Why Does Russia Invade Ukraine? Explore the reasons behind the Russia-Ukraine conflict, its history, and the current situation. WHY.EDU.VN provides insightful analysis, examining geopolitical strategies, historical narratives, and the perspectives of key actors involved. Uncover the deep-rooted causes of the crisis, including security concerns, national identity, and geopolitical ambitions.
Understanding the intricacies of international conflicts can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex historical and political contexts. At WHY.EDU.VN, we strive to provide clear, concise, and well-researched answers to your questions. Dive into the multifaceted reasons behind the Russia-Ukraine conflict, a crisis shaped by a combination of historical grievances, geopolitical strategies, and national identity concerns. Keep reading to discover the facts or ask our experts for personalized assistance.
1. Unveiling the Core Reasons Behind Russia’s Invasion of Ukraine
When Russian President Vladimir Putin initiated the large-scale military operation in Ukraine, the stated goals were to “demilitarize and denazify” the country. However, the underlying motives are far more complex.
1.1. The “Demilitarization” and “Denazification” Narrative
Putin’s claim of “demilitarizing” Ukraine aimed to neutralize its military capabilities, preventing it from posing a threat to Russia. The assertion of “denazification” is a gross misrepresentation, falsely portraying Ukraine as a Nazi state. This narrative overlooks the fact that Ukraine’s government is democratically elected and has no ties to Nazism.
1.2. Historical Revisionism and Ukraine’s Identity
Putin has repeatedly questioned Ukraine’s legitimacy as an independent state, claiming that modern Ukraine was created by Russia. He has argued that Russians and Ukrainians are one people, disregarding Ukraine’s distinct cultural and historical identity. This historical revisionism serves to undermine Ukraine’s sovereignty and justify Russia’s actions.
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s address reflected a desire to redefine Ukraine’s historical narrative.
1.3. Geopolitical Ambitions and NATO Expansion
Russia views NATO’s eastward expansion as a direct threat to its security. The possibility of Ukraine joining NATO is considered a red line, as it would bring the alliance’s military infrastructure closer to Russia’s borders. Putin has long sought to push back against what he perceives as Western encroachment on Russia’s sphere of influence.
2. The Pursuit of Regime Change and Zelensky’s Role
Putin has long aimed to remove Ukraine’s pro-Western government, with President Volodymyr Zelensky being a primary target from the outset of the invasion.
2.1. Attempts to Overthrow Zelensky’s Government
Shortly after the invasion began, Russian troops made multiple attempts to storm the presidential compound, indicating a clear intention to depose Zelensky. The aim was to replace him with a pro-Russian figure, such as Viktor Medvedchuk, who was accused of treason in Ukraine.
2.2. Delegitimizing Zelensky and Disrupting Peace Talks
Even after years of conflict, Putin refuses to engage in direct peace talks with Zelensky, questioning his legitimacy as president. This narrative gained traction when Ukraine’s March 2024 presidential election was postponed due to martial law, a consequence of Russia’s ongoing war.
3. NATO Expansion: A Perceived Security Threat?
Putin has consistently voiced concerns about NATO’s eastward expansion, viewing it as an encroachment on Russia’s security interests.
3.1. Demands for NATO Withdrawal
Prior to the 2022 invasion, Russia demanded that NATO remove its multinational deployments from Central and Eastern European states that joined the alliance after 1997. This demand reflects Russia’s desire to revert to a pre-1997 security arrangement in Europe.
3.2. NATO’s Defensive Stance and Expansion Dynamics
NATO has always maintained that its purpose is defensive, with no aggressive intentions. The expansion of NATO, particularly with the addition of Sweden and Finland, is a direct response to the perceived threat posed by Russia’s actions.
The geographical expansion of NATO over time is perceived by Russia as an increasing threat to its borders.
3.3. Ukraine’s Aspirations and NATO’s Reluctance
While Ukraine’s constitution stipulates joining the European Union and NATO, there was no immediate prospect of this occurring when the full-scale war commenced. Zelensky has acknowledged NATO’s reluctance to accept Ukraine, highlighting the complex dynamics of the situation.
4. Debunking the Claims of Nazism and Genocide
Russia has repeatedly accused Ukraine of being a Nazi state and committing genocide in the eastern regions, but these claims lack factual basis.
4.1. False Allegations of Genocide
Putin has alleged that Ukraine has been engaging in “bullying and genocide” in the occupied areas of eastern Ukraine. However, no international body has recognized these claims as valid, and they have been widely dismissed as propaganda.
4.2. The Absence of Far-Right Influence in Ukraine’s Government
Contrary to Russian claims, there are no far-right parties represented in Ukraine’s parliament. Moreover, Zelensky himself is Jewish, and his family suffered during the Holocaust, making the accusations of Nazism absurd and offensive.
4.3. Condemnation of Putin’s Claims
The US Holocaust Memorial Museum has condemned Putin’s claims, stating that he has “misrepresented and misappropriated Holocaust history.” This condemnation underscores the baselessness of Russia’s accusations.
5. The Historical Context: A Timeline of Conflict
Russia’s efforts to keep Ukraine within its sphere of influence date back years, with the initial invasion occurring in 2014.
5.1. The 2014 Annexation of Crimea
In 2014, after months of mass demonstrations ousted pro-Russian President Viktor Yanukovych, Putin seized Ukraine’s Crimean peninsula and supported Russian proxies in occupying parts of the eastern Luhansk and Donetsk regions.
5.2. The Minsk Agreements: A Failed Attempt at Peace
Two attempts to halt the conflict, known as the Minsk agreements, were brokered by France, Germany, and Russia. However, these agreements ultimately failed to bring about a lasting peace, with both sides accusing each other of violations.
5.3. The Full-Scale Invasion of 2022
The failure of the Minsk agreements paved the way for Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022. This invasion marked a significant escalation of the conflict and has had devastating consequences for Ukraine.
6. The Current State of the War: A War of Attrition
After years of offensives and counter-offensives, the conflict between Russian and Ukrainian forces has devolved into a war of attrition.
6.1. Stalemate on the Front Lines
The active front line stretches over 1,000 kilometers (629 miles), with neither side making significant territorial gains. The war has become a grinding battle of attrition, with both sides suffering heavy losses.
6.2. Economic Impact on Russia and Ukraine
The war has had a significant impact on both Russia’s and Ukraine’s economies. Russia’s economy is strained by high interest rates, inflation, and increased defense spending. Ukraine has lost a significant portion of its economic wealth due to Russian occupation and destruction.
6.3. Human Cost of the War
The war has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths and has forced millions of Ukrainians to flee their homes. The conflict has created a humanitarian crisis of immense proportions, with long-lasting consequences for the region.
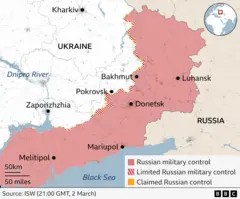
A visual representation of the areas in eastern Ukraine under Russian control, highlighting the ongoing territorial dispute.
7. The Devastating Human Toll of the Ukraine War
The conflict in Ukraine has resulted in staggering casualties and displacement, leaving a lasting impact on the nation’s population.
7.1. Military Casualties
While exact figures are difficult to ascertain, estimates suggest that tens of thousands of soldiers have lost their lives on both sides of the conflict. Ukraine’s president has spoken of 43,000 Ukrainian military deaths, but open source sites suggest the number is higher.
7.2. Civilian Casualties
According to the UN, more than 12,000 civilians have been killed in Ukraine since the start of the war. The actual number is likely much higher, as many casualties go unreported in areas of active fighting.
7.3. Displacement and Refugee Crisis
The war has forced millions of Ukrainians to flee their homes, with 6.9 million seeking refuge abroad and another 3.7 million internally displaced within Ukraine. This displacement has created a humanitarian crisis, with many people in need of food, shelter, and medical assistance.
8. Unraveling the Historical Ties Between Ukraine and Russia
To understand the conflict, it is crucial to examine the historical relationship between Ukraine and Russia.
8.1. Ukraine’s Soviet Past
From 1922 to 1991, Ukraine was part of the Soviet Union. During this period, Russian language and culture were promoted, particularly in eastern Ukraine.
8.2. Crimea’s Complex History
Crimea has a complex history, having been annexed by Catherine the Great in 1783 and later transferred to Ukraine by Soviet leader Khrushchev in 1954. The majority population in Crimea is ethnic Russian, which has been a point of contention in the conflict.
8.3. Ukraine’s Independence and Shifting Identity
Since gaining independence in 1991, Ukraine has sought to forge its own identity and align itself with the West. This has led to a growing sense of national identity and a rejection of Russian influence.
9. Expert Opinions and Analysis
To provide a comprehensive understanding of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, it is essential to consult expert opinions and analysis from various fields, including political science, history, and international relations.
9.1. Geopolitical Perspectives
Experts argue that the conflict is rooted in geopolitical competition between Russia and the West. Russia views Ukraine as a buffer zone and is determined to prevent it from aligning with NATO or the European Union.
9.2. Historical Narratives
Historians emphasize the importance of understanding the historical narratives that shape the conflict. Russia’s revisionist view of history, which denies Ukraine’s distinct identity, plays a key role in justifying its actions.
9.3. Security Concerns
Security analysts argue that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is driven by a combination of security concerns, geopolitical ambitions, and domestic political considerations. Putin seeks to restore Russia’s status as a major power and to protect his own political standing.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
Navigating the complexities of the Russia-Ukraine conflict can be daunting. Here are some frequently asked questions to provide clarity:
10.1. What were Russia’s stated goals in invading Ukraine?
Russia’s stated goals were to “demilitarize” and “denazify” Ukraine, protect Russian speakers, and prevent Ukraine from joining NATO.
10.2. Is there any historical basis for Russia’s claims over Ukraine?
Russia argues that Ukraine has always been part of its sphere of influence due to historical and cultural ties, but Ukraine asserts its right to independence and self-determination.
10.3. How has NATO expansion influenced the conflict?
Russia views NATO expansion as a threat, while NATO maintains its defensive posture and the right of countries to choose their alliances.
10.4. What is the current military situation in Ukraine?
The conflict is currently a war of attrition, with neither side making significant territorial gains.
10.5. What is the human cost of the war?
Tens of thousands have died, and millions have been displaced, creating a severe humanitarian crisis.
10.6. What is the role of international actors in the conflict?
International actors, including the US, EU, and UN, have condemned Russia’s actions and provided aid to Ukraine, but direct military intervention has been avoided.
10.7. What are the prospects for a peaceful resolution to the conflict?
The prospects for a peaceful resolution are uncertain, as both sides remain far apart on key issues.
10.8. How has the conflict impacted the global economy?
The conflict has disrupted global supply chains, increased energy prices, and contributed to inflation.
10.9. What is the role of propaganda in the conflict?
Both sides have engaged in propaganda to shape public opinion and justify their actions.
10.10. How can I help those affected by the conflict?
You can help by donating to reputable humanitarian organizations providing aid to Ukraine.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What were Russia’s stated goals in invading Ukraine? | To “demilitarize” and “denazify” Ukraine, protect Russian speakers, and prevent Ukraine from joining NATO. |
| Is there any historical basis for Russia’s claims over Ukraine? | Russia argues cultural ties justify its influence, but Ukraine asserts its right to independence. |
| How has NATO expansion influenced the conflict? | Russia views it as a threat; NATO defends its right to expand. |
| What is the current military situation in Ukraine? | A war of attrition with no major gains by either side. |
| What is the human cost of the war? | Tens of thousands dead; millions displaced; severe humanitarian crisis. |
| What is the role of international actors in the conflict? | Condemnation, aid to Ukraine; no direct military intervention. |
| What are the prospects for a peaceful resolution to the conflict? | Uncertain; both sides far apart on key issues. |
| How has the conflict impacted the global economy? | Supply chain disruptions, increased energy prices, inflation. |
| What is the role of propaganda in the conflict? | Both sides use propaganda to shape opinion and justify actions. |
| How can I help those affected by the conflict? | Donate to reputable humanitarian organizations aiding Ukraine. |

Seeking Answers? We’re Here to Help
Navigating complex issues like the Russia-Ukraine conflict requires reliable information and expert perspectives. At WHY.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with accurate, comprehensive answers.
Have more questions? Our team of experts is ready to assist. Visit WHY.EDU.VN, located at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101.
Let why.edu.vn be your guide to understanding the world.