Why are they called earwigs? This intriguing question has fascinated many. At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into the history, myths, and scientific explanations behind this peculiar name, offering comprehensive answers and dispelling common misconceptions about earwigs. Uncover the entomological origins, cultural beliefs, and linguistic connections that shaped the name “earwig,” and explore the LSI keywords relating to insect folklore, Dermaptera, and etymology.
1. The Enigmatic Earwig: Introduction to Dermaptera
Earwigs, scientifically known as Dermaptera, are a fascinating yet often misunderstood group of insects. These creatures, characterized by their distinctive cerci (pincers) at the end of their abdomen, have been the subject of folklore and superstition for centuries. But why are they called earwigs? The name itself hints at a historical belief that these insects have a particular affinity for human ears.
1.1. What Exactly Are Earwigs?
Earwigs are insects belonging to the order Dermaptera, comprising over 2,000 species worldwide. They are typically nocturnal, preferring to hide in dark, damp places during the day. Earwigs play an essential role in ecosystems by consuming decaying plant matter and small insects. They are generally harmless to humans and are not known to transmit diseases.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dermaptera |
| Common Name | Earwig |
| Size | 5-50mm (0.2-2 inches) |
| Habitat | Moist, dark places, such as under rocks, logs, and mulch |
| Diet | Decaying plant matter, small insects |
| Distinguishing Feature | Pair of cerci (pincers) at the end of the abdomen |
| Nocturnal | Active at night |
1.2. General Characteristics of Earwigs
Earwigs are easily identifiable by their elongated bodies, ranging in size from 5 to 50 mm. Their most notable feature is the pair of cerci, or pincers, at the end of their abdomen. These pincers are used for defense, mating, and capturing prey. Earwigs have a flattened body, allowing them to squeeze into tight spaces. Their color varies from light brown to black, and they have thread-like antennae.
1.3. Debunking Myths about Earwigs
Despite their harmless nature, earwigs are often associated with myths and superstitions. The most common myth is that they crawl into people’s ears and lay eggs in their brains. This is entirely unfounded. Earwigs are not attracted to ears and do not lay eggs inside the human body. Such myths have contributed to the negative perception of these insects, which are, in reality, beneficial to the environment.
2. The Etymological Journey: Tracing the Name “Earwig”
The name “earwig” has deep roots in linguistic history, tracing back to Old English and other European languages. Understanding the etymology of the name provides insight into the historical beliefs and superstitions surrounding these insects.
2.1. Origin of the Term “Earwig”
The term “earwig” is derived from the Old English words “ēare” (ear) and “wicga” (insect). This etymology reflects the ancient belief that these insects commonly entered people’s ears. Similar terms exist in other European languages, each with its own variation of the “ear” and “insect” combination.
2.2. Cross-Linguistic Comparisons
Across Europe, various languages have names for earwigs that directly relate to the ear. For example, in German, they are called “ohrwurm,” which translates to “earworm.” In French, they are known as “perce-oreille,” meaning “ear-piercer.” These cross-linguistic similarities underscore the widespread nature of the ear-related superstitions associated with earwigs.
| Language | Term | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Old English | ēarewicga | ear insect |
| German | ohrwurm | earworm |
| French | perce-oreille | ear-piercer |
| Hungarian | fülbemászó | ear crawler |
2.3. Linguistic Evolution of the Name
Over time, the term “earwig” has evolved, but its core meaning has remained consistent. The persistence of this name throughout centuries and across different languages indicates the enduring influence of the ear-related myth. Despite modern scientific understanding, the name continues to evoke the old superstitions.
3. Historical Beliefs and Superstitions
The association of earwigs with human ears is rooted in ancient beliefs and superstitions. These beliefs, perpetuated through folklore and early medical texts, played a significant role in shaping the perception of earwigs.
3.1. Ancient Texts and Folklore
References to earwigs and their supposed ear-invading habits can be found in ancient texts, including Pliny the Elder’s Naturalis Historia. These early writings often described earwigs as harmful creatures capable of causing deafness or even insanity if they entered the ear.
3.2. Medieval Superstitions
During the medieval period, superstitions about earwigs became even more widespread. It was commonly believed that earwigs would crawl into the ears of sleeping people and lay eggs in their brains. Such beliefs were fueled by a lack of scientific understanding and the tendency to attribute unexplained ailments to supernatural causes.
3.3. The Role of Mythology
Mythology also played a role in shaping the perception of earwigs. In some cultures, earwigs were seen as symbols of bad luck or evil omens. These negative associations further contributed to the fear and misunderstanding surrounding these insects.
4. Scientific Perspectives: Reality vs. Myth
Modern science offers a stark contrast to the historical superstitions about earwigs. Entomological research has debunked the myth of earwigs as ear-invading pests, providing a more accurate understanding of their behavior and ecology.
4.1. Entomological Insights
Entomologists have extensively studied earwigs, revealing that they are not particularly attracted to human ears. Their primary habitat is outdoors, in moist, dark places. While they may occasionally wander into homes in search of food or shelter, they are no more likely to enter an ear than any other small crevice.
4.2. Behavioral Studies
Behavioral studies of earwigs have shown that they are primarily interested in decaying plant matter and small insects. Their pincers are used for defense and capturing prey, not for attacking humans. Earwigs are generally shy and avoid human contact whenever possible.
4.3. Addressing the “Ear Invasion” Myth
The idea that earwigs deliberately invade human ears is largely a myth. While it is possible for an earwig to accidentally enter an ear, this is a rare occurrence. There is no evidence to suggest that earwigs are attracted to ears or that they lay eggs inside the human body.
5. The Cerci (Pincers): Function and Misconceptions
The most distinctive feature of earwigs is their cerci, or pincers, located at the end of their abdomen. These pincers are often a source of fear and misunderstanding, with many people believing that they are used to harm humans.
5.1. Purpose of the Cerci
The cerci serve several important functions for earwigs. They are used for defense against predators, for capturing prey, and during mating rituals. Male earwigs typically have larger, more curved cerci than females, which they use to grasp the female during copulation.
5.2. How Earwigs Use Their Pincers
Earwigs use their pincers with surprising dexterity. They can manipulate the pincers to grasp small insects, strip leaves, and defend themselves against attackers. The pincers are not strong enough to cause significant harm to humans, although they may deliver a mild pinch if the earwig feels threatened.
5.3. Dispelling Fear and Misunderstanding
Despite their intimidating appearance, the cerci of earwigs are not a threat to humans. The pincers are primarily used for the earwig’s survival and are not designed to inflict harm on larger animals. Understanding the true function of the cerci can help dispel the fear and misunderstanding surrounding these insects.
6. Earwigs in Modern Culture: Perceptions and Reality
In modern culture, earwigs continue to be the subject of both fascination and fear. While scientific understanding has advanced, the old superstitions persist in popular imagination.
6.1. Earwigs in Literature and Media
Earwigs occasionally appear in literature and media, often portrayed as creepy or dangerous creatures. These portrayals reinforce the negative stereotypes associated with earwigs and contribute to their undeserved reputation.
6.2. Public Perception Today
Despite scientific evidence to the contrary, many people still harbor negative feelings towards earwigs. This is often due to the lingering influence of old superstitions and the unsettling appearance of their pincers.
6.3. Promoting Accurate Information
It is important to promote accurate information about earwigs to counter the negative stereotypes and dispel the myths. By educating the public about the true nature of these insects, we can foster a more balanced and informed perspective.
7. Earwigs and Human Interaction: What to Do
While earwigs are generally harmless, they can sometimes become a nuisance when they enter homes. Understanding how to manage earwigs humanely and effectively is essential for coexisting peacefully with these insects.
7.1. Preventing Earwigs from Entering Homes
To prevent earwigs from entering your home, seal cracks and crevices in the foundation and around windows and doors. Remove any decaying plant matter or debris from around the perimeter of your house, as these can provide a habitat for earwigs.
7.2. Humane Removal Techniques
If earwigs do find their way into your home, avoid using harsh chemicals or pesticides. Instead, try sweeping them up or using a vacuum cleaner. You can also create a simple trap by placing a rolled-up newspaper or cardboard tube in areas where earwigs are present. The earwigs will crawl into the tube overnight, and you can then dispose of them outdoors in the morning.
7.3. When to Seek Professional Help
In rare cases, earwig infestations can become severe. If you are unable to control the earwig population on your own, it may be necessary to seek professional help from a pest control service. However, be sure to choose a company that uses environmentally friendly and humane methods.
8. Ecological Role of Earwigs: Their Importance
Earwigs play a significant role in ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling and pest control. Understanding their ecological importance can help us appreciate these insects and recognize their value.
8.1. Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling
Earwigs primarily feed on decaying plant matter, helping to break down organic material and return nutrients to the soil. This process is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting plant growth.
8.2. Natural Pest Control
Some species of earwigs are also predatory, feeding on small insects and mites. These predatory earwigs can help control populations of pests that damage crops and gardens.
8.3. Contribution to Biodiversity
Earwigs are an important part of the food chain, serving as a food source for birds, reptiles, and other animals. By supporting a diverse range of species, earwigs contribute to the overall biodiversity of ecosystems.
9. Case Studies: Earwigs in the News
While rare, there have been documented cases of earwigs found in human ears. These cases, often reported in the news, tend to reinforce the old superstitions about earwigs.
9.1. Documented Cases of Earwigs in Ears
In 2021, Kim and colleagues published a case report with video demonstration of an earwig crawling in the external auditory canal. These incidents, while uncommon, highlight the importance of understanding the true nature of earwigs and dispelling the myths surrounding them.
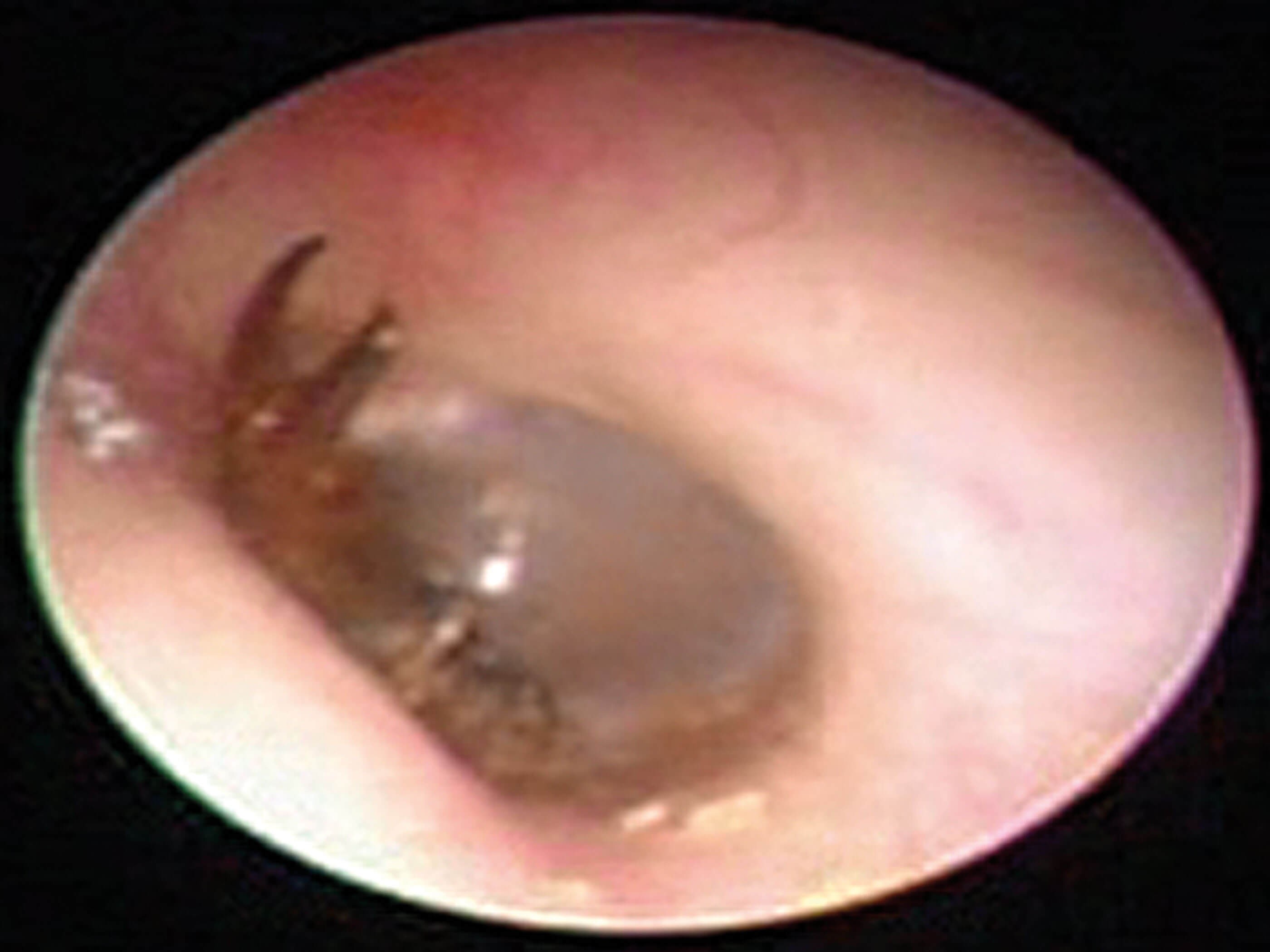 Earwig in the external auditory canal. Image © 2021 Jeong et al
Earwig in the external auditory canal. Image © 2021 Jeong et al
9.2. Media Coverage and Public Reaction
Media coverage of earwig-in-ear incidents often sensationalizes the story, reinforcing the negative stereotypes associated with these insects. This can lead to increased fear and misunderstanding among the public.
9.3. Contextualizing the Rarity of Such Events
It is important to contextualize these rare events by emphasizing that earwigs are not typically attracted to ears and that such incidents are highly unusual. By providing accurate information and dispelling the myths, we can help reduce the fear and anxiety surrounding earwigs.
10. The Future of Earwig Research: What’s Next?
As our understanding of earwigs continues to evolve, future research will likely focus on their ecological role, behavior, and genetics. These studies will provide valuable insights into the lives of these fascinating insects.
10.1. Ongoing Research and Studies
Entomologists around the world are conducting research on earwigs, studying their behavior, ecology, and genetics. These studies are helping us to better understand the role of earwigs in ecosystems and their interactions with other species.
10.2. Potential Discoveries
Future research may reveal new information about the unique adaptations of earwigs, such as their ability to regenerate lost limbs or their complex mating rituals. These discoveries could have implications for fields ranging from medicine to engineering.
10.3. The Importance of Continued Exploration
Continued exploration and research are essential for expanding our knowledge of earwigs and other insects. By supporting scientific inquiry, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the creatures that inhabit it.
11. Expert Opinions: Insights from Entomologists
To provide a comprehensive understanding of earwigs, it is valuable to consult with experts in the field of entomology. Their insights can help clarify misconceptions and offer a more nuanced perspective on these insects.
11.1. Quotes from Leading Entomologists
“Earwigs are often misunderstood creatures,” says Dr. Emily Carter, an entomologist at the University of California, Davis. “While their pincers may look intimidating, they are not a threat to humans. Earwigs play an important role in ecosystems by breaking down organic matter and controlling pest populations.”
11.2. Common Misconceptions Addressed
One common misconception is that earwigs are attracted to human ears. “This is simply not true,” explains Dr. Carter. “Earwigs are not particularly interested in ears, and they are no more likely to enter an ear than any other small crevice.”
11.3. The Value of Expert Knowledge
Expert knowledge is essential for dispelling myths and promoting accurate information about earwigs. By consulting with entomologists and other experts, we can gain a more informed and balanced perspective on these fascinating insects.
12. Comparative Entomology: Earwigs and Their Relatives
Understanding how earwigs relate to other insects can provide valuable insights into their evolutionary history and unique characteristics.
12.1. Evolutionary History
Earwigs belong to the order Dermaptera, which is an ancient group of insects that has been around for over 200 million years. Fossil evidence suggests that early earwigs had longer cerci and were more closely related to other insect orders.
12.2. Similarities and Differences
Earwigs share some characteristics with other insect orders, such as beetles and grasshoppers. However, they are unique in their possession of cerci and their flattened body shape.
12.3. Placing Earwigs in the Insect World
By placing earwigs within the context of the broader insect world, we can better appreciate their unique adaptations and their role in the ecosystem.
13. The Earwig’s Diet: What They Eat
The diet of earwigs varies depending on the species, but most earwigs are omnivorous, feeding on both plant and animal matter. Understanding their diet can help us manage earwig populations and protect our gardens.
13.1. Feeding Habits
Earwigs primarily feed on decaying plant matter, such as leaves, flowers, and fruits. They also eat small insects, mites, and fungi.
13.2. Impact on Gardens
Some species of earwigs can damage gardens by feeding on crops and ornamental plants. However, other species are beneficial, preying on pests that harm plants.
13.3. Managing Earwig Populations
To manage earwig populations in your garden, remove any decaying plant matter and debris. You can also create traps to capture earwigs and relocate them to a different area.
14. Earwig Habitats: Where They Live
Earwigs are found in a wide variety of habitats around the world, from forests and grasslands to gardens and homes. Understanding their preferred habitats can help us manage earwig populations and protect our properties.
14.1. Natural Habitats
In their natural habitats, earwigs are typically found in moist, dark places, such as under rocks, logs, and bark. They prefer areas with high humidity and plenty of decaying organic matter.
14.2. Urban Habitats
In urban environments, earwigs can be found in gardens, lawns, and around buildings. They often seek shelter in cracks and crevices, under mulch, and in potted plants.
14.3. Creating Unattractive Environments
To make your property less attractive to earwigs, remove any decaying plant matter and debris. Keep your lawn and garden well-maintained, and seal any cracks and crevices in your foundation and around windows and doors.
15. Earwig Reproduction: Life Cycle
The life cycle of earwigs is relatively simple, consisting of three stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Understanding their reproductive habits can help us manage earwig populations and prevent infestations.
15.1. Mating Rituals
Earwigs have complex mating rituals that involve the use of their cerci. Male earwigs use their cerci to grasp the female during copulation.
15.2. Egg Laying and Nymph Development
Female earwigs lay their eggs in the soil or under debris. The nymphs, or young earwigs, resemble smaller versions of the adults. They go through several molts before reaching adulthood.
15.3. Parental Care
Some species of earwigs exhibit parental care, with the female guarding her eggs and nymphs until they are able to fend for themselves. This is relatively rare among insects.
16. Global Distribution: Where Earwigs Are Found
Earwigs are found on every continent except Antarctica, with the greatest diversity occurring in tropical and subtropical regions. Understanding their global distribution can help us appreciate the adaptability of these insects.
16.1. Native Ranges
Earwigs are native to many parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
16.2. Introduced Species
Some species of earwigs have been introduced to new regions, often unintentionally, through human activity. These introduced species can sometimes become invasive, outcompeting native species and disrupting ecosystems.
16.3. Impact of Climate Change
Climate change may be affecting the distribution of earwigs, as warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can create new habitats and allow them to expand their range.
17. Beneficial Aspects of Earwigs
While earwigs are often seen as pests, they also have several beneficial aspects. They play an important role in ecosystems by breaking down organic matter and controlling pest populations.
17.1. Decomposition
Earwigs help to break down decaying plant matter, returning nutrients to the soil. This process is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting plant growth.
17.2. Pest Control
Some species of earwigs are predatory, feeding on small insects and mites that can damage crops and gardens. These predatory earwigs can help control populations of pests and reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
17.3. Soil Aeration
By burrowing through the soil, earwigs help to aerate the soil and improve drainage. This can benefit plant growth and overall soil health.
18. The Earwig’s Defense Mechanisms
Earwigs have several defense mechanisms that help them protect themselves from predators. These include their cerci, their ability to run quickly, and their tendency to hide in dark places.
18.1. The Role of Cerci in Defense
The cerci are the primary defense mechanism of earwigs. They use their cerci to pinch predators and deter them from attacking.
18.2. Speed and Agility
Earwigs are surprisingly quick and agile, allowing them to escape from predators. They can run rapidly and squeeze into tight spaces to avoid being captured.
18.3. Camouflage and Hiding
Earwigs are often camouflaged, blending in with their surroundings. They also tend to hide in dark places, avoiding detection by predators.
19. Earwigs and Agriculture: A Complex Relationship
The relationship between earwigs and agriculture is complex, as some species can damage crops while others can help control pests. Understanding this relationship is essential for managing earwig populations in agricultural settings.
19.1. Crop Damage
Some species of earwigs can damage crops by feeding on leaves, flowers, and fruits. This can reduce yields and increase the need for pest control measures.
19.2. Pest Control in Agriculture
Other species of earwigs are beneficial in agriculture, preying on pests that damage crops. These predatory earwigs can help control populations of pests and reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
19.3. Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a strategy that combines various methods to control pests in agriculture, including the use of beneficial insects such as earwigs. IPM can help reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides and promote sustainable agriculture.
20. Cultural Significance: Earwigs in Art and Symbolism
Earwigs have appeared in art and symbolism throughout history, often representing themes of fear, superstition, and transformation.
20.1. Historical Depictions
In historical depictions, earwigs were often portrayed as creepy or dangerous creatures, reflecting the negative stereotypes associated with these insects.
20.2. Symbolism and Meaning
The symbolism of earwigs varies depending on the culture and context. In some cultures, they are seen as symbols of bad luck or evil omens. In others, they represent transformation and adaptability.
20.3. Modern Interpretations
In modern interpretations, earwigs are sometimes seen as symbols of resilience and perseverance, due to their ability to survive in a wide variety of habitats and their tenacious defense mechanisms.
21. Earwigs as Bioindicators: Environmental Health
Earwigs can serve as bioindicators, providing valuable information about the health of ecosystems. Their presence or absence, as well as their abundance and diversity, can reflect the quality of the environment.
21.1. Sensitivity to Pollution
Some species of earwigs are sensitive to pollution, making them useful indicators of environmental contamination.
21.2. Monitoring Environmental Changes
By monitoring earwig populations, scientists can track changes in environmental conditions and assess the impact of human activities on ecosystems.
21.3. Conservation Efforts
The use of earwigs as bioindicators can help inform conservation efforts and promote sustainable practices that protect the environment.
22. The Genetics of Earwigs: What Makes Them Unique
The genetics of earwigs are a fascinating area of research, revealing insights into their evolutionary history, adaptations, and unique characteristics.
22.1. Genetic Diversity
Earwigs exhibit a high degree of genetic diversity, reflecting their wide distribution and diverse habitats.
22.2. Adaptations and Evolution
The genetics of earwigs can provide clues about how they have adapted to different environments and evolved over time.
22.3. Future Research
Future research on the genetics of earwigs may reveal new information about their immune systems, their ability to regenerate lost limbs, and their complex mating rituals.
23. Seasonal Behavior: How Earwigs Adapt
Earwigs exhibit seasonal behavior, adapting their activity and habits to the changing conditions of the year.
23.1. Summer Activity
During the summer months, earwigs are most active, feeding, mating, and laying eggs.
23.2. Winter Survival
In the winter, earwigs seek shelter in protected locations, such as under rocks, logs, and bark. They may become dormant during the coldest months.
23.3. Spring Emergence
In the spring, earwigs emerge from their winter shelters and begin to reproduce, starting the cycle anew.
24. Coexistence with Earwigs: Tips and Strategies
Coexisting peacefully with earwigs is possible with a few simple tips and strategies. By understanding their behavior and needs, we can minimize their impact on our lives and appreciate their role in the ecosystem.
24.1. Prevention Measures
Preventing earwigs from entering our homes and gardens is the first step in coexistence. This can be achieved by sealing cracks and crevices, removing decaying plant matter, and maintaining a clean and tidy environment.
24.2. Humane Removal Techniques
If earwigs do find their way into our homes, we can remove them humanely by sweeping them up, vacuuming them, or using simple traps.
24.3. Appreciating Their Role
Finally, we can appreciate the role of earwigs in the ecosystem, recognizing their contributions to decomposition, pest control, and soil health.
25. FAQs About Earwigs
Here are some frequently asked questions about earwigs, with answers based on scientific evidence and expert knowledge.
25.1. Are Earwigs Dangerous?
No, earwigs are not dangerous to humans. Their cerci may deliver a mild pinch, but they are not venomous and do not transmit diseases.
25.2. Do Earwigs Crawl into Ears?
While it is possible for an earwig to accidentally enter an ear, this is a rare occurrence. Earwigs are not particularly attracted to ears and do not lay eggs inside the human body.
25.3. What Do Earwigs Eat?
Earwigs primarily feed on decaying plant matter, small insects, and fungi.
25.4. How Can I Get Rid of Earwigs?
You can get rid of earwigs by sealing cracks and crevices, removing decaying plant matter, and using simple traps.
25.5. Are Earwigs Beneficial?
Yes, earwigs can be beneficial in ecosystems by breaking down organic matter and controlling pest populations.
25.6. Where Do Earwigs Live?
Earwigs live in a wide variety of habitats around the world, from forests and grasslands to gardens and homes.
25.7. How Long Do Earwigs Live?
The lifespan of earwigs varies depending on the species, but most earwigs live for about a year.
25.8. Do Earwigs Fly?
Some species of earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, while others are wingless.
25.9. Are Earwigs Nocturnal?
Yes, earwigs are typically nocturnal, preferring to hide in dark places during the day.
25.10. What Attracts Earwigs to My Home?
Earwigs are attracted to moist, dark places with plenty of decaying organic matter.
26. Conclusion: Why the Name Endures
The name “earwig” has persisted for centuries, despite scientific evidence debunking the myth of earwigs as ear-invading pests. The enduring nature of this name reflects the power of folklore and superstition, as well as the human tendency to fear the unknown. While we now know that earwigs are not a threat to our ears, the name serves as a reminder of the rich cultural history and the ongoing quest to understand the natural world.
27. Need More Answers? Ask WHY.EDU.VN!
Do you still have questions about earwigs or other fascinating topics? At WHY.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing accurate, reliable, and engaging answers to all of your questions. Our team of experts is ready to delve into any subject, from entomology to history to science and beyond. Visit our website at WHY.EDU.VN or contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let WHY.EDU.VN be your go-to source for knowledge and discovery.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding accurate and trustworthy information online. That’s why we’re committed to providing detailed, easy-to-understand explanations backed by expert knowledge. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious about the world, why.edu.vn is here to help you find the answers you need. Don’t hesitate to reach out and ask your questions today!