Why Does My Text Message Say Rcs? Let’s explore Rich Communication Services (RCS) messaging, a modern protocol designed to enhance your texting experience. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by why.edu.vn, will delve into the intricacies of RCS, its advantages, and how it compares to older technologies like SMS and MMS. Understand message delivery, enhanced features, and the future of mobile communication.
1. Unveiling RCS: What is Rich Communication Services?
Rich Communication Services (RCS) represents the evolution of text messaging, aiming to replace SMS (Short Message Service) and MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) with a richer, more interactive experience. As a next-generation protocol, RCS brings features previously exclusive to Over-The-Top (OTT) messaging apps like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger to standard text messaging. RCS enhances the mobile messaging landscape.
1.1. The Core Objectives of RCS
RCS was developed to provide:
- Enhanced Features: Integrating features like high-resolution image and video sharing, read receipts, typing indicators, and group chats.
- Improved User Experience: Offering a more seamless and engaging communication platform.
- Business Messaging: Enabling businesses to interact with customers through branded messages, rich media, and interactive elements.
1.2. Key Features That Define RCS
RCS is distinguished by several key features:
- High-Quality Media Sharing: Share photos, videos, and files in high resolution without compression.
- Read Receipts and Typing Indicators: Know when your message has been read and when the recipient is typing a response.
- Group Chat Enhancements: Enjoy improved group chat functionality with features like adding/removing participants and naming groups.
- Branded Business Messaging: Interact with businesses through verified profiles, rich cards, and call-to-action buttons.
2. Delving Into the Technical Aspects of RCS
RCS is built on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) infrastructure, which allows it to support a wide range of multimedia services. Unlike SMS, which uses the signaling channels of the mobile network, RCS leverages data connections (Wi-Fi or cellular data) for transmitting messages.
2.1. How RCS Works
- Device Compatibility: Both the sender and recipient’s devices must support RCS.
- Network Support: The mobile carrier must support RCS on their network.
- RCS Client: The device uses an RCS client (such as Google Messages) to send and receive RCS messages.
- IMS Connection: The RCS client connects to the carrier’s IMS network to establish a communication channel.
- Message Transmission: Messages are transmitted over the data connection, utilizing the features and capabilities of RCS.
2.2. RCS Architecture
The architecture of RCS involves several key components:
- RCS Client: The messaging app on the user’s device that supports RCS.
- IMS Core: The core network infrastructure that provides the foundation for RCS services.
- Application Servers: Servers that host and manage RCS applications and services.
- Interconnect: Connections to other networks, allowing RCS users to communicate with users on different networks.
3. RCS vs. SMS/MMS: A Detailed Comparison
To fully appreciate RCS, it’s essential to understand how it differs from its predecessors, SMS and MMS. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | SMS | MMS | RCS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Message Type | Text only | Multimedia (text, images, audio, video) | Rich media (high-resolution images, videos, files, interactive elements) |
| Data Usage | Minimal data usage | Higher data usage | Data-based (Wi-Fi or cellular data) |
| Message Length Limit | 160 characters | Varies, typically around 300KB | No practical limit |
| Features | Basic text messaging | Multimedia messaging | High-quality media sharing, read receipts, typing indicators, group chat enhancements, branded business messaging, location sharing, file transfer, interactive carousels, suggested replies, and actions |
| Encryption | No end-to-end encryption | No end-to-end encryption | Some implementations offer encryption, but not universally end-to-end |
| Compatibility | Universal, supported by all phones | Supported by most phones | Requires RCS-enabled devices and carrier support |
| Business Messaging | Limited, primarily through shortcodes | Limited, primarily through shortcodes | Rich, interactive business messaging with branding and interactive elements |
| Delivery Reports | No delivery reports | Basic delivery reports | Detailed delivery and read receipts |
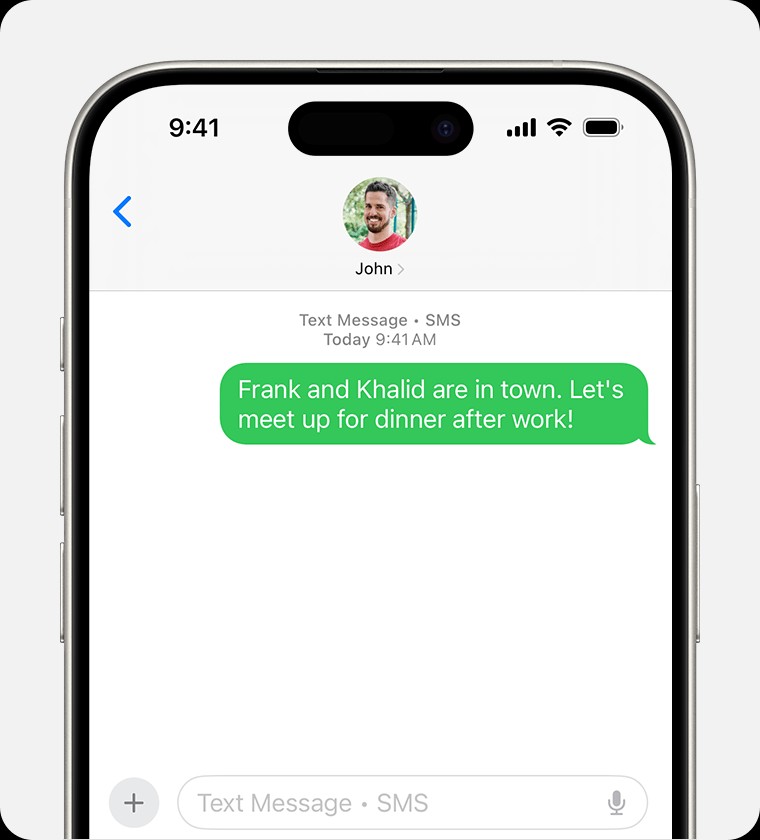
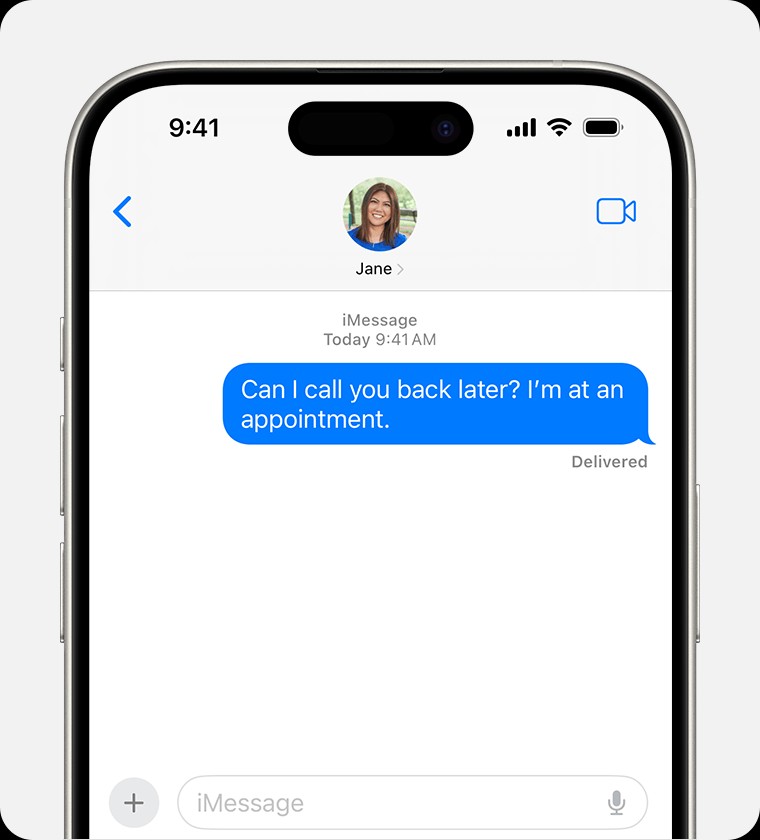
3.1. Advantages of RCS Over SMS/MMS
RCS offers several advantages over SMS and MMS:
- Enhanced Features: RCS provides a richer, more interactive messaging experience with features like high-quality media sharing, read receipts, and typing indicators.
- Improved Security: While not always end-to-end encrypted, RCS can offer better security than SMS/MMS, which are unencrypted.
- Better Business Messaging: RCS enables businesses to create branded, interactive messaging experiences that can improve customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Cost Efficiency: Since RCS uses data connections, it can be more cost-effective than SMS/MMS, especially for sending multimedia content.
3.2. Limitations of RCS
Despite its advantages, RCS also has some limitations:
- Compatibility: RCS requires both the sender and recipient to have RCS-enabled devices and carrier support, which is not yet universal.
- Encryption: End-to-end encryption is not universally implemented in RCS, raising privacy concerns for some users.
- Carrier Dependence: RCS relies on carrier support, which can vary by region and provider, leading to fragmentation.
4. Why Your Text Message Says RCS
If your text message indicates “RCS,” it means your device and carrier are using the Rich Communication Services protocol to send and receive messages. This typically happens when:
- Both Sender and Recipient Support RCS: Both devices must be RCS-enabled.
- RCS is Enabled in Messaging App: The messaging app (e.g., Google Messages) has RCS enabled in its settings.
- Carrier Support: Your mobile carrier supports RCS on their network.
4.1. How to Check if RCS is Enabled
To check if RCS is enabled on your device, follow these steps (using Google Messages as an example):
- Open Google Messages: Launch the Google Messages app on your Android device.
- Access Settings: Tap the three dots in the top right corner and select “Settings.”
- Check RCS Settings: Look for “RCS chats” or “Chat features.” If RCS is enabled, it will indicate its status (e.g., “Connected”).
4.2. Troubleshooting RCS Issues
If RCS is not working as expected, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Verify RCS Support: Ensure your device and carrier support RCS.
- Enable RCS in Settings: Check that RCS is enabled in your messaging app’s settings.
- Update Messaging App: Make sure you have the latest version of your messaging app.
- Restart Device: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve connectivity issues.
- Contact Carrier: If problems persist, contact your mobile carrier for assistance.
5. The Role of Google in RCS Adoption
Google has been a significant proponent of RCS, pushing for its adoption as the universal standard for text messaging. Google’s efforts include:
- Developing RCS Client: Google developed the “Messages” app, which supports RCS and is pre-installed on many Android devices.
- Partnering with Carriers: Google has partnered with mobile carriers worldwide to enable RCS on their networks.
- Promoting RCS Standard: Google has actively promoted RCS as the successor to SMS, advocating for its adoption across the industry.
5.1. Google Messages and RCS
Google Messages is a key component of Google’s RCS strategy. It offers a seamless RCS experience, with features like:
- Automatic RCS Upgrade: Automatically upgrades SMS to RCS when available.
- Enhanced Messaging Features: Supports high-quality media sharing, read receipts, typing indicators, and group chat enhancements.
- Business Messaging: Enables branded business messaging with rich cards and interactive elements.
5.2. Challenges and Controversies
Despite Google’s efforts, RCS adoption has faced challenges:
- Fragmentation: The lack of a single, unified RCS standard has led to fragmentation, with different carriers and devices supporting different features.
- Apple’s Resistance: Apple has been slow to adopt RCS, which has hindered its widespread adoption, particularly in regions where iPhones are popular.
- Privacy Concerns: The lack of universal end-to-end encryption has raised privacy concerns among some users.
6. The Security Aspects of RCS Messaging
Security is a critical consideration for any messaging protocol. While RCS offers some security improvements over SMS/MMS, it’s essential to understand its limitations.
6.1. Encryption in RCS
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): RCS uses TLS to encrypt messages in transit between the user’s device and the carrier’s network.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): Some RCS implementations offer E2EE, but it’s not universally supported. Google Messages, for example, offers E2EE for one-on-one RCS chats.
6.2. Privacy Considerations
- Metadata Collection: RCS may collect metadata about your messages, such as timestamps and participants.
- Carrier Access: Mobile carriers have access to RCS messages, which raises privacy concerns for some users.
- Data Retention: Carriers may retain RCS messages for a certain period, depending on their policies and legal requirements.
6.3. Best Practices for Secure RCS Messaging
To enhance your security and privacy when using RCS, consider the following best practices:
- Use E2EE When Available: If your messaging app supports E2EE, enable it for sensitive conversations.
- Review Privacy Settings: Check your messaging app’s privacy settings and adjust them to your preferences.
- Be Mindful of Sharing Sensitive Information: Avoid sharing highly sensitive information over RCS, especially if E2EE is not enabled.
- Keep Your App Updated: Regularly update your messaging app to ensure you have the latest security patches.
7. Business Messaging with RCS: Opportunities and Benefits
RCS offers significant opportunities for businesses to engage with customers through richer, more interactive messaging experiences.
7.1. Enhanced Customer Engagement
- Branded Messages: Businesses can send branded messages with their logo and company information.
- Rich Cards and Carousels: RCS supports rich cards and carousels that can showcase products, services, and promotions in an engaging format.
- Interactive Elements: Businesses can include interactive elements like buttons, suggested replies, and actions in their messages.
7.2. Improved Customer Service
- Real-Time Support: RCS enables businesses to provide real-time customer support through chat.
- Appointment Scheduling: Customers can schedule appointments directly through RCS messages.
- Order Tracking: Businesses can send order updates and tracking information via RCS.
7.3. Marketing and Promotions
- Targeted Campaigns: Businesses can send targeted marketing campaigns to specific customer segments.
- Promotional Offers: RCS supports promotional offers with discounts and coupons.
- Loyalty Programs: Businesses can integrate loyalty programs with RCS messaging.
7.4. Examples of RCS Business Messaging
- Retail: A retailer sends a rich card showcasing new arrivals with a “Shop Now” button.
- Travel: An airline sends flight updates and boarding passes via RCS.
- Banking: A bank sends transaction alerts and fraud warnings through RCS.
8. The Future of RCS: Trends and Predictions
The future of RCS looks promising, with several trends and predictions shaping its evolution:
8.1. Universal Adoption
- Carrier Support: As more mobile carriers adopt RCS, its reach and availability will expand.
- Device Compatibility: As more devices come with RCS support, its adoption will increase.
- Apple’s Adoption: If Apple adopts RCS, it would significantly accelerate its widespread use.
8.2. Enhanced Security
- End-to-End Encryption: The widespread adoption of E2EE will enhance the security and privacy of RCS messaging.
- Advanced Security Features: Future versions of RCS may include advanced security features like biometric authentication and secure key exchange.
8.3. Integration with Other Technologies
- AI and Chatbots: RCS may be integrated with AI and chatbots to provide more intelligent and personalized messaging experiences.
- IoT Devices: RCS may be used to communicate with and control IoT devices, enabling new use cases for messaging.
- 5G Integration: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance the performance and capabilities of RCS, enabling faster speeds and lower latency.
9. Understanding RCS Messaging on Different Platforms
RCS messaging experiences can vary slightly depending on the platform and device you are using. Here’s a look at how RCS works on some popular platforms:
9.1. RCS on Android Devices
On Android devices, RCS is primarily supported through the Google Messages app. Google Messages offers a comprehensive RCS experience with features like:
- Automatic RCS Upgrade: Seamlessly upgrades SMS to RCS when available.
- Enhanced Messaging Features: Supports high-quality media sharing, read receipts, typing indicators, and group chat enhancements.
- Business Messaging: Enables branded business messaging with rich cards and interactive elements.
- End-to-End Encryption: Offers E2EE for one-on-one RCS chats, providing enhanced security.
9.2. RCS on iOS Devices (iPhones)
As of now, Apple has not fully embraced RCS on iOS devices. iPhones use iMessage for messaging between Apple devices, and SMS/MMS for messaging with non-Apple devices. However, there is growing industry pressure for Apple to adopt RCS to improve interoperability with Android devices.
Potential Future Support: If Apple were to adopt RCS, it would likely integrate it into the Messages app, providing iPhone users with access to RCS features when communicating with Android users.
9.3. RCS on Other Platforms
RCS is also supported on some other platforms and devices, including:
- KaiOS: KaiOS, a mobile operating system for feature phones, supports RCS, bringing enhanced messaging capabilities to users in emerging markets.
- Web Browsers: Some web-based messaging platforms support RCS, allowing users to send and receive RCS messages from their computers.
- Enterprise Messaging Platforms: Several enterprise messaging platforms support RCS, enabling businesses to communicate with customers through rich, interactive messaging experiences.
10. RCS and Privacy: What You Need to Know
Privacy is a crucial consideration when using any messaging service. While RCS offers some security improvements over SMS/MMS, it’s essential to understand its privacy implications.
10.1. Data Collection and Usage
- Metadata: RCS providers and mobile carriers may collect metadata about your messages, such as timestamps, participants, and location information.
- Message Content: In some cases, RCS providers may have access to the content of your messages, especially if end-to-end encryption is not enabled.
- Data Retention: Mobile carriers and RCS providers may retain your message data for a certain period, depending on their policies and legal requirements.
10.2. Security Measures
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): RCS uses TLS to encrypt messages in transit between your device and the carrier’s network, protecting them from eavesdropping.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): Some RCS implementations offer E2EE, which ensures that only the sender and recipient can read the contents of the messages.
10.3. Steps to Protect Your Privacy
- Use E2EE Whenever Possible: If your messaging app supports E2EE, enable it for sensitive conversations to ensure that your messages are protected from third-party access.
- Review Privacy Settings: Take the time to review the privacy settings of your messaging app and adjust them to your preferences.
- Be Mindful of Sharing Personal Information: Exercise caution when sharing personal or sensitive information over RCS, especially if you are not sure whether E2EE is enabled.
- Keep Your App Updated: Regularly update your messaging app to ensure that you have the latest security patches and privacy enhancements.
- Use a VPN: Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your IP address, especially when using RCS over public Wi-Fi networks.
- Read the Privacy Policy: Take the time to read the privacy policy of your messaging app and understand how your data is collected, used, and protected.
11. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for RCS Messaging
While RCS offers many benefits, users may encounter issues from time to time. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
11.1. RCS Not Connecting or Activating
- Check Carrier Support: Ensure that your mobile carrier supports RCS messaging in your region.
- Enable RCS in Settings: Verify that RCS is enabled in your messaging app settings (e.g., Google Messages).
- Update Messaging App: Make sure you have the latest version of your messaging app installed on your device.
- Restart Device: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve connectivity issues and allow RCS to connect properly.
- Clear Cache and Data: Try clearing the cache and data of your messaging app to resolve any potential conflicts or errors.
- Check Internet Connection: Ensure that you have a stable internet connection (Wi-Fi or cellular data) as RCS relies on data to send and receive messages.
- Contact Carrier Support: If you have tried all the above steps and RCS is still not connecting, contact your mobile carrier for assistance.
11.2. Messages Sending as SMS/MMS Instead of RCS
- Verify Recipient Support: Ensure that the recipient also has RCS-enabled devices and carrier support.
- Check Default Messaging App: Make sure your RCS-enabled messaging app is set as the default messaging app on your device.
- Disable SMS/MMS Fallback: In your messaging app settings, check if there is an option to disable SMS/MMS fallback. This will force messages to be sent via RCS if available.
- Resend the Message: Try resending the message to see if it is sent via RCS this time.
- Check Contact Details: Ensure that the recipient’s phone number is correctly saved in your contacts.
11.3. Issues with Media Sharing
- Check File Size Limits: RCS may have file size limits for media sharing. Ensure that the files you are trying to send are within the allowed size limits.
- Ensure Stable Internet Connection: Media sharing requires a stable internet connection. Make sure you have a strong Wi-Fi or cellular data connection when sending or receiving media files.
- Clear Cache and Data: Try clearing the cache and data of your messaging app to resolve any potential conflicts or errors with media sharing.
- Update Messaging App: Ensure that you have the latest version of your messaging app installed on your device to benefit from any bug fixes or performance improvements.
- Contact Carrier Support: If you continue to experience issues with media sharing, contact your mobile carrier for assistance.
11.4. Battery Drain Issues
- Optimize App Settings: Review the settings of your messaging app and optimize them to reduce battery drain.
- Limit Background Activity: Restrict the background activity of your messaging app to prevent it from consuming excessive battery power.
- Enable Battery Saver Mode: Enable battery saver mode on your device to conserve battery life.
- Update Messaging App: Ensure that you have the latest version of your messaging app installed on your device to benefit from any bug fixes or performance improvements related to battery usage.
12. How RCS is Transforming Mobile Communication
RCS is not just an incremental improvement over SMS/MMS; it’s a fundamental shift in how we communicate on mobile devices. Here’s how RCS is transforming mobile communication:
12.1. Richer and More Engaging Messaging Experiences
- High-Quality Media Sharing: RCS allows users to share photos, videos, and files in high resolution, providing a richer and more engaging messaging experience.
- Interactive Elements: With interactive elements like buttons, suggested replies, and actions, RCS enables users to engage with messages in more meaningful ways.
- Branded Business Messaging: RCS allows businesses to create branded messaging experiences that are more visually appealing and informative than traditional SMS messages.
12.2. Seamless Integration with Other Apps and Services
- App Integrations: RCS can be integrated with other apps and services, allowing users to perform various tasks directly from their messaging app.
- Chatbots and AI: RCS can be used to power chatbots and AI assistants, providing users with personalized and interactive experiences.
- IoT Device Control: RCS can be used to communicate with and control IoT devices, enabling users to manage their connected devices from their messaging app.
12.3. Improved Business-Customer Communications
- Enhanced Customer Service: RCS enables businesses to provide real-time customer support through chat, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: RCS allows businesses to send targeted marketing campaigns to specific customer segments, increasing the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
- Secure and Verified Communications: RCS provides businesses with a secure and verified channel for communicating with customers, reducing the risk of fraud and phishing attacks.
12.4. Closing the Gap with OTT Messaging Apps
- Feature Parity: RCS brings many of the features that were previously exclusive to OTT messaging apps like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger to standard text messaging.
- Universal Reach: Unlike OTT messaging apps, which require users to install a specific app, RCS is a universal standard that is supported by all modern mobile devices.
- Carrier Integration: RCS is integrated with mobile carrier networks, providing a more reliable and secure messaging experience than OTT messaging apps.
13. Debunking Common Myths About RCS Messaging
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding RCS messaging. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones:
Myth 1: RCS is only for Android users.
Fact: While Google has been a strong proponent of RCS on Android, RCS is a universal standard that can be supported on any mobile platform, including iOS.
Myth 2: RCS is not secure.
Fact: While RCS may not always offer end-to-end encryption by default, it does use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt messages in transit, and some implementations offer end-to-end encryption as an option.
Myth 3: RCS is just a rebranded version of SMS.
Fact: RCS is a completely new messaging protocol that offers a wide range of features and capabilities that are not available with SMS, such as high-quality media sharing, read receipts, and interactive elements.
Myth 4: RCS requires a special app.
Fact: RCS is typically supported through the default messaging app on your device, such as Google Messages on Android. You do not need to install a separate app to use RCS.
Myth 5: RCS is not supported by all mobile carriers.
Fact: While RCS support is not yet universal, it is rapidly expanding as more mobile carriers adopt the standard.
14. Exploring the Technical Specifications of RCS
For those interested in the technical details of RCS, here’s a brief overview of its specifications:
14.1. Core Standards
- GSMA Specifications: RCS is defined by a set of specifications developed by the GSM Association (GSMA).
- IMS Architecture: RCS is based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) architecture, which provides the foundation for multimedia services over IP networks.
14.2. Key Protocols
- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): SIP is used to establish and manage communication sessions between RCS clients.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): HTTP is used to transfer data between RCS clients and servers.
- MSRP (Message Session Relay Protocol): MSRP is used to relay messages between RCS clients in a session.
14.3. Data Formats
- MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions): MIME is used to encapsulate different types of data, such as text, images, and audio, within RCS messages.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): JSON is used to format data in a structured and human-readable format.
14.4. Security Protocols
- TLS (Transport Layer Security): TLS is used to encrypt messages in transit between RCS clients and servers.
- E2EE (End-to-End Encryption): Some RCS implementations use E2EE protocols, such as Signal Protocol, to encrypt messages end-to-end.
15. The Global Adoption of RCS: A Geographical Perspective
The adoption of RCS varies significantly across different regions and countries. Here’s a look at the global landscape of RCS adoption:
15.1. North America
- United States: RCS adoption in the United States has been driven primarily by Google and some mobile carriers.
- Canada: RCS is supported by some mobile carriers in Canada, but adoption is still in its early stages.
15.2. Europe
- Western Europe: RCS is widely supported by mobile carriers in Western Europe, with many countries seeing significant adoption rates.
- Eastern Europe: RCS adoption in Eastern Europe is growing, but it is still less prevalent than in Western Europe.
15.3. Asia-Pacific
- Japan and South Korea: Japan and South Korea have been early adopters of RCS, with widespread support from mobile carriers and device manufacturers.
- China: RCS adoption in China is growing, but it faces competition from popular local messaging apps.
- India: RCS adoption in India is rapidly expanding, driven by Google’s efforts to partner with mobile carriers.
15.4. Latin America
- Brazil: RCS adoption in Brazil is growing, with support from some mobile carriers and device manufacturers.
- Mexico: RCS adoption in Mexico is still in its early stages, but there is growing interest from mobile carriers.
15.5. Africa
- South Africa: RCS adoption in South Africa is growing, with support from some mobile carriers.
- Nigeria: RCS adoption in Nigeria is still in its early stages, but there is potential for growth in the future.
16. Addressing Concerns: The Drawbacks of RCS Messaging
While RCS offers many advantages, it also has some drawbacks and limitations that users should be aware of:
16.1. Lack of Universal End-to-End Encryption
- Privacy Concerns: The lack of universal end-to-end encryption in RCS raises privacy concerns for some users, as messages may be accessible to mobile carriers and other third parties.
- Security Risks: The absence of E2EE makes RCS more vulnerable to eavesdropping and interception than messaging apps that offer E2EE by default.
16.2. Dependency on Mobile Carrier Support
- Fragmentation: RCS relies on mobile carrier support, which can vary by region and provider, leading to fragmentation and inconsistent experiences.
- Limited Control: Users have limited control over RCS settings and features, as they are determined by the mobile carrier.
16.3. Potential for Spam and Phishing
- Business Messaging Risks: The increased use of RCS for business messaging may lead to a rise in spam and phishing attempts, as businesses can send branded messages and interactive elements.
- Verification Challenges: It can be challenging for users to verify the authenticity of business messages, making them more vulnerable to scams and fraud.
16.4. Complexity and Technical Challenges
- Implementation Complexity: Implementing RCS can be technically complex, requiring significant investment and expertise from mobile carriers and device manufacturers.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring interoperability between different RCS implementations can be challenging, leading to compatibility issues and inconsistent experiences.
16.5. Reliance on Data Connectivity
- Data Costs: RCS relies on data connectivity, which can be expensive for users in some regions.
- Connectivity Issues: Users may experience issues with RCS messaging in areas with poor or unreliable data connectivity.
17. How to Stay Updated on the Latest RCS Developments
The world of RCS is constantly evolving, with new features, updates, and developments emerging regularly. Here’s how to stay informed about the latest RCS news:
17.1. Follow Industry News Sources
- Tech Blogs and Websites: Stay updated on RCS news by following reputable tech blogs and websites that cover mobile messaging and telecommunications.
- GSMA Website: The GSM Association (GSMA) website provides information about RCS standards, specifications, and industry initiatives.
- Google’s Android Developers Blog: Google’s Android Developers Blog often features articles and updates about RCS and its implementation on Android devices.
17.2. Join Online Communities and Forums
- Reddit: Participate in discussions about RCS on relevant Reddit communities, such as r/Android and r/RCSmessaging.
- Online Forums: Join online forums and communities dedicated to mobile messaging and telecommunications to exchange information and insights about RCS.
17.3. Attend Industry Events and Webinars
- Mobile World Congress (MWC): Attend Mobile World Congress (MWC) and other industry events to learn about the latest RCS developments and network with experts and professionals.
- Webinars and Online Conferences: Participate in webinars and online conferences focused on RCS to stay updated on the latest trends and best practices.
17.4. Follow Social Media Accounts
- Twitter: Follow relevant Twitter accounts, such as those of industry analysts, mobile carriers, and device manufacturers, to stay updated on RCS news and announcements.
- LinkedIn: Connect with professionals in the mobile messaging and telecommunications industries on LinkedIn to share insights and information about RCS.
17.5. Subscribe to Newsletters and Mailing Lists
- Industry Newsletters: Subscribe to newsletters and mailing lists from industry organizations and news sources to receive regular updates about RCS.
- Google’s RCS Newsletter: Sign up for Google’s RCS newsletter to receive updates about RCS developments and initiatives.
18. The Impact of 5G on RCS Messaging: A Synergistic Relationship
The rollout of 5G networks is poised to have a significant impact on RCS messaging, enhancing its capabilities and expanding its potential. Here’s how 5G and RCS are set to work together:
18.1. Faster Speeds and Lower Latency
- Improved Media Sharing: 5G’s faster speeds and lower latency will enable users to share high-resolution photos, videos, and files more quickly and seamlessly via RCS.
- Real-Time Communications: 5G will enhance real-time communications features in RCS, such as video calling and interactive messaging, providing a more responsive and engaging experience.
18.2. Enhanced Capacity and Scalability
- Increased Message Volume: 5G’s increased capacity and scalability will allow mobile carriers to handle a larger volume of RCS messages without experiencing congestion or performance issues.
- Support for New Use Cases: 5G will enable RCS to support new use cases and applications, such as IoT device control and augmented reality experiences.
18.3. Edge Computing and AI Integration
- Localized Processing: 5G’s edge computing capabilities will allow for localized processing of RCS messages, reducing latency and improving performance.
- AI-Powered Features: 5G will facilitate the integration of AI-powered features into RCS, such as chatbots, personalized recommendations, and contextual messaging.
18.4. Enhanced Security and Reliability
- Secure Communications: 5G’s enhanced security features will provide a more secure channel for RCS messaging, reducing the risk of eavesdropping and interception.
- Reliable Connectivity: 5G’s reliable connectivity will ensure that RCS messages are delivered promptly and reliably, even in areas with poor network coverage.
18.5. New Business Opportunities
- Enhanced Business Messaging: 5G will enable businesses to create richer and more interactive RCS messaging experiences, improving customer engagement and driving sales.
- Innovative Services: 5G will facilitate the development of innovative services and applications that leverage RCS messaging, creating new revenue streams for mobile carriers and businesses.
19. Real-World Applications: How RCS is Being Used Today
RCS is already being used in a variety of real-world applications across different industries. Here are some examples:
19.1. Retail and E-Commerce
- Order Updates: Retailers send order updates and tracking information to customers via RCS, providing a seamless and convenient shopping experience.
- Promotional Offers: E-commerce businesses send targeted promotional offers and discounts to customers via RCS, driving sales and increasing customer loyalty.
- Customer Support: Retailers provide real-time customer support via RCS, resolving customer inquiries and issues quickly and efficiently.
19.2. Travel and Hospitality
- Flight Updates: Airlines send flight updates and gate information to passengers via RCS, keeping them informed about their travel plans.
- Hotel Bookings: Hotels send booking confirmations and check-in instructions to guests via RCS, providing a seamless and convenient arrival experience.
- Concierge Services: Hotels provide concierge services via RCS, allowing guests to request amenities, make reservations, and ask questions.
19.3. Banking and Financial Services
- Transaction Alerts: Banks send transaction alerts and fraud warnings to customers via RCS, helping them monitor their accounts and protect against fraud.
- Account Balances: Banks provide account balance information to customers via RCS, allowing them to check their balances quickly and easily.
- Customer Support: Banks provide customer support via RCS, resolving customer inquiries and issues securely and efficiently.
19.4. Healthcare
- Appointment Reminders: Healthcare providers send appointment reminders to patients via RCS, reducing no-shows and improving patient care.
- Medication Reminders: Pharmacies send medication reminders to patients via RCS, helping them adhere to their medication schedules and improve their health outcomes.
- Health Information: Healthcare providers provide health information and advice to patients via RCS, promoting health education and disease prevention.
19.5. Automotive
- Vehicle Diagnostics: Automakers send vehicle diagnostics and maintenance reminders to car owners via RCS, helping them keep their vehicles in good condition.
- Emergency Assistance: Automakers provide emergency assistance via RCS, allowing car owners to request roadside assistance and report accidents.
- Navigation Information: Automakers send navigation information and traffic updates to drivers via RCS, helping them navigate safely and efficiently.
20. Expert Opinions: What Industry Leaders Are Saying About RCS
To provide a balanced perspective on RCS, let’s consider the opinions of industry leaders and experts:
20.1. Positive Outlooks
- Google: “RCS is the future of messaging, and we’re committed to working with mobile carriers and device manufacturers to make it a universal standard.”
- GSMA: “RCS has the potential to transform the mobile messaging landscape, providing consumers and businesses with richer and more engaging communication experiences.”
- Industry Analysts: “RCS is poised to become a key enabler of digital transformation, allowing businesses to engage with customers in more personalized and interactive ways.”
20.2. Cautious Perspectives
- Mobile Carriers: “Implementing RCS can be complex and requires significant investment, but we believe it’s worth it to provide our customers with a better messaging experience.”
- Device Manufacturers: “We’re evaluating RCS and considering how it could be integrated into
