Why Does My Throat Hurt When I Cough, and what can I do about it? At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the discomfort and concern a sore throat accompanied by a cough can bring, so we aim to provide clarity and effective solutions. Explore potential causes, from viral infections to environmental irritants, and discover practical remedies to soothe your throat and ease your cough and find lasting relief from throat discomfort. We’ll cover postnasal drip, acid reflux, and even preventative measures.
1. Understanding the Connection: Coughing and Sore Throat
Coughing and a sore throat often go hand in hand, creating a cycle of irritation and discomfort. The reasons behind this connection are varied, ranging from simple viral infections to more complex underlying conditions. Understanding why your throat hurts when you cough is the first step toward finding effective relief. This is where WHY.EDU.VN can help, offering reliable information and expert insights.
1.1 The Mechanics of Coughing
Coughing is a reflex action designed to clear irritants and mucus from your airways. This forceful expulsion of air can put a strain on the delicate tissues of your throat. The repetitive nature of coughing, especially during a prolonged illness, can lead to inflammation and soreness. Each cough episode can further irritate the throat lining, worsening the pain and discomfort.
1.2 How Coughing Irritates the Throat
When you cough, the muscles in your chest and abdomen contract forcefully, pushing air up through your windpipe and out of your mouth. This process can cause friction and irritation in the throat, especially if the coughing is frequent or violent. The throat’s mucous membranes, which are naturally moist and protective, can become dry and inflamed from the constant pressure.
1.3 The Role of Inflammation
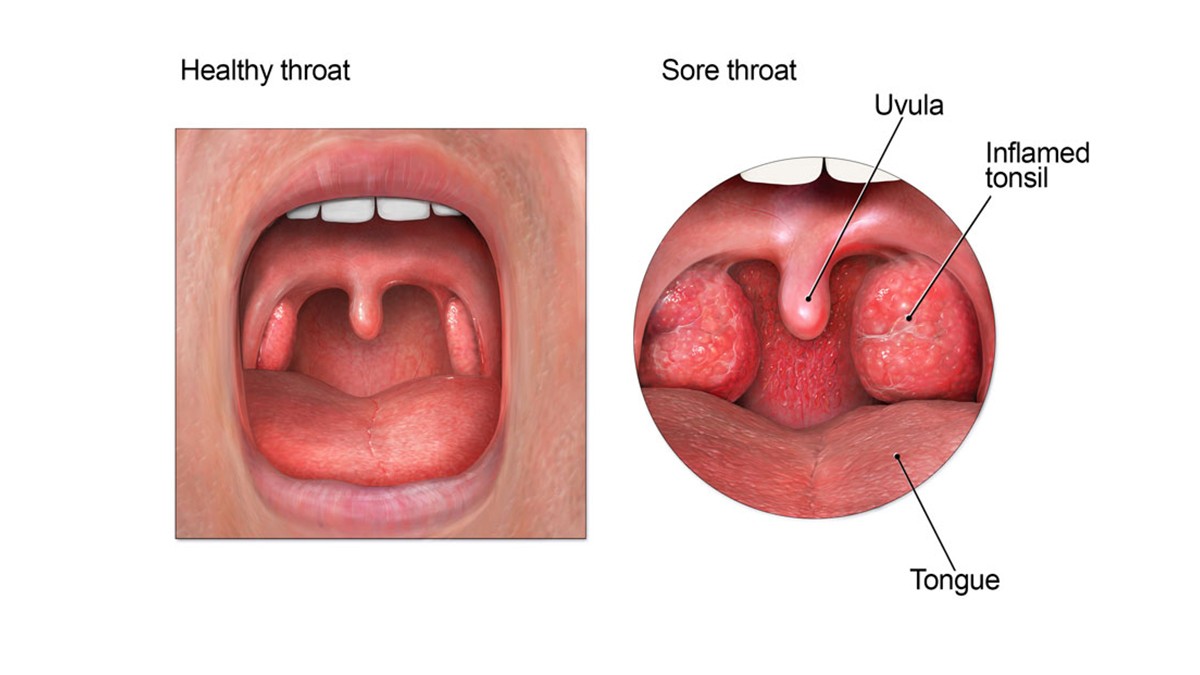
Inflammation is a key factor in the sore throat-cough connection. Whether the cause is a virus, bacteria, or irritant, the body responds with inflammation to try to heal and protect the affected area. In the throat, inflammation leads to swelling, redness, and pain, all of which contribute to the sensation of a sore throat. This inflammatory response can be exacerbated by persistent coughing, creating a cycle of irritation and pain.
 Anatomy of a cough showing the epiglottis opening and closing.
Anatomy of a cough showing the epiglottis opening and closing.
2. Common Causes of Throat Pain When Coughing
Several conditions can cause a sore throat accompanied by a cough. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s an overview of some of the most common culprits:
2.1 Viral Infections (Colds, Flu)
Viral infections, such as the common cold and flu (influenza), are frequent causes of both cough and sore throat. Viruses attack the upper respiratory tract, causing inflammation in the nose, throat, and airways. This inflammation leads to a range of symptoms, including coughing, sneezing, runny nose, and throat pain.
2.1.1 How Viruses Cause Sore Throat and Cough
Viruses invade the cells lining the throat, causing them to become inflamed and irritated. This inflammation triggers the sensation of a sore throat. At the same time, the virus can stimulate the cough reflex as the body tries to clear the infection from the airways. The cough, in turn, further irritates the throat, worsening the soreness.
2.1.2 Distinguishing Cold vs. Flu Symptoms
While both colds and the flu can cause similar symptoms, there are some key differences. Colds tend to come on gradually and are typically milder, with symptoms like a runny nose, sore throat, and mild cough. The flu, on the other hand, often has a sudden onset and can cause more severe symptoms, including fever, body aches, fatigue, and a dry cough. Regardless of which virus you have, WHY.EDU.VN offers guidance on managing symptoms and promoting recovery.
| Symptom | Common Cold | Flu (Influenza) |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
| Severity | Mild | Moderate to Severe |
| Fever | Rare, usually low-grade | Common, often high (100°F or higher) |
| Body Aches | Mild | Common, often severe |
| Fatigue | Mild | Common, can be prolonged |
| Cough | Mild to moderate | Dry, often severe |
| Sore Throat | Common | Common |
| Runny/Stuffy Nose | Common | Sometimes |
| Headache | Rare | Common |
2.2 Bacterial Infections (Strep Throat)
Strep throat, caused by Streptococcus bacteria, is another common cause of sore throat, although it doesn’t always present with a cough. Strep throat is more common in children, but adults can also contract the infection. Unlike viral infections, strep throat requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications.
2.2.1 Identifying Strep Throat Symptoms
Symptoms of strep throat typically include a sudden onset of sore throat, pain when swallowing, fever, red and swollen tonsils, and white patches or streaks on the tonsils. Unlike viral infections, strep throat is less likely to be accompanied by a cough or runny nose.
2.2.2 Why Strep Throat Requires Antibiotics
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to serious complications, such as rheumatic fever (which can damage the heart) and kidney inflammation. Antibiotics are necessary to kill the bacteria and prevent these complications. If you suspect you have strep throat, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
2.3 Postnasal Drip
Postnasal drip occurs when excess mucus drains down the back of the throat, often due to allergies, colds, or sinus infections. This constant dripping can irritate the throat lining, leading to a sore throat and triggering a cough.
2.3.1 How Postnasal Drip Irritates the Throat
The excess mucus from postnasal drip can be thick and sticky, clinging to the throat and causing irritation. The body responds by coughing to try to clear the mucus, which further aggravates the throat.
2.3.2 Managing Postnasal Drip
Managing postnasal drip involves addressing the underlying cause. This may include taking antihistamines or decongestants for allergies, using nasal saline rinses to clear congestion, or treating a sinus infection with antibiotics. Staying hydrated can also help thin the mucus, making it easier to clear.
2.4 Allergies
Allergies can cause a variety of respiratory symptoms, including a sore throat and cough. When you’re exposed to allergens like pollen, dust, or pet dander, your body releases histamine, which can lead to inflammation and irritation in the nasal passages and throat.
2.4.1 Allergy Symptoms and Throat Irritation
Allergy symptoms that contribute to throat irritation include sneezing, runny nose, and postnasal drip. The constant dripping of mucus down the throat, combined with the inflammation caused by histamine, can lead to a sore throat and a persistent cough.
2.4.2 Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
Identifying and avoiding allergens is key to managing allergy-related throat pain and cough. This may involve allergy testing to determine specific triggers, using air purifiers to remove allergens from the air, and taking antihistamines or other allergy medications as needed.
2.5 Environmental Irritants (Smoke, Pollution)
Environmental irritants like smoke, pollution, and dry air can also cause a sore throat and cough. These irritants can damage the delicate tissues of the throat, leading to inflammation and discomfort.
2.5.1 How Irritants Affect the Throat
Exposure to smoke, pollution, or dry air can strip the throat of its natural moisture, making it more susceptible to irritation. The body may respond by coughing to try to clear the irritants, which further aggravates the throat.
2.5.2 Protecting Your Throat from Irritants
Protecting your throat from environmental irritants involves avoiding exposure whenever possible. This may include staying indoors on high-pollution days, using a humidifier to add moisture to the air, and avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke.
2.6 Acid Reflux (GERD)
Acid reflux, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus and throat. This acid can irritate the lining of the throat, causing a sore throat, hoarseness, and a chronic cough.
2.6.1 The Link Between Acid Reflux and Throat Pain
The stomach acid that refluxes into the throat is highly irritating and can cause significant inflammation. This inflammation leads to the sensation of a sore throat. Additionally, the acid can trigger a cough reflex as the body tries to clear the irritant from the airways.
2.6.2 Managing Acid Reflux to Reduce Throat Pain
Managing acid reflux involves lifestyle changes and medications to reduce stomach acid production. Lifestyle changes may include avoiding trigger foods (like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods), eating smaller meals, and not lying down immediately after eating. Medications like antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors can also help reduce acid production.
2.7 Vocal Strain
Excessive talking, yelling, or singing can strain the vocal cords and surrounding tissues, leading to a sore throat and hoarseness. This is particularly common in people who use their voices extensively, such as teachers, singers, and public speakers.
2.7.1 How Vocal Strain Causes Throat Soreness
Vocal strain can cause inflammation and swelling in the vocal cords and throat. This inflammation leads to pain and discomfort. The throat may feel raw, scratchy, or tender to the touch.
2.7.2 Resting Your Voice
The best treatment for vocal strain is to rest your voice. Avoid talking, yelling, or singing as much as possible. When you do need to speak, use a soft, gentle voice and avoid straining. Staying hydrated can also help keep your vocal cords lubricated.
3. Effective Home Remedies for Sore Throat and Cough
Fortunately, many home remedies can help soothe a sore throat and ease a cough. These remedies are often effective for mild to moderate symptoms and can provide relief while your body heals.
3.1 Gargling with Salt Water
Gargling with warm salt water is a classic remedy for sore throat. The salt helps to draw fluid out of the throat tissues, reducing inflammation and pain.
3.1.1 How Salt Water Gargling Works
The salt in the water creates a high-salt environment that draws fluid out of the swollen tissues in the throat. This reduces inflammation and can help relieve pain.
3.1.2 The Right Salt Water Solution
To make a salt water gargle, mix 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of warm water. Gargle the solution for 30 seconds, then spit it out. Avoid swallowing the salt water. Repeat several times a day.
3.2 Honey and Warm Liquids
Honey has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an effective remedy for sore throat and cough. Warm liquids like tea or broth can also soothe the throat and help loosen mucus.
3.2.1 The Benefits of Honey
Honey coats the throat, providing a soothing effect. It also has antibacterial properties that can help fight infection. Studies have shown that honey can be as effective as cough suppressants in relieving cough symptoms.
3.2.2 Soothing Liquid Combinations
Combine honey with warm water, tea, or broth for added benefits. Add a squeeze of lemon to help break up mucus and provide vitamin C. Avoid giving honey to infants under one year of age due to the risk of botulism.
3.3 Steam Inhalation
Steam inhalation can help loosen congestion and soothe a sore throat. The moist air helps to hydrate the throat tissues and relieve inflammation.
3.3.1 How Steam Helps
Steam helps to loosen mucus in the nasal passages and throat, making it easier to cough up. It also hydrates the throat tissues, reducing inflammation and pain.
3.3.2 Safe Steam Inhalation Techniques
There are several ways to inhale steam. You can take a hot shower and breathe in the steam, use a humidifier, or fill a bowl with hot water, cover your head with a towel, and inhale the steam. Be careful not to burn yourself with the hot water.
3.4 Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide relief from sore throat and cough symptoms. These medications include pain relievers, cough suppressants, and decongestants.
3.4.1 Pain Relievers (Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen)
Pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can help reduce pain and fever. Follow the instructions on the label and do not exceed the recommended dose.
3.4.2 Cough Suppressants (Dextromethorphan, Guaifenesin)
Cough suppressants like dextromethorphan can help reduce coughing. Expectorants like guaifenesin can help loosen mucus, making it easier to cough up. Choose the appropriate medication based on your symptoms.
3.4.3 Decongestants (Pseudoephedrine, Phenylephrine)
Decongestants like pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine can help clear nasal congestion, reducing postnasal drip and throat irritation. Be aware that decongestants can raise blood pressure and should be used with caution by people with hypertension.
3.5 Lozenges and Throat Sprays
Lozenges and throat sprays can provide temporary relief from sore throat pain. They often contain ingredients like menthol or benzocaine, which have a numbing effect.
3.5.1 The Soothing Effect of Lozenges
Lozenges stimulate saliva production, which helps to keep the throat moist and soothed. They can also contain ingredients that numb the throat, providing temporary pain relief.
3.5.2 Choosing the Right Throat Spray
Throat sprays can provide targeted relief to the throat. Look for sprays that contain ingredients like phenol or benzocaine for numbing effects. Follow the instructions on the label and do not use throat sprays for extended periods.
4. When to Seek Medical Attention
While most sore throats and coughs can be managed with home remedies, it’s important to know when to seek medical attention. Certain symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires professional treatment.
4.1 Persistent or Severe Symptoms
If your sore throat and cough persist for more than a week, or if your symptoms are severe, see a healthcare provider. Persistent or severe symptoms may indicate a bacterial infection or other underlying condition that requires medical intervention.
4.2 Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing
Difficulty breathing or swallowing is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a severe infection or swelling in the throat that is obstructing the airway.
4.3 High Fever
A high fever (101°F or higher) may indicate a bacterial infection like strep throat or a more serious viral infection like the flu. See a healthcare provider to determine the cause of the fever and receive appropriate treatment.
4.4 Blood in Phlegm
Coughing up blood is a concerning symptom that requires medical evaluation. It may indicate a serious respiratory infection, bronchitis, or other underlying condition.
4.5 Other Concerning Symptoms
Other concerning symptoms that warrant medical attention include:
- Severe body aches
- Dehydration
- Rash
- Joint pain
- Swollen glands
5. Preventing Sore Throat and Cough
Preventing sore throat and cough involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to irritants, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
5.1 Practicing Good Hygiene
Good hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of respiratory infections. This includes:
- Washing your hands frequently with soap and water
- Avoiding touching your face
- Covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
5.2 Avoiding Irritants
Avoiding exposure to irritants like smoke, pollution, and allergens can help prevent throat irritation and coughing. This may involve:
- Staying indoors on high-pollution days
- Using an air purifier to remove allergens from the air
- Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke
5.3 Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help boost your immune system and reduce your risk of developing respiratory infections. This includes:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
6. Understanding the Role of Environment
The environment you live in can significantly impact the frequency and severity of your sore throats and coughs. Factors like humidity, air quality, and seasonal changes play a crucial role.
6.1 The Impact of Dry Air
Dry air, common during winter months or in arid climates, can exacerbate throat irritation. When the air lacks moisture, it can dry out the mucous membranes in your throat, making them more susceptible to irritation and infection.
6.1.1 How Dry Air Affects Your Throat
Dry air can strip the throat of its natural moisture, leading to a scratchy, sore sensation. This dryness can also make it harder for your body to clear irritants and pathogens from your airways, increasing your risk of infection.
6.1.2 Using a Humidifier
Using a humidifier can add moisture to the air, helping to alleviate throat dryness and reduce irritation. Place a humidifier in your bedroom or other areas where you spend a lot of time. Clean the humidifier regularly to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria.
6.2 Air Quality and Pollution
Poor air quality and pollution can irritate the throat and trigger coughing. Exposure to pollutants like smoke, smog, and particulate matter can inflame the respiratory system, leading to a sore throat and cough.
6.2.1 The Effects of Pollution on Your Throat
Pollutants can directly irritate the lining of the throat, causing inflammation and pain. They can also trigger an immune response, leading to increased mucus production and coughing.
6.2.2 Protecting Yourself from Air Pollution
Protecting yourself from air pollution involves limiting your exposure to pollutants whenever possible. This may include:
- Staying indoors on high-pollution days
- Using an air purifier with a HEPA filter
- Wearing a mask when outdoors in polluted areas
- Avoiding areas with heavy traffic or industrial activity
6.3 Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes can also impact the frequency of sore throats and coughs. Winter months, in particular, are associated with an increased risk of respiratory infections due to factors like dry air and increased indoor crowding.
6.3.1 The Winter Effect
During winter, people tend to spend more time indoors, which increases the risk of spreading respiratory infections. Additionally, the dry air can exacerbate throat irritation and make you more susceptible to infection.
6.3.2 Adapting to Seasonal Changes
Adapting to seasonal changes involves taking steps to protect yourself from respiratory infections and throat irritation. This may include:
- Getting a flu shot
- Washing your hands frequently
- Using a humidifier
- Staying hydrated
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
7. Lifestyle Adjustments to Alleviate Throat Pain
In addition to home remedies and medical treatments, certain lifestyle adjustments can help alleviate throat pain and reduce the frequency of coughing.
7.1 Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for keeping your throat moist and soothed. Drinking plenty of fluids helps to thin mucus, making it easier to clear from your airways.
7.1.1 The Importance of Fluids
Fluids help to lubricate the throat and prevent dryness. They also help to flush out irritants and pathogens from your system.
7.1.2 Best Fluids for Sore Throat
The best fluids for a sore throat include:
- Water
- Herbal tea
- Warm broth
- Honey and lemon water
- Avoid sugary drinks, caffeine, and alcohol, as these can dehydrate you.
7.2 Diet and Nutrition
Eating a healthy diet can help boost your immune system and reduce your risk of respiratory infections. Certain foods may also help soothe a sore throat.
7.2.1 Foods to Soothe Your Throat
Foods that are soft, easy to swallow, and soothing to the throat include:
- Soup
- Yogurt
- Mashed potatoes
- Oatmeal
- Smoothies
7.2.2 Foods to Avoid
Avoid foods that are irritating to the throat, such as:
- Spicy foods
- Acidic foods (like citrus fruits)
- Hard or crunchy foods
7.3 Rest and Sleep
Getting enough rest and sleep is essential for allowing your body to heal. When you’re sick, your body needs extra energy to fight off infection.
7.3.1 The Healing Power of Sleep
Sleep allows your body to repair and regenerate tissues. It also helps to boost your immune system.
7.3.2 Creating a Restful Environment
Create a restful environment by:
- Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day
- Making sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool
- Avoiding screen time before bed
8. Exploring Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief from sore throat and cough symptoms through alternative therapies like acupuncture, herbal remedies, and aromatherapy.
8.1 Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate healing. Some people find that acupuncture can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with a sore throat.
8.1.1 How Acupuncture Works
Acupuncture is believed to stimulate the release of endorphins, which are natural pain relievers. It may also help to reduce inflammation and boost the immune system.
8.1.2 Finding a Qualified Acupuncturist
If you’re interested in trying acupuncture, it’s important to find a qualified and licensed practitioner.
8.2 Herbal Remedies
Many herbal remedies are traditionally used to treat sore throat and cough symptoms. Some popular options include:
- Echinacea: May help boost the immune system and fight infection.
- Ginger: Has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Slippery elm: Can coat and soothe the throat.
- Licorice root: Has anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties.
8.2.1 Using Herbal Remedies Safely
It’s important to use herbal remedies with caution, as they can interact with medications or have side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider before trying any new herbal remedy.
8.3 Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy involves using essential oils to promote healing and well-being. Some essential oils may help relieve sore throat and cough symptoms.
8.3.1 Essential Oils for Sore Throat
Essential oils that may help soothe a sore throat include:
- Eucalyptus: Can help clear congestion and relieve coughing.
- Peppermint: Has anti-inflammatory and cooling properties.
- Tea tree: Has antibacterial and antiviral properties.
- Lemon: Can help break up mucus and boost the immune system.
8.3.2 Safe Aromatherapy Practices
Essential oils should be used with caution. Never ingest essential oils, and always dilute them with a carrier oil before applying them to the skin.
9. Special Considerations for Children
Children are more susceptible to respiratory infections and sore throats. It’s important to take special precautions when treating children with sore throat and cough.
9.1 When to See a Doctor
See a doctor if your child has:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- High fever
- Blood in phlegm
- Severe body aches
- Dehydration
- Rash
- Joint pain
- Swollen glands
9.2 Safe Home Remedies for Children
Safe home remedies for children include:
- Honey (for children over one year old)
- Warm liquids
- Steam inhalation
- Salt water gargle (for older children who can gargle safely)
9.3 Medications to Avoid
Avoid giving children the following medications:
- Aspirin (can cause Reye’s syndrome)
- Over-the-counter cough and cold medicines (for children under four years old)
10. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures for Persistent Cough and Sore Throat
When cough and sore throat symptoms persist despite conventional treatments, advanced diagnostic procedures can help identify underlying causes. These procedures offer a more detailed evaluation of the respiratory system and can uncover conditions that might be missed during a standard examination.
10.1 Endoscopy
Endoscopy involves using a flexible tube with a camera to visualize the airways, including the throat, larynx, and trachea. This procedure can help identify inflammation, infections, structural abnormalities, or tumors.
10.1.1 Types of Endoscopy
- Laryngoscopy: Examines the larynx (voice box) to identify vocal cord problems or other abnormalities.
- Bronchoscopy: Examines the bronchi (airways in the lungs) to diagnose infections, inflammation, or tumors.
10.1.2 What to Expect During Endoscopy
During an endoscopy, the patient is typically given a local anesthetic to numb the throat. The endoscope is then gently inserted through the nose or mouth and guided through the airways. The procedure usually takes 15-30 minutes, and patients can typically return home the same day.
10.2 Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays and CT scans, can provide detailed images of the lungs and airways. These tests can help identify infections, inflammation, or structural abnormalities.
10.2.1 Types of Imaging Tests
- Chest X-ray: Can detect pneumonia, bronchitis, or other lung infections.
- CT Scan: Provides more detailed images of the lungs and can identify smaller abnormalities, such as tumors or inflammation.
10.2.2 When Imaging Tests are Necessary
Imaging tests are typically ordered when a patient has persistent cough and sore throat symptoms, especially if they are accompanied by fever, chest pain, or shortness of breath.
10.3 Allergy Testing
Allergy testing can help identify specific allergens that may be contributing to chronic cough and sore throat symptoms. These tests can be performed through skin prick tests or blood tests.
10.3.1 Types of Allergy Tests
- Skin Prick Test: Involves pricking the skin and applying a small amount of allergen to see if a reaction occurs.
- Blood Test: Measures the levels of specific antibodies in the blood to identify allergens.
10.3.2 How Allergy Testing Can Help
Identifying allergens can help patients avoid exposure and manage their symptoms with appropriate medications, such as antihistamines or nasal corticosteroids.
10.4 Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) assess how well the lungs are working. These tests measure lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange.
10.4.1 What PFTs Measure
PFTs can help diagnose conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other lung disorders that may be causing chronic cough and sore throat.
10.4.2 How PFTs are Performed
During PFTs, the patient breathes into a device called a spirometer, which measures the amount of air inhaled and exhaled. The tests usually take about 30-60 minutes to complete.
11. Innovative Treatments for Chronic Cough and Sore Throat
When chronic cough and sore throat symptoms persist despite conventional treatments, innovative therapies can offer relief. These advanced approaches target the underlying causes of chronic symptoms and provide personalized solutions.
11.1 Neuromodulators
Neuromodulators are medications that can help reduce nerve sensitivity and suppress the cough reflex. These drugs are often used to treat chronic cough caused by nerve irritation or hypersensitivity.
11.1.1 Types of Neuromodulators
- Gabapentin: An anticonvulsant drug that can reduce nerve pain and suppress the cough reflex.
- Amitriptyline: A tricyclic antidepressant that can also reduce nerve pain and suppress the cough reflex.
11.1.2 How Neuromodulators Work
Neuromodulators work by modulating the activity of nerves in the respiratory system, reducing their sensitivity to irritants and suppressing the cough reflex.
11.2 Speech Therapy
Speech therapy can help patients improve their vocal technique and reduce vocal strain, which can contribute to chronic cough and sore throat.
11.2.1 The Role of Speech Therapy
Speech therapists can teach patients how to use their voices more efficiently and reduce the strain on their vocal cords. They can also help patients manage other symptoms, such as hoarseness and throat pain.
11.2.2 Techniques Used in Speech Therapy
- Vocal Exercises: Improve vocal strength and flexibility.
- Breathing Techniques: Enhance breath control and reduce vocal strain.
- Voice Hygiene: Strategies to protect and maintain vocal health.
11.3 Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a technique that helps patients become more aware of their body’s physiological responses and learn how to control them. It can be used to manage chronic cough and sore throat symptoms by reducing muscle tension and promoting relaxation.
11.3.1 How Biofeedback Works
Biofeedback involves using sensors to monitor physiological responses, such as muscle tension and heart rate. Patients then receive feedback on their responses and learn techniques to control them.
11.3.2 Benefits of Biofeedback
Biofeedback can help patients reduce muscle tension in the throat and chest, which can contribute to chronic cough and sore throat. It can also promote relaxation and reduce stress, which can exacerbate symptoms.
11.4 Precision Medicine
Precision medicine involves tailoring treatment to the individual based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. This approach can help identify the most effective treatments for chronic cough and sore throat.
11.4.1 Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can identify genetic variations that may be contributing to chronic cough and sore throat symptoms. This information can help healthcare providers choose the most appropriate treatments.
11.4.2 Personalized Treatment Plans
Precision medicine involves creating personalized treatment plans based on the individual’s unique characteristics. This approach can lead to more effective and targeted treatments for chronic cough and sore throat.
12. Addressing Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, and depression, can contribute to chronic cough and sore throat symptoms. Addressing these factors can be an important part of managing chronic conditions.
12.1 The Role of Stress
Stress can exacerbate chronic cough and sore throat symptoms by increasing muscle tension, inflammation, and immune dysfunction.
12.1.1 How Stress Affects the Body
Stress triggers the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can suppress the immune system and increase inflammation.
12.1.2 Stress Management Techniques
- Meditation: Promotes relaxation and reduces stress.
- Yoga: Combines physical exercise with mindfulness and breathing techniques.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Can help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation.
12.2 Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression can also contribute to chronic cough and sore throat symptoms. These conditions can affect the immune system and increase sensitivity to pain and discomfort.
12.2.1 The Impact of Mental Health
Mental health conditions can affect the body’s ability to heal and fight off infection.
12.2.2 Seeking Mental Health Support
- Therapy: Can help patients identify and manage the underlying causes of anxiety and depression.
- Medication: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can help manage symptoms.
12.3 Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques, such as mindfulness and guided imagery, can help patients manage chronic cough and sore throat symptoms by reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
12.3.1 Benefits of Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques can help patients become more aware of their body’s responses and learn how to control them.
12.3.2 Types of Mind-Body Techniques
- Mindfulness Meditation: Involves focusing on the present moment and accepting thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- Guided Imagery: Involves visualizing peaceful and relaxing scenes to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we recognize that finding reliable answers to your health questions can be challenging. That’s why we’re committed to providing you with accurate, expert-backed information to help you understand your symptoms and make informed decisions about your health.
If you’re experiencing a persistent sore throat and cough and are struggling to find relief, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHY.EDU.VN. Our team of experts is here to answer your questions and guide you toward the best possible solutions. Visit us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. You can also explore our website at why.edu.vn to discover a wealth of knowledge and resources.
Why does my throat hurt when I cough? With the right information and support, you can find lasting relief and improve your quality of life.