Experiencing pain on your left side can be unsettling, prompting you to wonder, “Why Is My Left Side Hurting?”. It’s a common concern, and while often attributed to something as simple as trapped gas, left side pain can sometimes signal a more serious underlying medical condition. Understanding the potential causes can help you determine when it’s a minor discomfort and when it’s crucial to seek medical attention.
This article delves into the various reasons behind pain in the left side of your abdomen. We’ll explore common culprits, ranging from digestive issues to conditions affecting specific organs, and guide you on when left side pain warrants a visit to the doctor or even the emergency room.
Often, lower left abdominal pain accompanied by symptoms like burping, bloating, or a feeling of tightness in your abdomen points towards indigestion or gas. However, it’s essential to be vigilant. If your left side pain, whether in the upper or lower abdomen, is coupled with alarming symptoms such as a high fever, persistent nausea, vomiting, or intense stomach pain, prompt medical evaluation is necessary. These could be indicators of serious conditions like diverticulitis, appendicitis, or stomach ulcers.
To better understand what your lower abdominal pain might signify, let’s explore some of the common causes:
- Appendicitis
- Diverticulitis
- Constipation
- Kidney stones
- Stomach ulcers
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD)
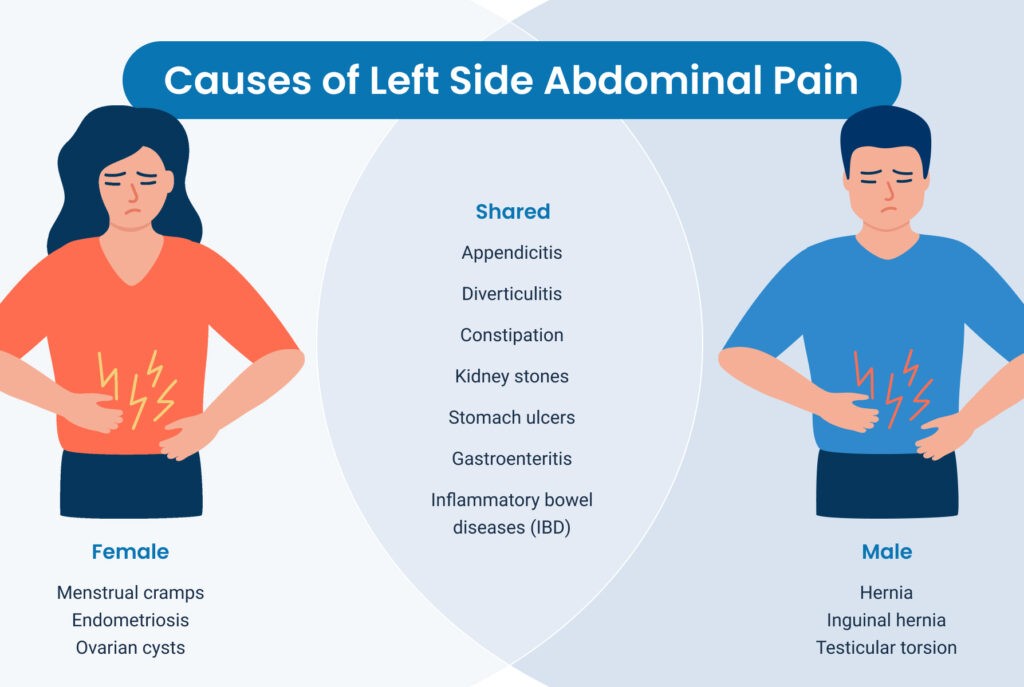 Diagram illustrating potential causes of abdominal pain in males and females.
Diagram illustrating potential causes of abdominal pain in males and females.
7 Frequent Causes of Abdominal Pain on Your Left Side
While digestive issues are often the first thought when experiencing left-side pain, it’s important to remember that several organs reside in the left abdomen. Pinpointing the exact location and nature of your pain can be helpful in understanding the potential cause. The organs situated in your left abdomen include:
- Colon (Descending Colon and Sigmoid Colon): Part of the large intestine responsible for processing waste.
- Left Kidney: Filters waste and excess fluid from the blood.
- Spleen: Part of the immune system, filtering blood and fighting infections.
- Stomach: Responsible for the initial digestion of food.
- Pancreas (Tail): Produces enzymes for digestion and hormones like insulin.
If your left side pain isn’t related to gas or indigestion, it often signals an issue within one of these organs or related systems. If the pain persists, it’s crucial to observe any accompanying symptoms that can provide further clues. Let’s examine some specific conditions associated with left side abdominal pain:
1. Appendicitis
Although typically associated with right-sided abdominal pain, appendicitis can sometimes manifest as left side pain, particularly in its early stages. Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. The pain often begins around the belly button and may be felt slightly to the left before migrating to the lower right abdomen. Ignoring appendicitis can lead to serious complications, including rupture and infection.
Key Symptoms of Appendicitis to Watch For:
- Initial Pain: Dull pain starting near the navel or upper abdomen, which intensifies and shifts to the lower right abdomen.
- Appetite Loss: A noticeable decrease in appetite.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often occurring shortly after the abdominal pain begins.
- Abdominal Swelling: The abdomen may become distended or bloated.
- Inability to Pass Gas: Difficulty or inability to relieve gas.
- Fever: A mild fever ranging from 100–102˚F (37.7–38.8˚C).
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Diarrhea or constipation may occur.
If you experience pain that starts around your belly button and shifts to the right, especially accompanied by other appendicitis symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
2. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a frequent cause of left side abdominal pain, particularly in individuals over 40. It involves the inflammation or infection of diverticula, small pouches that can form in the lining of the large intestine, most commonly in the sigmoid colon located in the lower left abdomen.
Common Symptoms of Diverticulitis Include:
- Abdominal Pain: Often localized in the lower left abdomen, which can be persistent and range from mild to severe.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature indicating infection.
- Nausea: Feeling of sickness and urge to vomit.
- Bloating and Abdominal Swelling: Distention and discomfort in the abdomen.
- Stomach Cramping or Tenderness: Painful spasms or sensitivity to touch in the abdomen.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Painful bowel movements, constipation, or diarrhea.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
While mild cases of diverticulitis can often be managed with rest, dietary changes, and antibiotics, severe infections may necessitate hospitalization and even surgery. Consult your doctor if you suspect diverticulitis, especially if you experience persistent left side pain along with fever or nausea.
3. Constipation
Constipation, characterized by infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stools, is a common cause of abdominal discomfort and pain, which can sometimes be felt on the left side. It’s often triggered by factors like insufficient fiber intake, dehydration, and lack of physical activity.
Recognizable Symptoms of Constipation:
- Hard, Dry Stools: Difficulty passing bowel movements due to their consistency.
- Straining During Bowel Movements: Significant effort required to defecate.
- Abdominal Pain or Cramping: Discomfort and spasms in the abdomen.
- Feeling of Incomplete Bowel Evacuation: Sensation that the bowels are not fully emptied after a bowel movement.
Most cases of constipation are manageable with lifestyle adjustments like increasing fluid and fiber intake and engaging in regular exercise. Over-the-counter laxatives can also provide relief. However, if sharp lower left abdominal pain persists despite these measures, or if constipation is severe or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, seeking medical advice is recommended.
Continue reading: How to treat dehydration
4. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones, also known as nephrolithiasis, are solid masses formed from crystals that separate from the urine and build up on the inner surfaces of the kidneys. As these stones move through the urinary tract, they can cause intense pain, often felt in the side, back, or groin.
Typical Symptoms of Kidney Stones:
- Flank Pain: Severe pain in the side and back, often radiating to the lower abdomen and groin. This pain can be felt on either side depending on which kidney is affected, and can certainly present as left side pain if the stone is in the left kidney.
- Groin Pain: Pain that extends down into the groin area.
- Frequent Urination: Increased urge to urinate.
- Blood in Urine (Hematuria): Urine may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Accompanying the intense pain.
- Fever: Elevated temperature, especially if infection is present (101˚F (38.3˚C) or higher).
Kidney stone pain can be excruciating and often requires medical intervention for pain relief and to facilitate stone passage. If you experience unbearable pain, notice blood in your urine, or have other symptoms of kidney stone pain, seek immediate medical care, potentially at an emergency room.
5. Stomach Ulcers
Stomach ulcers, also known as gastric ulcers or peptic ulcers, are sores that develop on the lining of the stomach. They are often caused by bacterial infection (H. pylori) or the prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Stomach ulcers can cause pain in the upper abdomen, which may be felt on the left side.
Associated Symptoms of Stomach Ulcers:
- Upper Abdominal Pain: A gnawing or burning pain in the stomach area, potentially radiating to the left upper side.
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia): Discomfort or pain after eating.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach and throwing up.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased desire to eat.
- Feeling of Fullness: Feeling overly full after eating only a small amount.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained decrease in body weight.
Untreated stomach ulcers can lead to serious complications such as internal bleeding, anemia, and perforation of the stomach wall. If you experience symptoms suggestive of a stomach ulcer, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation and treatment.
6. Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
Gastroenteritis, commonly known as the stomach flu, is an infection of the digestive system, affecting the stomach and intestines. It’s usually caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites and is highly contagious. Gastroenteritis can cause abdominal cramps and pain, which may be felt throughout the abdomen, including the left side.
Typical Symptoms of Gastroenteritis:
- Abdominal Cramps and Pain: Spasms and discomfort in the abdomen, potentially felt on the left side.
- Diarrhea: Frequent, loose bowel movements, sometimes bloody.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
- Muscle Aches and Pains: Body aches.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak.
Gastroenteritis usually resolves on its own within a few days with rest and fluid intake to prevent dehydration. However, if symptoms are severe, persist beyond 48 hours, or if you suspect dehydration, medical attention is advisable.
7. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are chronic conditions that cause inflammation in the digestive tract. The two main types of IBD are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. IBD can cause pain in various parts of the abdomen, including the lower left side, depending on the location and extent of inflammation.
Common Signs and Symptoms of IBD:
- Abdominal Pain: Chronic or recurring pain, often in the lower left abdomen.
- Cramps and Bloating: Spasms and distention in the abdomen.
- Diarrhea: Frequent bowel movements, often bloody.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
- Lethargy (Fatigue): Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Unintentional Weight Loss: Weight loss without trying.
- Blood in Stool: Visible blood in bowel movements.
- Fever and Chills: Elevated temperature and shivering.
IBD is a chronic condition requiring ongoing medical management. If you experience persistent symptoms suggestive of IBD, consulting a doctor for diagnosis and treatment is essential. Treatment often involves medication, dietary modifications, and in some cases, surgery.
Common Causes of Left Abdominal Pain in Women
In addition to the general causes, women may experience left side abdominal pain due to conditions specific to their reproductive system:
1. Menstrual Cramps (Dysmenorrhea)
Menstrual cramps, or dysmenorrhea, are a common cause of lower left side pain experienced by women before and during their menstrual periods. These cramps are caused by uterine contractions as the uterus sheds its lining.
Typical Symptoms of Menstrual Cramps:
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Pain or cramping in the lower abdomen, often felt on the left side, but can be generalized.
- Lower Back Pain: Pain radiating to the lower back.
- Bloating and Swelling: Abdominal distention and fluid retention.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired.
- Headache: Pain in the head.
For most women, menstrual cramps are a manageable monthly occurrence. However, if cramps are severe, debilitating, or interfere with daily life, seeking medical advice is recommended. Doctors can suggest pain relief strategies, including over-the-counter pain relievers or hormonal birth control.
2. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside of the uterus. This misplaced tissue can affect various organs, including those in the pelvic region, and can cause significant pain, often felt in the lower left abdomen.
Common Symptoms of Endometriosis:
- Painful Periods (Dysmenorrhea): Severe pain during menstruation.
- Lower Back Pain: Pain in the lower back, possibly radiating to the left side.
- Abdominal Cramps: Painful spasms in the abdomen.
- Abnormal Bleeding: Spotting or bleeding between periods.
- Painful Intercourse (Dyspareunia): Discomfort during sexual activity.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Diarrhea or constipation, particularly during periods.
- Painful Urination (Dysuria): Discomfort when urinating.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving.
Endometriosis can be a painful and challenging condition. If you suspect you have endometriosis, seeking diagnosis and management from a healthcare professional is crucial. Treatment options range from pain medication and hormonal therapy to surgery.
3. Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries. Many ovarian cysts are small and cause no symptoms, resolving on their own. However, larger cysts or those that rupture can cause pelvic pain, which may be felt on the left side depending on which ovary is affected.
Potential Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts:
- Pelvic Pain: Pain in the lower abdomen, possibly localized to the left side.
- Painful Intercourse (Dyspareunia): Discomfort during sexual activity.
- Abdominal Bloating and Swelling: Distention and fluid retention in the abdomen.
- Pelvic Pressure: Feeling of heaviness or pressure in the pelvis.
- Urinary Issues: Difficulty urinating or frequent urination.
- Menstrual Cycle Changes: Spotting or heavier periods.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up.
- Painful Bowel Movements: Discomfort during defecation.
If you experience symptoms suggestive of ovarian cysts, consulting your doctor for evaluation and management is recommended. Treatment depends on the size and type of cyst, and may range from observation to medication or surgery.
Common Causes of Left Abdominal Pain in Men
Men can also experience left side abdominal pain due to conditions more prevalent in males:
1. Hernia
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue protrudes through a weakness in the surrounding muscle or tissue wall. Hernias can occur in various locations, and an abdominal hernia can cause pain and discomfort in the affected area, potentially on the left side.
Common Symptoms of a Hernia:
- Pain or Discomfort: Localized pain in the abdomen, possibly on the left side, which may worsen with straining or lifting.
- Visible Bulge: A noticeable lump or protrusion in the abdomen or groin area.
- Urinary or Bowel Issues: Difficulty urinating, passing gas, or having a bowel movement.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up (in more severe cases).
- Fever and Chills: Elevated temperature and shivering (if the hernia is strangulated or infected).
Hernias often require surgical repair. If you suspect you have a hernia, consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment options.
2. Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal hernias are a specific type of hernia occurring in the groin area. While they can affect women, they are significantly more common in men. An inguinal hernia happens when tissue, often part of the intestine, pushes through the inguinal canal in the groin. This can cause left side pain, particularly in the lower abdomen and groin.
Symptoms of an Inguinal Hernia are Similar to General Hernias and May Include:
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, possibly localized to the left side and groin.
- Groin Bulge: A noticeable lump in the groin area, which may be more prominent when standing or straining.
- Urinary or Bowel Issues: Difficulty urinating, passing gas, or having a bowel movement.
- Painful Coughing: Discomfort in the groin when coughing.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up (in severe cases).
Inguinal hernias typically require surgical repair to prevent complications. If you experience symptoms suggestive of an inguinal hernia, seek medical evaluation.
3. Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that occurs when the spermatic cord, which supplies blood to the testicle, twists. This twisting cuts off blood flow to the testicle and can cause sudden, severe pain, often felt in the abdomen and groin, potentially on the left side if the left testicle is affected.
Key Symptoms of Testicular Torsion:
- Severe Pain: Sudden and intense pain in the abdomen, groin, or testicle, often on the left side.
- Scrotal Swelling: Swelling of the scrotum.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick and throwing up.
- Fever and Chills: Elevated temperature and shivering.
Testicular torsion requires immediate medical attention and often surgery to untwist the spermatic cord and restore blood flow to the testicle. If you experience sudden, severe pain in your testicle or groin area, seek emergency medical care immediately.
When Should You Worry About Left Side Pain?
Occasional, mild left side pain is often related to gas or indigestion and usually resolves on its own. However, certain symptoms accompanying left side pain should prompt you to seek medical attention.
Seek Medical Help If You Experience Left Side Abdominal Pain With Any of the Following:
- Fever: Elevated body temperature.
- Persistent Nausea or Vomiting: Ongoing sickness and throwing up.
- Cold or Clammy Skin: Cool, moist skin.
- Rapid Breathing: Increased respiratory rate.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling faint or unsteady.
- Muscle Weakness: Loss of strength in muscles.
- Bloody Stools or Vomit: Presence of blood in bowel movements or vomit.
- Abdominal Pain Lasting More Than a Week: Prolonged discomfort.
- Severe or Worsening Pain: Pain that is intense or progressively getting worse.
Seek Prompt Care for Severe Left Side Pain
If you or someone you know is experiencing significant abdominal pain on the left side, or chest and stomach pain, it’s crucial to seek timely medical evaluation. Complete Care emergency rooms are equipped to provide rapid assessment and treatment. Our facilities offer advanced diagnostic tools, including ER imaging, to quickly identify the underlying cause of your left lower abdominal pain.
Don’t delay seeking help for concerning left side pain. Visit Complete Care for efficient and effective urgent care, avoiding the lengthy wait times often associated with traditional emergency rooms. We have conveniently located 24/7 ER facilities across Texas (Austin, Corpus Christi, Dallas/Fort Worth, East Texas, Lubbock, and San Antonio) and in Colorado Springs, ready to provide comprehensive care when you need it most.
Explore More Helpful Articles from Complete Care:
Share this on