfort. Dogs may scoot their rear end along the ground, lick or bite at the anal area, or show signs of pain when sitting or defecating. Regular expression can relieve this discomfort and improve the dog’s quality of life.
3. Recognizing the Signs of Anal Gland Problems
It’s important to recognize the signs of anal gland problems so you can seek appropriate treatment for your dog. Common signs include:
- Scooting: Dragging the rear end along the ground.
- Excessive licking or biting: Focusing on the anal area.
- Straining to defecate: Showing discomfort or difficulty during bowel movements.
- Foul odor: A strong, fishy smell emanating from the anal area.
- Swelling or redness: Visible inflammation around the anus.
- Pain or discomfort: Showing signs of pain when sitting or being touched near the tail.
3.1. The Connection Between Scooting and Anal Glands
Scooting is one of the most common signs of anal gland issues. Dogs scoot to relieve the itching and irritation caused by impacted or inflamed glands. While scooting can also be caused by other issues, such as parasites, it’s essential to consider anal gland problems as a potential cause.
3.2. Identifying Unusual Odors
A strong, foul odor is another telltale sign of anal gland issues. The fluid secreted by the anal glands has a distinctive, musky smell, but when the glands are impacted or infected, the odor becomes much more intense and unpleasant.
3.3. Changes in Defecation Habits
Dogs with anal gland problems may exhibit changes in their defecation habits. They may strain to pass stool, show signs of discomfort during bowel movements, or have blood in their stool.
4. How to Express Dog Anal Glands: A Step-by-Step Guide
If your veterinarian has recommended that you express your dog’s anal glands at home, it’s important to follow their instructions carefully. Here’s a general step-by-step guide:
- Gather your supplies: You’ll need gloves, lubricant (such as petroleum jelly), and a damp cloth or paper towels.
- Position your dog: Have someone assist you in holding your dog still, or position them in a way that is comfortable and secure.
- Locate the anal glands: Gently lift your dog’s tail and locate the anal glands on either side of the anus.
- Lubricate your gloved index finger: Apply lubricant to your gloved index finger for comfort.
- Insert your finger: Gently insert your lubricated finger into the rectum.
- Express the glands: Use your thumb and index finger to gently squeeze the glands, moving in an upward and inward motion.
- Clean the area: Use a damp cloth or paper towels to clean any expressed fluid from the anal area.
4.1. Internal vs. External Expression Techniques
There are two main techniques for expressing anal glands: internal and external. The internal method, described above, involves inserting a finger into the rectum to milk the glands. The external method involves applying pressure to the outside of the anus to express the glands. The internal method is generally more effective, but it may be uncomfortable for some dogs.
4.2. Safety Precautions and Hygiene
When expressing anal glands, it’s crucial to take safety precautions and maintain proper hygiene. Always wear gloves to protect yourself from bacteria and unpleasant odors. Be gentle and avoid applying too much pressure, as this can cause pain or injury to your dog. After expressing the glands, thoroughly clean the anal area to prevent infection.
4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If you are uncomfortable expressing your dog’s anal glands, or if you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus, it’s important to seek professional help from your veterinarian.
5. Alternatives to Manual Expression
While manual expression is a common treatment for anal gland problems, there are also alternative approaches that can help maintain healthy anal glands.
5.1. High-Fiber Diets
A diet high in fiber can promote healthy digestion and proper stool formation. The firm, bulky stool can help express the anal glands naturally during bowel movements. Good sources of fiber for dogs include:
- Pumpkin: A natural source of fiber that can help bulk up stool.
- Sweet potatoes: Rich in fiber and other essential nutrients.
- Bran: Can be added to your dog’s food to increase fiber intake.
- Fiber supplements: Available in powder or chewable form.
5.2. Anal Gland Supplements
Several supplements are specifically formulated to support healthy anal gland function. These supplements often contain a blend of fiber, probiotics, enzymes, and other beneficial ingredients.
5.3. The Role of Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can improve gut health and promote healthy digestion. They can also help reduce inflammation and support a healthy immune system. Probiotics can be found in supplements or in certain foods, such as yogurt.
6. Medical Treatments for Anal Gland Issues
In some cases, anal gland problems may require medical treatment from a veterinarian.
6.1. Antibiotics and Anti-Inflammatory Medications
If the anal glands are infected, your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria. Anti-inflammatory medications can also help reduce swelling and pain.
6.2. Surgical Options
In severe cases, such as when an abscess has ruptured or when cancer is present, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include:
- Abscess drainage: Draining the pus from an abscess to relieve pressure and promote healing.
- Anal sacculectomy: Surgical removal of the anal glands.
- Tumor removal: Surgical removal of cancerous tumors.
6.3. Understanding Anal Sacculectomy
An anal sacculectomy is a surgical procedure in which the anal glands are removed. This procedure is typically reserved for cases of chronic anal gland problems that do not respond to other treatments, or for cases of anal gland cancer. While an anal sacculectomy can be effective, it is a major surgery that carries risks, such as infection, incontinence, and nerve damage.
7. The Importance of Regular Veterinary Checkups
Regular veterinary checkups are essential for maintaining your dog’s overall health, including their anal gland health. During a checkup, your veterinarian can examine your dog’s anal glands and identify any potential problems early on. They can also provide guidance on how to properly care for your dog’s anal glands and prevent future issues.
7.1. Early Detection of Anal Gland Problems
Early detection is key to preventing serious complications from anal gland problems. Your veterinarian can identify subtle signs of impaction or infection that you may not notice at home.
7.2. Professional Advice on Anal Gland Care
Your veterinarian can provide personalized advice on how to care for your dog’s anal glands based on their individual needs. They can recommend dietary changes, supplements, or other treatments to help maintain healthy anal glands.
7.3. Addressing Underlying Health Issues
Anal gland problems can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying health issue, such as allergies or obesity. Your veterinarian can help identify and address these underlying issues to improve your dog’s overall health.
8. Debunking Myths About Dog Anal Glands
There are many misconceptions about dog anal glands. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths.
8.1. Myth: All Dogs Need Their Anal Glands Expressed Regularly
Fact: Most dogs express their anal glands naturally during bowel movements and do not require regular manual expression.
8.2. Myth: Expressing Anal Glands Is Painful for Dogs
Fact: When done correctly, expressing anal glands should not be painful for dogs. However, if the glands are severely impacted or infected, it may cause some discomfort.
8.3. Myth: Anal Gland Problems Are Always Caused by Diet
Fact: While diet can play a role in anal gland health, other factors, such as genetics, anatomy, and allergies, can also contribute to problems.
9. Dog Breeds Predisposed to Anal Gland Issues
While any dog can experience anal gland problems, certain breeds are more prone to these issues. These breeds include:
- Small breeds: Chihuahuas, Toy Poodles, and Miniature Poodles.
- Cocker Spaniels: Known for their tendency to develop anal gland impactions and infections.
- Lhasa Apsos: Often have narrow anal ducts, making them prone to impaction.
- Basset Hounds: Their body structure may contribute to anal gland issues.
9.1. Why Small Breeds Are More Susceptible
Small breeds tend to have smaller anal glands and ducts, which can make them more prone to impaction. Additionally, they may not produce as much stool, which can reduce the pressure on the glands during bowel movements.
9.2. Breed-Specific Anatomical Considerations
Certain breeds have anatomical features that make them more prone to anal gland problems. For example, Lhasa Apsos often have narrow anal ducts, while Basset Hounds have a body structure that may reduce pressure on the glands.
9.3. Genetic Factors
Genetics can also play a role in anal gland health. Some breeds may be predisposed to developing anal gland problems due to inherited traits.
10. Diet and Nutrition for Anal Gland Health
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in maintaining healthy anal glands.
10.1. The Importance of Fiber
As mentioned earlier, fiber is essential for promoting healthy digestion and proper stool formation. A diet high in fiber can help ensure that the anal glands are expressed naturally during bowel movements.
10.2. Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can contribute to anal gland problems. These include:
- Processed foods: Often contain artificial ingredients and fillers that can disrupt digestion.
- High-fat foods: Can lead to soft stool, which may not exert enough pressure on the glands.
- Allergenic foods: Can cause inflammation in the anal area.
10.3. Homemade vs. Commercial Diets
Both homemade and commercial diets can be beneficial for anal gland health, as long as they are properly balanced and contain adequate fiber. Consult with your veterinarian or a veterinary nutritionist to determine the best diet for your dog.
11. The Connection Between Allergies and Anal Gland Problems
Allergies can play a significant role in anal gland problems.
11.1. How Allergies Cause Inflammation
Food or environmental allergies can cause inflammation throughout the body, including in the anal area. This inflammation can lead to swelling and irritation, which can block the anal ducts and prevent proper drainage.
11.2. Identifying and Managing Allergies
If you suspect that your dog has allergies, it’s important to work with your veterinarian to identify the specific allergens and develop a management plan. This may involve allergy testing, dietary changes, or medication.
11.3. Allergy-Friendly Diet Options
If your dog has food allergies, there are many allergy-friendly diet options available. These diets often contain novel protein sources, such as duck or salmon, and are free of common allergens, such as wheat, corn, and soy.
12. Lifestyle Factors Affecting Anal Gland Health
Lifestyle factors can also impact anal gland health.
12.1. Exercise and Activity Levels
Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and improve muscle tone in the anal area. This can make it easier for the anal glands to express naturally.
12.2. Grooming Practices
Proper grooming practices can help prevent anal gland problems. Keep the anal area clean and free of mats or debris.
12.3. Environmental Considerations
Environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens or irritants, can also contribute to anal gland problems. Minimize your dog’s exposure to these factors to help maintain healthy anal glands.
13. Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Anal Gland Management
Let’s look at some real-life examples of how anal gland problems can be managed.
13.1. Case Study 1: Managing Chronic Impaction with Diet and Supplements
A small breed dog with a history of chronic anal gland impaction was successfully managed with a high-fiber diet and anal gland supplements. The diet included pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and a commercial food formulated for digestive health. The supplements contained fiber, probiotics, and enzymes.
13.2. Case Study 2: Treating an Abscess with Antibiotics and Drainage
A large breed dog developed an anal gland abscess due to infection. The abscess was treated with antibiotics and drainage. The dog also underwent surgery to remove the affected anal gland.
13.3. Case Study 3: Surgical Intervention for Anal Gland Cancer
An older dog was diagnosed with anal gland cancer. The dog underwent surgery to remove the cancerous tumor. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy were also used to treat the cancer.
14. Innovations in Anal Gland Treatment
Researchers are constantly developing new and innovative treatments for anal gland problems.
14.1. Novel Therapies
New therapies, such as laser therapy and stem cell therapy, are being investigated as potential treatments for anal gland problems.
14.2. Advanced Surgical Techniques
Advanced surgical techniques, such as laparoscopic surgery, are being used to improve the outcomes of anal gland surgeries.
14.3. Research and Development
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on finding new ways to prevent and treat anal gland problems in dogs.
15. Resources for Dog Owners
There are many resources available to help dog owners learn more about anal gland health.
15.1. Veterinary Websites and Blogs
Many veterinary websites and blogs offer information on anal gland health. These resources can provide valuable insights and tips for caring for your dog’s anal glands.
15.2. Books and Publications
Several books and publications cover dog health and wellness, including information on anal gland health.
15.3. Support Groups and Online Forums
Support groups and online forums can provide a sense of community and support for dog owners dealing with anal gland problems.
16. Expert Opinions on Anal Gland Care
We consulted with several veterinarians and veterinary specialists to gather expert opinions on anal gland care.
16.1. Insights from Veterinarians
Veterinarians emphasized the importance of regular veterinary checkups and early detection of anal gland problems. They also recommended a balanced diet, proper grooming practices, and regular exercise.
16.2. Advice from Veterinary Specialists
Veterinary specialists provided insights on the latest treatments and therapies for anal gland problems. They also stressed the importance of working with a qualified veterinarian to develop a personalized treatment plan for your dog.
16.3. The Role of Veterinary Technicians
Veterinary technicians play a crucial role in anal gland care. They can assist with expressing anal glands, administering medications, and providing education and support to dog owners.
17. Future Trends in Anal Gland Management
The field of anal gland management is constantly evolving. Here are some future trends to watch for:
17.1. Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine, which involves tailoring treatments to the individual needs of each dog, is likely to become more common in anal gland management.
17.2. Preventative Strategies
Preventative strategies, such as early dietary interventions and targeted supplementation, are likely to become more important in preventing anal gland problems.
17.3. Integrative Approaches
Integrative approaches, which combine conventional and complementary therapies, are likely to become more popular in anal gland management.
18. Common Misconceptions and FAQs About Anal Glands in Dogs
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about anal glands in dogs.
18.1. What Happens If a Dog’s Anal Glands Aren’t Expressed?
If a dog’s anal glands aren’t expressed, they can become impacted, infected, or develop an abscess.
18.2. Can I Empty My Dog’s Anal Glands Myself?
Yes, you can empty your dog’s anal glands yourself, but it’s important to follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully and seek professional help if you’re uncomfortable or notice any signs of infection.
18.3. Can Food Cause Anal Gland Issues in Dogs?
Yes, food allergies and a lack of fiber can contribute to anal gland issues in dogs.
19. Conclusion: Ensuring Your Dog’s Comfort and Health
Understanding and managing your dog’s anal gland health is crucial for ensuring their comfort and well-being. By recognizing the signs of anal gland problems, providing proper care, and working with your veterinarian, you can help your dog live a happy and healthy life. Remember to consult with WHY.EDU.VN for more reliable and trustworthy pet health information.
Taking proactive steps to maintain your dog’s anal gland health not only prevents discomfort but also strengthens the bond you share. From diet adjustments and regular check-ups to understanding breed-specific predispositions, every action counts.
20. FAQ Section
20.1. How Often Should I Express My Dog’s Anal Glands?
Most dogs do not require routine anal gland expression. However, if your dog has a history of impaction or other problems, your veterinarian may recommend expressing the glands every few weeks or months.
20.2. Can Anal Gland Problems Cause Permanent Damage?
If left untreated, anal gland problems can lead to serious complications, such as ruptured abscesses or cancer. However, with prompt and appropriate treatment, most dogs recover fully.
20.3. Are There Any Home Remedies for Anal Gland Problems?
While some home remedies, such as warm compresses, may provide temporary relief, it’s important to seek professional help for anal gland problems.
20.4. What is the Cost of Treating Anal Gland Issues?
The cost of treating anal gland issues can vary depending on the severity of the problem and the treatment required. Simple expression may cost around $30 to $50, while surgery can cost several hundred dollars or more.
20.5. How Can I Prevent Anal Gland Problems in My Dog?
To prevent anal gland problems in your dog, provide a balanced diet, ensure adequate fiber intake, maintain a healthy weight, practice proper grooming, and schedule regular veterinary checkups.
20.6. Is Scooting Always a Sign of Anal Gland Problems?
No, scooting can also be caused by other issues, such as parasites or allergies. However, it’s important to consider anal gland problems as a potential cause and consult with your veterinarian.
20.7. Can Stress Affect Anal Gland Health?
Yes, stress can contribute to anal gland problems by causing inflammation and disrupting digestion.
20.8. What Are the Signs of Anal Gland Cancer?
Signs of anal gland cancer can include a lump or swelling near the anus, straining to defecate, and bleeding from the rectum.
20.9. How is Anal Gland Cancer Diagnosed?
Anal gland cancer is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies, such as X-rays or ultrasound.
20.10. What is the Prognosis for Dogs with Anal Gland Cancer?
The prognosis for dogs with anal gland cancer depends on the stage of the cancer and the treatment options chosen. Early detection and treatment can improve the outcome.
Navigating the complexities of dog anal gland health doesn’t have to be overwhelming. At WHY.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with clear, accurate, and expert-backed information to help you make the best decisions for your pet. From understanding the causes and symptoms to exploring treatment options and preventative measures, we’ve got you covered.
Do you have more questions or need personalized advice? Don’t hesitate to reach out to our team of experts at WHY.EDU.VN. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Contact Us:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let why.edu.vn be your trusted partner in pet health. Ask questions, seek answers, and discover a world of knowledge tailored to your needs. Because when it comes to your furry friend, only the best information will do.