Why Is Mexico So Poor? This is a question that prompts exploration into the nation’s historical, geographical, political, and socioeconomic dynamics. At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into this multifaceted issue, providing insights that go beyond simple explanations. Understand Mexico’s poverty challenges, income inequality, and economic development through our expert analysis.
1. Geographic and Historical Challenges
Mexico’s path to economic prosperity has been significantly influenced by its geographic features and historical events.
1.1 The Geographic Fortress and Its Weakness
Mexico’s geography presents a paradox. Initially appearing as a fortress, it boasts a central population core, protective coastlines, strong mountain ranges, and inhospitable deserts to the north and dense jungles to the south.
- Central Population Core: Concentrated in the middle of the country.
- Coastlines: Protected by the sea and ocean on both sides.
- Mountain Ranges: Defending the country.
- Northern Deserts: One of the most inhospitable deserts in North America.
- Southern Jungles: Dense jungles bordering Guatemala and Belize.
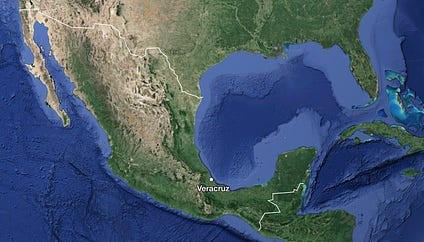
However, this “geographic fortress” has a critical weakness: Veracruz.
1.2 Veracruz: Mexico’s Achilles Heel
For 400 years, Veracruz was Mexico’s primary port on the Gulf of Mexico due to its deeper waters. Yet, it is not an ideal natural deep-water port.
It’s a bad anchorage among sand banks.— Alexander von Humboldt, 1988, Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain.
The port is very insecure. It is not only open to this wind… No vessel is considered secure, unless made fast to rings fixed in the castle wall.—Joel Roberts Pinsett, 1969, Notes on Mexico Made in the Autumn of 1822.
Veracruz’s proximity to Mexico City (CDMX), only 400 km away, makes it a vulnerable point. Its flat terrain and poor natural defenses have historically exposed Mexico City to invasions.
Mexico has been invaded via Veracruz six times, with invaders conquering the capital on three occasions. Notable instances include:
- Hernán Cortés: Used Veracruz to conquer Tenochtitlan.
- The French: Landed in Veracruz in the 1860s, eventually controlling Mexico City.
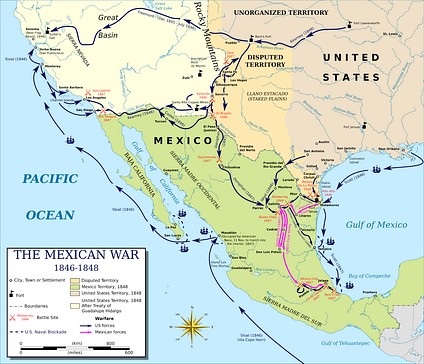
- The U.S. Attack: The U.S. attacked Veracruz in 1847, leading to the loss of 55% of Mexican territory after reaching Mexico City.
This vulnerability has made it difficult for Mexico to control sea access to the Gulf of Mexico, limiting its geostrategic independence.
1.3 The Impact of Geography
| Geographic Feature | Impact on Mexico’s Development |
|---|---|
| Mountainous Terrain | Makes transportation and infrastructure development challenging, hindering trade and economic integration. |
| Arid and Semi-Arid Lands | Limits agricultural productivity, impacting food security and rural incomes. |
| Coastal Vulnerability | Exposure to hurricanes and other natural disasters, causing economic disruption and requiring resources for recovery. |
1.4 Loss of Territory to the United States
One of the most significant historical factors contributing to Mexico’s poverty is the loss of over half its territory to the United States in the 19th century. The Mexican-American War (1846-1848) resulted in Mexico ceding territories that now comprise California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, and parts of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Wyoming. This land contained valuable resources such as minerals and arable land. Losing these resources significantly stunted Mexico’s potential for economic growth.
1.5 Legacy of Colonialism
The legacy of Spanish colonialism also plays a significant role. For three centuries, Spain extracted vast amounts of wealth from Mexico in the form of silver, gold, and other resources. This exploitation left Mexico with a legacy of inequality and underdevelopment. The colonial structure created a system where a small elite controlled most of the wealth, while the indigenous population was marginalized and impoverished.
1.6 Dependence on a Powerful Neighbor
Mexico’s relationship with the United States, its northern neighbor, significantly impacts its economic and political landscape.
- The U.S. controls Florida and neutralizes Cuba.
- The U.S. dominates global seas.
- The U.S. supported the independence of Texas and seized 55% of Mexico’s land in the 19th century.
- The U.S. is a short distance from Veracruz and Mexico City.
- The U.S. boasts one of the best geographies globally, particularly with the Mississippi River Basin.
This dynamic forces Mexico into a subordinate partnership with the U.S., limiting its geostrategic independence.
2. Economic and Political Factors Contributing to Poverty
Several economic and political factors contribute to Mexico’s persistent poverty.
2.1 Income Inequality
Mexico has one of the highest levels of income inequality among OECD countries. According to the World Bank, the richest 10% of the population hold a disproportionately large share of the country’s wealth. This disparity limits social mobility and perpetuates poverty among marginalized communities.
2.2 Corruption and Governance
Corruption remains a significant obstacle to economic development in Mexico. Transparency International’s Corruption Perception Index consistently ranks Mexico low, indicating widespread corruption in the public sector. Corruption diverts resources away from essential services, undermines the rule of law, and discourages foreign investment, all of which exacerbate poverty.
2.3 Education and Human Capital
Despite improvements in education, Mexico still lags behind other developed nations in terms of educational attainment and quality. According to UNESCO, a significant portion of the population lacks access to quality education, particularly in rural areas. This deficiency in human capital limits productivity and economic opportunities for many Mexicans.
2.4 Trade Policies and Economic Dependence
Mexico’s economic policies, particularly its dependence on trade with the United States, have had mixed results. While the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), now replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), has boosted trade, it has also exposed Mexican industries to competition, leading to job losses in some sectors. Additionally, reliance on remittances from Mexicans working abroad can create economic vulnerabilities.
2.5 Social Safety Nets
Mexico’s social safety nets are not always sufficient to alleviate poverty. Programs like Prospera provide conditional cash transfers to poor families, but their impact is limited by funding constraints and administrative challenges. Expanding and strengthening social safety nets is crucial for reducing poverty and inequality.
2.6 Land Ownership and Agriculture
Land ownership patterns in Mexico are highly unequal. A significant portion of arable land is controlled by a small number of large landowners, while many small farmers lack access to sufficient land to support their families. This inequality in land ownership contributes to rural poverty and food insecurity.
2.7 The Informal Economy
A large segment of Mexico’s workforce is employed in the informal economy, which includes jobs that are not regulated or taxed. While the informal economy provides livelihoods for many, it also leaves workers vulnerable to exploitation and without access to social security benefits. Formalizing the economy is essential for improving working conditions and reducing poverty.
3. Social and Cultural Factors
Social and cultural factors also play a role in perpetuating poverty in Mexico.
3.1 Indigenous Populations
Indigenous populations in Mexico face disproportionately high rates of poverty and discrimination. According to the National Council for the Evaluation of Social Development Policy (CONEVAL), indigenous communities often lack access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Addressing the needs of indigenous populations is essential for achieving inclusive development.
3.2 Gender Inequality
Gender inequality is another significant factor contributing to poverty in Mexico. Women often face discrimination in the labor market, earning less than men for similar work and having fewer opportunities for advancement. Empowering women through education and economic opportunities is crucial for reducing poverty and promoting gender equality.
3.3 Regional Disparities
Mexico experiences significant regional disparities in poverty rates. Southern states like Chiapas and Oaxaca have much higher poverty rates than northern states like Nuevo León and Baja California. These regional disparities reflect differences in economic opportunities, infrastructure, and access to services. Addressing regional disparities requires targeted policies and investments.
4. Policy Recommendations for Reducing Poverty in Mexico
To effectively combat poverty in Mexico, a comprehensive and multifaceted approach is needed.
4.1 Strengthening Social Safety Nets
Expanding and improving social safety nets is essential for providing a safety net for the poor and vulnerable. This includes increasing funding for programs like Prospera and ensuring that they reach those who need them most.
4.2 Investing in Education
Investing in education is crucial for improving human capital and creating economic opportunities. This includes increasing access to quality education, particularly in rural areas, and improving the relevance of education to the needs of the labor market.
4.3 Combating Corruption
Combating corruption is essential for improving governance and creating a level playing field for businesses. This includes strengthening anti-corruption laws, increasing transparency in government, and holding corrupt officials accountable.
4.4 Promoting Inclusive Growth
Promoting inclusive growth is essential for ensuring that the benefits of economic development are shared by all segments of society. This includes promoting job creation, supporting small businesses, and investing in infrastructure in marginalized communities.
4.5 Empowering Indigenous Populations
Empowering indigenous populations requires addressing historical injustices and providing them with access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. This includes recognizing indigenous rights and promoting cultural preservation.
4.6 Promoting Gender Equality
Promoting gender equality is crucial for reducing poverty and promoting inclusive development. This includes enacting laws that protect women’s rights, promoting equal pay for equal work, and increasing women’s access to education and economic opportunities.
4.7 Addressing Regional Disparities
Addressing regional disparities requires targeted policies and investments that focus on the needs of marginalized regions. This includes investing in infrastructure, promoting economic diversification, and improving access to services.
5. Mexico’s Economic Trajectory: A Closer Look
Mexico’s economic progress is intertwined with global economic shifts and its own internal policies. Understanding its trajectory requires a detailed analysis of various sectors and their impact on the nation’s wealth.
5.1 Key Economic Sectors
Mexico’s economy is diversified, with key sectors including manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, and services. The manufacturing sector, particularly automotive and electronics, has been a major driver of growth, benefiting from its proximity to the United States. The agricultural sector employs a significant portion of the population, especially in rural areas, while tourism generates substantial revenue and employment.
5.2 Trade and Global Integration
Mexico’s trade relationships, especially with the United States, are crucial to its economy. The USMCA agreement aims to modernize trade relations, but also presents challenges for certain sectors. Balancing trade benefits and protecting domestic industries is an ongoing challenge for Mexico.
5.3 Government Initiatives
The Mexican government has implemented various initiatives to promote economic development, including infrastructure projects, tax reforms, and programs to support small businesses. The effectiveness of these initiatives depends on their design, implementation, and the broader economic context.
| Government Initiative | Description | Impact on Poverty Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Projects | Investments in roads, railways, and ports to improve connectivity and facilitate trade. | Can create jobs, improve access to markets, and reduce transportation costs, but may also lead to displacement. |
| Tax Reforms | Changes to the tax system to increase government revenue and promote investment. | Can fund social programs and infrastructure projects, but may also burden businesses and reduce competitiveness. |
| Support for SMEs | Programs to provide financing, training, and technical assistance to small and medium-sized enterprises. | Can create jobs, stimulate innovation, and promote entrepreneurship, but may also face challenges in reaching target groups. |
5.4 Global Economic Factors
Global economic factors, such as commodity prices, exchange rates, and global demand, can significantly impact Mexico’s economy. Fluctuations in these factors can affect export revenues, investment flows, and overall economic growth.
6. Real Stories: The Human Impact of Poverty
To truly understand the complexities of poverty in Mexico, it’s essential to look at the real stories of individuals and communities affected by it.
6.1 Voices from Rural Communities
In rural areas, poverty is often linked to lack of access to land, education, and healthcare. Many small farmers struggle to make a living due to low prices, lack of access to credit, and climate change. Indigenous communities face additional challenges, including discrimination and lack of recognition of their rights.
6.2 Experiences in Urban Slums
Urban slums in Mexico are home to millions of people who lack access to basic services, such as water, sanitation, and electricity. Crime and violence are also prevalent in many urban slums, creating additional challenges for residents.
6.3 The Impact on Children
Poverty has a particularly devastating impact on children in Mexico. Many children are forced to work to support their families, missing out on education and opportunities for a better future. Malnutrition and lack of healthcare also affect children’s health and development.
6.4 Resilience and Hope
Despite the challenges they face, many Mexicans living in poverty demonstrate remarkable resilience and hope. They work hard to support their families, organize to improve their communities, and advocate for change. Their stories are a testament to the human spirit and the potential for progress.
7. Future Prospects: Can Mexico Overcome Poverty?
The question of whether Mexico can overcome poverty is complex, but there are reasons for optimism.
7.1 Economic Reforms
Economic reforms that promote inclusive growth, such as investments in education, infrastructure, and small businesses, can help reduce poverty and create economic opportunities.
7.2 Social Inclusion
Policies that promote social inclusion, such as addressing discrimination against indigenous populations and promoting gender equality, can help ensure that all segments of society benefit from economic development.
7.3 Good Governance
Good governance, including combating corruption and promoting transparency, is essential for creating a stable and predictable environment for businesses and investors.
7.4 International Cooperation
International cooperation, including trade agreements, development assistance, and knowledge sharing, can help Mexico address poverty and promote sustainable development.
7.5 Long-Term Vision
Overcoming poverty in Mexico requires a long-term vision and commitment from government, businesses, civil society, and international partners. By working together, it is possible to create a more prosperous and equitable future for all Mexicans.
8. The Role of WHY.EDU.VN in Understanding Mexico’s Poverty
At WHY.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing in-depth, accurate, and accessible information on complex issues like poverty in Mexico. Our team of experts is dedicated to researching and analyzing the root causes of poverty and identifying potential solutions.
8.1 Expert Analysis
Our articles and reports are based on rigorous research and analysis from leading experts in economics, sociology, and development studies. We strive to provide a balanced and nuanced perspective on the challenges and opportunities facing Mexico.
8.2 Accessible Information
We believe that information should be accessible to everyone, regardless of their background or education. That’s why we write in clear, concise language and use visual aids to illustrate complex concepts.
8.3 Interactive Platform
Our website provides an interactive platform for users to ask questions, share their experiences, and engage in discussions about poverty and other important issues. We believe that by fostering dialogue and collaboration, we can contribute to finding solutions.
8.4 Global Perspective
We offer a global perspective on poverty, drawing lessons from other countries and regions. By understanding what works and what doesn’t, we can help Mexico develop more effective strategies for reducing poverty and promoting sustainable development.
9. Conclusion: Towards a More Prosperous Mexico
Addressing the question of why Mexico is so poor requires a comprehensive understanding of its historical, geographical, economic, and social factors. By implementing effective policies, promoting inclusive growth, and fostering good governance, Mexico can overcome poverty and create a more prosperous future for all its citizens.
10. FAQ About Poverty in Mexico
- What are the main causes of poverty in Mexico?
The main causes include historical factors, income inequality, corruption, lack of education, and regional disparities. - How does Mexico’s relationship with the United States affect its economy?
Trade and economic dependence on the U.S. have mixed results, with both benefits and vulnerabilities. - What role does corruption play in perpetuating poverty?
Corruption diverts resources, undermines the rule of law, and discourages foreign investment, exacerbating poverty. - How do social safety nets in Mexico help alleviate poverty?
Programs like Prospera provide conditional cash transfers, but their impact is limited by funding and administrative challenges. - What is the impact of land ownership inequality on rural poverty?
Unequal land ownership limits access to resources for small farmers, contributing to rural poverty and food insecurity. - How does the informal economy contribute to poverty?
The informal economy leaves workers vulnerable to exploitation and without social security benefits. - Why do indigenous populations face higher rates of poverty?
Indigenous communities often lack access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities, facing discrimination. - How does gender inequality contribute to poverty?
Women face discrimination in the labor market, earning less and having fewer opportunities for advancement. - What are the main policy recommendations for reducing poverty in Mexico?
Recommendations include strengthening social safety nets, investing in education, combating corruption, and promoting inclusive growth. - What is WHY.EDU.VN’s role in understanding poverty in Mexico?
WHY.EDU.VN provides expert analysis, accessible information, and a global perspective on poverty in Mexico.
Do you have more questions about why Mexico is so poor or any other topic? Visit WHY.EDU.VN at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Our experts are ready to provide the answers you seek. Explore, learn, and discover with why.edu.vn.