Why Is Trump Imposing Tariffs On Canada And Mexico? This is a question that has been on the minds of many, and at WHY.EDU.VN, we aim to provide you with a clear and comprehensive answer. By exploring the economic implications, trade policy decisions, and geopolitical strategies behind this move, we’ll shed light on this complex issue. Learn about the impact on consumers, businesses, and the global economy.
1. Understanding Tariffs: An Overview
Tariffs, in essence, are taxes imposed on goods imported from other countries. These taxes are typically a percentage of the product’s value. The implementation of tariffs can significantly affect international trade, impacting both businesses and consumers.
1.1. How Tariffs Work
When a country imposes a tariff, the cost of imported goods increases. For instance, a 25% tariff on a product valued at $10 would add an additional $2.50 to its price. Companies importing these goods are required to pay the tariff to the government.
1.2. The Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Businesses often have to decide whether to absorb the cost of the tariff or pass it on to consumers. If a company chooses to pass on the cost, consumers may see higher prices for imported goods. Alternatively, businesses may opt to import fewer foreign goods, which could lead to a scarcity of certain products and, consequently, higher prices.
2. Trump’s Rationale for Imposing Tariffs
During his presidency, Donald Trump frequently used tariffs as a central part of his economic strategy. His reasons for doing so were multifaceted, aiming to reshape trade relationships and bolster the U.S. economy.
2.1. Encouraging Domestic Consumption
One of Trump’s primary arguments for imposing tariffs was to incentivize U.S. consumers to purchase more American-made goods. By making imported products more expensive, the aim was to shift consumer demand towards domestically produced items. This, in turn, was expected to stimulate the U.S. economy and increase tax revenues.
2.2. Reducing Trade Deficits
Trump administration aimed to reduce the trade deficit, which is the difference between the value of goods the U.S. imports and the value of goods it exports. For example, the U.S. had a significant trade deficit with the European Union (EU), which Trump described as an “atrocity”. Tariffs were seen as a tool to level the playing field and encourage more balanced trade relationships.
2.3. Addressing Non-Trade Issues
In some cases, Trump also linked tariffs to non-trade issues. For example, he suggested that tariffs were intended to pressure countries like China, Mexico, and Canada to do more to stop illegal immigration and drug trafficking into the U.S. This approach broadened the scope of tariffs beyond purely economic considerations.
3. Specific Tariffs Imposed on Canada and Mexico
Trump’s administration imposed several tariffs specifically targeting goods from Canada and Mexico. These actions were often framed as necessary to protect American industries and jobs.
3.1. Tariffs on Steel and Aluminum
In March, Trump imposed a 25% tariff on steel imports and a 10% tariff on aluminum imports from various countries, including Canada and Mexico. The stated reason was to protect U.S. steel and aluminum industries, which Trump argued were essential for national security.
3.2. Impact on the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry was significantly affected by these tariffs. Component parts often cross the U.S., Mexican, and Canadian borders multiple times before a vehicle is fully assembled. Tariffs on steel and aluminum increased the cost of manufacturing cars, potentially raising prices for consumers.
For instance, analysts at the Anderson Economic Group estimated that the cost of a car made using parts from Mexico and Canada alone could rise by $4,000-$10,000, depending on the vehicle.
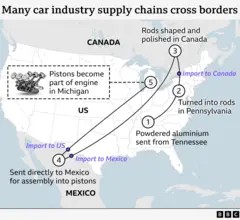 Car industry supply chains crossing North American borders
Car industry supply chains crossing North American borders
3.3. The USMCA and Trade Negotiations
The imposition of tariffs on Canada and Mexico occurred amidst negotiations for the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which was intended to replace the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The tariffs were seen by some as a negotiating tactic to gain leverage in these trade discussions.
4. Economic Consequences for the U.S. Consumers
Economists generally agreed that tariffs would lead to higher prices for U.S. consumers. When firms pass on the increased costs, the prices of many imported goods rise.
4.1. Increased Prices on Imported Goods
The tariffs affected a wide range of products, from consumer goods like beer, whisky, and tequila to essential items like fuel and avocados. Consumers felt the pinch as the cost of these goods increased.
4.2. Reduced Choice and Availability
Firms might choose to import fewer foreign goods in response to tariffs, which could reduce the availability of certain products. This limited choice could also drive up prices further.
4.3. Historical Data on Tariff Impact
Data from the US International Trade Commission indicated that tariffs imposed during Trump’s first term raised the average price of steel and aluminum in the U.S. by 2.4% and 1.6%, respectively. Similarly, tariffs on imported washing machines between 2018 and 2023 increased the price of laundry equipment by 34%.
5. Responses from Canada and Mexico
Canada and Mexico responded to the U.S. tariffs by implementing their own tariffs on U.S. goods. These retaliatory measures escalated trade tensions and added to fears of a global trade war.
5.1. Retaliatory Tariffs
Canada imposed 25% tariffs on U.S. steel, aluminum, and a range of other goods. Mexico also considered retaliatory tariffs while negotiations continued. These actions aimed to pressure the U.S. to reconsider its tariffs.
5.2. Impact on U.S. Exporters
The retaliatory tariffs affected U.S. exporters, who faced higher costs and reduced demand for their products in Canada and Mexico. This hurt various sectors, including agriculture and manufacturing.
5.3. Negotiations and Agreements
Despite the trade tensions, negotiations for the USMCA continued. The agreement was eventually signed, replacing NAFTA and establishing new trade rules between the three countries.
6. Global Implications of Trump’s Trade Policies
Trump’s tariffs had broader implications for the global economy, contributing to trade uncertainty and raising concerns about protectionism.
6.1. Trade Wars and Global Uncertainty
The imposition of tariffs led to trade disputes with multiple countries, including China and the EU. These trade wars created uncertainty for businesses and investors, impacting global economic growth.
6.2. Impact on Global Supply Chains
Tariffs disrupted global supply chains, as companies had to adjust their sourcing and production strategies to account for the increased costs. This led to inefficiencies and higher prices.
6.3. Responses from Other Countries
Many countries responded to Trump’s tariffs by implementing their own trade barriers, further escalating trade tensions. The EU, for example, imposed tariffs on U.S. goods worth billions of euros.
7. Potential for Recession
Some economists and analysts raised concerns that Trump’s trade policies could lead to a recession. The uncertainty created by trade wars and the increased costs associated with tariffs could dampen economic activity.
7.1. Economic Indicators
Various economic indicators were monitored closely to assess the potential for a recession. These included GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation.
7.2. Expert Opinions
While opinions varied, some experts warned that the negative impacts of tariffs could outweigh any potential benefits. Concerns were raised about the long-term effects on the U.S. and global economies.
7.3. Historical Context
Looking back at historical examples of trade wars and protectionist policies, analysts noted the potential for negative consequences. These historical precedents served as a cautionary tale.
8. The Current Status of Tariffs
The tariffs imposed during the Trump administration have been subject to changes and adjustments under subsequent administrations. Some tariffs have been modified, while others remain in place.
8.1. Changes Under the Biden Administration
The Biden administration has taken a different approach to trade policy, focusing on diplomacy and multilateral engagement. However, some tariffs imposed by the Trump administration remain in effect.
8.2. Ongoing Trade Negotiations
The U.S. continues to engage in trade negotiations with various countries, seeking to address trade imbalances and promote fair trade practices. These negotiations play a crucial role in shaping the future of international trade.
8.3. Future Outlook
The future of tariffs and trade policy remains uncertain, as global economic conditions and political dynamics continue to evolve. Ongoing monitoring and analysis are essential to understanding the potential impacts.
9. Case Studies: Impact on Specific Industries
To illustrate the effects of tariffs, it is helpful to examine specific industries that have been significantly impacted.
9.1. The Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a prime example of how tariffs can affect complex supply chains. Tariffs on steel and aluminum, as well as tariffs on auto parts, have increased the cost of manufacturing vehicles.
For example, the cost of a car made using parts from Mexico and Canada alone could rise significantly, depending on the vehicle, according to analysts at the Anderson Economic Group.
9.2. The Agricultural Sector
The agricultural sector has also been heavily affected by tariffs, particularly due to retaliatory measures from other countries. Tariffs on U.S. agricultural goods have reduced demand for these products in key export markets.
9.3. The Consumer Goods Sector
The consumer goods sector has seen increased prices on a variety of imported products, from electronics to clothing. These higher prices have affected consumers’ purchasing power and overall spending.
10. Alternative Trade Policies
Instead of tariffs, there are alternative trade policies that countries can pursue to achieve their economic goals.
10.1. Free Trade Agreements
Free trade agreements (FTAs) aim to reduce or eliminate trade barriers between countries, promoting increased trade and economic integration. The USMCA is an example of a free trade agreement.
10.2. Trade Negotiations
Engaging in constructive trade negotiations can help countries address trade imbalances and resolve disputes without resorting to tariffs. Diplomacy and dialogue are key to successful trade negotiations.
10.3. Domestic Policies
Investing in domestic industries and infrastructure can help countries become more competitive in the global market. Strengthening education, innovation, and productivity can boost economic growth.
11. Expert Opinions and Economic Analysis
Economists and trade experts offer diverse perspectives on the use of tariffs and their potential impacts.
11.1. Arguments for Tariffs
Some argue that tariffs can protect domestic industries, create jobs, and improve a country’s trade balance. They may also see tariffs as a tool to address unfair trade practices.
11.2. Arguments Against Tariffs
Others argue that tariffs lead to higher prices for consumers, disrupt supply chains, and harm overall economic growth. They may advocate for alternative trade policies that promote free and fair trade.
11.3. Comprehensive Analysis
A comprehensive economic analysis considers both the potential benefits and costs of tariffs, taking into account the specific context and circumstances. Such analysis can inform policy decisions and help countries achieve their economic goals.
12. Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Tariffs
The imposition of tariffs by the Trump administration on Canada and Mexico was a complex issue with far-reaching economic and geopolitical implications. While the stated goals were to protect American industries and jobs, the actual effects have been multifaceted and often controversial. As global trade dynamics continue to evolve, understanding the complexities of tariffs remains essential for policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike.
Navigating these complexities requires access to reliable information and expert analysis. At WHY.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge you need to understand the world around you.
Do you have more questions about tariffs, trade policy, or other economic issues? Visit WHY.EDU.VN today and get the answers you’re looking for. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with the insights you need to stay informed and make informed decisions.
WHY.EDU.VN
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: WHY.EDU.VN
13. FAQ Section: Addressing Common Questions About Tariffs
13.1. What is a tariff, and how does it work?
A tariff is a tax imposed on goods imported from other countries. It increases the cost of imported goods, potentially affecting both businesses and consumers.
13.2. Why did Trump impose tariffs on Canada and Mexico?
Trump’s reasons included encouraging domestic consumption, reducing trade deficits, and addressing non-trade issues like immigration and drug trafficking.
13.3. How do tariffs affect U.S. consumers?
Tariffs can lead to higher prices on imported goods, reduced choice and availability, and overall increased costs for consumers.
13.4. What were the responses from Canada and Mexico to the U.S. tariffs?
Canada and Mexico responded by implementing their own tariffs on U.S. goods, leading to trade tensions and fears of a global trade war.
13.5. What is the USMCA, and how does it relate to the tariffs?
The USMCA is the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement, which replaced NAFTA. The imposition of tariffs occurred amidst negotiations for the USMCA.
13.6. What are the global implications of Trump’s trade policies?
Trump’s tariffs led to trade wars, global uncertainty, and disruptions in global supply chains, affecting economic growth worldwide.
13.7. Can tariffs lead to a recession?
Some economists and analysts raised concerns that Trump’s trade policies could lead to a recession due to increased costs and uncertainty.
13.8. What is the current status of the tariffs imposed during the Trump administration?
The tariffs have been subject to changes and adjustments under subsequent administrations, with some modified and others remaining in place.
13.9. What are some alternative trade policies to tariffs?
Alternative policies include free trade agreements, trade negotiations, and domestic policies aimed at improving competitiveness.
13.10. Where can I get reliable information and expert analysis on tariffs and trade policy?
Visit WHY.EDU.VN for comprehensive information and expert analysis on tariffs, trade policy, and other economic issues. Our team of experts is here to provide you with the knowledge you need to stay informed.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of why Trump imposed tariffs on Canada and Mexico, offering insights into the economic consequences, responses from affected countries, and broader global implications. By addressing common questions and providing access to expert analysis, why.edu.vn aims to empower readers with the knowledge they need to understand this complex issue.