Introduction
Why Does My Car Vibrate When Idle? This is a common question, and understanding the reasons behind it can save you from potential headaches and costly repairs. At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into the intricacies of automotive mechanics to provide clear, reliable answers. A car vibration at idle can stem from various sources, including engine misfires, worn-out components, or issues within the fuel or air intake systems. Let’s explore the common causes, how to diagnose the problem, and the importance of regular maintenance to prevent such issues, addressing common symptoms like shaking, rough idling, and erratic RPMs.
1. Understanding the Basics of Engine Idling
1.1 What Does It Mean When Your Car Is Idling?
When your car is idling, the engine is running but the vehicle is not in motion. This usually happens when you’re stopped at a traffic light or parked with the engine on. During idle, the engine needs to maintain a certain RPM (revolutions per minute) to keep running smoothly. A normal idle speed typically ranges from 600 to 1000 RPM.
1.2 Why Is a Smooth Idle Important?
A smooth idle indicates that all engine components are working harmoniously. The right mixture of air and fuel is being delivered, combustion is occurring efficiently, and the engine is generating enough power to keep all systems running, such as the cooling system, power steering, and air conditioning.
1.3 What Is Considered a Normal Idle RPM?
A normal idle RPM generally falls between 600 and 1000 RPM. However, this can vary slightly depending on the make and model of your vehicle. Consult your car’s manual for the specific recommended idle speed.
2. Common Causes of Car Vibration When Idle
2.1 Engine Misfires
Engine misfires are a primary cause of vibrations when idling. A misfire occurs when one or more of the engine’s cylinders fails to fire properly. This can be due to a variety of reasons, including faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
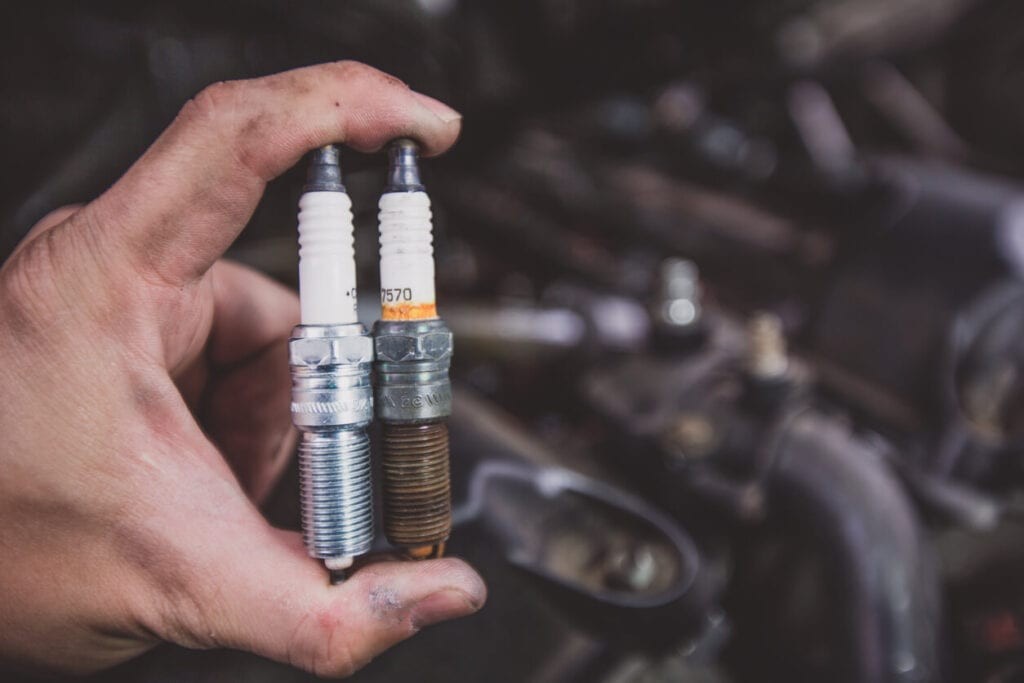
2.2 Faulty Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are essential for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders. Over time, spark plugs can become worn or fouled, leading to weak or inconsistent sparks.
Signs of Faulty Spark Plugs:
- Rough idling
- Engine misfires
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Difficulty starting the engine
Expert Insights: According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), replacing spark plugs every 30,000 to 50,000 miles can prevent significant ignition system damage and maintain optimal engine performance.
2.3 Failing Ignition Coils
Ignition coils provide the high-voltage spark needed to ignite the fuel-air mixture. If an ignition coil fails, the cylinder it serves will not fire, leading to a misfire and vibration.
Symptoms of a Bad Ignition Coil:
- Rough idle
- Check engine light
- Decreased power
- Poor fuel economy
2.4 Dirty or Clogged Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors spray fuel into the engine’s cylinders. Over time, these injectors can become clogged with deposits, affecting the fuel spray pattern and causing a lean or rich fuel mixture.
Signs of Clogged Fuel Injectors:
- Rough idling
- Poor acceleration
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Engine misfires
Table: Comparing Clean vs. Clogged Fuel Injectors
| Feature | Clean Fuel Injector | Clogged Fuel Injector |
|---|---|---|
| Spray Pattern | Fine, conical spray | Uneven, dripping, or restricted spray |
| Fuel Delivery | Precise and consistent | Inconsistent and reduced |
| Engine Performance | Smooth and efficient | Rough idling, misfires, poor acceleration |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimal | Reduced |


2.5 Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks occur when there is an unintended opening in the engine’s vacuum system. This can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to rough idling and vibrations.
Common Locations for Vacuum Leaks:
- Hoses
- Intake manifold gaskets
- Throttle body
- PCV valve
Signs of a Vacuum Leak:
- Rough idle
- Hissing sound from the engine bay
- Increased RPMs at idle
- Check engine light
2.6 Problems with the Air Intake System
The air intake system ensures that the engine receives the right amount of clean air. Issues such as a clogged air filter or a malfunctioning mass airflow (MAF) sensor can cause vibrations at idle.
2.7 Clogged Air Filter
The air filter prevents dirt and debris from entering the engine. When it becomes clogged, it restricts airflow, causing the engine to run rich (too much fuel, not enough air).
Symptoms of a Clogged Air Filter:
- Rough idle
- Reduced fuel economy
- Decreased acceleration
- Check engine light
2.8 Malfunctioning Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor
The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, providing this data to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the fuel mixture. A faulty MAF sensor can send incorrect data, leading to an improper air-fuel ratio.
Signs of a Faulty MAF Sensor:
- Rough idle
- Poor fuel economy
- Stalling
- Check engine light
2.9 Issues with the Exhaust System
The exhaust system removes combustion gases from the engine. Problems such as a blocked catalytic converter or exhaust leaks can cause backpressure, leading to vibrations.
2.10 Blocked Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions. If it becomes clogged, it can restrict exhaust flow, causing the engine to work harder and vibrate.
Symptoms of a Blocked Catalytic Converter:
- Rough idle
- Reduced power
- Overheating
- Rattling noise from under the car
2.11 Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks can disrupt the engine’s backpressure, leading to rough idling and vibrations.
Signs of an Exhaust Leak:
- Rough idle
- Loud exhaust noise
- Reduced fuel economy
- Smell of exhaust fumes inside the car
2.12 Worn or Damaged Motor Mounts
Motor mounts secure the engine to the car’s frame. Over time, these mounts can wear out or break, causing the engine to vibrate excessively, especially at idle.
Signs of Worn Motor Mounts:
- Excessive vibration at idle
- Loud clunking noise when accelerating or braking
- Engine movement in the engine bay
Table: Motor Mount Materials and Lifespan
| Material | Average Lifespan | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | 5-7 years or 60,000 miles | Absorbs vibrations well but degrades over time due to heat and oil exposure |
| Polyurethane | 7-10 years or 80,000 miles | More durable than rubber but transmits more vibration to the cabin |
| Hydraulic | 5-7 years or 60,000 miles | Provides excellent vibration damping but can leak and fail |
2.13 Low Engine Compression
Engine compression is the pressure created in the cylinders during the compression stroke. Low compression in one or more cylinders can cause an imbalance, leading to vibrations.
Causes of Low Compression:
- Worn piston rings
- Leaking valves
- Damaged cylinder walls
Symptoms of Low Compression:
- Rough idle
- Reduced power
- Poor fuel economy
- Engine misfires
2.14 Torque Converter Problems (Automatic Transmissions)
In vehicles with automatic transmissions, the torque converter transfers power from the engine to the transmission. A failing torque converter can cause vibrations, especially at idle.
Signs of a Failing Torque Converter:
- Rough idle
- Stalling
- Slipping gears
- Unusual noises from the transmission
2.15 Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Issues
The IAC valve regulates the amount of air that bypasses the throttle plate at idle, maintaining a steady RPM. A malfunctioning IAC valve can cause the engine to idle too high or too low, leading to vibrations.
Symptoms of a Faulty IAC Valve:
- Rough idle
- Stalling
- High idle speed
- Fluctuating RPMs
3. Diagnosing the Vibration
3.1 Visual Inspection
Start with a visual inspection of the engine bay. Look for any obvious signs of damage, such as cracked hoses, loose connections, or leaking fluids.
3.2 Listening for Unusual Noises
Listen carefully to the engine while it’s idling. Note any unusual noises, such as hissing, knocking, or rattling, which can provide clues about the source of the vibration.
3.3 Checking the Check Engine Light
If the check engine light is on, use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the error codes. These codes can help pinpoint the problematic component.
Common OBD-II Codes Related to Rough Idle:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0301-P0312: Cylinder Misfire Detected (specific cylinder number)
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1)
- P0175: System Too Rich (Bank 2)
- P0505: Idle Air Control System Malfunction
3.4 Testing Individual Components
If a specific component is suspected, it can be tested using various methods:
- Spark Plugs: Inspect for wear, carbon buildup, or damage.
- Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to check for proper resistance.
- Fuel Injectors: Listen for a clicking sound to verify they are firing.
- Vacuum Leaks: Use a smoke machine to identify leaks.
- MAF Sensor: Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s output voltage.
3.5 Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can provide valuable data, such as engine RPM, fuel trim, and sensor readings, helping to diagnose the cause of the vibration.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a Vibrating Car at Idle
4.1 Gathering Necessary Tools and Materials
Before starting any repairs, gather the necessary tools and materials. This may include:
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- Screwdrivers
- OBD-II scanner
- Multimeter
- Replacement parts (spark plugs, ignition coils, etc.)
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
4.2 Addressing Spark Plug Issues
If the spark plugs are worn or fouled, replace them with new ones. Ensure the spark plug gap is set correctly according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Step-by-Step Spark Plug Replacement:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Remove the ignition coil or spark plug wire from the spark plug.
- Use a spark plug socket to remove the old spark plug.
- Inspect the spark plug for signs of wear or damage.
- Install the new spark plug, tightening it to the specified torque.
- Reinstall the ignition coil or spark plug wire.
- Repeat for all spark plugs.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
4.3 Fixing Ignition Coil Problems
If an ignition coil is faulty, replace it with a new one. Ensure the new coil is compatible with your vehicle.
Step-by-Step Ignition Coil Replacement:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the faulty ignition coil.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the coil.
- Remove the mounting bolts or screws.
- Remove the old ignition coil.
- Install the new ignition coil, tightening the mounting bolts or screws.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
4.4 Cleaning or Replacing Fuel Injectors
If the fuel injectors are dirty, they can be cleaned using a fuel injector cleaner additive or by removing them and having them professionally cleaned. In severe cases, replacement may be necessary.
Fuel Injector Cleaning Methods:
- Fuel Injector Cleaner Additive: Add the cleaner to the fuel tank and run the engine.
- Professional Cleaning: Remove the injectors and send them to a shop for ultrasonic cleaning.
4.5 Repairing Vacuum Leaks
Locate and repair any vacuum leaks. This may involve replacing cracked hoses or tightening loose connections.
Vacuum Leak Repair Tips:
- Use a smoke machine to locate leaks.
- Replace any cracked or damaged hoses.
- Tighten loose hose clamps.
- Replace worn intake manifold gaskets.
4.6 Replacing Air Filter
Replace the air filter if it is clogged. This is a simple and inexpensive maintenance task that can improve engine performance.
Step-by-Step Air Filter Replacement:
- Locate the air filter housing.
- Remove the air filter housing cover.
- Remove the old air filter.
- Install the new air filter, ensuring it is properly seated.
- Reinstall the air filter housing cover.
4.7 Addressing Motor Mount Issues
If the motor mounts are worn or damaged, replace them. This can be a more complex repair, so consider seeking professional assistance.
Motor Mount Replacement Considerations:
- Support the engine properly before removing the old mounts.
- Ensure the new mounts are compatible with your vehicle.
- Tighten the mounting bolts to the specified torque.
4.8 Checking and Cleaning the IAC Valve
Inspect the IAC valve for dirt and debris. Clean it with a carburetor cleaner if necessary. If the valve is malfunctioning, it may need to be replaced.
IAC Valve Cleaning Steps:
- Locate the IAC valve.
- Disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove the valve from the throttle body.
- Spray the valve with carburetor cleaner.
- Wipe away any dirt and debris.
- Reinstall the valve and electrical connector.
5. Preventing Vibrations Through Regular Maintenance
5.1 Scheduled Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance is key to preventing vibrations and other engine problems. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, which typically includes:
- Oil changes
- Spark plug replacement
- Air filter replacement
- Fuel filter replacement
- Inspection of hoses and belts
5.2 Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect your vehicle for any signs of trouble, such as unusual noises, leaks, or vibrations. Addressing these issues early can prevent more significant problems down the road.
5.3 The Importance of Timely Repairs
Addressing issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more costly and complex repairs. Ignoring symptoms can lead to further damage and reduced vehicle performance.
6. When to Seek Professional Help
6.1 Complex Diagnostic Procedures
Some diagnostic procedures require specialized tools and knowledge. If you are unable to diagnose the cause of the vibration, seek professional help.
6.2 Intricate Repair Work
Certain repairs, such as replacing motor mounts or addressing internal engine issues, are best left to experienced mechanics.
6.3 Ensuring Proper Repairs and Safety
Professional mechanics can ensure that repairs are done correctly and safely, preventing further damage and ensuring your vehicle’s reliability.
7. The Role of WHY.EDU.VN in Automotive Education
7.1 Providing Reliable Automotive Information
WHY.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing accurate and reliable automotive information, helping car owners understand and maintain their vehicles.
7.2 Expert Advice and Guidance
We offer expert advice and guidance on a wide range of automotive topics, from basic maintenance to complex repairs.
7.3 Empowering Car Owners with Knowledge
Our goal is to empower car owners with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their vehicles.
8. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
8.1 Case Study 1: The Case of the Rough-Idling Sedan
A car owner noticed their sedan was vibrating excessively at idle. After checking the spark plugs and finding them worn, they replaced them. The vibration disappeared, and the car ran smoothly again.
8.2 Case Study 2: The Vacuum Leak Mystery
Another car owner experienced rough idling and a hissing sound from the engine bay. After using a smoke machine, they discovered a vacuum leak in a cracked hose. Replacing the hose resolved the issue.
8.3 Case Study 3: The Motor Mount Dilemma
A third car owner noticed excessive vibration and clunking noises when accelerating. A mechanic diagnosed worn motor mounts. Replacing the mounts eliminated the vibration and noise.
9. Troubleshooting Chart for Common Vibration Issues
| Symptom | Possible Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rough idle | Worn spark plugs, vacuum leak, dirty fuel injectors | Replace spark plugs, repair vacuum leak, clean injectors |
| Excessive vibration | Worn motor mounts, low engine compression | Replace motor mounts, address compression issues |
| Check engine light on | Misfires, faulty sensors | Use OBD-II scanner, replace faulty sensors |
| Reduced fuel economy | Clogged air filter, faulty MAF sensor | Replace air filter, replace MAF sensor |
| Stalling | Faulty IAC valve, vacuum leak | Replace IAC valve, repair vacuum leak |
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
10.1 Why does my car vibrate when I’m stopped at a light?
Vibrations when stopped at a light are often due to engine misfires, worn motor mounts, or issues with the idle air control system.
10.2 Can low-quality fuel cause my car to vibrate?
Yes, low-quality fuel can lead to poor combustion and engine misfires, causing vibrations.
10.3 How often should I replace my spark plugs?
Spark plugs should be replaced every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, depending on the manufacturer’s recommendation.
10.4 Is it safe to drive with a vibrating car?
Driving with a vibrating car can be unsafe, as it may indicate a serious mechanical issue. It is best to have the car inspected and repaired as soon as possible.
10.5 Can a dirty air filter cause my car to vibrate?
Yes, a dirty air filter can restrict airflow to the engine, causing it to run rich and vibrate.
10.6 What is the role of the oxygen sensor in preventing vibrations?
The oxygen sensor helps the engine control unit (ECU) maintain the correct air-fuel ratio. A faulty oxygen sensor can lead to an imbalance, causing vibrations.
10.7 How do I check for vacuum leaks in my car?
You can check for vacuum leaks using a smoke machine or by listening for a hissing sound from the engine bay.
10.8 Can worn tires cause my car to vibrate at idle?
Worn tires are more likely to cause vibrations while driving, but in rare cases, severe tire issues can transmit vibrations to the chassis, which may be felt at idle.
10.9 What is the average cost to fix a vibrating car at idle?
The cost to fix a vibrating car varies depending on the cause. Simple fixes like replacing spark plugs or an air filter may cost $50-$200, while more complex repairs like replacing motor mounts or addressing engine issues could cost $500-$2000 or more.
10.10 How can I find a reliable mechanic to diagnose and fix my car?
You can find a reliable mechanic through online reviews, recommendations from friends and family, and by checking for certifications such as ASE (Automotive Service Excellence).
Conclusion
Experiencing a car vibration when idle can be unsettling, but understanding the potential causes can help you address the issue effectively. From engine misfires to worn motor mounts, various factors can contribute to this problem. Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and professional inspections are essential for keeping your vehicle running smoothly. At WHY.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to maintain your car and ensure a safe and comfortable driving experience. Remember to check your car regularly and consult with a trusted mechanic when needed.
Do you have more questions or need expert advice? Visit WHY.EDU.VN at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Let our experts at why.edu.vn help you find the answers you’re looking for and keep your vehicle in top condition!