Why Is My Keyboard Not Responding? This is a common frustration, and at WHY.EDU.VN, we understand how disruptive a non-responsive keyboard can be. Whether it’s a wired or wireless connection, a laptop or desktop, we’ll provide solutions to get you back on track, including checking connections, updating drivers, and cleaning tips, along with keyboard failure and connectivity issues.
1. Understanding the Reasons Behind a Non-Responsive Keyboard
A keyboard failing to respond can stem from a multitude of causes, ranging from simple connection issues to complex hardware failures. Understanding these potential causes is the first step toward resolving the problem.
1.1. Physical Connection Problems
The most basic cause of keyboard malfunction is a faulty physical connection.
-
Wired Keyboards: For USB or PS/2 keyboards, the cable itself might be damaged, or the port on the computer could be malfunctioning. Ensure the cable is securely plugged into both the keyboard and the computer. Try a different USB port to rule out a faulty port.
-
Wireless Keyboards: Wireless keyboards rely on Bluetooth or a USB receiver to communicate with the computer. The keyboard may not be properly paired, the batteries could be dead, or there might be interference disrupting the signal.
1.2. Software and Driver Issues
The keyboard’s software and drivers play a crucial role in enabling communication between the keyboard and the operating system.
- Outdated or Corrupted Drivers: Drivers are the software that allows your operating system to communicate with your hardware. If these drivers are outdated, corrupted, or incompatible, the keyboard may not function properly.
- Operating System Conflicts: Sometimes, operating system updates or changes can cause conflicts with the keyboard driver, leading to unresponsiveness.
1.3. Hardware Malfunctions
In some cases, the keyboard’s unresponsiveness may be due to a hardware failure.
- Internal Keyboard Damage: Accidental spills, drops, or general wear and tear can damage the internal components of the keyboard, leading to malfunction.
- Faulty Motherboard: In desktop computers, the motherboard is responsible for facilitating communication between all hardware components. If the motherboard has issues, it can affect the keyboard’s functionality.
1.4. System Conflicts and Settings
Certain system settings or conflicting programs can also interfere with the keyboard’s operation.
- Filter Keys or Sticky Keys: These accessibility features can sometimes cause unintended keyboard behavior, such as delayed or ignored keystrokes.
- Power Saving Settings: Power-saving settings may disable USB ports to conserve energy, which can affect the keyboard’s responsiveness.
1.5. Identifying Search Intent
Understanding why users search for “why is my keyboard not responding” helps tailor the solutions. Here are five potential search intents:
- Troubleshooting: Users want to fix their non-responsive keyboard quickly.
- Diagnosis: Users want to identify the cause of the problem.
- DIY Repair: Users want to attempt fixing the keyboard themselves.
- Warranty Check: Users want to know if the issue is covered under warranty.
- Replacement Advice: Users want recommendations for a new keyboard.
2. Initial Troubleshooting Steps
Before diving into more complex solutions, start with these basic troubleshooting steps to rule out common issues.
2.1. Check Physical Connections
- Wired Keyboard: Ensure the USB or PS/2 cable is securely plugged into both the keyboard and the computer. Try a different USB port on the computer. If using a USB hub, plug the keyboard directly into the computer.
- Wireless Keyboard: Verify that the keyboard is turned on. Check the batteries and replace them if necessary. Ensure the USB receiver is properly plugged into the computer. If using Bluetooth, ensure the keyboard is paired with the computer.
2.2. Restart Your Computer
A simple restart can often resolve temporary software glitches that may be causing the keyboard to malfunction.
- Save Your Work: Ensure you save any open documents or projects before restarting.
- Restart Process: Use the mouse to navigate to the Start menu (Windows) or the Apple menu (Mac) and select “Restart.”
2.3. Test on Another Computer
To determine if the problem lies with the keyboard itself or the computer, test the keyboard on another computer.
- Connect the Keyboard: Plug the keyboard into another computer.
- Test Functionality: Try typing in a text editor or any application to see if the keyboard responds.
- Interpret Results: If the keyboard works on another computer, the problem is likely with the original computer. If the keyboard still doesn’t work, it may be faulty.
2.4. Examine the Keyboard for Physical Damage
Inspect the keyboard for any signs of physical damage, such as spills, broken keys, or loose connections.
- Visual Inspection: Look for any visible damage to the keyboard, including cracks, broken keys, or signs of liquid damage.
- Key Stability: Gently press each key to check for stability. Loose or wobbly keys may indicate a mechanical issue.
3. Advanced Troubleshooting for Windows
If the initial steps don’t resolve the issue, these advanced troubleshooting techniques can help pinpoint and fix the problem on Windows systems.
3.1. Update or Reinstall Keyboard Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause keyboard malfunction. Updating or reinstalling the drivers can resolve this issue.
- Open Device Manager: Press the Windows key + X and select “Device Manager.”
- Locate Keyboards: Expand the “Keyboards” category.
- Update Driver: Right-click on your keyboard and select “Update driver.” Choose “Search automatically for drivers.”
- Reinstall Driver (if updating doesn’t work): Right-click on your keyboard and select “Uninstall device.” Restart your computer, and Windows will automatically reinstall the driver.
3.2. Check Filter Keys and Sticky Keys
Filter Keys and Sticky Keys are accessibility features that can sometimes interfere with normal keyboard operation.
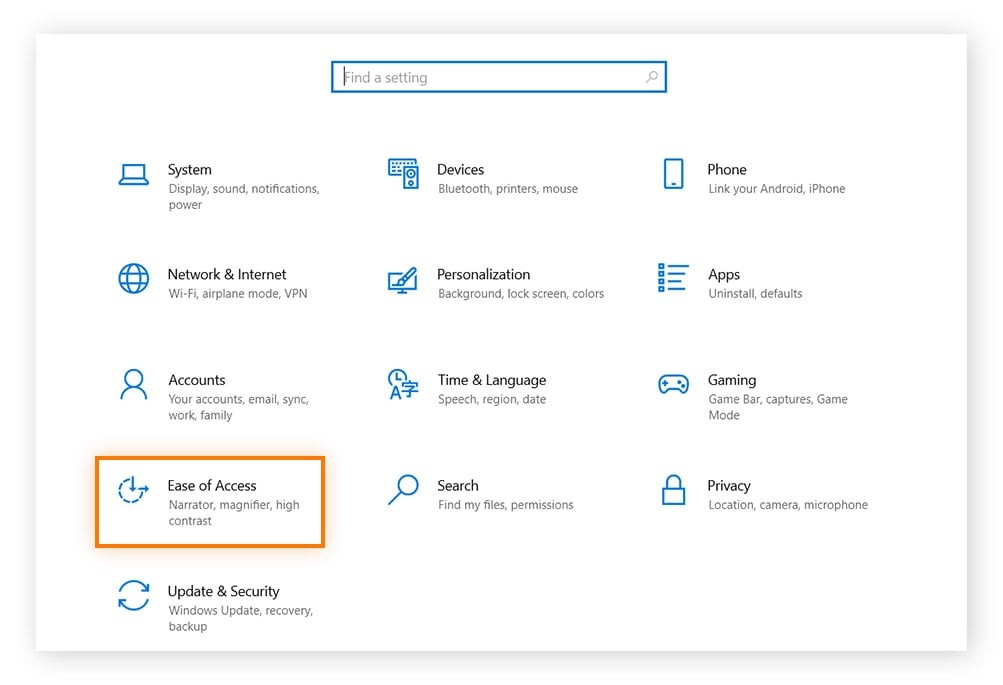
- Open Control Panel: Type “Control Panel” in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Access Ease of Access Center: Click on “Ease of Access” and then “Ease of Access Center.”
- Change Keyboard Settings: Click on “Make the keyboard easier to use.”
- Disable Filter Keys and Sticky Keys: Ensure that “Turn on Filter Keys” and “Turn on Sticky Keys” are unchecked.
3.3. Disable Fast Startup
Fast Startup can sometimes cause issues with hardware recognition. Disabling it may resolve keyboard problems.
- Open Control Panel: Type “Control Panel” in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Access Power Options: Click on “Hardware and Sound” and then “Power Options.”
- Choose Power Button Behavior: Click on “Choose what the power buttons do.”
- Change Unavailable Settings: Click on “Change settings that are currently unavailable.”
- Disable Fast Startup: Uncheck “Turn on fast startup (recommended).”
- Save Changes: Click “Save changes” and restart your computer.
3.4. System Restore
If the keyboard issue started after a recent system change, performing a system restore to a previous point may resolve the problem.
- Open System Restore: Type “System Restore” in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Choose a Restore Point: Select “Choose a different restore point” and click “Next.”
- Select a Restore Point: Choose a restore point before the keyboard issue started and click “Next.”
- Confirm and Start: Click “Finish” to start the system restore process.
3.5. Boot into Safe Mode
Booting into Safe Mode can help determine if third-party software is causing the keyboard malfunction.
- Open System Configuration: Press the Windows key + R, type “msconfig,” and press Enter.
- Boot Tab: Go to the “Boot” tab.
- Safe Boot: Check the “Safe boot” option and select “Minimal.”
- Apply and Restart: Click “Apply” and then “OK.” Restart your computer.
- Test Keyboard: If the keyboard works in Safe Mode, a third-party program is likely causing the issue.
4. Advanced Troubleshooting for macOS
For macOS users, these advanced techniques can help identify and fix keyboard-related problems.
4.1. Reset NVRAM/PRAM
Resetting NVRAM (Non-Volatile Random-Access Memory) or PRAM (Parameter Random-Access Memory) can resolve various hardware-related issues, including keyboard problems.
- Shut Down Your Mac: Turn off your Mac completely.
- Restart and Press Keys: Turn on your Mac and immediately press and hold the Option, Command, P, and R keys simultaneously.
- Release After Second Chime: Release the keys after you hear the second startup chime or see the Apple logo appear and disappear twice.
4.2. Check Keyboard Viewer
The Keyboard Viewer can help determine if the keyboard is sending the correct signals to the operating system.
- Open System Preferences: Click on the Apple menu and select “System Preferences.”
- Access Keyboard Settings: Click on “Keyboard.”
- Show Keyboard Viewer: Check the box next to “Show Keyboard, Emoji & Symbols Viewers in menu bar.”
- Open Keyboard Viewer: Click on the new icon in the menu bar and select “Show Keyboard Viewer.”
- Test Keys: Press keys on your physical keyboard and observe if they light up in the Keyboard Viewer.
4.3. Create a New User Account
Creating a new user account can help determine if the keyboard issue is specific to your user profile.
- Open System Preferences: Click on the Apple menu and select “System Preferences.”
- Access Users & Groups: Click on “Users & Groups.”
- Add a New User: Click the “+” button to add a new user account.
- Test Keyboard: Log in to the new user account and test the keyboard.
4.4. Boot into Safe Mode
Booting into Safe Mode can help identify if third-party software is causing the keyboard malfunction.
- Shut Down Your Mac: Turn off your Mac completely.
- Restart and Press Shift: Turn on your Mac and immediately press and hold the Shift key.
- Release When Login Window Appears: Release the Shift key when you see the login window.
- Test Keyboard: If the keyboard works in Safe Mode, a third-party program is likely causing the issue.
4.5. Reinstall macOS
As a last resort, reinstalling macOS can resolve deep-seated software issues that may be causing the keyboard to malfunction.
- Back Up Your Data: Back up your important files using Time Machine or another backup method.
- Boot into Recovery Mode: Restart your Mac and immediately press and hold the Command and R keys until you see the Apple logo.
- Reinstall macOS: Select “Reinstall macOS” from the macOS Utilities window and follow the on-screen instructions.
5. Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Regular cleaning and maintenance can prevent keyboard issues caused by dust, debris, and spills.
5.1. Regular Cleaning
- Turn Off and Unplug: Turn off your computer and unplug the keyboard.
- Invert and Shake: Turn the keyboard upside down and gently shake it to remove loose debris.
- Compressed Air: Use compressed air to blow out dust and debris from between the keys.
- Wipe Down: Use a slightly damp, lint-free cloth to wipe down the keyboard surface.
5.2. Dealing with Spills
- Immediately Unplug: Immediately unplug the keyboard to prevent electrical damage.
- Turn Upside Down: Turn the keyboard upside down to drain any liquid.
- Absorb Liquid: Use a clean cloth or paper towel to absorb as much liquid as possible.
- Clean Keys: Remove the keycaps and clean them with a mild soap and water solution.
- Dry Thoroughly: Allow all components to dry completely before reassembling the keyboard.
6. When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps and the keyboard still isn’t responding, it may be time to seek professional help.
6.1. Hardware Failure
If you suspect a hardware failure, such as a damaged circuit board or broken keys, a professional technician can diagnose and repair the keyboard.
6.2. Complex Software Issues
If you’re not comfortable performing advanced software troubleshooting, a professional can help identify and resolve complex system issues.
6.3. Warranty Considerations
If your keyboard is still under warranty, contact the manufacturer for repair or replacement options.
7. Choosing a New Keyboard
If your keyboard is beyond repair, here are some factors to consider when choosing a new keyboard.
7.1. Keyboard Type
- Mechanical Keyboards: Offer tactile feedback and durability, preferred by gamers and typists.
- Membrane Keyboards: More affordable and quieter, suitable for general use.
- Wireless Keyboards: Offer flexibility and convenience, ideal for clutter-free setups.
7.2. Ergonomics
- Ergonomic Keyboards: Designed to reduce strain and promote comfortable typing posture.
- Split Keyboards: Separate the keyboard into two halves to reduce wrist pronation.
7.3. Features
- Backlighting: Enhances visibility in low-light conditions.
- Programmable Keys: Allow customization for specific tasks and shortcuts.
- Media Controls: Provide convenient access to volume and playback controls.
8. Keyboard Shortcuts for Navigation
Even with a malfunctioning keyboard, using keyboard shortcuts can help you navigate your computer.
8.1. Basic Navigation
- Tab: Moves focus between selectable items.
- Shift + Tab: Moves focus backward between selectable items.
- Enter: Selects the focused item.
- Arrow Keys: Navigates menus and lists.
8.2. Windows Shortcuts
- Windows Key: Opens the Start menu.
- Windows Key + Tab: Opens Task View.
- Alt + Tab: Switches between open windows.
- Ctrl + Alt + Delete: Opens the security options screen.
8.3. macOS Shortcuts
- Command + Tab: Switches between open applications.
- Command + Spacebar: Opens Spotlight search.
- Control + F2: Moves focus to the menu bar.
- Control + F4: Closes the current window.
9. On-Screen Keyboard Solutions
If your physical keyboard is completely unresponsive, using an on-screen keyboard can provide a temporary solution.
9.1. Windows On-Screen Keyboard
- Open Settings: Use the mouse to navigate to the Start menu and select “Settings.”
- Access Ease of Access: Click on “Ease of Access.”
- Enable On-Screen Keyboard: Select “Keyboard” and turn on the “On-Screen Keyboard” option.
9.2. macOS Keyboard Viewer
- Open System Preferences: Click on the Apple menu and select “System Preferences.”
- Access Keyboard Settings: Click on “Keyboard.”
- Show Keyboard Viewer: Check the box next to “Show Keyboard, Emoji & Symbols Viewers in menu bar.”
- Open Keyboard Viewer: Click on the new icon in the menu bar and select “Show Keyboard Viewer.”
10. Optimizing Keyboard Settings for Efficiency
Customizing your keyboard settings can enhance your typing experience and increase productivity.
10.1. Adjusting Key Repeat Rate
- Windows: Open Control Panel, go to Keyboard, and adjust the “Repeat delay” and “Repeat rate” sliders.
- macOS: Open System Preferences, go to Keyboard, and adjust the “Key Repeat” and “Delay Until Repeat” sliders.
10.2. Creating Custom Shortcuts
- Windows: Use third-party software like AutoHotkey to create custom keyboard shortcuts.
- macOS: Open System Preferences, go to Keyboard, click on “Shortcuts,” and customize or add new shortcuts.
10.3. Using Text Expansion
- Windows: Use software like PhraseExpress to create text snippets that expand when you type a specific abbreviation.
- macOS: Go to System Preferences, click on Keyboard, select “Text,” and add new text replacements.
11. Common Keyboard Issues and Quick Fixes
Here are some common keyboard issues and their quick fixes.
11.1. Keys Not Responding
- Clean the Keyboard: Use compressed air to remove debris.
- Check Connections: Ensure the keyboard is properly connected.
- Update Drivers: Update or reinstall keyboard drivers.
11.2. Sticky Keys
- Disable Sticky Keys: Turn off the Sticky Keys feature in Accessibility settings.
- Clean the Keys: Remove keycaps and clean them.
11.3. Keyboard Typing Wrong Characters
- Check Language Settings: Ensure the correct language is selected.
- Update Drivers: Update keyboard drivers.
- Run Malware Scan: Malware can sometimes cause keyboard issues.
11.4. Keyboard Lag
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Reduce system load.
- Update Drivers: Update keyboard drivers.
- Check USB Port: Try a different USB port.
11.5. Wireless Keyboard Disconnecting
- Check Batteries: Replace batteries.
- Check Bluetooth Connection: Ensure Bluetooth is enabled and the keyboard is paired.
- Reduce Interference: Keep the keyboard close to the receiver and away from other wireless devices.
12. Utilizing WHY.EDU.VN for Expert Answers
Facing persistent keyboard issues? WHY.EDU.VN is here to provide expert assistance.
12.1. Ask Your Questions
Visit our website at WHY.EDU.VN and submit your specific questions regarding keyboard troubleshooting.
12.2. Connect with Experts
Our platform connects you with knowledgeable professionals who can offer tailored solutions to your unique problems.
12.3. Explore Existing Answers
Browse our extensive database of answered questions to find solutions to common keyboard issues and related topics.
13. Keyboard Layout Customization
Changing the keyboard layout can make typing more efficient and comfortable, especially for multilingual users or those with specific needs.
13.1. Changing Keyboard Layout on Windows
- Open Settings: Go to Start > Settings > Time & Language > Language.
- Add a Language: Click “Add a language” and choose the desired language.
- Select Keyboard Layout: Select the language, click “Options,” and add a keyboard layout.
- Switch Layouts: Use the language icon in the taskbar to switch between layouts.
13.2. Changing Keyboard Layout on macOS
- Open System Preferences: Go to System Preferences > Keyboard > Input Sources.
- Add Input Source: Click the “+” button and choose the desired language and layout.
- Show Input Menu: Check “Show Input menu in menu bar.”
- Switch Layouts: Use the input menu in the menu bar to switch between layouts.
14. Keyboard Accessibility Options
Accessibility options make keyboards easier to use for individuals with disabilities.
14.1. Sticky Keys
- Purpose: Allows modifier keys (Ctrl, Shift, Alt, Command) to remain active without being held down.
- Enable: Go to Accessibility settings and turn on Sticky Keys.
14.2. Filter Keys
- Purpose: Ignores brief or repeated keystrokes.
- Enable: Go to Accessibility settings and turn on Filter Keys.
14.3. Toggle Keys
- Purpose: Provides audio cues when Caps Lock, Num Lock, or Scroll Lock are activated.
- Enable: Go to Accessibility settings and turn on Toggle Keys.
15. Preventing Future Keyboard Issues
Taking proactive measures can help prevent future keyboard problems.
15.1. Regular Cleaning
- Frequency: Clean the keyboard at least once a month.
- Tools: Use compressed air, a soft brush, and a damp cloth.
15.2. Avoid Spills
- Keep Drinks Away: Keep drinks away from the keyboard.
- Use Keyboard Covers: Consider using a keyboard cover to protect against spills.
15.3. Proper Storage
- Store Properly: Store keyboards in a clean, dry place when not in use.
- Avoid Pressure: Avoid placing heavy objects on the keyboard.
16. Understanding Mechanical Keyboards
Mechanical keyboards are popular for their durability and tactile feedback.
16.1. Key Switches
- Types: Cherry MX, Gateron, and other switch types offer different tactile and auditory feedback.
- Customization: Switches can be replaced to customize the typing experience.
16.2. Keycaps
- Materials: ABS and PBT are common keycap materials with different textures and durability.
- Profiles: Different keycap profiles (e.g., OEM, Cherry) affect the typing feel.
16.3. Maintenance
- Cleaning: Remove keycaps and clean them regularly.
- Lubrication: Lubricate switches to improve smoothness and reduce noise.
17. Ergonomic Keyboard Setup
Proper ergonomic setup can prevent strain and discomfort.
17.1. Keyboard Position
- Placement: Position the keyboard directly in front of you.
- Elbow Angle: Maintain a 90-degree angle at the elbows.
17.2. Wrist Support
- Wrist Rest: Use a wrist rest to support your wrists.
- Neutral Position: Keep wrists in a neutral, straight position.
17.3. Monitor Height
- Eye Level: Position the monitor at eye level.
- Distance: Maintain an arm’s length distance from the monitor.
18. The Future of Keyboard Technology
Keyboard technology continues to evolve with innovative designs and features.
18.1. Wireless Technology
- Bluetooth 5.0: Offers improved connectivity and range.
- Low Latency: Reduced latency for faster response times.
18.2. Customization
- Programmable Keyboards: Allow users to customize key assignments and macros.
- RGB Lighting: Customizable lighting effects for visual appeal.
18.3. Alternative Input Methods
- Voice Recognition: Voice-to-text software for hands-free typing.
- Gesture Control: Keyboards with gesture recognition for additional functionality.
19. Economic Impact of Keyboard Malfunctions
Keyboard malfunctions can lead to productivity loss and economic impact.
19.1. Productivity Loss
- Downtime: Time spent troubleshooting and repairing keyboards.
- Reduced Efficiency: Slower typing speeds and increased errors.
19.2. Repair and Replacement Costs
- Repair Costs: Costs associated with professional repair services.
- Replacement Costs: Costs of purchasing new keyboards.
19.3. Business Impact
- Employee Productivity: Impact on employee productivity and efficiency.
- Customer Service: Delays in customer service due to keyboard issues.
20. Community Support and Forums
Online communities and forums can provide valuable support and solutions.
20.1. Online Forums
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/keyboards and r/techsupport offer community support.
- Tom’s Hardware: Provides forums for discussing hardware issues.
20.2. Manufacturer Support
- Official Forums: Check the manufacturer’s website for official support forums.
- Knowledge Bases: Access knowledge bases and FAQs for common issues.
20.3. Social Media
- Twitter: Use hashtags like #techsupport to seek help from the tech community.
- Facebook Groups: Join tech support groups for community assistance.
21. Common Myths About Keyboards
There are several misconceptions about keyboards that need clarification.
21.1. Myth: More Expensive Keyboards Are Always Better
- Reality: Price doesn’t always equate to better performance. Consider your specific needs and research before purchasing.
21.2. Myth: Wireless Keyboards Are Less Reliable
- Reality: Modern wireless keyboards offer reliable connections with minimal latency.
21.3. Myth: Mechanical Keyboards Are Only for Gamers
- Reality: Mechanical keyboards are excellent for anyone who types frequently and appreciates tactile feedback.
22. Step-by-Step Guide: Keyboard Disassembly and Cleaning
For thorough cleaning, disassembling the keyboard can be beneficial.
22.1. Gather Tools
- Keycap Puller: For removing keycaps.
- Screwdriver: For disassembling the keyboard.
- Compressed Air: For blowing out dust and debris.
- Cleaning Solution: Mild soap and water.
- Microfiber Cloth: For wiping surfaces.
22.2. Remove Keycaps
- Use Keycap Puller: Gently remove each keycap using a keycap puller.
- Organize Keycaps: Keep the keycaps organized to facilitate reassembly.
22.3. Disassemble Keyboard
- Remove Screws: Turn the keyboard over and remove all screws.
- Separate Components: Carefully separate the keyboard’s top and bottom halves.
22.4. Clean Components
- Vacuum Debris: Use a vacuum cleaner to remove loose debris.
- Wipe Surfaces: Wipe all surfaces with a microfiber cloth and cleaning solution.
- Clean Keycaps: Wash keycaps with mild soap and water.
22.5. Reassemble Keyboard
- Dry Components: Ensure all components are completely dry.
- Reassemble Keyboard: Reassemble the keyboard and replace all screws.
- Replace Keycaps: Replace all keycaps.
23. The Impact of Posture on Keyboard Use
Maintaining good posture is essential for preventing discomfort and injuries during keyboard use.
23.1. Sitting Position
- Upright Posture: Sit upright with your back straight.
- Chair Support: Use a chair with good lumbar support.
23.2. Keyboard Height
- Elbow Angle: Adjust the keyboard height so your elbows are at a 90-degree angle.
- Wrist Position: Keep your wrists straight and neutral.
23.3. Monitor Position
- Eye Level: Position the monitor at eye level to prevent neck strain.
- Distance: Maintain an arm’s length distance from the monitor.
24. Understanding Keyboard Firmware
Firmware is the software embedded in the keyboard’s hardware that controls its functions.
24.1. What Is Keyboard Firmware?
- Definition: Firmware is the low-level software that controls the keyboard’s basic operations.
- Function: It manages key detection, signal processing, and communication with the computer.
24.2. Updating Keyboard Firmware
- Purpose: Updates can improve performance, fix bugs, and add new features.
- Process: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for updating the firmware.
24.3. Custom Firmware
- QMK Firmware: An open-source firmware for mechanical keyboards, allowing extensive customization.
- Customization: Users can customize key mappings, macros, and lighting effects.
25. Tips for Speed Typing and Accuracy
Improving your typing speed and accuracy can significantly enhance productivity.
25.1. Proper Finger Placement
- Home Row: Position your fingers on the home row (ASDF JKL;).
- Reach: Reach for keys with the appropriate fingers without moving your hands.
25.2. Touch Typing
- Practice: Practice touch typing to type without looking at the keyboard.
- Online Tools: Use online typing tutors and games.
25.3. Ergonomic Techniques
- Posture: Maintain good posture.
- Breaks: Take regular breaks to prevent strain.
26. Common Keyboard Acronyms and Terminology
Understanding keyboard terminology can help you communicate effectively about keyboard issues.
26.1. Common Acronyms
- USB: Universal Serial Bus.
- PS/2: Personal System/2.
- LED: Light Emitting Diode.
- RGB: Red, Green, Blue.
26.2. Key Terminology
- Keycap: The plastic cover on top of a key.
- Switch: The mechanism under each key that registers the keystroke.
- Firmware: The software embedded in the keyboard’s hardware.
- Layout: The arrangement of keys on the keyboard.
27. How Environmental Factors Affect Keyboards
Environmental conditions can impact keyboard performance and longevity.
27.1. Temperature and Humidity
- Extreme Temperatures: Avoid exposing keyboards to extreme temperatures.
- Humidity: High humidity can cause corrosion and damage to internal components.
27.2. Dust and Debris
- Dust Buildup: Regular cleaning is essential to prevent dust buildup.
- Workspace Cleanliness: Keep your workspace clean to minimize debris.
27.3. Direct Sunlight
- UV Exposure: Avoid exposing keyboards to direct sunlight for extended periods.
- Fading: UV exposure can cause keycaps to fade and discolor.
28. Keyboard Innovations for Gamers
Gaming keyboards offer specialized features to enhance the gaming experience.
28.1. Anti-Ghosting
- Purpose: Ensures that multiple keystrokes are registered simultaneously.
- Function: Prevents key lockout when pressing multiple keys at once.
28.2. Macro Keys
- Purpose: Allow gamers to assign complex commands to a single key.
- Customization: Macros can be customized to perform various in-game actions.
28.3. RGB Lighting
- Customization: Offers customizable lighting effects.
- Synchronization: Can synchronize lighting with in-game events.
29. Assistive Technology for Keyboard Use
Assistive technology helps individuals with disabilities use keyboards more effectively.
29.1. On-Screen Keyboards
- Purpose: Provides a virtual keyboard that can be operated with a mouse or other input device.
- Accessibility: Useful for individuals with limited mobility.
29.2. Voice Recognition Software
- Purpose: Allows users to type using their voice.
- Accessibility: Useful for individuals with limited hand function.
29.3. Head Tracking Systems
- Purpose: Allows users to control the cursor and type using head movements.
- Accessibility: Useful for individuals with severe motor impairments.
30. Ethical Considerations in Keyboard Production
Ethical considerations play a role in keyboard manufacturing and disposal.
30.1. Labor Practices
- Fair Wages: Ensuring fair wages and working conditions for factory workers.
- Safe Environment: Providing a safe working environment.
30.2. Environmental Impact
- Sustainable Materials: Using sustainable and recyclable materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption during manufacturing.
30.3. E-Waste Disposal
- Proper Disposal: Encouraging proper disposal of e-waste to prevent environmental damage.
- Recycling Programs: Supporting recycling programs for electronic components.
At why.edu.vn, we aim to provide comprehensive and reliable solutions to all your tech-related questions. If you’re still wondering, “why is my keyboard not responding?” visit us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let our experts guide you towards a quick and effective resolution.