Economic growth is a frequently discussed topic, but its true importance and implications are often misunderstood. At WHY.EDU.VN, we believe understanding economic growth, prosperity, and sustainability is crucial for making informed decisions about our future. This article delves into the multifaceted reasons Why Is Economic Growth Important, exploring its impact on societal well-being, state capacity, and overall development, while also considering inclusive development and income inequality.
1. Economic Growth: A Catalyst for Societal Advancement
Economic growth is not simply about increasing a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). It’s a fundamental driver of progress, acting as a catalyst for improvements across various facets of society. It enables states to improve resource allocation, increase living standards, and foster social well-being.
1.1. Enhanced State Capacity and Public Goods Provision
Economic growth provides states with the financial muscle to invest in crucial public goods and services. As economies expand, governments can collect more tax revenue, which can be channeled into vital sectors like healthcare, education, social protection, and infrastructure.
1.1.1. Healthcare Improvements
Increased funding for healthcare leads to better access to medical facilities, advanced treatments, and preventative care, ultimately improving public health outcomes and life expectancy. With economic development, governments can respond to medical emergencies more effectively.
1.1.2. Educational Opportunities
Investment in education enhances human capital, equipping citizens with the skills and knowledge necessary to participate in the modern economy. Quality education can also promote upward social mobility.
1.1.3. Robust Social Protection
Economic growth enables governments to implement stronger social safety nets, providing support to vulnerable populations and reducing poverty. Social welfare programs can improve social cohesion.
1.1.4. Infrastructure Development
Improved infrastructure, including roads, transportation, and communication networks, facilitates economic activity, connects communities, and improves overall quality of life. This in turn, facilitates higher economic growth rates.
1.2. Material Gains and Improved Living Standards
Inclusive economic expansion leads to a broader distribution of wealth, directly benefiting employers and workers. As people earn higher incomes, they can afford better housing, nutrition, and other essential goods and services, leading to improved living standards.
1.2.1. Poverty Reduction
Economic growth has historically been a key factor in reducing poverty rates globally. As economies expand, more job opportunities are created, providing individuals with the means to escape poverty and improve their socio-economic status.
1.2.2. Increased Consumer Spending
Higher incomes translate to increased consumer spending, which further fuels economic growth and creates a positive feedback loop. Consumer demand drives production and innovation, leading to more jobs and opportunities.
1.3. Historical Evidence of Growth’s Impact
Globally, countries that have achieved significant progress in poverty reduction and access to public goods have typically done so on the back of strong and sustained economic growth.
1.3.1. Case Studies of Successful Economies
Countries like South Korea, Singapore, and Taiwan have demonstrated the transformative power of economic growth, transitioning from developing nations to high-income economies within a few decades.
1.3.2. The Role of Policy and Investment
These success stories highlight the importance of sound economic policies, strategic investments in education and infrastructure, and a favorable business environment.
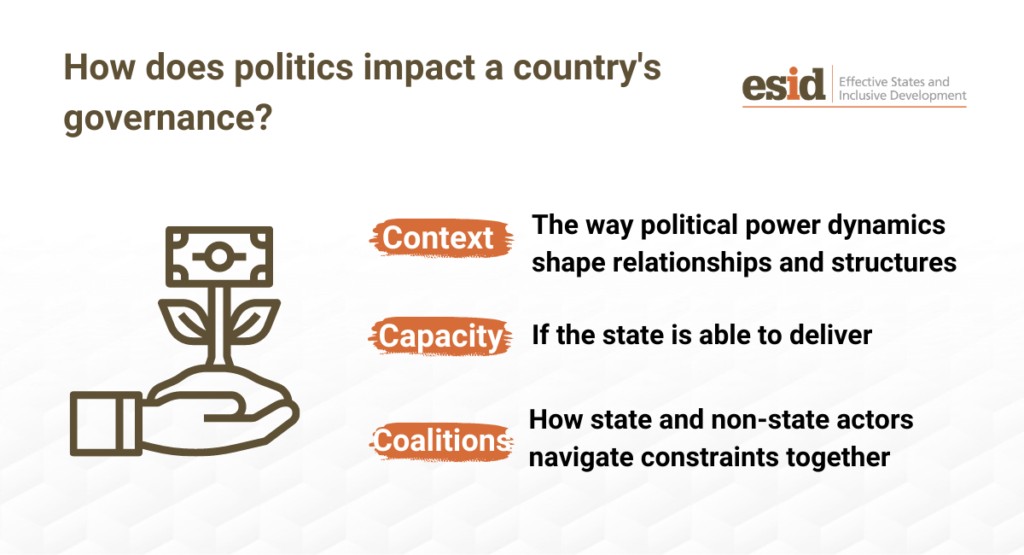
2. The Indispensable Role of Politics in Economic Growth
While economic policies are undoubtedly important, understanding the political landscape is equally crucial for comprehending why some countries experience sustained growth while others falter. At WHY.EDU.VN, we emphasize the interplay between economics and politics.
2.1. The Political Settlement Framework
ESID’s political settlement framework offers an integrated approach to understanding growth and governance, recognizing that the nature of a country’s political system significantly influences how growth occurs and how its benefits are distributed.
2.1.1. Distribution of Benefits
The political settlement determines whether the benefits of economic growth are concentrated among elite groups or more widely shared across society.
2.1.2. Consistency of Beneficiaries
It also influences whether the beneficiaries of growth remain consistent over time or change with shifts in the political landscape.
2.2. The Importance of Political Stability
Political stability is a prerequisite for sustained economic growth. Uncertainty and instability can deter investment, disrupt economic activity, and undermine investor confidence.
2.2.1. The Impact of Corruption
Corruption can distort resource allocation, undermine institutions, and create an uneven playing field, hindering economic growth and development.
2.2.2. The Rule of Law
A strong rule of law, characterized by impartial enforcement of contracts and protection of property rights, is essential for fostering a stable and predictable business environment.
2.3. Case Studies: Malaysia and Thailand
Malaysia and Thailand, once among the fastest-growing economies in Southeast Asia, experienced a slowdown after the East Asian financial crisis. This slowdown can be attributed, in part, to political settlements that prevented broader participation in economic activities necessary for sustained growth.
2.3.1. The Limits of Economic Policy
This example illustrates that economic policy alone is not sufficient to guarantee sustained growth. Shortcomings in economic policies can be compounded by unfavorable political settlements.
2.3.2. The Need for Inclusivity
For growth to be sustained, political settlements must evolve to allow for more open and participatory economic activity.
3. The Significance of Deals and Trust in Economic Transactions
Beyond formal institutions and regulations, the reliability of deals and agreements plays a critical role in fostering economic growth.
3.1. Ordered Deals: Building Investor Confidence
Ordered deals, characterized by trust and mutual agreement, are crucial for investors to feel confident in making investments. Without this confidence, economic progress can be slower and more fragmented.
3.1.1. Effective States and Commercial Agreements
Effective states are those that can offer ordered deals, ensuring that commercial agreements are honored and that both parties can trust the deal will proceed as agreed.
3.1.2. The Role of Government
The government plays a crucial role in creating an environment where deals can be reliably enforced and disputes can be resolved fairly.
3.2. Inclusive Deals: Broadening Participation
Inclusive deals, accessible to a wide range of investors and enterprises, are essential for fostering sustainable and inclusive growth.
3.2.1. Open Access to Opportunities
Development requires that deals evolve from closed to open, allowing a broader group of investors to participate, rather than just those connected to the government or political elite.
3.2.2. Structural Transformation
This transition is necessary for structural transformation and sustained inclusive growth.
3.3. The Pitfalls of Collusive Deals
While collusive deals, involving small groups of capitalists and those in power, can lead to rapid economic take-off, they can also create problems in the long run, hindering the conversion of growth into structural transformation.
3.3.1. The Importance of Competition
Competition is essential for driving innovation, improving efficiency, and ensuring that the benefits of growth are shared more broadly.
3.3.2. The Need for Transparency
Transparency in government procurement and contracting processes can help to prevent corruption and ensure that deals are awarded fairly.
4. Economic Growth as a Catalyst for Structural Transformation
Economic growth can spark significant social shifts, creating new economic opportunities, technologies, and ways of thinking.
4.1. The Evolution of Institutions and Social Relations
As society adapts to a new material status quo, growth can encourage the evolution of new forms of institutions and social relations.
4.1.1. Adaptation to Change
Societies must adapt to the changes brought about by economic growth, developing new skills, institutions, and social norms to thrive in a more complex and dynamic environment.
4.1.2. The Role of Innovation
Innovation is a key driver of structural transformation, leading to new products, services, and production processes that can boost productivity and create new jobs.
4.2. The Importance of Open Deals
Structural transformation occurs more frequently when deals are open and the benefits of growth are widely distributed.
4.2.1. The Interaction of Capitalists
Transformation requires the interaction of different capitalists with new technical abilities to exploit new areas and put labor to work on new things.
4.2.2. The Blocking Effect of Closed Deals
Closed deals are likely to block that transformative process, limiting opportunities for innovation and entrepreneurship.
4.3. Sustainability of Growth through Transformation
Structural transformation is important because it can make the gains of growth more sustainable. As economies move to produce higher-value goods and services, productivity increases, leading to more and better jobs.
4.3.1. Increased Productivity
Investment in technology and human capital can lead to significant increases in productivity, allowing countries to produce more goods and services with the same amount of resources.
4.3.2. Self-Sufficiency of Companies
Companies become more self-sufficient from a commercial point of view, rather than needing to rely on direct support from the state.
5. Navigating the Future of Economic Growth
Today, discussions around economic growth must consider sustainability and the need for targeted expansion in low-polluting, green sectors.
5.1. The Imperative of Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is no longer an optional add-on but a fundamental requirement for long-term economic growth.
5.1.1. Balancing Growth and Environment
Finding ways to balance economic growth with environmental protection is one of the biggest challenges facing policymakers today.
5.1.2. The Role of Technology
Technological innovation will be crucial for developing cleaner and more efficient ways to produce goods and services.
5.2. The Transition to Green Sectors
This may mean de-growth in some sectors, such as fossil fuels, as more environmental options are favored.
5.2.1. Investing in Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro, can create new jobs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
5.2.2. Promoting Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry can reduce energy consumption and lower carbon emissions.
5.3. The Dilemma of Untapped Resources
Should potential producers, sitting on untapped or mined reserves, even start to exploit those assets? Or is it recommended that they look to get ahead of the curve with a post-fossil fuel energy transition?
5.3.1. Strategic Planning for the Future
These are some of the big questions that will shape discussions around economic development for years to come.
5.3.2. The Importance of Adaptation
Countries that can adapt to the changing global landscape and embrace new technologies and business models will be best positioned for long-term economic success.
6. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Economic Growth
Economic growth is often subject to misconceptions and criticisms. Addressing these is essential for a balanced understanding.
6.1. Growth and Inequality
One common criticism is that economic growth exacerbates inequality. While growth can lead to increased inequality if not managed properly, it also provides opportunities to reduce poverty and improve living standards for all.
6.1.1. Progressive Taxation
Progressive taxation policies can help to redistribute wealth and ensure that the benefits of growth are shared more equitably.
6.1.2. Targeted Social Programs
Targeted social programs, such as cash transfers and job training, can help to lift vulnerable populations out of poverty and improve their economic opportunities.
6.2. Growth and Environmental Degradation
Another concern is that economic growth inevitably leads to environmental degradation. While this has been true in the past, it is not necessarily the case today.
6.2.1. Sustainable Development Practices
Sustainable development practices, such as investing in renewable energy and promoting energy efficiency, can help to minimize the environmental impact of economic growth.
6.2.2. Environmental Regulations
Strong environmental regulations can help to prevent pollution and protect natural resources.
6.3. Growth and Social Well-being
Some argue that economic growth does not necessarily translate into improved social well-being. While economic growth is not a panacea, it can provide the resources necessary to improve health, education, and other social outcomes.
6.3.1. Investing in Human Capital
Investing in human capital, such as education and healthcare, can improve social well-being and boost economic growth.
6.3.2. Promoting Social Inclusion
Promoting social inclusion, such as gender equality and equal opportunities for all, can help to ensure that the benefits of growth are shared more broadly.
7. The Role of Innovation and Technology in Driving Economic Growth
Innovation and technological advancements are critical drivers of economic growth in the modern era.
7.1. Technological Progress and Productivity
Technological progress leads to increased productivity, allowing businesses to produce more goods and services with the same amount of resources.
7.1.1. Automation and Efficiency
Automation and other technological advancements can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase output.
7.1.2. The Importance of Research and Development
Investing in research and development is essential for fostering innovation and technological progress.
7.2. The Digital Economy and New Opportunities
The digital economy has created new opportunities for economic growth, including e-commerce, online services, and digital platforms.
7.2.1. The Growth of E-commerce
E-commerce has made it easier for businesses to reach new customers and expand their markets.
7.2.2. The Rise of the Gig Economy
The rise of the gig economy has created new opportunities for flexible work arrangements and entrepreneurship.
7.3. The Importance of Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is essential for individuals and businesses to participate in the digital economy.
7.3.1. Bridging the Digital Divide
Bridging the digital divide, by providing access to technology and digital literacy training to underserved communities, can help to ensure that everyone benefits from the digital economy.
7.3.2. The Need for Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is also essential for protecting individuals and businesses from online threats.
8. The Importance of Education and Skills Development
Education and skills development are fundamental for economic growth and social progress.
8.1. Human Capital and Economic Productivity
A well-educated and skilled workforce is essential for economic productivity and innovation.
8.1.1. Investing in Education
Investing in education at all levels, from primary to higher education, can improve human capital and boost economic growth.
8.1.2. Promoting Lifelong Learning
Promoting lifelong learning can help individuals to adapt to changing job requirements and stay competitive in the global economy.
8.2. Skills for the 21st Century
Skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and collaboration are increasingly important in the modern workplace.
8.2.1. Adapting Education Systems
Education systems need to adapt to the changing needs of the economy, by focusing on developing these skills.
8.2.2. The Role of Vocational Training
Vocational training can provide individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in specific industries.
8.3. Addressing Skills Gaps
Addressing skills gaps, by providing training and education in high-demand areas, can help to reduce unemployment and boost economic growth.
8.3.1. Collaborating with Industry
Collaborating with industry to identify skills gaps and develop training programs can ensure that individuals are equipped with the skills that employers need.
8.3.2. The Importance of Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships can provide individuals with on-the-job training and experience, helping them to develop valuable skills.
9. The Impact of Globalization on Economic Growth
Globalization has had a profound impact on economic growth, creating new opportunities and challenges for countries around the world.
9.1. Increased Trade and Investment
Globalization has led to increased trade and investment, which can boost economic growth by creating new markets and opportunities for businesses.
9.1.1. The Benefits of Free Trade Agreements
Free trade agreements can reduce barriers to trade and investment, promoting economic growth and integration.
9.1.2. Attracting Foreign Investment
Attracting foreign investment can bring new capital, technology, and expertise to a country, boosting economic growth and development.
9.2. Global Supply Chains
Globalization has led to the development of global supply chains, which can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
9.2.1. The Importance of Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is essential for businesses to compete in the global economy.
9.2.2. The Risks of Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters or political instability, can have a significant impact on economic growth.
9.3. The Challenges of Globalization
Globalization also poses challenges, such as increased competition, income inequality, and job displacement.
9.3.1. Addressing Income Inequality
Addressing income inequality is essential for ensuring that the benefits of globalization are shared more broadly.
9.3.2. Supporting Displaced Workers
Supporting displaced workers, by providing training and education, can help them to find new jobs and adapt to the changing economy.
10. Measuring Economic Growth: Key Indicators and Metrics
Understanding how economic growth is measured is crucial for assessing progress and making informed policy decisions.
10.1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the most widely used measure of economic growth, representing the total value of goods and services produced in a country over a specific period.
10.1.1. Nominal GDP vs. Real GDP
Nominal GDP is measured in current prices, while real GDP is adjusted for inflation, providing a more accurate measure of economic growth.
10.1.2. GDP Growth Rate
The GDP growth rate is the percentage change in GDP from one period to another, indicating the pace of economic expansion or contraction.
10.2. Other Key Economic Indicators
Other key economic indicators include unemployment rate, inflation rate, interest rates, and trade balance.
10.2.1. Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate measures the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking work.
10.2.2. Inflation Rate
The inflation rate measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling.
10.2.3. Interest Rates
Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money, influencing investment and consumer spending.
10.2.4. Trade Balance
The trade balance is the difference between a country’s exports and imports, indicating its competitiveness in international trade.
10.3. Beyond GDP: Alternative Measures of Progress
While GDP is a valuable indicator, it does not capture all aspects of economic well-being and social progress.
10.3.1. Human Development Index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) combines measures of life expectancy, education, and income to provide a more comprehensive assessment of human development.
10.3.2. Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI)
The Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI) adjusts GDP to account for factors such as environmental degradation, income inequality, and unpaid work.
10.3.3. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for measuring progress towards a more sustainable and equitable future, encompassing a wide range of economic, social, and environmental indicators.
FAQ: Understanding the Importance of Economic Growth
Here are some frequently asked questions about why economic growth is important:
- Why is economic growth important for reducing poverty?
- Economic growth creates job opportunities and raises incomes, allowing individuals to escape poverty and improve their living standards.
- How does economic growth contribute to better healthcare?
- Economic growth generates tax revenue that can be used to fund healthcare systems, improve access to medical facilities, and promote public health.
- What role does education play in economic growth?
- Education enhances human capital, equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to participate in the modern economy and drive innovation.
- Why is political stability important for economic growth?
- Political stability creates a predictable environment for investment and economic activity, fostering investor confidence and long-term growth.
- How does innovation contribute to economic growth?
- Innovation leads to new products, services, and production processes, boosting productivity and creating new jobs and opportunities.
- What are the potential downsides of economic growth?
- Economic growth can lead to increased inequality, environmental degradation, and social disruption if not managed properly.
- How can countries ensure that economic growth is sustainable?
- Countries can promote sustainable economic growth by investing in renewable energy, promoting energy efficiency, and implementing strong environmental regulations.
- What is the role of globalization in economic growth?
- Globalization has increased trade and investment, creating new opportunities for economic growth, but also posing challenges such as increased competition and income inequality.
- How is economic growth measured?
- Economic growth is typically measured by the GDP growth rate, but other indicators such as unemployment rate, inflation rate, and trade balance are also important.
- What are some alternative measures of progress beyond GDP?
- Alternative measures of progress include the Human Development Index (HDI), the Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI), and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Economic growth is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon with far-reaching implications for society. By understanding its drivers, challenges, and potential benefits, we can work towards creating a more prosperous, sustainable, and equitable future for all. Remember, at WHY.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and insights you need to navigate the complexities of the modern world.
Are you curious to learn more or have specific questions about economic growth and its impact on your community or industry? Don’t hesitate to visit WHY.EDU.VN today. Our experts are ready to provide detailed answers and explore the topics that matter most to you.
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: why.edu.vn