Why doesn’t caffeine work on me? Discover the surprising reasons behind caffeine’s lack of effect and explore effective alternatives at WHY.EDU.VN. This guide provides insights into factors impacting caffeine sensitivity, offering strategies to boost your energy levels with sustainable methods and revealing potential health benefits. Let’s delve into the world of caffeine metabolism, adenosine receptors, and personalized energy solutions.
1. Unveiling the Mystery: Why Caffeine Has No Effect
Many individuals find themselves wondering, “Why doesn’t caffeine work on me?” despite consuming caffeinated beverages regularly. Several factors can contribute to this phenomenon, ranging from physiological tolerance to underlying health conditions. Understanding these reasons is crucial for finding effective strategies to boost your energy levels. Let’s explore these underlying causes:
1.1. High Sleep Debt Diminishes Caffeine’s Impact
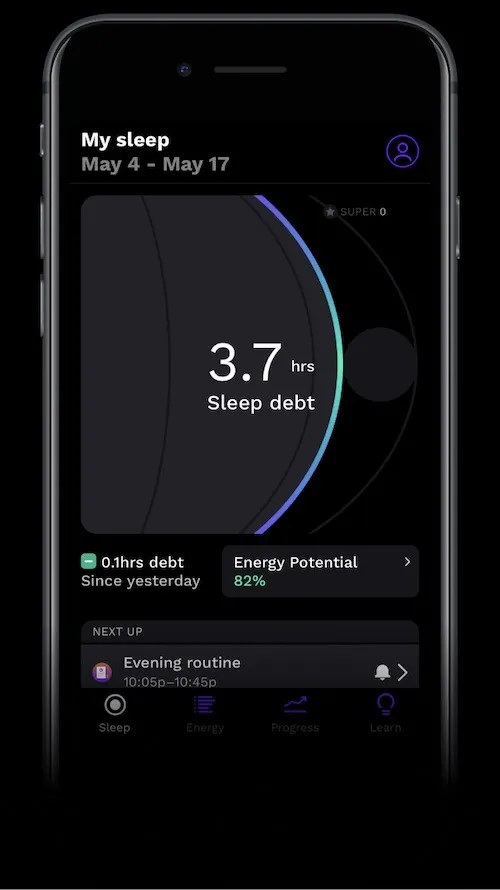 Person looking tired with a RISE app screenshot showing high sleep debt
Person looking tired with a RISE app screenshot showing high sleep debt
Alt text: Tired individual with high sleep debt shown on the RISE app.
Sleep debt, the cumulative amount of sleep you owe your body, significantly reduces caffeine’s effectiveness. A study showed that after three nights of restricted sleep (five hours per night), caffeine no longer provided a noticeable boost in alertness or performance. The RISE app can help you track your sleep debt and understand how it affects your energy levels.
Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal cognitive and physical function. When sleep deprived, the body accumulates adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleepiness. Caffeine temporarily blocks adenosine receptors in the brain, but if adenosine levels are excessively high due to chronic sleep deprivation, caffeine’s effects may be minimal.
1.2. Circadian Rhythm and Natural Energy Dips
Our internal body clock, the circadian rhythm, regulates our sleep-wake cycle and energy levels throughout the day. Natural dips in energy occur, particularly in the afternoon. Caffeine consumed during these dips may seem ineffective simply because the body is naturally inclined to feel sluggish. The RISE app can predict your circadian rhythm, helping you plan your day around your energy peaks and dips.
Alt text: Predicted energy peaks and dips on the RISE app.
While caffeine can temporarily mask the effects of these dips, it doesn’t alter the underlying circadian rhythm. Relying solely on caffeine to combat these natural fluctuations can lead to disrupted sleep patterns and increased sleep debt.
1.3. Caffeine Tolerance: The Body’s Adaptation
Regular caffeine consumption leads to tolerance, where the body adapts to the substance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects. A study showed that individuals who consistently consumed caffeine experienced reduced effects compared to those who took a placebo. Tolerance can develop within a few days, diminishing caffeine’s stimulating effects.
To combat caffeine tolerance, consider cycling your caffeine intake or taking periodic breaks. This allows your body to resensitize to caffeine, restoring its effectiveness.
1.4. Insufficient Caffeine Dosage
The amount of caffeine needed to produce a noticeable effect varies from person to person. Factors such as weight, age, and individual metabolism play a role. A 2019 meta-analysis indicated that higher caffeine doses may be more effective for some individuals.
Consider your body weight when determining your caffeine dosage. A general guideline is about 2 mg of caffeine per pound of body weight. However, it’s important to monitor your body’s response and adjust accordingly.
1.5. Genetic Predisposition and Caffeine Metabolism
Genetics significantly influence how individuals respond to caffeine. Some people have less “sticky” adenosine receptors, making it harder for caffeine to bind and block adenosine’s sleepiness effects. Enzymes in the liver, particularly CYP1A2, determine how quickly caffeine is metabolized. Variations in CYP1A2 can lead to faster or slower caffeine metabolism.
A meta-analysis concluded that genetics affect caffeine sensitivity, the likelihood of experiencing positive or negative effects, and the potential for developing tolerance or withdrawal symptoms.
1.6. Medication Interactions and Caffeine Absorption
Certain medications can interfere with caffeine metabolism, altering its effects. Some medications slow down caffeine metabolism, causing it to linger longer in your system, potentially leading to unwanted side effects.
Medications that can slow down caffeine metabolism include certain antibiotics, heartburn medications, high blood pressure medications, antifungal medications, estrogens, antidepressants, and diabetes medications. Additionally, alcohol can affect caffeine metabolism.
2. Strategies to Enhance Caffeine’s Effectiveness
If you’re seeking to regain caffeine’s stimulating effects, consider these strategies to optimize its impact:
2.1. Reduce Sleep Debt for Better Caffeine Response
Prioritizing sleep is essential for enhancing caffeine’s effectiveness. Aim to maintain a sleep debt below five hours. Strategies for reducing sleep debt include:
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate your circadian rhythm.
- Optimize Sleep Environment: Create a dark, quiet, and cool sleep environment.
- Wind-Down Routine: Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to prepare your body for sleep.
2.2. Reset Caffeine Tolerance for Enhanced Sensitivity
To regain caffeine sensitivity, gradually reduce your caffeine intake. Replace caffeinated beverages with decaffeinated alternatives, and avoid going “cold turkey” to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
2.3. Adjust Caffeine Dosage Based on Individual Needs
Experiment with different caffeine dosages to find the optimal amount that provides the desired effect without causing adverse reactions. Monitor your body’s response and adjust accordingly.
2.4. Time Caffeine Intake Strategically
Avoid consuming caffeine close to bedtime to prevent sleep disruption. Utilize the RISE app to determine your optimal caffeine cutoff time, allowing your body sufficient time to metabolize caffeine before sleep.
3. Caffeine-Free Alternatives for Sustained Energy
If caffeine isn’t working for you, explore these caffeine-free alternatives for sustained energy:
3.1. Exercise: A Natural Energy Booster
Regular physical activity increases heart rate and releases endorphins, enhancing energy levels and mood. Incorporate exercise into your daily routine for sustained energy throughout the day.
3.2. Natural Light Exposure for Circadian Rhythm Regulation
Exposure to natural light, particularly in the morning, helps suppress melatonin and regulate your circadian rhythm. Spend time outdoors or sit near a window to maximize light exposure.
3.3. Strategic Napping for Short-Term Energy Boost
Short naps (20-30 minutes) can provide a quick energy boost without causing grogginess. Napping can also help reduce sleep debt and improve overall alertness.
3.4. Cold Showers for Increased Alertness
Cold showers stimulate the body, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and metabolism. This can provide an immediate jolt of energy and improve alertness.
3.5. Balanced Diet and Hydration
Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide your body with essential nutrients for sustained energy. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
4. Understanding Caffeine: More Than Just an Energy Boost
Caffeine is a widely consumed stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate. It works by blocking adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleepiness. However, the effects of caffeine can vary significantly among individuals.
4.1. The Science Behind Caffeine’s Effects
Caffeine’s primary mechanism of action involves antagonizing adenosine receptors in the brain. By blocking these receptors, caffeine reduces the feeling of tiredness and promotes alertness. Additionally, caffeine can stimulate the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters, contributing to its mood-enhancing effects.
4.2. Potential Health Benefits of Caffeine
Beyond its energy-boosting properties, caffeine has been associated with several potential health benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Cognitive Function | Caffeine can enhance alertness, focus, and memory. |
| Enhanced Physical Performance | Caffeine can improve endurance, strength, and power during exercise. |
| Reduced Risk of Certain Diseases | Studies suggest caffeine may lower the risk of Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. |
| Antioxidant Properties | Caffeine contains antioxidants that can protect against cell damage. |
4.3. Potential Risks and Side Effects of Caffeine
While caffeine offers several benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and side effects:
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Anxiety and Jitters | Excessive caffeine intake can lead to anxiety, nervousness, and jitters. |
| Insomnia | Caffeine can interfere with sleep, leading to insomnia and daytime fatigue. |
| Digestive Issues | Caffeine can stimulate stomach acid production, potentially causing heartburn or other digestive problems. |
| Increased Heart Rate | Caffeine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which may be problematic for individuals with cardiovascular conditions. |
| Caffeine Dependence | Regular caffeine consumption can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation. |
| Medication Interactions | Caffeine can interact with certain medications, altering their effects. |
5. Navigating Caffeine Consumption: Tips for Optimal Use
To maximize the benefits of caffeine while minimizing potential risks, consider these tips:
5.1. Monitor Your Caffeine Intake
Pay attention to the amount of caffeine you consume from all sources, including coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate. Be mindful of serving sizes and caffeine content.
5.2. Time Your Caffeine Intake Strategically
Avoid consuming caffeine close to bedtime to prevent sleep disruption. Consume caffeine earlier in the day to align with your body’s natural energy patterns.
5.3. Stay Hydrated
Caffeine has a diuretic effect, meaning it can increase urine production. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and prevent dehydration.
5.4. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to how your body responds to caffeine. If you experience negative side effects, reduce your intake or discontinue use.
5.5. Consult with a Healthcare Professional
If you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications, consult with a healthcare professional before consuming caffeine.
6. Expert Insights on Caffeine and Energy Management
We consulted with leading experts in sleep science and nutrition to gather additional insights on caffeine and energy management:
6.1. Dr. Sarah Brewer, Registered Nutritionist
“Caffeine can be a useful tool for enhancing alertness and performance, but it’s important to use it judiciously. Prioritize sleep, hydration, and a balanced diet for sustained energy.”
6.2. Dr. Matthew Walker, Sleep Scientist
“Caffeine can mask the symptoms of sleep deprivation, but it doesn’t replace the need for adequate sleep. Chronic caffeine use can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to a vicious cycle of fatigue and dependence.”
6.3. Emily Carter, Certified Personal Trainer
“Caffeine can improve athletic performance, but it’s not a substitute for proper training and nutrition. Use caffeine strategically to enhance your workouts, but avoid overreliance on it.”
7. Addressing Common Concerns About Caffeine
Here are some frequently asked questions about caffeine:
7.1. Is Caffeine Addictive?
Yes, caffeine can be addictive. Regular consumption can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
7.2. How Long Does Caffeine Stay in Your System?
Caffeine has a half-life of about 5-6 hours. This means that half of the caffeine you consume will be eliminated from your body within that time frame.
7.3. Can Caffeine Interact With Medications?
Yes, caffeine can interact with certain medications, altering their effects. Consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
7.4. Is Decaf Coffee Caffeine-Free?
No, decaf coffee still contains a small amount of caffeine, typically about 2-12 mg per cup.
7.5. Can Caffeine Cause Anxiety?
Yes, excessive caffeine intake can lead to anxiety, nervousness, and jitters.
7.6. Is Caffeine Safe for Pregnant Women?
Pregnant women should limit their caffeine intake to no more than 200 mg per day.
7.7. Can Children Consume Caffeine?
Children are more sensitive to the effects of caffeine and should avoid it if possible.
7.8. Does Caffeine Affect Everyone the Same Way?
No, the effects of caffeine can vary significantly among individuals due to genetics, tolerance, and other factors.
7.9. Can Caffeine Help With Weight Loss?
Caffeine may promote weight loss by increasing metabolism and suppressing appetite, but it’s not a magic bullet.
7.10. What Are the Symptoms of Caffeine Withdrawal?
Symptoms of caffeine withdrawal can include headache, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
8. Real-Life Scenarios: Caffeine’s Impact on Daily Life
Let’s examine how caffeine affects different individuals in various scenarios:
8.1. The Student: Balancing Studies and Energy
Sarah, a college student, relies on caffeine to stay awake during late-night study sessions. However, she finds that caffeine disrupts her sleep, leading to daytime fatigue and reduced academic performance.
Solution: Sarah learns to manage her caffeine intake by avoiding it close to bedtime and prioritizing sleep. She also incorporates other energy-boosting strategies, such as exercise and healthy snacks.
8.2. The Office Worker: Combating the Afternoon Slump
John, an office worker, experiences a significant energy dip in the afternoon. He turns to caffeine to power through his work, but finds that it only provides a temporary fix and leads to jitters and anxiety.
Solution: John discovers that strategic napping and exposure to natural light help him combat the afternoon slump without relying solely on caffeine. He also adjusts his workload to align with his energy levels.
8.3. The Athlete: Enhancing Performance Safely
Maria, a marathon runner, uses caffeine to improve her endurance and performance. However, she’s concerned about the potential risks and side effects of caffeine.
Solution: Maria consults with a sports nutritionist to determine the optimal caffeine dosage for her needs. She also ensures that she stays hydrated and listens to her body to avoid overstimulation.
9. Seeking Personalized Solutions at WHY.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of caffeine and energy management can be challenging. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide personalized solutions to help you optimize your energy levels and overall well-being.
9.1. Expert Q&A Sessions
Participate in live Q&A sessions with our team of experts to get answers to your specific questions about caffeine, sleep, and energy management.
9.2. Personalized Assessments
Take our comprehensive assessments to identify factors that may be affecting your energy levels. Receive personalized recommendations based on your individual needs and goals.
9.3. Community Forums
Connect with other individuals who are seeking to optimize their energy levels. Share your experiences, ask questions, and learn from others.
9.4. Informative Articles and Resources
Access our extensive library of articles and resources on caffeine, sleep, nutrition, and other topics related to energy management.
9.5. Contact Information
For personalized assistance, contact us at:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
10. Embrace a Holistic Approach to Energy Management
Ultimately, managing your energy levels effectively requires a holistic approach that encompasses sleep, nutrition, exercise, and stress management. By understanding the factors that influence your energy and adopting healthy habits, you can achieve sustained energy and optimal well-being.
If you’re struggling to find answers to your questions about caffeine, sleep, and energy management, don’t hesitate to reach out to the experts at WHY.EDU.VN. We’re here to provide you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to thrive. Ask your questions and explore more answers at why.edu.vn today!