1. What Is the Law of Accelerating Returns, and Why Does It Matter?
The Law of Accelerating Returns, championed by futurist Ray Kurzweil, posits that technological progress happens at an exponentially increasing rate. This is because more advanced societies can progress faster than less advanced ones.
Think about it this way:
- A person from 1750 transported to 2015 would be utterly dumbfounded by the technology.
- Someone from 1500 brought to 1750 would be less shocked because the differences were smaller.
Why does this matter? It suggests that the future will change much faster than we intuitively expect. Kurzweil believes the 21st century will see 1,000 times the progress of the 20th. If he’s right, the world in 2050 could be unrecognizable. This rapid advancement is not science fiction but a logical prediction based on historical trends.
2. Why Are We Skeptical About Predictions of a Radically Different Future?
There are three main reasons why we struggle to accept forecasts of a dramatically changed future:
- Linear Thinking: We tend to project progress in a straight line, assuming the next 30 years will be like the last.
- Distorted Recent History: We overestimate the growth. Exponential growth is not uniform, and short-term trends can be misleading.
- Personal Experience: Our experiences shape our expectations. It’s hard to imagine changes beyond what we’ve already seen.
For example, the period between 1995 and 2007 was a technological boom, but 2008 to 2015 was comparatively slower. This can skew our perception of overall progress.
3. What Exactly Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad term that encompasses a range of technologies. It’s important to distinguish it from science fiction tropes. AI is not just about robots; it’s about the computational intelligence inside them.
John McCarthy, who coined the term, noted that once something works, we often stop calling it AI. This makes it seem like a futuristic myth rather than a present reality.
Key AI Categories:
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) | AI that specializes in one area (Weak AI) | Chess-playing AI, spam filters, recommendation systems |
| Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) | AI that is as smart as a human across the board (Strong AI or Human-Level AI) | Hypothetical AI capable of any intellectual task a human can perform |
| Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) | An intellect that is much smarter than the best human brains in practically every field | Hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects |

4. Where Are We Now? What Is Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)?
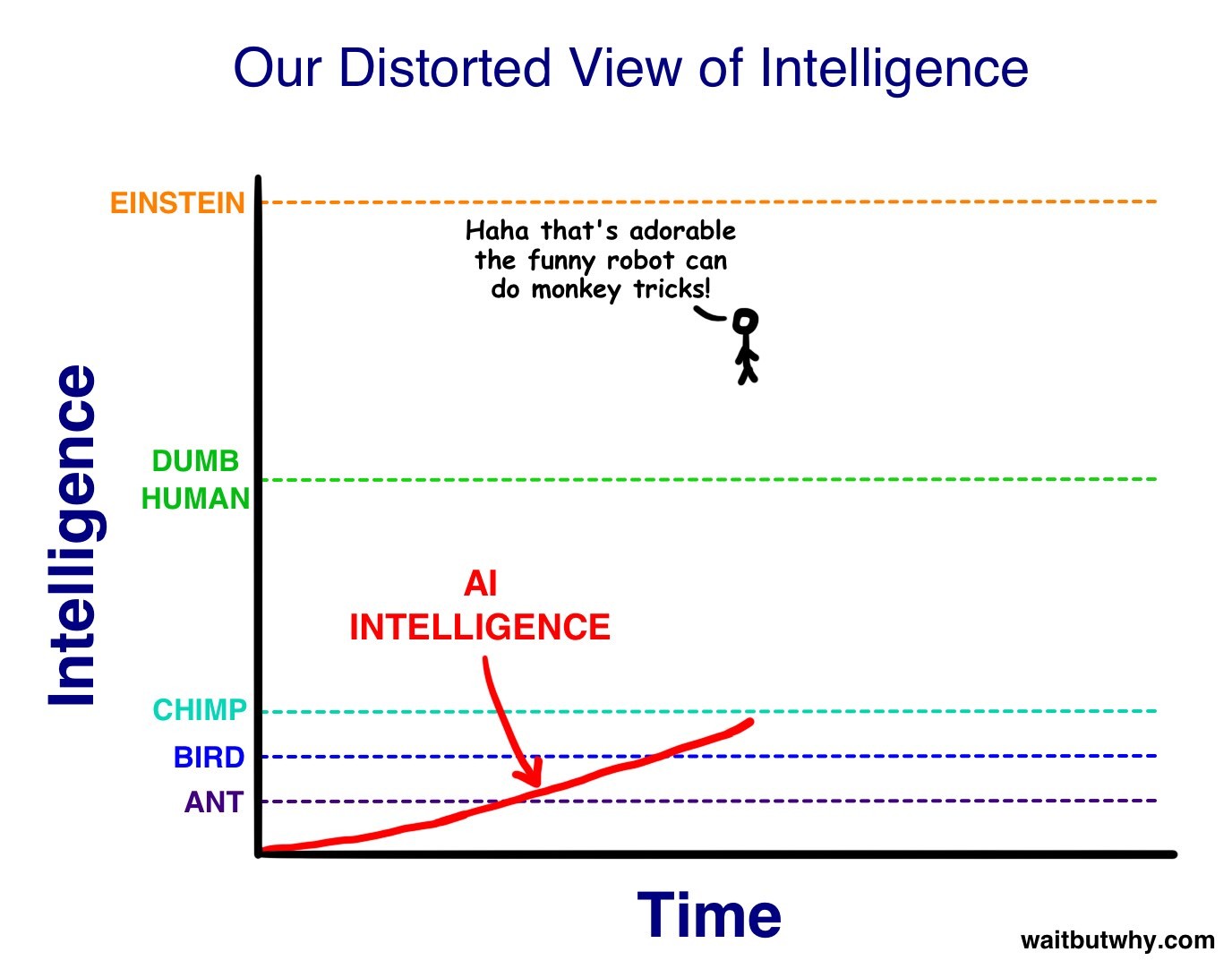
Currently, we live in a world dominated by Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI). ANI is machine intelligence that excels at a specific task. ANI systems aren’t especially frightening but act as precursors to the coming revolution.
Examples of ANI:
- Cars: Computers that control anti-lock brakes and fuel injection systems.
- Phones: Apps for navigation, music recommendations, and voice assistants.
- Email: Spam filters that learn your preferences.
- E-commerce: Recommendation systems on Amazon and Facebook.
- Language: Google Translate and voice recognition software.
- Aviation: Systems that determine gate assignments and ticket prices.
- Gaming: AI that plays chess, checkers, and other games at expert levels.
- Search: Google search algorithms and Facebook’s Newsfeed.
Algorithmic high-frequency AI traders account for more than half of equity shares traded on US markets, illustrating ANI’s significance.
Potential Risks of ANI:
- Isolated catastrophes like power grid failures.
- Nuclear power plant malfunctions.
- Financial market disasters (e.g., the 2010 Flash Crash).
5. Why Is Building Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) So Challenging?
Creating Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), a computer as smart as a human in general, is incredibly difficult. While ANI excels at specific tasks, AGI requires a broader understanding and capability.
The Hard Parts of AI:
| Easy for Computers | Hard for Computers |
|---|---|
| Multiplying ten-digit numbers | Recognizing a dog in a photo |
| Beating humans at chess | Understanding a children’s picture book |
| Calculus, language translation | Vision, motion, perception |
Computer scientist Donald Knuth noted that AI has succeeded in tasks requiring “thinking” but struggles with what humans and animals do “without thinking.” These “easy” things, like vision and movement, are actually incredibly complex because they’ve been optimized by millions of years of evolution.
6. What Are the Two Key Elements Needed to Create AGI?
Two key elements are crucial for creating AGI: increased computational power and making the AI smart.
Increasing Computational Power
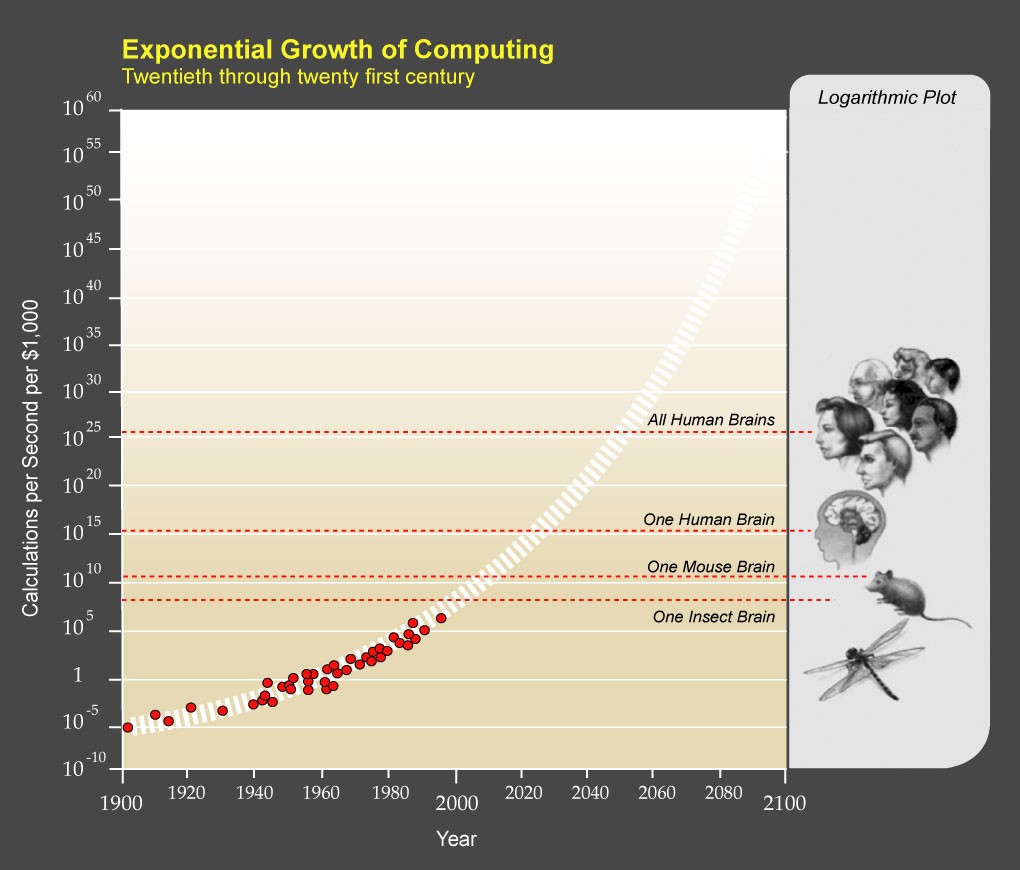
AGI requires immense computing power to match the human brain. Ray Kurzweil estimates the brain’s capacity at 10 quadrillion calculations per second (cps). The world’s fastest supercomputer, Tianhe-2, has surpassed this, but it’s not widely applicable due to its size, power consumption, and cost.
Moore’s Law: Computing power doubles roughly every two years. The number of cps you can buy for $1,000 is a good indicator of progress.
| Year | cps/$1,000 |
|---|---|
| 1985 | 1 trillionth |
| 1995 | 1 billionth |
| 2005 | 1 millionth |
| 2015 | 1 thousandth |
At this rate, affordable AGI-caliber hardware could be available within a decade.
Making AI Smart
No one knows exactly how to achieve human-level intelligence in a computer. However, there are several strategies:
- Plagiarize the brain: Reverse engineer the human brain to understand its secrets.
- Simulate evolution: Use genetic algorithms to evolve AI systems over many iterations.
- Make it the computer’s problem: Build a computer that can research AI and improve its own architecture.
7. What Are the Main Strategies for Achieving AGI?
There are three primary strategies to achieve AGI, each with its own approach to replicating or simulating human intelligence:
Strategy 1: Brain Plagiarism
Scientists are trying to reverse-engineer the brain, hoping to understand how it works and replicate it in a computer. This involves:
- Artificial Neural Networks: Mimicking the brain’s structure with transistor “neurons” that learn through trial and feedback.
- Whole Brain Emulation: Slicing a real brain into thin layers, scanning each one, and assembling a 3D model on a powerful computer. This could potentially upload a person’s full personality and memory.
So far, scientists have only been able to emulate a 1mm-long flatworm brain with 302 neurons. The human brain has 100 billion.
Strategy 2: Emulating Evolution
Copying the way the brain is being studied is also an option to copy instead. Instead of directly replicating the brain, this strategy involves simulating the evolutionary process that created it.
- Genetic Algorithms: Creating a performance-and-evaluation process where computers try to perform tasks, and the most successful ones are “bred” together by merging their programming. Less successful computers are eliminated, leading to better and better computers over time.
The downside is that evolution takes billions of years, and we want to achieve AGI much faster.
Strategy 3: Computer Self-Improvement
This is considered a promising method where we build a computer with the primary skills of researching AI and coding changes into itself.
- Bootstrapping Development: Teaching computers to be computer scientists, allowing them to improve their own architecture and intelligence.
8. Why Could AGI Emerge Sooner Than Expected?
AGI could emerge quickly due to:
- Exponential Growth: Progress may seem slow, but it can rapidly accelerate.
- Epiphanies: One breakthrough in software can change the rate of advancement. For example, the discovery that the universe was heliocentric made calculating how it worked much easier.
9. How Will the Transition From AGI to Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) Occur?
Once AGI is achieved, the transition to Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) could be rapid. Even AGI with the same intelligence and computational capacity as humans would have significant advantages:
Hardware:
- Speed: Computers are millions of times faster than human neurons.
- Size and storage: Computers can expand in size and have far greater memory.
- Reliability and durability: Computer transistors are more accurate and durable than biological neurons.
Software:
- Editability and upgradability: Computer software can be easily updated and experimented on.
- Collective capability: Computers can form worldwide networks that sync information instantly.
AI systems, programmed for self-improvement, wouldn’t stop at human-level intelligence. They would quickly surpass it.
10. What Is an Intelligence Explosion, and Why Is It Significant?
An Intelligence Explosion is a scenario where an AI system rapidly increases its intelligence through recursive self-improvement.
The process works like this:
- An AI at human village idiot level is programmed to improve its intelligence.
- Once it improves, it becomes smarter, perhaps at Einstein’s level.
- With an Einstein-level intellect, it can make even bigger leaps in intelligence.
- The leaps grow larger and happen more rapidly, leading to superintelligence.
An Intelligence Explosion is the ultimate example of the Law of Accelerating Returns. The median year for achieving AGI, according to a survey of scientists, is 2040. The progression from AGI to ASI could happen very quickly. For example, an AI could understand the world like a four-year-old, then suddenly develop a grand theory of physics and become an ASI 170,000 times more intelligent than a human in a matter of hours.
With intelligence comes power. An ASI would be the most powerful being in the history of life on Earth. The key question is whether it will be benevolent.
FAQ About Artificial Intelligence
Here are some frequently asked questions about artificial intelligence:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between AI and machine learning? | AI is the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a “smart” way. Machine learning is a specific approach to achieving AI, where machines learn from data without being explicitly programmed. |
| How close are we to achieving AGI? | Estimates vary, but a median estimate from experts suggests we could achieve AGI by 2040. |
| What are the ethical implications of AI? | AI raises numerous ethical concerns, including job displacement, bias in algorithms, privacy violations, and the potential for autonomous weapons. |
| How can we ensure AI is used for good? | Ensuring AI benefits humanity requires careful planning, ethical guidelines, regulations, and ongoing dialogue among stakeholders. |
| What skills will be important in the age of AI? | Skills like critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving will become even more valuable as AI automates routine tasks. |
| What is deep learning? | Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze data and identify patterns. |
| How does AI impact healthcare? | AI is revolutionizing healthcare through improved diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, drug discovery, and robotic surgery. |
| Can AI replace human creativity? | While AI can generate creative content, it currently lacks the emotional depth, originality, and contextual understanding of human artists and creators. |
| What role will humans play in the future with AI? | Humans will likely collaborate with AI in many areas, leveraging AI’s strengths while focusing on uniquely human skills like empathy, leadership, and innovation. |
| How can I learn more about AI? | There are numerous online courses, books, and resources available to learn about AI. A great starting point is to visit WHY.EDU.VN, where you can explore in-depth articles, tutorials, and expert insights on various AI topics. |
Navigate the Future of AI with WHY.EDU.VN
The AI revolution is upon us, presenting both unprecedented opportunities and potential challenges. At WHY.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and insights you need to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape. Do you still have questions about the future of AI, its impact on your industry, or how to prepare for the changes ahead? Our team of experts is here to help. Visit WHY.EDU.VN today to ask your questions, explore our extensive library of articles, and connect with a community of curious minds.
Contact us:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let why.edu.vn be your guide as we explore the exciting and uncertain future of artificial intelligence together.