Having microphone issues can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you need it for important online meetings, gaming with friends, or recording audio. Whether you’re using a headset, webcam mic, or a standalone microphone, encountering problems is not uncommon. If you’re asking yourself, “Why Is My Mic Not Working?”, this guide is here to help. We’ll walk you through a series of troubleshooting steps to diagnose and resolve common microphone problems in Windows, ensuring you can get back to clear communication and recording.
First, let’s address a fundamental aspect of microphone functionality in Windows: application permissions.
Ensuring Apps Have Microphone Access
After a Windows update, or even due to system settings adjustments, applications might lose permission to access your microphone. This is a common reason why your mic might suddenly stop working. You need to explicitly grant apps the necessary permissions. Here’s how to check and enable microphone access in both Windows 10 and Windows 11:
For Windows 11:
- Click on Start and navigate to Settings.
- Select Privacy & security, then click on Microphone.
- At the top, ensure that Microphone access is toggled On.
- Next, verify that Let apps access your microphone is also turned On.
- Scroll down to see a list of apps and toggle the switch next to each app to control individual access. Note that desktop applications are managed under a separate setting.
- To enable microphone access for desktop apps, make sure Let desktop apps access your microphone is turned On. Remember, you cannot disable microphone access for individual desktop apps; it’s an all-or-nothing setting for them.
Alt Text: Windows 11 Microphone Privacy Settings showing microphone access toggled on and options to allow apps and desktop apps to access the microphone.
For Windows 10:
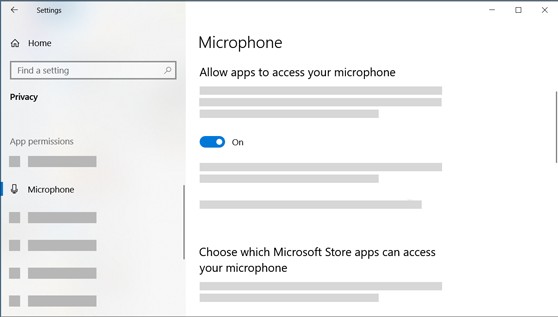
- Click the Start button, then select Settings > Privacy > Microphone.
- Click Change under “Microphone access for this device” and ensure it is On.
- Verify that Allow apps to access your microphone is also toggled On.
- Under “Choose which Microsoft Store apps can access your microphone”, you can enable or disable access for specific apps from the Microsoft Store.
- Finally, ensure that Allow desktop apps to access your microphone is set to On to enable microphone usage for all desktop applications.
If you’re using a webcam that includes a microphone, you might also need to check camera permissions. Go to Settings > Privacy & security (or Privacy in Windows 10) > Camera and ensure camera access is enabled for both the device and for apps.
Basic Troubleshooting: Others Can’t Hear Me
If your microphone is enabled and permissions are correctly configured, but others still can’t hear you, let’s move on to some basic hardware and software checks.
- Mute Button: Many headsets and some microphones come with a physical mute button. Ensure this button is not activated. It’s easy to accidentally mute yourself!
- Physical Connections: Double-check that your microphone or headset is properly connected to your computer.
- For wired microphones, ensure the cable is securely plugged into the correct port (usually a pink microphone port or a USB port). Try unplugging and replugging it to ensure a firm connection.
- For wireless Bluetooth headsets, confirm that your headset is correctly paired and connected to your computer. You can refer to Pair a Bluetooth device in Windows for detailed steps on Bluetooth pairing. Sometimes, disconnecting and reconnecting the Bluetooth device can resolve connectivity glitches.
- Default Recording Device: Windows allows you to select default input and output devices. You need to ensure your microphone is set as the default recording device. Here’s how to do it:
For Windows 11:
- Go to Start > Settings > System > Sound.
- In the Input section, look for “Choose a device for speaking or recording” and select your microphone from the dropdown menu.
- To test if Windows is detecting your microphone, speak into it. Under Input, you should see the Volume bar move as you speak. If the blue bar is moving, it indicates that Windows is receiving audio input from your microphone.
For Windows 10:
- Go to Start > Settings > System > Sound.
- In the Input section, under “Choose your input device“, select your microphone.
- Below the input device selection, you’ll find “Test your microphone“. Speak into your microphone and observe the bar. If it shows activity, your microphone is likely working at a basic level.
- Run the Recording Audio Troubleshooter: Windows includes built-in troubleshooters that can automatically diagnose and fix common problems. The Recording Audio troubleshooter can help identify and resolve microphone issues.
For Windows 11:
- Go to Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.
- Find and select Recording Audio and click Run.
For Windows 10:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional troubleshooters.
- Select Recording Audio and click Run the troubleshooter.
Follow the on-screen prompts provided by the troubleshooter, as it may offer solutions or further diagnostic steps.
Microphone Not Detected by Windows
If you’ve gone through the above steps and Windows is still not detecting your microphone at all (the volume bar doesn’t move during testing, and it might not even appear in the input device list), the issue might be with your audio drivers.
- Reinstalling Audio Drivers: Corrupted or outdated audio drivers can prevent Windows from recognizing your microphone. Reinstalling them can often resolve this problem.
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager.
- In Device Manager, expand the “Sound, video and game controllers” section.
- Look for your audio devices or drivers in this list. It might be listed under a generic name like “High Definition Audio Device” or the specific name of your microphone or sound card.
- Right-click on the audio device and select “Uninstall device“.
- In the uninstall confirmation dialog, very importantly, check the box that says “Delete the driver software for this device” before clicking Uninstall. This ensures that the old driver files are completely removed.
- Repeat this uninstall process for any other audio devices listed under “Sound, video and game controllers” if you suspect they might be related to the microphone issue.
- Restart your computer.
- After restarting, Windows will attempt to automatically reinstall the audio drivers. If it doesn’t, or to ensure you have the latest drivers, go back to Device Manager.
- Right-click on the “Sound, video and game controllers” section and select “Scan for hardware changes“. This prompts Windows to look for newly connected or changed hardware and install drivers.
- Alternatively, you can manually update the drivers. Expand “Sound, video and game controllers“, right-click on your audio driver, and select “Update driver“. You can choose to search automatically for updated drivers, or if you have downloaded the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website, you can choose to browse your computer for driver software.
Low Microphone Volume Issues
Sometimes, the microphone is working, but the volume is just too low, making it difficult for others to hear you.
- Adjust Microphone Volume: You can manually increase the microphone volume in Windows settings.
For Windows 11 & 10:
- Go to Start > Settings > System > Sound.
- In the Input section, select your microphone to access its properties.
- Look for the “Input volume” slider. Adjust this slider to increase the microphone’s input level. Speak into your microphone while adjusting to see if the blue volume bar moves adequately.
For Windows 10 specifically, you have additional volume boost options:
- After selecting your microphone in Sound Settings and clicking “Device properties” (or similar option to access more settings), look for a tab labeled “Levels” in the Microphone Properties window.
- Here, you’ll find sliders for “Microphone” and “Microphone Boost“. Adjust the “Microphone” slider to increase the base volume. Use the “Microphone Boost” slider cautiously, as excessive boost can introduce background noise or distortion.
- Click OK to save the changes.
- Test your microphone again to check if the volume is now adequate. The “Test your microphone” feature in Sound Settings is useful for real-time feedback.
App-Specific Microphone Problems (e.g., Skype)
Sometimes, microphone issues are specific to certain applications like Skype, Zoom, Discord, or other communication platforms.
- Check App Audio Settings: Most applications have their own audio input settings, which might override the system defaults. You need to ensure the correct microphone is selected within the application’s settings.
Example for Skype:
- If Skype is not open, launch it.
- Click on the More menu (usually three dots) in the upper left corner, then select Settings.
- Go to the “Audio & Video” section.
- Under “Microphone“, use the dropdown menu to ensure your desired microphone or headset is selected.
- Similarly, check the “Speakers” setting to ensure your preferred output device is selected.
Alt Text: Skype Audio & Video settings showing microphone dropdown menu to select the input device and speakers dropdown menu for output device selection.
The process is similar for other applications. Look for audio or voice settings within the app and ensure the correct microphone is selected as the input device.
By systematically going through these troubleshooting steps, you should be able to identify and fix most common reasons why your microphone is not working in Windows. If you continue to experience issues, it might be indicative of a hardware problem with the microphone itself, or potentially more complex software conflicts. In such cases, consulting with technical support or seeking professional assistance might be necessary.