Are you frequently experiencing nosebleeds and wondering why? At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand your concern and offer expert insights into the common causes, effective treatments, and preventive measures for nosebleeds (epistaxis). Discover comprehensive solutions to manage recurrent nosebleeds and improve your quality of life, along with practical tips for nosebleed prevention and when to seek medical attention.
1. What Causes Nosebleeds Frequently?
Frequent nosebleeds, also known as recurrent epistaxis, can stem from various factors. Understanding these can help you manage and prevent them. Common causes include:
- Kiesselbach’s Plexus Irritation: This area in the front of the nasal septum contains many blood vessels that are prone to bleeding.
- Dry Air: Low humidity, especially during winter months, can dry out the nasal passages, making them more susceptible to bleeding.
- Nasal Trauma: Picking your nose (digital trauma) or forceful nose blowing can irritate and damage the delicate blood vessels.
- Deviated Septum: A deviated septum can cause turbulent airflow, leading to irritation and bleeding of the mucous membrane.
- Medications: Antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications like aspirin, warfarin, and clopidogrel can increase the risk of nosebleeds by impairing blood clotting.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), tumors, and high blood pressure can contribute to frequent nosebleeds.
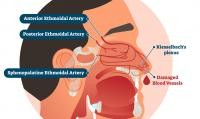 Illustration of Kiesselbach's Plexus
Illustration of Kiesselbach's Plexus
2. What Are the Risk Factors for Frequent Nosebleeds?
Several risk factors can increase your likelihood of experiencing recurrent nosebleeds. Being aware of these factors can help you take preventive measures. Key risk factors include:
- Age: Nosebleeds are more common in children (2-10 years old) and older adults (50-80 years old).
- Medications: Regular use of blood-thinning medications. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, patients on antiplatelet drugs had a 30% higher risk of nosebleeds.
- Environmental Factors: Living in dry climates or during winter months. Research from the Mayo Clinic indicates that dry air is a significant contributor to nasal dryness and bleeding.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like hypertension, bleeding disorders, and HHT. A study in the American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy found that HHT patients experience more severe and frequent nosebleeds.
- Nasal Irritants: Exposure to chemical irritants, allergens, and pollutants can inflame the nasal passages.
- Nasal Trauma: Frequent nose picking or injuries to the nose.
3. How Can I Stop a Nosebleed Quickly at Home?
Knowing how to stop a nosebleed quickly can prevent unnecessary anxiety and discomfort. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Stay Calm: Panic can elevate blood pressure, potentially prolonging the bleeding.
- Sit Upright and Lean Forward: This position prevents blood from flowing down your throat, which can cause nausea or choking.
- Pinch Your Nose: Use your thumb and index finger to firmly pinch the soft part of your nose, just below the bony bridge.
- Maintain Pressure: Hold the pinch continuously for 10-15 minutes. Do not release to check if the bleeding has stopped, as this can disrupt the clotting process.
- Apply Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the bridge of your nose can help constrict blood vessels.
- Release and Rest: After 10-15 minutes, release the pressure. If the bleeding has stopped, rest quietly for a while. Avoid blowing your nose or engaging in strenuous activities for the next few hours.
4. When Should I Seek Medical Attention for a Nosebleed?
While most nosebleeds are not serious and can be managed at home, certain situations require immediate medical attention. Seek medical help if:
- Prolonged Bleeding: The nosebleed lasts longer than 20 minutes despite applying pressure.
- Severe Bleeding: The bleeding is heavy and fills more than a cup with blood.
- Difficulty Breathing: You have trouble breathing or swallowing due to the bleeding.
- Weakness or Dizziness: You feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
- Nosebleed After Injury: The nosebleed occurs after a head injury or trauma.
- Recurrent Nosebleeds: You experience frequent nosebleeds (more than once a week).
- Underlying Conditions: You have a bleeding disorder, are on blood-thinning medication, or have other medical conditions that may complicate the nosebleed.
5. What Are the Different Types of Nosebleeds?
Nosebleeds are generally categorized into two types based on the location of the bleeding:
- Anterior Nosebleeds: These are the most common type, accounting for about 90% of all nosebleeds. They occur in the front part of the nose (Kiesselbach’s plexus) and are usually easy to manage.
- Posterior Nosebleeds: These are less common but more severe. They occur in the back part of the nose and often require medical intervention to stop the bleeding. Posterior nosebleeds are more likely to occur in older adults, people with high blood pressure, or those with blood clotting disorders.
6. How Are Frequent Nosebleeds Diagnosed by a Doctor?
When you see a doctor for frequent nosebleeds, they will perform a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause. This may include:
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about your medical history, including any medications you are taking, previous nosebleeds, and family history of bleeding disorders.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will examine your nose using a nasal speculum and light to visualize the nasal passages and identify the source of the bleeding.
- Endoscopy: In some cases, the doctor may use a flexible endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) to get a better view of the nasal passages and identify any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to check for bleeding disorders, anemia, or other underlying conditions.
- Imaging Studies: In rare cases, imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs may be necessary to rule out tumors or other structural abnormalities.
7. What Are the Medical Treatments Available for Frequent Nosebleeds?
If home remedies are not effective, several medical treatments are available to manage frequent nosebleeds:
- Cauterization: This involves sealing off the bleeding blood vessel with a chemical (silver nitrate) or heat (electrocautery). Cauterization is typically performed in the doctor’s office and is effective for anterior nosebleeds. According to a study in the * journal, silver nitrate cauterization successfully stopped nosebleeds in 80% of patients.
- Nasal Packing: This involves placing a gauze or sponge-like material into the nasal cavity to apply pressure and stop the bleeding. Nasal packing is often used for posterior nosebleeds or when cauterization is not effective.
- Medications: Topical creams or ointments containing antibiotics or vasoconstrictors may be prescribed to promote healing and reduce bleeding.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to correct a deviated septum, remove tumors, or repair damaged blood vessels.
- Ligation: For severe posterior nosebleeds, a surgeon may need to tie off (ligate) the bleeding vessel to stop the bleeding.
- Embolization: This procedure involves blocking the bleeding vessel with a special material. Embolization is typically performed by an interventional radiologist.
8. How Can I Prevent Nosebleeds?
Preventing nosebleeds involves keeping the nasal passages moist and avoiding irritants. Here are some effective strategies:
- Use a Humidifier: Keep the air moist, especially in your bedroom, to prevent nasal dryness. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), maintaining indoor humidity between 30-50% can help prevent dryness and irritation.
- Saline Nasal Spray: Use saline nasal spray to keep your nasal passages moist. A study in the American Journal of Rhinology found that regular use of saline nasal spray significantly reduced the frequency of nosebleeds.
- Nasal Gel: Apply a small amount of nasal gel or petroleum jelly to the inside of your nostrils to keep them moist.
- Avoid Nose Picking: Refrain from picking your nose to prevent trauma to the nasal lining.
- Control Allergies: Manage allergies with antihistamines or other medications to reduce nasal congestion and irritation. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) recommends avoiding allergens and using appropriate medications to control allergy symptoms.
- Proper Use of Nasal Sprays: Use nasal sprays correctly to avoid irritating the nasal passages.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep your body and nasal passages hydrated.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimize exposure to smoke, dust, and other irritants.
- Manage Blood Pressure: Keep your blood pressure under control if you have hypertension. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends regular blood pressure monitoring and lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension.
- Consult Your Doctor: If you are on blood-thinning medications, talk to your doctor about the risk of nosebleeds and whether any adjustments are necessary.
9. How Does Dry Air Contribute to Nosebleeds?
Dry air is a significant factor in causing nosebleeds because it dries out the nasal passages, leading to cracking and irritation of the delicate blood vessels. When the nasal lining becomes dry, it is more prone to bleeding, especially with minor trauma like nose picking or blowing your nose. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), maintaining adequate humidity levels can significantly reduce the incidence of nosebleeds.
10. What Is Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) and How Does It Cause Nosebleeds?
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, is a genetic disorder that causes abnormal blood vessel formation in various parts of the body, including the nose. These abnormal blood vessels, called telangiectasias, are fragile and prone to bleeding. Frequent and severe nosebleeds are a hallmark symptom of HHT. The Cleveland Clinic notes that HHT affects about 1 in 5,000 people and can lead to significant health issues if not properly managed.
11. Are Nosebleeds More Common in Certain Age Groups?
Yes, nosebleeds are more common in certain age groups:
- Children (2-10 years old): Children are more prone to anterior nosebleeds due to nose picking, colds, and allergies.
- Older Adults (50-80 years old): Older adults are more likely to experience posterior nosebleeds due to high blood pressure, blood-thinning medications, and age-related changes in the nasal lining.
12. What Medications Increase the Risk of Nosebleeds?
Certain medications can increase the risk of nosebleeds by impairing blood clotting or irritating the nasal passages:
- Anticoagulants: Medications like warfarin, heparin, and rivaroxaban prevent blood from clotting and increase the risk of bleeding.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Medications like aspirin, clopidogrel, and ticagrelor prevent blood platelets from clumping together and increase the risk of bleeding.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when taken regularly.
- Topical Nasal Sprays: Overuse of decongestant nasal sprays can dry out the nasal passages and increase the risk of bleeding.
13. How Does High Blood Pressure Contribute to Nosebleeds?
High blood pressure (hypertension) can contribute to nosebleeds by weakening the blood vessels in the nose. Over time, the increased pressure can damage the delicate blood vessels, making them more prone to rupture and bleed. Posterior nosebleeds are more common in people with high blood pressure. The Mayo Clinic advises that managing blood pressure is crucial for preventing recurrent nosebleeds in hypertensive individuals.
14. Can Allergies Cause Nosebleeds?
Yes, allergies can cause nosebleeds. Allergic rhinitis (hay fever) can lead to inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages, making them more susceptible to bleeding. Frequent nose blowing and rubbing the nose due to allergy symptoms can also contribute to nosebleeds. The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) recommends managing allergies with antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and allergen avoidance to reduce the risk of nosebleeds.
15. What Role Does Humidity Play in Preventing Nosebleeds?
Humidity plays a crucial role in preventing nosebleeds by keeping the nasal passages moist. Adequate humidity levels prevent the nasal lining from drying out, cracking, and bleeding. Using a humidifier, especially during dry winter months, can significantly reduce the incidence of nosebleeds. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends maintaining indoor humidity between 30-50% to prevent dryness and irritation.
16. How Effective Is Silver Nitrate Cauterization in Treating Nosebleeds?
Silver nitrate cauterization is a highly effective treatment for anterior nosebleeds. The chemical cauterizes the bleeding blood vessel, sealing it off and stopping the bleeding. The procedure is quick, simple, and can be performed in the doctor’s office. A study published in the Laryngoscope found that silver nitrate cauterization successfully stopped nosebleeds in 80% of patients.
17. What Are the Potential Complications of Frequent Nosebleeds?
While most nosebleeds are not serious, frequent and severe nosebleeds can lead to complications:
- Anemia: Significant blood loss can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
- Hypovolemic Shock: In rare cases, severe blood loss can lead to hypovolemic shock, a life-threatening condition caused by decreased blood volume.
- Airway Obstruction: Severe nosebleeds can obstruct the airway, leading to difficulty breathing.
- Infection: Nasal packing can increase the risk of sinus infection.
- Anxiety and Stress: Frequent nosebleeds can cause anxiety and stress, impacting quality of life.
18. How Does Nasal Packing Help in Stopping Nosebleeds?
Nasal packing helps in stopping nosebleeds by applying direct pressure to the bleeding blood vessels in the nasal cavity. The packing material, typically gauze or a sponge-like material, compresses the vessels and promotes clot formation. Nasal packing is often used for posterior nosebleeds or when cauterization is not effective.
19. Are There Any Alternative Remedies for Nosebleeds?
While medical treatments are often necessary for frequent or severe nosebleeds, some alternative remedies may provide relief:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C can strengthen blood vessels and reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Iron Supplements: If you have anemia due to frequent nosebleeds, iron supplements can help replenish iron stores.
- Witch Hazel: Witch hazel has astringent properties that can help constrict blood vessels and stop bleeding.
- Yarrow: Yarrow is an herb with anti-inflammatory and anti-bleeding properties.
Disclaimer: Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative remedies.
20. What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Reduce the Frequency of Nosebleeds?
Several lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency of nosebleeds:
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking irritates the nasal passages and increases the risk of bleeding.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can dilate blood vessels and increase the risk of bleeding.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep your body and nasal passages hydrated.
- Use a Humidifier: Keep the air moist, especially in your bedroom.
- Avoid Nose Picking: Refrain from picking your nose.
- Manage Allergies: Control allergies with appropriate medications and allergen avoidance.
21. How Can Parents Prevent Nosebleeds in Children?
Parents can take several steps to prevent nosebleeds in children:
- Keep Nails Trimmed: Trim your child’s nails to prevent trauma from nose picking.
- Use a Humidifier: Keep the air moist in your child’s bedroom.
- Saline Nasal Spray: Use saline nasal spray to keep your child’s nasal passages moist.
- Teach Proper Nose Blowing: Teach your child to blow their nose gently.
- Avoid Smoke Exposure: Keep your child away from smoke and other irritants.
- Manage Allergies: Control your child’s allergies with appropriate medications and allergen avoidance.
22. What Are the Latest Research and Advancements in Treating Nosebleeds?
Recent research has focused on developing new and improved methods for treating nosebleeds:
- Tranexamic Acid: Topical tranexamic acid has been shown to be effective in stopping nosebleeds by promoting blood clotting. A study in the Annals of Emergency Medicine found that topical tranexamic acid significantly reduced bleeding time in patients with nosebleeds.
- Bioadhesive Sealants: Bioadhesive sealants are being developed to seal off bleeding blood vessels in the nose.
- Improved Nasal Packing Materials: New nasal packing materials are designed to be more comfortable and effective in stopping bleeding.
23. How Can WHY.EDU.VN Help Me with My Questions About Nosebleeds?
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges and concerns associated with frequent nosebleeds. Our platform offers:
- Expert Answers: Access detailed, easy-to-understand answers to all your questions about nosebleeds.
- Reliable Information: Our information is based on the latest research and expert opinions from trusted sources.
- Community Support: Connect with others who have experienced nosebleeds and share your experiences.
- Personalized Advice: Get personalized advice from our team of experts to help you manage and prevent nosebleeds.
Don’t let frequent nosebleeds disrupt your life. Visit WHY.EDU.VN today to get the answers and support you need to take control of your health.
24. What Are Some Home Remedies That May Help Stop a Nosebleed?
While medical intervention may be necessary for frequent or severe nosebleeds, several home remedies may help stop a nosebleed:
- Pinch Your Nose: Pinch the soft part of your nose just below the bony bridge for 10-15 minutes.
- Apply a Cold Compress: Apply a cold compress or ice pack to the bridge of your nose.
- Elevate Your Head: Keep your head elevated to reduce blood flow to the nose.
- Use a Decongestant Spray: A decongestant nasal spray can help constrict blood vessels and stop bleeding.
- Apply Pressure to the Upper Lip: Placing a piece of gauze or cotton under your upper lip and pressing against your nose can help stop bleeding.
25. Is There a Link Between Nosebleeds and Sinus Infections?
Yes, there can be a link between nosebleeds and sinus infections. Sinus infections can cause inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages, making them more susceptible to bleeding. Additionally, frequent nose blowing due to sinus congestion can also contribute to nosebleeds. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends seeking medical treatment for sinus infections to prevent complications and reduce the risk of nosebleeds.
26. What Are the Long-Term Effects of Frequent Nosebleeds?
The long-term effects of frequent nosebleeds can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause:
- Chronic Anemia: Persistent blood loss can lead to chronic iron deficiency anemia.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Frequent nosebleeds can cause anxiety, stress, and disruption of daily activities.
- Nasal Septal Perforation: In rare cases, repeated cauterization can lead to nasal septal perforation (a hole in the nasal septum).
- Increased Risk of Infection: Nasal packing can increase the risk of sinus infections.
- Need for Repeated Medical Interventions: Frequent nosebleeds may require repeated medical interventions, such as cauterization or nasal packing.
27. How Can I Find a Specialist for Treating Frequent Nosebleeds?
Finding a specialist for treating frequent nosebleeds involves several steps:
- Consult Your Primary Care Physician: Your primary care physician can evaluate your condition and provide a referral to a specialist.
- Check Online Directories: Use online directories such as the American Academy of Otolaryngology to find otolaryngologists (ENT doctors) in your area.
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or other healthcare providers for recommendations.
- Check Credentials: Verify the specialist’s credentials and experience.
- Read Reviews: Read online reviews to get an idea of the specialist’s reputation and patient satisfaction.
28. Are There Any Foods That Can Help Prevent Nosebleeds?
While there is no specific diet to prevent nosebleeds, certain foods can promote overall health and reduce the risk of bleeding:
- Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Foods like leafy green vegetables, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts promote blood clotting.
- Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Foods like citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers strengthen blood vessels.
- Iron-Rich Foods: Foods like red meat, beans, and spinach can help prevent anemia.
- Hydrating Foods: Foods with high water content, like watermelon and cucumbers, can help keep you hydrated.
29. What Should I Do If I Have a Nosebleed While Taking Blood Thinners?
If you have a nosebleed while taking blood thinners, take the following steps:
- Stay Calm: Panic can elevate blood pressure and worsen the bleeding.
- Pinch Your Nose: Pinch the soft part of your nose just below the bony bridge for 10-15 minutes.
- Contact Your Doctor: Contact your doctor to discuss whether any adjustments to your medication are necessary.
- Seek Medical Attention: If the bleeding is severe or does not stop after 20 minutes, seek immediate medical attention.
30. What Is the Connection Between Nosebleeds and Weather Conditions?
Weather conditions, particularly dry air, can significantly impact the frequency of nosebleeds. Low humidity levels, especially during winter months, can dry out the nasal passages, making them more susceptible to bleeding. The National Weather Service recommends using a humidifier to maintain adequate indoor humidity levels and prevent nasal dryness.
31. What Are Some Uncommon Causes of Nosebleeds?
While most nosebleeds are caused by common factors like dry air and nose picking, some uncommon causes include:
- Tumors: Benign or malignant tumors in the nasal passages can cause nosebleeds.
- Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: This rare autoimmune disorder can cause inflammation and bleeding in the nasal passages.
- Cocaine Use: Snorting cocaine can damage the nasal lining and cause nosebleeds.
- Foreign Bodies: Foreign objects in the nose can cause irritation and bleeding.
32. How Can I Differentiate Between an Anterior and Posterior Nosebleed at Home?
Differentiating between an anterior and posterior nosebleed at home can be challenging, but here are some clues:
- Location of Bleeding: Anterior nosebleeds typically originate from the front part of the nose, while posterior nosebleeds originate from the back part of the nose.
- Severity of Bleeding: Posterior nosebleeds are often more severe and may involve heavy bleeding that flows down the back of the throat.
- Difficulty Stopping Bleeding: Posterior nosebleeds are often more difficult to stop with home remedies.
- Associated Symptoms: Posterior nosebleeds may be associated with nausea, vomiting, or difficulty breathing.
If you suspect you have a posterior nosebleed, seek immediate medical attention.
33. What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor About Frequent Nosebleeds?
When you see your doctor about frequent nosebleeds, ask the following questions:
- What is causing my nosebleeds?
- What treatments are available?
- Are there any lifestyle changes I can make to prevent nosebleeds?
- Should I see a specialist?
- What are the potential complications of frequent nosebleeds?
- What medications can increase the risk of nosebleeds?
- How can I manage nosebleeds at home?
- When should I seek medical attention for a nosebleed?
34. How Can I Help Someone Else Who Is Having a Nosebleed?
If someone else is having a nosebleed, follow these steps to help:
- Stay Calm: Help the person stay calm to prevent anxiety and elevated blood pressure.
- Sit Upright and Lean Forward: Encourage the person to sit upright and lean forward to prevent blood from flowing down the throat.
- Pinch the Nose: Pinch the soft part of the nose just below the bony bridge for 10-15 minutes.
- Apply a Cold Compress: Apply a cold compress or ice pack to the bridge of the nose.
- Seek Medical Attention: If the bleeding is severe or does not stop after 20 minutes, seek immediate medical attention.
35. What Are Some Myths and Misconceptions About Nosebleeds?
There are several myths and misconceptions about nosebleeds:
- Myth: Tilting your head back will stop a nosebleed.
- Fact: Tilting your head back can cause blood to flow down your throat, leading to nausea and choking.
- Myth: Putting a cold key down your back will stop a nosebleed.
- Fact: There is no scientific evidence to support this claim.
- Myth: Nosebleeds are always a sign of a serious medical condition.
- Fact: Most nosebleeds are not serious and can be managed at home.
- Myth: You should blow your nose immediately after a nosebleed.
- Fact: Avoid blowing your nose for several hours after a nosebleed to allow the blood vessels to heal.
36. What Is the Role of Vasoconstrictors in Treating Nosebleeds?
Vasoconstrictors are medications that constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow and helping to stop bleeding. They are often used in nasal sprays and topical solutions to treat nosebleeds. Common vasoconstrictors include:
- Oxymetazoline (Afrin): This decongestant nasal spray can help constrict blood vessels and stop bleeding.
- Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine): This decongestant can also help constrict blood vessels and stop bleeding.
Disclaimer: Use vasoconstrictors sparingly, as overuse can lead to rebound congestion and other side effects.
37. How Can I Prevent Nosebleeds While Flying?
Flying can increase the risk of nosebleeds due to the dry air and changes in air pressure. To prevent nosebleeds while flying:
- Use a Saline Nasal Spray: Use saline nasal spray to keep your nasal passages moist.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Apply Nasal Gel: Apply a small amount of nasal gel or petroleum jelly to the inside of your nostrils.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Alcohol and caffeine can dehydrate you and increase the risk of nosebleeds.
38. What Are the Benefits of Using a Humidifier to Prevent Nosebleeds?
Using a humidifier to prevent nosebleeds offers several benefits:
- Keeps Nasal Passages Moist: Humidifiers add moisture to the air, preventing the nasal passages from drying out.
- Reduces Irritation: Moist air can reduce irritation and inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Promotes Healing: Moist air can promote healing of damaged blood vessels.
- Prevents Cracking: Adequate humidity prevents the nasal lining from cracking and bleeding.
For reliable information and expert answers to all your health-related questions, visit WHY.EDU.VN. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and support you need to take control of your health. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States or WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101.
FAQ:
-
Why do I get frequent nosebleeds in the winter?
- Winter air is drier, leading to nasal passage dryness and increased risk of bleeding.
-
Can stress cause nosebleeds?
- Stress can indirectly contribute to nosebleeds by causing behaviors like nose picking or elevated blood pressure.
-
Is it normal to have nosebleeds every day?
- Daily nosebleeds are not normal and warrant medical evaluation to determine the cause.
-
What should I eat to prevent nosebleeds?
- Consume foods rich in Vitamin K and C to strengthen blood vessels and promote clotting.
-
How long should I pinch my nose to stop a nosebleed?
- Pinch your nose continuously for 10-15 minutes without releasing to check for bleeding.
-
Can allergies cause nosebleeds?
- Yes, allergies can inflame and irritate the nasal passages, increasing the risk of nosebleeds.
-
What is the best way to keep my nasal passages moist?
- Use a humidifier, saline nasal spray, or apply nasal gel to keep nasal passages moist.
-
When is a nosebleed considered a medical emergency?
- A nosebleed is an emergency if it lasts longer than 20 minutes, involves heavy bleeding, or causes difficulty breathing.
-
Are nosebleeds more common in children?
- Yes, nosebleeds are more common in children due to nose picking and increased susceptibility to colds.
-
Can high blood pressure cause nosebleeds?
- Yes, high blood pressure can weaken blood vessels in the nose, making them more prone to bleeding.
This comprehensive guide, brought to you by why.edu.vn, provides detailed insights into the causes, treatments, and prevention of nosebleeds. Remember, for any persistent health concerns, consulting with a healthcare professional is always the best course of action.