Dry needling legality is a complex issue, sparking debate among healthcare professionals. This comprehensive guide from WHY.EDU.VN explores why the therapeutic technique faces restrictions in certain areas and examines the underlying legal and regulatory considerations. We aim to offer you clarity on dry needling regulations, dry needling restrictions, and dry needling controversies.
Table of Contents
- What is Dry Needling?
- States Where Dry Needling Is Banned
- Potential Risks: What Happens When Dry Needling Hits a Nerve?
- Reasons for Legal Restrictions and Controversy
- The Legal Status of Dry Needling: A Detailed Examination
- Navigating the Controversy: A Balanced Perspective
- FAQ: Common Questions About Dry Needling and Its Legality
- Conclusion: Ensuring Safe and Effective Patient Care
1. What is Dry Needling?
Dry needling is a technique utilized by healthcare professionals, most commonly physical therapists, to address myofascial pain, muscle tension, and musculoskeletal dysfunction. The procedure involves inserting a thin, sterile, filiform needle into trigger points within muscles. Unlike acupuncture, dry needling is based on Western medicine principles and focuses on stimulating specific anatomical points to elicit a therapeutic response, rather than balancing energy flow (Qi). The goal is to relieve pain, reduce muscle tension, and improve function.
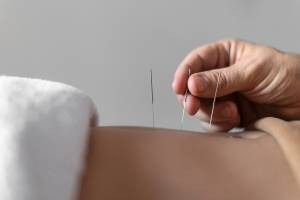 Dry Needling Procedure
Dry Needling Procedure
Dry needling aims to cause a local twitch response (LTR), a spinal cord reflex that causes the muscle fibers to contract. This response is thought to reset the muscle spindle and decrease pain.
2. States Where Dry Needling Is Banned
The legality of dry needling varies significantly across the United States. While many states permit licensed healthcare professionals, such as physical therapists and chiropractors, to perform dry needling within their scope of practice, a few states have explicitly banned or restricted the procedure. As of the latest information available, the states with the most stringent restrictions include:
- California
- Hawaii
- New York
- Oregon
- Washington
It’s crucial to note that legal regulations can change, so it is advisable to consult with relevant state licensing boards for the most up-to-date information. This variance underscores the ongoing debate and the need for standardized regulations concerning dry needling practices.
3. Potential Risks: What Happens When Dry Needling Hits a Nerve?
While dry needling is generally considered safe when performed by trained and qualified practitioners, there are potential risks involved. One significant concern is the possibility of the needle contacting or damaging a nerve. Here’s a breakdown of potential consequences:
- Immediate Pain and Discomfort: If a nerve is contacted, the patient may experience a sharp, shooting pain.
- Nerve Irritation or Damage: Depending on the severity of the contact, the nerve could become irritated, leading to prolonged pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness. In rare cases, nerve damage could be permanent.
- Inflammation and Swelling: Nerve irritation can trigger an inflammatory response in the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Potential Complications: Depending on the location and severity of the nerve injury, complications such as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) could develop, though this is rare.
Table 1: Potential Risks of Hitting a Nerve During Dry Needling
| Risk | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Pain | Sharp, shooting pain at the site of needle insertion. | Mild-Severe |
| Nerve Irritation | Prolonged pain, tingling, or numbness. | Mild-Moderate |
| Inflammation & Swelling | Inflammatory response around the affected nerve. | Mild-Moderate |
| Nerve Damage | Weakness, loss of function; potentially permanent (rare). | Severe |
| CRPS (Rare) | Chronic pain condition that can develop after nerve injury. | Severe |
Proper training in anatomy, needle placement, and safety protocols is crucial to minimize these risks. Practitioners must have a thorough understanding of nerve pathways and take precautions to avoid nerve contact.
4. Reasons for Legal Restrictions and Controversy
The legal status of dry needling is a subject of considerable debate and controversy within the healthcare community. Several factors contribute to the existing restrictions and differing opinions.
Scope of Practice
One of the primary reasons for the controversy lies in the scope of practice. Dry needling is often performed by physical therapists, chiropractors, and other healthcare professionals. However, some argue that the procedure falls within the scope of practice of acupuncture, which typically requires extensive training and certification. This overlap has led to disputes between different professional groups.
Opponents of allowing physical therapists and other non-acupuncturists to perform dry needling contend that it encroaches upon the expertise and training required for acupuncture, potentially compromising patient safety and outcomes. Conversely, proponents argue that dry needling is a distinct technique with a different theoretical basis and should be within the scope of practice for appropriately trained healthcare professionals.
Lack of Regulation
Another significant concern is the lack of standardized regulation for dry needling. Unlike acupuncture, which is typically governed by strict licensing requirements, the regulation of dry needling varies widely across different jurisdictions. Some states have specific guidelines and training requirements, while others have no regulations.
This lack of standardized training and oversight raises concerns about the qualifications of practitioners performing dry needling and the potential risks to patients. Without consistent standards, it can be difficult to ensure that practitioners have the necessary knowledge and skills to perform the procedure safely and effectively.
Safety Concerns
While proponents of dry needling emphasize its effectiveness in treating musculoskeletal pain, opponents raise questions about its safety, particularly when performed by inadequately trained practitioners. Improper needle insertion or inadequate sterilization techniques can lead to adverse events such as:
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Punctured organs (rare but serious)
- Bleeding
These safety concerns underscore the importance of proper training, technique, and adherence to safety protocols. Critics argue that without strict regulations and oversight, patients may be exposed to unnecessary risks.
5. The Legal Status of Dry Needling: A Detailed Examination
The legal framework surrounding dry needling is complex and varies significantly across different regions. Understanding the underlying issues that shape this landscape is crucial for both practitioners and patients.
Lack of Standardization
The absence of standardized training requirements and certification processes for dry needling is a major regulatory challenge. Unlike professions such as acupuncture or physical therapy, which have established educational pathways and licensure exams, dry needling lacks uniformity in training curricula and credentialing criteria.
This variability complicates efforts to establish clear regulatory guidelines and oversight mechanisms, leading to inconsistencies in practice standards across different jurisdictions. Accreditation bodies and professional organizations play a crucial role in establishing quality standards and promoting best practices in dry needling education.
Scope of Practice Concerns
The overlapping scope of practice between various healthcare professions further complicates the regulatory landscape of dry needling. In many regions, questions arise regarding which professionals are qualified to perform dry needling procedures and under what circumstances.
This uncertainty can lead to legal disputes among different healthcare disciplines, disrupting efforts to establish cohesive regulatory frameworks that prioritize patient safety and quality of care.
Credentialing and Accreditation
The absence of standardized credentialing processes for dry needling intensifies regulatory challenges, as practitioners may seek training from a wide range of sources with varying levels of rigor and supervision.
Accreditation bodies and professional organizations play a crucial role in establishing quality standards and promoting best practices in dry needling education. However, the proliferation of training programs with differing philosophies and methodologies poses challenges in ensuring consistent quality control and accountability.
Risk Management and Liability
Practitioners engaging in dry needling must navigate complex legal and ethical considerations related to risk management and liability. Concerns about adverse events, patient injuries, and malpractice claims emphasize the importance of comprehensive informed consent procedures, adequate malpractice insurance coverage, and adherence to established safety protocols.
However, the lack of general agreement on safety guidelines and risk mitigation strategies further complicates efforts to mitigate liability risks associated with dry needling practice.
Regulatory Variability
The regulatory landscape of dry needling exhibits significant variability across different regions, with some jurisdictions imposing stringent licensure requirements and others adopting more permissive approaches.
This discrepancy in regulations creates challenges for practitioners operating across multiple jurisdictions, as they must navigate divergent legal frameworks and compliance obligations. Harmonizing regulatory standards and promoting interstate or international reciprocity agreements can facilitate professional mobility while ensuring consistent standards of care.
Table 2: Regulatory Landscape of Dry Needling
| Aspect | Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Lack of uniform training & certification requirements. | Development of standardized curricula and credentialing criteria. |
| Scope of Practice | Overlapping scope between different healthcare professions. | Clear delineation of scope of practice for each profession, based on education and training. |
| Credentialing | Variability in rigor and supervision across training programs. | Accreditation of training programs by recognized bodies, ensuring consistent quality and accountability. |
| Risk Management | Concerns about adverse events, patient injuries, and malpractice claims. | Comprehensive informed consent procedures, adequate malpractice insurance coverage, and adherence to established safety protocols. |
| Regulatory Variability | Significant discrepancies in regulations across different regions/jurisdictions. | Harmonizing regulatory standards and promoting interstate or international reciprocity agreements to facilitate professional mobility while ensuring consistent standards of care. |
6. Navigating the Controversy: A Balanced Perspective
The debate surrounding the legality and appropriateness of dry needling is complex and multifaceted. It is essential to approach this issue with a balanced perspective, considering the potential benefits and risks, as well as the perspectives of different stakeholders.
Arguments in Favor of Dry Needling:
- Effective Pain Relief: Proponents argue that dry needling can be an effective treatment for myofascial pain, muscle tension, and other musculoskeletal conditions.
- Improved Function: By reducing pain and muscle tension, dry needling can improve range of motion, function, and overall quality of life.
- Non-Pharmacological Approach: Dry needling offers a non-pharmacological alternative to pain management, which may be appealing to patients who prefer to avoid medications or have contraindications to them.
- Complementary Therapy: Dry needling can be used as a complementary therapy in conjunction with other treatments, such as physical therapy, exercise, and manual therapy.
Arguments Against Dry Needling or for Stricter Regulation:
- Scope of Practice Concerns: As mentioned previously, some argue that dry needling falls within the scope of practice of acupuncture and should only be performed by licensed acupuncturists.
- Lack of Standardized Training: The lack of standardized training and regulation raises concerns about the qualifications of practitioners and the potential risks to patients.
- Safety Concerns: Improper needle insertion or inadequate sterilization techniques can lead to adverse events, such as infection, nerve damage, or punctured organs.
- Limited Evidence: Some critics argue that there is limited high-quality evidence to support the effectiveness of dry needling for certain conditions.
7. FAQ: Common Questions About Dry Needling and Its Legality
Here are some frequently asked questions about dry needling and its legal status:
- Is dry needling the same as acupuncture? No, while both involve inserting needles into the skin, they are based on different theoretical frameworks. Dry needling focuses on stimulating trigger points to relieve pain, while acupuncture aims to balance energy flow.
- Is dry needling safe? When performed by trained and qualified practitioners, dry needling is generally considered safe. However, there are potential risks, such as infection, nerve damage, and bleeding.
- What qualifications should a dry needling practitioner have? Ideally, practitioners should have extensive training in anatomy, physiology, and dry needling techniques. They should also be licensed healthcare professionals, such as physical therapists or chiropractors.
- How can I find a qualified dry needling practitioner? Ask your doctor or physical therapist for a referral, or check with your state licensing board to verify credentials.
- What are the potential side effects of dry needling? Common side effects include soreness, bruising, and mild bleeding at the needle insertion site. More serious side effects, such as infection or nerve damage, are rare.
- What conditions can dry needling treat? Dry needling is often used to treat myofascial pain, muscle tension, headaches, and other musculoskeletal conditions.
- Does insurance cover dry needling? Coverage varies depending on your insurance plan and the provider performing the procedure. Check with your insurance company to determine if dry needling is covered.
- Are there any contraindications to dry needling? Certain conditions, such as bleeding disorders, pregnancy, and active infections, may be contraindications to dry needling.
- What should I expect during a dry needling session? The practitioner will insert thin needles into specific trigger points. You may feel a brief twitch or ache. Sessions typically last 15-30 minutes.
- Where can I find more information about dry needling regulations in my state? Contact your state’s physical therapy or medical board for the most up-to-date information.
Table 3: Quick Guide to Dry Needling FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Dry needling vs acupuncture? | Different techniques; dry needling targets trigger points, acupuncture focuses on energy flow. |
| Is it safe? | Generally safe when performed by trained practitioners, but risks exist. |
| Practitioner qualifications? | Extensive training, licensed healthcare professional. |
| How to find a qualified practitioner? | Referrals, state licensing board verification. |
| Potential side effects? | Soreness, bruising; rare: infection, nerve damage. |
| Conditions treated? | Myofascial pain, muscle tension, musculoskeletal issues. |
| Insurance coverage? | Varies; check with your insurance company. |
| Contraindications? | Bleeding disorders, pregnancy, active infections. |
| What to expect during a session? | Needles inserted into trigger points; sessions last 15-30 minutes. |
| State regulations information? | Contact your state’s physical therapy or medical board. |
8. Conclusion: Ensuring Safe and Effective Patient Care
The debate surrounding the legality of dry needling reflects broader issues within the healthcare community regarding scope of practice, patient safety, and professional standards. While supporters argue for the benefits of integrating dry needling into clinical practice, opponents emphasize the importance of regulation and oversight to protect patients from potential harm.
Ultimately, resolving the controversy requires careful consideration of the evidence, stakeholder perspectives, and ethical considerations to ensure safe and effective patient care. Standardized training, clear regulatory guidelines, and ongoing research are essential to ensure that dry needling is practiced safely and effectively, and that patients receive the highest quality of care.
Are you still curious about dry needling or other healthcare topics? At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide detailed, easy-to-understand answers from experts. Whether you have questions about medical treatments, scientific breakthroughs, or any other subject, we’re here to help. Visit why.edu.vn today to ask your question and get the reliable answers you need. You can also reach us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let us help you explore the world with confidence!