Why Does My Chest Crack When I Stretch? It’s a common question, and at WHY.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide a clear and comprehensive answer. This cracking sound is often related to joint cavitation, a normal phenomenon, and other factors. Explore WHY.EDU.VN for reliable answers about crepitus, joint noises, and skeletal sounds.
1. Understanding the Cracking Sound
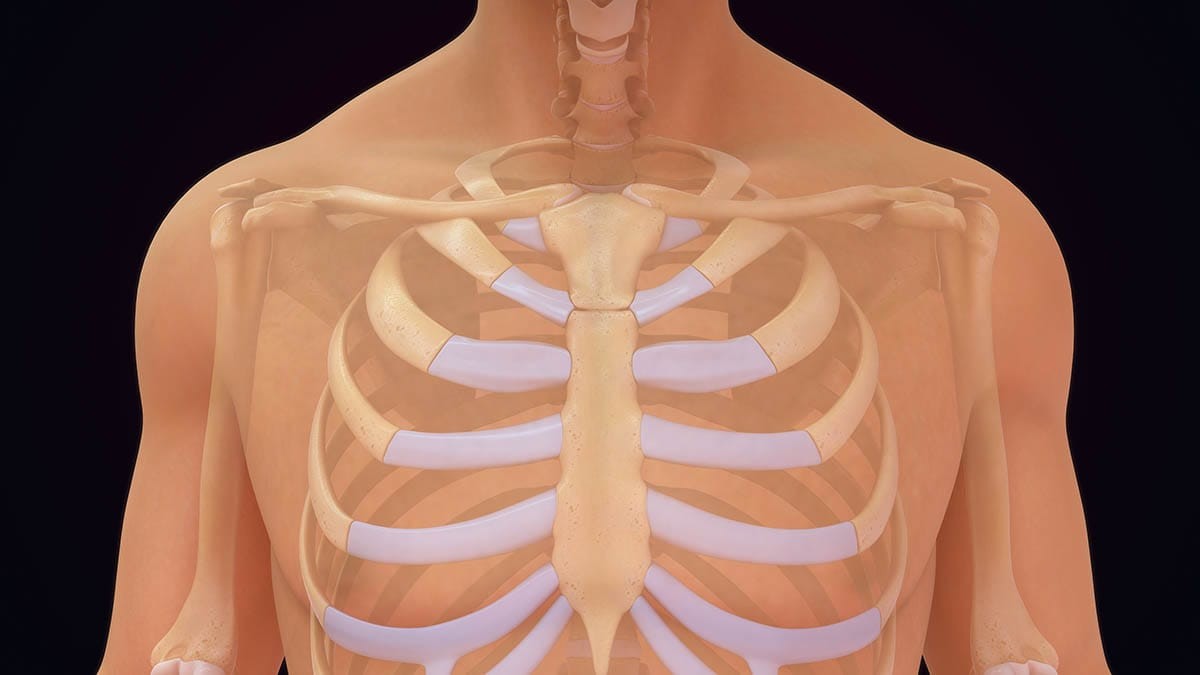
The sound you hear when your chest cracks during a stretch is often attributed to joint cavitation. This involves the formation and collapse of gas bubbles within the synovial fluid, which lubricates your joints. This fluid is crucial for joint health, and these sounds are generally harmless. This process occurs due to changes in pressure within the joint, causing a popping or cracking sound that can be surprising but is usually a normal occurrence.
2. Decoding Chest Cracking: Specific Causes
There are several reasons why your chest might crack when you stretch. Let’s explore some of the most common:
-
2.1 Joint Cavitation: As mentioned earlier, this is a primary reason. The pressure changes when you move can cause gas bubbles to form and collapse in the synovial fluid, leading to that cracking sound. This is especially common in the costosternal joints (where your ribs meet your sternum) and the costovertebral joints (where your ribs meet the spine).
-
2.2 Tendon and Ligament Movement: Your tendons and ligaments may snap or slide over bony structures during movement. This can happen, especially if you’ve been inactive or if you’re increasing your activity level. These tissues might shift position as they adjust to the new range of motion.
-
2.3 Cartilage Changes: The cartilage in your joints can change over time. As you age, the cartilage may become rougher or thinner, leading to increased joint noises. This is more common as you get older, but it can happen at any age.
-
2.4 Muscle Tightness: Tight muscles can cause increased pressure on the joints, which can lead to cracking sounds when you stretch. Stretching and regular exercise can help to alleviate this tightness and reduce the likelihood of cracking.
-
2.5 Posture and Alignment: Poor posture can contribute to joint cracking. When your body is misaligned, it can put extra stress on certain joints, making them more prone to cracking. Maintaining good posture and proper body alignment can help reduce this.
3. When Chest Cracking is Normal vs. Concerning
Generally, chest cracking is normal and not a cause for concern. It’s usually just a sign that your joints are moving and that gas bubbles are forming and collapsing in the synovial fluid. However, there are situations where chest cracking could indicate a more serious issue.
- 3.1 Normal Cracking: Normal joint cracking is usually painless and doesn’t limit your range of motion. It might be accompanied by a slight sensation of popping or clicking, but it shouldn’t be painful.
- 3.2 Concerning Cracking: If the cracking is accompanied by pain, swelling, redness, or a limited range of motion, it’s important to seek medical attention. These symptoms could indicate an underlying condition such as arthritis, bursitis, or a ligament injury.
- 3.3 Other Symptoms: Other symptoms to watch out for include numbness, tingling, and weakness. If you experience any of these symptoms along with chest cracking, it’s important to consult a doctor to determine the cause.
4. Conditions That May Cause Chest Cracking
Several medical conditions can cause or contribute to chest cracking. These include:
- 4.1 Costochondritis: This is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects your ribs to your sternum. It can cause chest pain and tenderness, and it may also be accompanied by cracking or popping sounds.
- 4.2 Tietze Syndrome: Similar to costochondritis, Tietze syndrome is an inflammation of the cartilage in the chest. However, it usually affects only one rib, and it can cause more severe pain than costochondritis.
- 4.3 Arthritis: Arthritis is a common condition that causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can affect any joint in the body, including the joints in the chest.
- 4.4 Bursitis: Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursae, which are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints. It can cause pain and swelling in the affected joint, and it may also be accompanied by cracking or popping sounds.
- 4.5 Joint Hypermobility Syndrome: This condition involves having unusually flexible joints, which can make them more prone to cracking and popping.
5. Diagnosing the Cause of Chest Cracking
If you’re concerned about chest cracking, it’s important to see a doctor to determine the cause. They will likely perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history. In some cases, they may also order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to get a better look at the joints in your chest.
6. Self-Assessment: Assessing Chest Flexibility
To check your chest flexibility, you can perform a simple mobility test at home. This test can help you understand if mobility issues might be contributing to why your chest cracks when you stretch.
-
6.1 Wall Angel Exercise:
- Stand with your back against a wall, feet a few inches away from the baseboard.
- Press your lower back, shoulders, and head against the wall.
- Raise your arms to shoulder height, bending your elbows so your arms form a 90-degree angle.
- Slowly slide your arms up and down the wall, keeping your elbows and wrists in contact with the wall.
- Assessment: If you can perform this movement smoothly without discomfort or significant gaps between your arms and the wall, your chest and shoulder mobility are likely in good shape.
-
6.2 Overhead Reach:
- Stand upright and reach both arms straight up towards the ceiling.
- Try to keep your biceps close to your ears without arching your back.
- Assessment: If you can extend your arms fully without pain or compensation in your posture, your mobility is likely adequate.
These tests offer insights into your joint and muscle flexibility.
7. Effective Ways to Reduce Chest Cracking
If you find the chest cracking bothersome, there are several steps you can take to minimize it:
-
7.1 Regular Stretching: Stretching can help improve joint mobility and reduce muscle tightness, which can decrease the likelihood of cracking. Focus on stretches that target your chest, shoulders, and back.
-
7.2 Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining joint health. Water helps to lubricate the joints and keep the cartilage healthy.
-
7.3 Warm-Up Exercises: Warming up before physical activity can help prepare your joints and muscles for movement, reducing the risk of cracking. Incorporate light cardio and dynamic stretching into your warm-up routine.
-
7.4 Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles around your chest and shoulders can provide better support for your joints and reduce the likelihood of cracking. Focus on exercises that target the pectoral muscles, deltoids, and back muscles.
-
7.5 Good Posture: Maintaining good posture can reduce unnecessary strain on the muscles and joints, potentially minimizing cracking. Be mindful of your posture throughout the day, especially when sitting or standing for long periods.
8. Debunking the Myths: Cracking and Arthritis
One common myth is that cracking your joints will lead to arthritis. However, numerous studies have shown that joint cracking does not correlate with the development of arthritis. So, if your chest cracks when you stretch, it’s not a sign that arthritis is on the way.
- 8.1 Scientific Evidence: Scientific studies have debunked the myth that joint cracking leads to arthritis. These studies have shown no correlation between joint cracking and the development of arthritis.
- 8.2 Focus on Healthy Joints: Instead of worrying about cracking sounds, focus on maintaining healthy joints through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper hydration.
9. The Importance of Addressing Painful Chest Cracking
It’s important to address any painful chest cracking. While occasional, painless cracking is usually harmless, persistent pain or discomfort should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
10. Expert Insights on Joint Health
Experts in the field of orthopedics and sports medicine often emphasize the importance of maintaining healthy joints through a combination of exercise, nutrition, and lifestyle choices. They recommend incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine, as well as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that put excessive stress on your joints.
11. Advanced Techniques for Joint Care
There are several advanced techniques for joint care that can help improve joint health and reduce the likelihood of cracking:
- 11.1 Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and strengthen the muscles around the joints. A physical therapist can develop a customized treatment plan based on your individual needs.
- 11.2 Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic care can help improve spinal alignment and reduce pressure on the joints. A chiropractor can use various techniques to adjust the spine and other joints in the body.
- 11.3 Massage Therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension and improve blood flow to the joints. A massage therapist can use various techniques to release tight muscles and improve joint mobility.
12. Lifestyle Adjustments for Joint Comfort
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can also help improve joint comfort and reduce the likelihood of cracking:
- 12.1 Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on your joints.
- 12.2 Ergonomics: Using proper ergonomics at work and at home can help reduce strain on your joints.
- 12.3 Avoiding Overuse: Avoiding activities that put excessive stress on your joints can help prevent injuries and reduce the likelihood of cracking.
13. Preventative Measures for Long-Term Joint Health
Taking preventative measures can help maintain long-term joint health and reduce the risk of joint problems:
- 13.1 Regular Exercise: Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles around your joints and improve joint mobility.
- 13.2 Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to maintain healthy joints.
- 13.3 Proper Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help lubricate your joints and keep the cartilage healthy.
14. Future Research on Joint Sounds
Future research on joint sounds may provide further insights into the mechanisms behind joint cracking and popping. This research may also lead to new and improved treatments for joint problems.
- 14.1 Understanding the Science: Further research is needed to fully understand the science behind joint sounds. This research may help to identify the specific factors that contribute to joint cracking and popping.
- 14.2 New Treatments: Future research may lead to new and improved treatments for joint problems. These treatments may focus on reducing pain, improving joint mobility, and preventing joint damage.
15. Understanding Synovial Fluid Dynamics
Synovial fluid plays a critical role in joint function, acting as a lubricant and shock absorber. Its composition and dynamics can influence joint sounds.
- 15.1 Viscosity: The viscosity of synovial fluid affects how easily joints move.
- 15.2 Composition: Changes in synovial fluid composition can impact joint health.
- 15.3 Lubrication: Adequate synovial fluid ensures smooth joint movement.
16. The Role of Genetics in Joint Health
Genetics can play a significant role in joint health. Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to joint problems, while others may have genes that protect against joint damage.
- 16.1 Predisposition: Genetic factors can increase the risk of joint problems.
- 16.2 Protection: Some genes may offer protection against joint damage.
- 16.3 Family History: A family history of joint problems can increase your risk.
17. The Impact of Inflammation on Joint Sounds
Inflammation can significantly impact joint sounds. Inflamed joints may produce more frequent and louder cracking sounds.
- 17.1 Increased Noise: Inflammation often leads to increased joint noise.
- 17.2 Pain and Swelling: Inflammation can cause pain and swelling in the affected joint.
- 17.3 Underlying Conditions: Inflammation may indicate underlying conditions like arthritis.
18. Alternative Therapies for Joint Health
Several alternative therapies can help improve joint health and reduce the likelihood of cracking.
- 18.1 Acupuncture: Acupuncture can help reduce pain and inflammation in the joints.
- 18.2 Yoga: Yoga can help improve joint mobility and reduce muscle tension.
- 18.3 Herbal Remedies: Some herbal remedies may help reduce pain and inflammation in the joints.
19. Chest Cracking and Breathing Mechanics
Chest cracking can sometimes be related to breathing mechanics. Deep breathing exercises may help improve chest mobility and reduce cracking.
- 19.1 Deep Breathing: Deep breathing exercises can improve chest mobility.
- 19.2 Posture: Proper posture can improve breathing mechanics.
- 19.3 Muscle Activation: Activating chest muscles during breathing can reduce cracking.
20. Addressing Psychological Factors
Psychological factors such as stress and anxiety can also contribute to joint pain and cracking. Addressing these factors can help improve joint health.
- 20.1 Stress Reduction: Reducing stress can improve joint health.
- 20.2 Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness can help manage pain and discomfort.
- 20.3 Relaxation Techniques: Relaxation techniques can reduce muscle tension and improve joint mobility.
21. Ergonomic Considerations for Desk Workers
For those who spend long hours at a desk, ergonomic adjustments can significantly reduce joint strain and the likelihood of chest cracking. Proper chair height, keyboard placement, and regular breaks can make a big difference.
- 21.1 Chair Height: Adjust your chair so your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are at a 90-degree angle.
- 21.2 Keyboard Placement: Position your keyboard so your elbows are at a 90-degree angle and your wrists are straight.
- 21.3 Regular Breaks: Take frequent breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around.
22. The Influence of Diet on Joint Lubrication
What you eat can influence joint lubrication and overall joint health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can support healthy synovial fluid and reduce inflammation.
- 22.1 Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s can reduce inflammation.
- 22.2 Antioxidants: Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants can protect joint tissue from damage.
- 22.3 Vitamins: Vitamins C and D are essential for joint health and collagen production.
23. Importance of Balanced Muscle Strength
Balanced muscle strength around the chest and shoulders is crucial for preventing joint issues. Weak or tight muscles can contribute to misalignment and increased cracking.
- 23.1 Chest Exercises: Exercises like push-ups and chest presses can strengthen the pectoral muscles.
- 23.2 Back Exercises: Rows and pull-ups can strengthen the back muscles, ensuring balance.
- 23.3 Shoulder Exercises: Exercises like lateral raises and front raises can strengthen the shoulder muscles.
24. Understanding Thoracic Spine Mobility
Thoracic spine mobility is closely linked to chest movement and joint sounds. Improving the flexibility of the thoracic spine can reduce strain on the rib cage and minimize cracking.
- 24.1 Stretching Exercises: Thoracic spine stretches can improve mobility.
- 24.2 Foam Rolling: Foam rolling can release tension in the thoracic spine.
- 24.3 Posture Correction: Correcting poor posture can improve thoracic spine alignment.
25. The Connection Between Rib Cage Movement and Chest Sounds
Rib cage movement during breathing and stretching can directly influence chest sounds. Understanding this connection can help in identifying the causes of cracking.
- 25.1 Breathing Techniques: Proper breathing techniques can optimize rib cage movement.
- 25.2 Stretching Exercises: Targeted stretching can improve rib cage flexibility.
- 25.3 Muscle Balance: Ensuring balanced muscle strength can stabilize the rib cage.
26. Innovations in Joint Imaging Technologies
Advancements in joint imaging technologies are providing more detailed insights into joint structures and potential causes of cracking. MRI and ultrasound technologies are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
- 26.1 MRI: Provides detailed images of soft tissues and joint structures.
- 26.2 Ultrasound: Allows real-time visualization of joint movement.
- 26.3 CT Scans: Offers detailed bone imaging and structural analysis.
27. Tailored Exercise Programs for Chest Mobility
Customized exercise programs designed to improve chest mobility can reduce cracking and enhance overall joint health. These programs should be tailored to individual needs and fitness levels.
- 27.1 Assessment: A thorough assessment to identify specific mobility issues.
- 27.2 Goal Setting: Setting realistic and achievable goals for improvement.
- 27.3 Progression: Gradually increasing the intensity and complexity of exercises.
28. The Impact of Sleep Quality on Joint Health
Sleep quality significantly impacts joint health. Poor sleep can exacerbate inflammation and pain, increasing the likelihood of joint cracking.
- 28.1 Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- 28.2 Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- 28.3 Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques to improve sleep quality.
29. Considerations for Athletes and Active Individuals
Athletes and active individuals should take extra precautions to protect their joints and minimize the risk of injury. Proper warm-up, cool-down, and conditioning are essential.
- 29.1 Warm-Up: Prepare the joints and muscles for activity with dynamic stretching.
- 29.2 Cool-Down: Gradually reduce activity intensity and perform static stretching.
- 29.3 Conditioning: Strengthen the muscles around the joints to provide support and stability.
30. Resources and Support for Joint Health
Numerous resources and support networks are available for individuals seeking to improve their joint health. These include online forums, support groups, and professional healthcare providers.
- 30.1 Online Forums: Connect with others and share experiences.
- 30.2 Support Groups: Find emotional support and practical advice.
- 30.3 Healthcare Providers: Consult with doctors, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
Why does my chest crack when I stretch? Understanding the reasons behind chest cracking, differentiating between normal and concerning sounds, and taking appropriate measures can help you maintain healthy joints. If you have more questions or need expert advice, visit WHY.EDU.VN, where our experts are ready to provide clear, reliable answers. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101. Your journey to better understanding starts here.
FAQ: Decoding Your Chest Cracking
-
Q1: Is chest cracking always a sign of a problem?
- A: Not necessarily. It’s often due to normal joint movement and gas bubbles in the synovial fluid.
-
Q2: When should I worry about chest cracking?
- A: If it’s accompanied by pain, swelling, or limited range of motion.
-
Q3: Can stretching prevent chest cracking?
- A: Regular stretching can improve joint mobility and reduce the likelihood of cracking.
-
Q4: Does joint cracking lead to arthritis?
- A: No, scientific studies have debunked this myth.
-
Q5: What role does hydration play in joint health?
- A: Adequate hydration keeps joints lubricated and cartilage healthy.
-
Q6: How can I improve my posture to reduce joint strain?
- A: Be mindful of your posture, especially when sitting or standing, and use ergonomic support.
-
Q7: Are there any exercises that can help?
- A: Strengthening exercises targeting the chest, shoulders, and back can provide better support.
-
Q8: What if I have other symptoms like numbness or tingling?
- A: Consult a doctor, as these symptoms could indicate an underlying issue.
-
Q9: Can diet influence joint health?
- A: Yes, a balanced diet with omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can support joint health.
-
Q10: Where can I find reliable answers to my health questions?
- A: Visit why.edu.vn for expert advice and comprehensive information on health-related topics.