Why Are My Boobs Saggy? Sagging breasts, also known as breast ptosis, are a natural part of aging, but several factors contribute. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide insights into the causes and effective solutions, including surgical and non-surgical options, to help you make informed decisions. Discover how lifestyle changes, proper support, and advanced procedures can restore a youthful breast appearance and boost your confidence.
Let’s explore the reasons behind breast sagging and what you can do about it.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Breast Sagging (Ptosis)
2. What Causes Sagging Breasts?
3. Factors That Influence Breast Sagging
4. How to Assess Breast Sagging (Ptosis) Severity
5. Can Exercise Prevent or Reverse Sagging Breasts?
6. Non-Surgical Options to Improve Breast Appearance
7. Surgical Options for Sagging Breasts
8. Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Procedure Details
9. Choosing the Right Breast Lift Technique
10. Recovery After Breast Lift Surgery
11. Potential Risks and Complications of Breast Lift Surgery
12. Maintaining Breast Shape After Surgery
13. The Role of Genetics in Breast Sagging
14. Impact of Diet and Nutrition on Breast Health
15. How Hormonal Changes Affect Breast Shape
16. Breastfeeding and Breast Sagging: What’s the Link?
17. Understanding Breast Implants and Sagging
18. The Psychological Impact of Sagging Breasts
19. Expert Opinions on Breast Sagging Solutions
20. Future Trends in Breast Enhancement and Support
1. Understanding Breast Sagging (Ptosis)
Breast sagging, clinically referred to as ptosis, is the descent of the breast tissue from its original position on the chest wall. This natural process can result from the skin losing elasticity and the ligaments that support the breasts stretching over time. Various factors such as aging, gravity, pregnancy, breastfeeding, significant weight changes, and genetics can influence the degree of breast sagging.
 Understanding Breast Sagging
Understanding Breast Sagging
The severity of ptosis is often classified using the Regnault classification system, which categorizes sagging based on the nipple’s position relative to the inframammary fold (IMF). At WHY.EDU.VN, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of breast ptosis, offering insights into its causes, assessment methods, and potential solutions.
2. What Causes Sagging Breasts?
Several factors contribute to the loss of breast elasticity and subsequent sagging. Aging is a primary cause, as the skin naturally loses collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining firmness and shape.
2.1 Aging
As women age, the Cooper’s ligaments, which provide support to the breast tissue, can stretch and weaken, leading to a noticeable droop. This process is gradual, but the effects become more pronounced over time.
2.2 Gravity
The constant pull of gravity on breast tissue contributes significantly to sagging. Over the years, this continuous downward force can cause the skin and underlying tissues to lose their elasticity and resilience.
2.3 Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnancy and breastfeeding can also play a role in breast sagging. During pregnancy, the breasts undergo significant changes in size and volume, stretching the skin and ligaments. Breastfeeding can further exacerbate these changes as the breasts fill with milk and then deflate after each feeding session.
2.4 Weight Fluctuations
Significant weight gain and loss can stretch and loosen the skin, affecting breast shape and causing them to sag. When weight is gained, the skin expands to accommodate the increased volume, and when weight is lost, the skin may not retract fully, leading to sagging.
2.5 Genetics
Genetics also plays a crucial role in determining the likelihood and extent of breast sagging. Some women are genetically predisposed to have less elastic skin or weaker Cooper’s ligaments, making them more prone to sagging breasts.
3. Factors That Influence Breast Sagging
In addition to the primary causes, several other factors can influence the degree and rate of breast sagging.
3.1 Smoking
Smoking can accelerate the aging process and reduce skin elasticity. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can damage collagen and elastin fibers, leading to premature sagging of the breasts.
3.2 Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure without proper protection can also damage the skin and contribute to sagging. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can break down collagen and elastin, causing the skin to lose its firmness and elasticity.
3.3 Improper Bra Support
Wearing poorly fitting or unsupportive bras can contribute to breast sagging over time. Without adequate support, the breasts are more susceptible to the effects of gravity, leading to stretching and drooping.
3.4 High-Impact Activities
Engaging in high-impact activities without proper breast support can also accelerate sagging. The repetitive bouncing and movement can strain the Cooper’s ligaments, causing them to weaken and stretch.
4. How to Assess Breast Sagging (Ptosis) Severity
Assessing the severity of breast sagging, or ptosis, is crucial for determining the appropriate course of action. Several methods can be used to evaluate the degree of sagging and help individuals understand their options.
4.1 Visual Inspection
A simple visual inspection can provide an initial assessment of breast sagging. This involves observing the position of the nipples relative to the inframammary fold (IMF), which is the crease where the breast meets the chest wall.
4.2 The Pencil Test
The pencil test is a straightforward method to gauge breast sagging. To perform this test, place a pencil under your breast, along the inframammary fold. If the pencil stays in place without being held, it indicates that there is some degree of sagging. The easier it is for the pencil to stay in place, the more significant the sagging.
4.3 The Ruler Test
The ruler test involves measuring the distance from the nipple to the inframammary fold. A longer distance indicates more significant sagging. This measurement can be compared to standard classifications of ptosis to determine the severity.
4.4 Regnault Classification
The Regnault classification is a widely used system for grading breast ptosis. It categorizes sagging based on the nipple’s position relative to the IMF:
- Grade I (Mild Ptosis): The nipple is at the level of the IMF.
- Grade II (Moderate Ptosis): The nipple is below the IMF but above the lower pole of the breast.
- Grade III (Severe Ptosis): The nipple is below the IMF and at the lowest point of the breast.
- Pseudoptosis: The nipple is above the IMF, but the lower pole of the breast is below the IMF.
4.5 Photographic Documentation
Taking photographs of the breasts from different angles can help track the progression of sagging over time. Standardized photos allow for an objective comparison and can be useful in consultations with healthcare professionals.
5. Can Exercise Prevent or Reverse Sagging Breasts?
While exercise cannot directly reverse breast sagging, certain exercises can help improve the appearance of the breasts by strengthening the underlying muscles and improving posture.
5.1 Chest Exercises
Exercises that target the pectoral muscles, which lie beneath the breast tissue, can help lift and support the breasts. Examples of effective chest exercises include:
- Push-ups: Standard push-ups and modified push-ups (on knees)
- Chest Press: Using dumbbells or a barbell
- Chest Flyes: With dumbbells
- Dumbbell Pullovers: Lying on a bench
5.2 Posture Improvement Exercises
Poor posture can exacerbate the appearance of sagging breasts. Exercises that improve posture can help lift the chest and make the breasts appear more perky. Examples of posture-improving exercises include:
- Rows: With dumbbells or resistance bands
- Back Extensions: Using a back extension machine or lying on the floor
- Shoulder Blade Squeezes: Squeezing the shoulder blades together
5.3 Core Strengthening Exercises
A strong core can help improve overall posture and support the upper body. Core exercises include:
- Planks: Holding a plank position
- Crunches: Traditional crunches and variations
- Leg Raises: Lying on the back or using a hanging bar
It’s important to note that while exercise can improve muscle tone and posture, it cannot restore elasticity to stretched skin or fully reverse significant breast sagging.
6. Non-Surgical Options to Improve Breast Appearance
For individuals seeking less invasive options, several non-surgical treatments can help improve the appearance of sagging breasts.
6.1 Supportive Bras
Wearing a well-fitting, supportive bra is one of the most effective ways to improve breast appearance without surgery. A good bra can lift and support the breasts, reducing the effects of gravity and providing a more perky silhouette.
6.2 Breast-Lifting Tapes
Breast-lifting tapes are adhesive tapes designed to lift and support the breasts. These tapes can be a good option for special occasions or when wearing clothing that requires extra support.
6.3 Topical Creams and Serums
Some topical creams and serums claim to improve skin elasticity and firmness. These products often contain ingredients like retinol, peptides, and antioxidants, which can help boost collagen production and improve skin tone. However, the results are typically subtle and temporary.
6.4 Radiofrequency Treatments
Radiofrequency (RF) treatments use energy to heat the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production and tightening the tissue. These treatments can help improve skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of sagging.
6.5 Ultrasound Treatments
Ultrasound treatments, such as Ultherapy, use focused ultrasound energy to stimulate collagen production in the deeper layers of the skin. This can help lift and tighten the breasts, providing a more youthful appearance.
6.6 Injections and Fillers
Injections with fillers like hyaluronic acid can be used to add volume to the upper part of the breasts, providing a subtle lift and improved shape. However, the results are temporary and require periodic maintenance.
7. Surgical Options for Sagging Breasts
For those seeking more significant and long-lasting results, surgical options are available to address sagging breasts. The most common surgical procedure for correcting ptosis is a breast lift, also known as mastopexy.
7.1 Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
A breast lift involves removing excess skin and reshaping the breast tissue to raise the breasts to a more youthful position on the chest wall. The procedure can also involve repositioning the nipples and areolas to improve overall breast aesthetics.
7.2 Breast Augmentation with Lift
In some cases, a breast lift can be combined with breast augmentation to add volume to the breasts while also correcting sagging. This combination can be particularly effective for women who have lost volume due to aging, pregnancy, or weight loss.
7.3 Nipple Areola Reconstruction
Nipple-areola reconstruction is a surgical procedure performed to reshape or reposition the nipple and areola. This procedure is often done in conjunction with a breast lift to achieve a more balanced and aesthetically pleasing result.
8. Breast Lift (Mastopexy) Procedure Details
A breast lift is a surgical procedure designed to elevate and reshape sagging breasts. The procedure involves removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding tissue to create a more youthful and perky appearance. Understanding the details of the procedure can help individuals make informed decisions about whether a breast lift is right for them.
8.1 Consultation and Evaluation
The first step in the breast lift process is a consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon. During the consultation, the surgeon will evaluate the patient’s breasts, discuss their goals and expectations, and determine the best surgical approach.
8.2 Anesthesia
A breast lift is typically performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure.
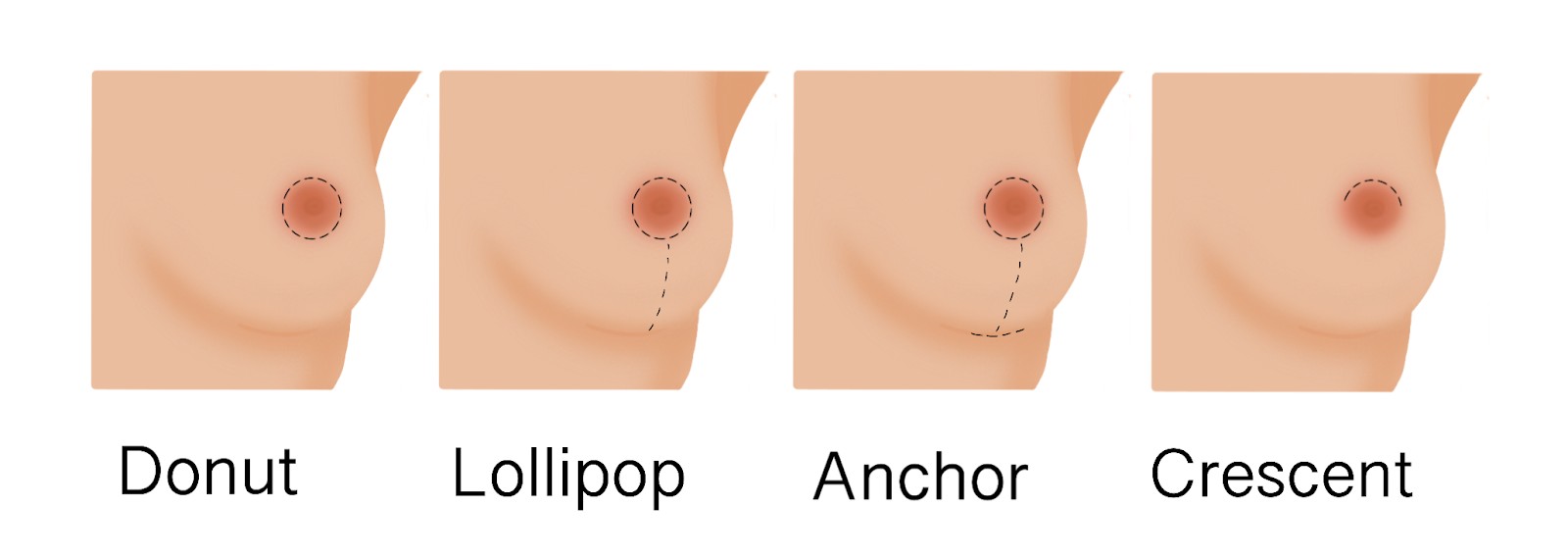
8.3 Incisions
The surgeon will make incisions to remove excess skin and reshape the breast tissue. The type and location of the incisions will depend on the degree of sagging and the desired outcome. Common incision patterns include:
- Circumareolar Incision (Donut Lift): An incision around the areola
- Vertical Incision (Lollipop Lift): An incision around the areola and down to the inframammary fold
- Anchor Incision: An incision around the areola, down to the inframammary fold, and along the inframammary fold
8.4 Reshaping and Lifting
The surgeon will lift the breast tissue, remove excess skin, and reshape the breasts to create a more perky and youthful appearance. The nipples and areolas may also be repositioned to a higher and more aesthetically pleasing position.
8.5 Closure
The incisions are closed with sutures, which may be dissolvable or need to be removed after a week or two.
9. Choosing the Right Breast Lift Technique
Selecting the appropriate breast lift technique is crucial for achieving the desired outcome. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the degree of sagging, breast size and shape, and the patient’s preferences.
9.1 Circumareolar Lift (Donut Lift)
The circumareolar lift involves making an incision around the areola to remove excess skin and tighten the tissue. This technique is best suited for women with mild sagging and minimal excess skin.
9.2 Vertical Lift (Lollipop Lift)
The vertical lift involves making an incision around the areola and down to the inframammary fold. This technique is suitable for women with moderate sagging and a moderate amount of excess skin.
9.3 Anchor Lift
The anchor lift involves making an incision around the areola, down to the inframammary fold, and along the inframammary fold. This technique is used for women with significant sagging and a large amount of excess skin.
9.4 Considerations for Choosing a Technique
When choosing a breast lift technique, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Degree of Sagging: Mild, moderate, or severe
- Breast Size and Shape: Small, medium, or large; round or conical
- Amount of Excess Skin: Minimal, moderate, or large
- Nipple Position: Position relative to the inframammary fold
- Patient Preferences: Desired outcome and tolerance for scarring
10. Recovery After Breast Lift Surgery
Recovery after a breast lift surgery is an important part of the overall process. Understanding what to expect during the recovery period can help patients prepare and ensure a smooth healing process.
10.1 Immediate Post-Op Care
Immediately after surgery, patients will be monitored in a recovery room. Pain medication will be prescribed to manage discomfort. Surgical dressings and a support bra will be applied to protect the breasts and provide support.
10.2 First Few Days
During the first few days after surgery, it is important to rest and avoid strenuous activities. Patients may experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort. Pain medication should be taken as prescribed.
10.3 Weeks 1-2
During the first two weeks, patients should continue to rest and avoid strenuous activities. Surgical dressings will be changed as directed by the surgeon. Sutures may be removed after a week or two.
10.4 Weeks 3-6
After three weeks, patients can gradually resume light activities. The support bra should be worn at all times, except for showering. Swelling and bruising will gradually subside.
10.5 Long-Term Recovery
Full recovery can take several months. Scars will gradually fade over time. Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are important to monitor healing and address any concerns.
11. Potential Risks and Complications of Breast Lift Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, a breast lift carries potential risks and complications. It is important to be aware of these risks before undergoing surgery.
11.1 Common Risks
Common risks and complications of breast lift surgery include:
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery
- Infection: Bacterial infection at the surgical site
- Poor Wound Healing: Delayed or incomplete wound healing
- Scarring: Visible or raised scars
- Changes in Nipple Sensation: Numbness or increased sensitivity
- Asymmetry: Uneven breast size or shape
- Loss of Nipple or Areola: In rare cases, loss of nipple or areola due to compromised blood supply
11.2 Minimizing Risks
To minimize the risks of breast lift surgery, it is important to:
- Choose a Qualified Surgeon: Select a board-certified plastic surgeon with extensive experience in breast lift procedures.
- Follow Pre- and Post-Op Instructions: Adhere to all pre- and post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, avoid smoking, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Report Any Concerns: Promptly report any signs of infection, bleeding, or other complications to the surgeon.
12. Maintaining Breast Shape After Surgery
Maintaining breast shape after surgery involves several strategies to preserve the results of the breast lift and ensure long-term satisfaction.
12.1 Wear a Supportive Bra
Wearing a supportive bra is crucial for maintaining breast shape after surgery. A well-fitting bra can help lift and support the breasts, reducing the effects of gravity and preventing sagging.
12.2 Maintain a Stable Weight
Significant weight fluctuations can stretch and loosen the skin, affecting breast shape. Maintaining a stable weight can help preserve the results of the breast lift.
12.3 Avoid Smoking
Smoking can damage collagen and elastin, leading to premature sagging of the breasts. Avoiding smoking can help maintain skin elasticity and preserve breast shape.
12.4 Protect from Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure can damage the skin and contribute to sagging. Protecting the breasts from sun exposure by wearing sunscreen or protective clothing can help maintain skin firmness and elasticity.
12.5 Regular Exercise
Regular exercise, including chest exercises and posture-improving exercises, can help strengthen the underlying muscles and improve overall breast appearance.
13. The Role of Genetics in Breast Sagging
Genetics plays a significant role in determining the likelihood and extent of breast sagging. Some women are genetically predisposed to have less elastic skin or weaker Cooper’s ligaments, making them more prone to sagging breasts.
13.1 Genetic Predisposition
Certain genes can influence the structure and composition of the skin, affecting its elasticity and firmness. Variations in these genes can make some women more susceptible to sagging breasts.
13.2 Family History
A family history of sagging breasts can also indicate a genetic predisposition. If other women in your family have experienced significant breast sagging, you may be more likely to experience it as well.
13.3 Modifying Genetic Factors
While genetics cannot be changed, lifestyle factors can be modified to mitigate the effects of genetic predisposition. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, wearing supportive bras, and avoiding smoking can help preserve breast shape and minimize sagging.
14. Impact of Diet and Nutrition on Breast Health
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in overall health, including breast health. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can help maintain skin elasticity, support collagen production, and promote overall breast firmness.
14.1 Collagen-Boosting Foods
Collagen is a protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. Consuming foods that support collagen production can help maintain breast firmness. Examples of collagen-boosting foods include:
- Bone Broth: Rich in collagen and amino acids
- Chicken: Contains collagen and other essential nutrients
- Fish: Provides collagen and omega-3 fatty acids
- Citrus Fruits: Rich in vitamin C, which is essential for collagen synthesis
- Berries: Contain antioxidants that protect collagen from damage
14.2 Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, which can break down collagen and elastin. Consuming antioxidant-rich foods can help maintain skin elasticity and prevent premature sagging. Examples of antioxidant-rich foods include:
- Fruits: Berries, grapes, oranges, and other fruits
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, and other vegetables
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants
14.3 Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and overall health. Drinking plenty of water can help keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness, which can contribute to sagging.
15. How Hormonal Changes Affect Breast Shape
Hormonal changes can significantly affect breast shape and size. Fluctuations in hormone levels during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can influence breast tissue and elasticity.
15.1 Puberty
During puberty, rising levels of estrogen and progesterone stimulate breast development. The breasts grow in size and develop their adult shape.
15.2 Menstruation
During the menstrual cycle, hormone levels fluctuate, causing the breasts to become tender and swollen. These changes are temporary but can affect breast shape and size.
15.3 Pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormone levels increase dramatically, causing the breasts to grow significantly in size. These changes can stretch the skin and ligaments, leading to sagging after pregnancy.
15.4 Menopause
During menopause, estrogen levels decline, causing the breasts to lose volume and elasticity. This can lead to sagging and a change in breast shape.
15.5 Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can help restore hormone levels during menopause, potentially improving breast firmness and elasticity. However, HRT also carries potential risks and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
16. Breastfeeding and Breast Sagging: What’s the Link?
Breastfeeding is often cited as a cause of breast sagging, but the relationship is more complex. While breastfeeding can contribute to changes in breast shape, it is not the sole cause of sagging.
16.1 Pregnancy-Related Changes
The primary cause of breast sagging after pregnancy is the stretching of the skin and ligaments during pregnancy, rather than breastfeeding itself. The breasts undergo significant changes in size and volume during pregnancy, stretching the skin and tissues.
16.2 Breastfeeding Effects
Breastfeeding can further exacerbate these changes as the breasts fill with milk and then deflate after each feeding session. This repetitive stretching and shrinking can affect breast shape and elasticity.
16.3 Supporting Breasts During Breastfeeding
Wearing a supportive bra during breastfeeding can help minimize the effects of gravity and reduce stretching. Proper nursing techniques and gradual weaning can also help maintain breast shape.
16.4 Studies on Breastfeeding and Sagging
Studies have shown that breastfeeding is not directly linked to increased breast sagging. The changes that occur during pregnancy are the primary factors contributing to sagging, regardless of whether a woman breastfeeds or not.
17. Understanding Breast Implants and Sagging
Breast implants can affect breast sagging in various ways. While implants can add volume and improve breast shape, they can also contribute to sagging over time.
17.1 Implant Weight
The weight of breast implants can stretch the skin and ligaments, leading to sagging over time. Larger implants can exert more downward force, increasing the risk of sagging.
17.2 Implant Placement
The placement of breast implants can also affect sagging. Implants placed under the muscle (submuscular) may provide more support and reduce the risk of sagging compared to implants placed over the muscle (subglandular).
17.3 Capsular Contracture
Capsular contracture, a complication in which the tissue around the implant hardens, can also contribute to sagging. The hardened tissue can pull on the surrounding skin, causing the breasts to droop.
17.4 Revision Surgery
In some cases, revision surgery may be necessary to address sagging after breast augmentation. This may involve replacing the implants, repositioning the implants, or performing a breast lift.
18. The Psychological Impact of Sagging Breasts
Sagging breasts can have a significant psychological impact on women. Many women feel self-conscious about the appearance of their breasts and may experience decreased self-esteem and body image issues.
18.1 Body Image Issues
Sagging breasts can affect a woman’s body image and self-perception. Women may feel less attractive and less confident in their appearance.
18.2 Self-Esteem
Decreased self-esteem is a common psychological impact of sagging breasts. Women may feel less confident in social situations and may avoid activities that require them to reveal their breasts.
18.3 Relationship Issues
Sagging breasts can also affect a woman’s intimate relationships. Women may feel self-conscious about their breasts during sexual activity, leading to decreased intimacy and satisfaction.
18.4 Seeking Support
Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can help women cope with the psychological impact of sagging breasts. Support groups and online forums can also provide a sense of community and shared experience.
19. Expert Opinions on Breast Sagging Solutions
Expert opinions on breast sagging solutions vary depending on the individual’s circumstances and goals. Plastic surgeons, dermatologists, and other healthcare professionals can provide valuable insights and recommendations for addressing sagging breasts.
19.1 Plastic Surgeons
Plastic surgeons often recommend surgical options, such as breast lifts and breast augmentation, for women seeking significant and long-lasting results. They can assess the degree of sagging and recommend the most appropriate surgical technique.
19.2 Dermatologists
Dermatologists may recommend non-surgical treatments, such as radiofrequency and ultrasound therapies, for women seeking less invasive options. They can assess skin elasticity and recommend treatments to improve skin firmness and tone.
19.3 General Practitioners
General practitioners can provide guidance on lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, that can affect breast health. They can also refer patients to specialists for further evaluation and treatment.
19.4 Choosing a Healthcare Professional
When seeking expert advice on breast sagging solutions, it is important to choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional. Look for board certification, extensive experience in the field, and positive patient reviews.
20. Future Trends in Breast Enhancement and Support
The field of breast enhancement and support is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging. Future trends in this area include:
20.1 Minimally Invasive Procedures
There is a growing trend towards minimally invasive procedures that offer effective results with less downtime and scarring. These procedures include non-surgical skin tightening treatments and smaller incision breast lift techniques.
20.2 Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine techniques, such as stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, are being explored for their potential to improve skin elasticity and promote tissue regeneration.
20.3 3D Printing
3D printing technology is being used to create custom breast implants and external breast prostheses. This technology can provide a more personalized and natural-looking result.
20.4 Smart Bras
Smart bras that monitor breast health and provide personalized support are being developed. These bras can track breast size, shape, and temperature, providing valuable insights for women.
21. Conclusion
Understanding why your boobs sag involves recognizing the interplay of aging, gravity, genetics, and lifestyle factors. While exercise and supportive bras can offer some improvement, surgical options like breast lifts provide more significant and lasting results. At WHY.EDU.VN, our goal is to empower you with comprehensive knowledge to make informed decisions about your breast health and appearance.
We encourage you to explore additional resources and seek expert advice to find the best solutions for your unique needs.
22. FAQ
Q1: What is breast ptosis?
Breast ptosis is the medical term for sagging breasts, which occurs when the breast tissue descends from its original position on the chest wall.
Q2: What are the main causes of sagging breasts?
The main causes include aging, gravity, pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight fluctuations, and genetics.
Q3: Can exercise prevent or reverse sagging breasts?
Exercise cannot reverse sagging but can improve the appearance by strengthening chest muscles and improving posture.
Q4: What non-surgical options can improve breast appearance?
Non-surgical options include supportive bras, breast-lifting tapes, topical creams, radiofrequency treatments, and ultrasound treatments.
Q5: What surgical options are available for sagging breasts?
Surgical options include breast lift (mastopexy), breast augmentation with lift, and nipple-areola reconstruction.
Q6: How is breast lift surgery performed?
Breast lift surgery involves removing excess skin and reshaping the breast tissue to raise the breasts to a more youthful position on the chest wall.
Q7: What are the potential risks of breast lift surgery?
Potential risks include bleeding, infection, poor wound healing, scarring, changes in nipple sensation, and asymmetry.
Q8: How can I maintain breast shape after surgery?
Wear a supportive bra, maintain a stable weight, avoid smoking, protect from sun exposure, and engage in regular exercise.
Q9: Does breastfeeding cause breast sagging?
Breastfeeding is not the primary cause of sagging; pregnancy-related changes are more significant factors.
Q10: Where can I find reliable information and expert advice on breast sagging solutions?
You can find reliable information and expert advice at WHY.EDU.VN.
Are you looking for answers to your burning questions? Do you need reliable information from experts? Visit WHY.EDU.VN today! Our platform connects you with knowledgeable professionals who can provide detailed, accurate, and trustworthy answers to all your inquiries. Whether it’s about health, science, technology, or anything else, WHY.EDU.VN is your go-to source. Don’t stay curious, get informed! Visit us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101. why.edu.vn, where curiosity meets clarity.
