That sudden, sharp pain in your back that catches you when you inhale deeply can be alarming. You might be settling down for the evening, take a relaxing breath, and then – ouch! Back pain with breathing can range from a fleeting discomfort to a persistent ache that affects your daily life. Is it a minor issue, or could it signal something more serious, like a problem with your lungs or heart? Do you need to seek medical attention?
This article will explore the primary reasons behind back pain when breathing, what you can do to alleviate it, and when it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
The Importance of Addressing Back Pain
It’s easy to dismiss back pain as commonplace. You might think, “Everyone experiences back pain now and then, right? Maybe I just need some over-the-counter pain relievers and it will go away.” While occasional minor back discomfort might resolve on its own, persistent or breathing-related back pain should not be ignored.
At why.edu.vn, we believe that pain is never simply “normal.” Pain is your body’s way of communicating that something is not functioning optimally. Ignoring back pain, especially when it’s linked to breathing, can be detrimental to your overall well-being. Determining when to worry about back pain is crucial, and experiencing pain with each breath is definitely a signal to pay attention to your body and consider seeking professional advice before it impacts your quality of life.
Procrastinating treatment for back pain stemming from an underlying condition can potentially lead to further complications. Early diagnosis allows for prompt intervention and a tailored treatment plan to relieve your pain and address the root cause. It’s always better to be proactive about your health and seek timely medical attention.
Disclaimer: If you experience acute or worsening back pain, or if your pain persists, always consult with your doctor.
Unpacking the Causes of Back Pain When Breathing
When you experience back pain that intensifies with each breath, it’s natural to wonder about the underlying cause. Several conditions can trigger back pain when breathing, each requiring a specific approach to treatment. Let’s delve into some of the most common culprits:
1. Muscle Strain: The Respiratory Muscle Connection
Breathing, an essential and seemingly effortless function, actually involves a complex interplay of various muscles. These muscles, including the diaphragm, intercostals (muscles between ribs), and even back muscles like the serratus posterior and quadratus lumborum, work in concert to expand and contract your chest cavity, facilitating respiration.
If any of these respiratory muscles are strained or injured due to events like a slip and fall, a car accident, overexertion during exercise, or even poor posture, it can lead to significant discomfort, especially when breathing deeply. The injured muscle may spasm or become inflamed, causing pain that radiates to the back and intensifies with respiratory movements.
Fortunately, muscle strain is often a straightforward issue to resolve. Typical self-care remedies include gentle stretching to improve muscle flexibility, applying heat packs to relax tense muscles and cold packs to reduce inflammation, and using over-the-counter pain relievers for temporary pain management. Muscle strains usually improve within a few days and fully heal within a few weeks with proper care.
However, relying solely on painkillers for extended periods can have adverse side effects. If your back pain doesn’t improve noticeably after a week or two of self-care, it’s wise to seek professional guidance to determine the best course of action.
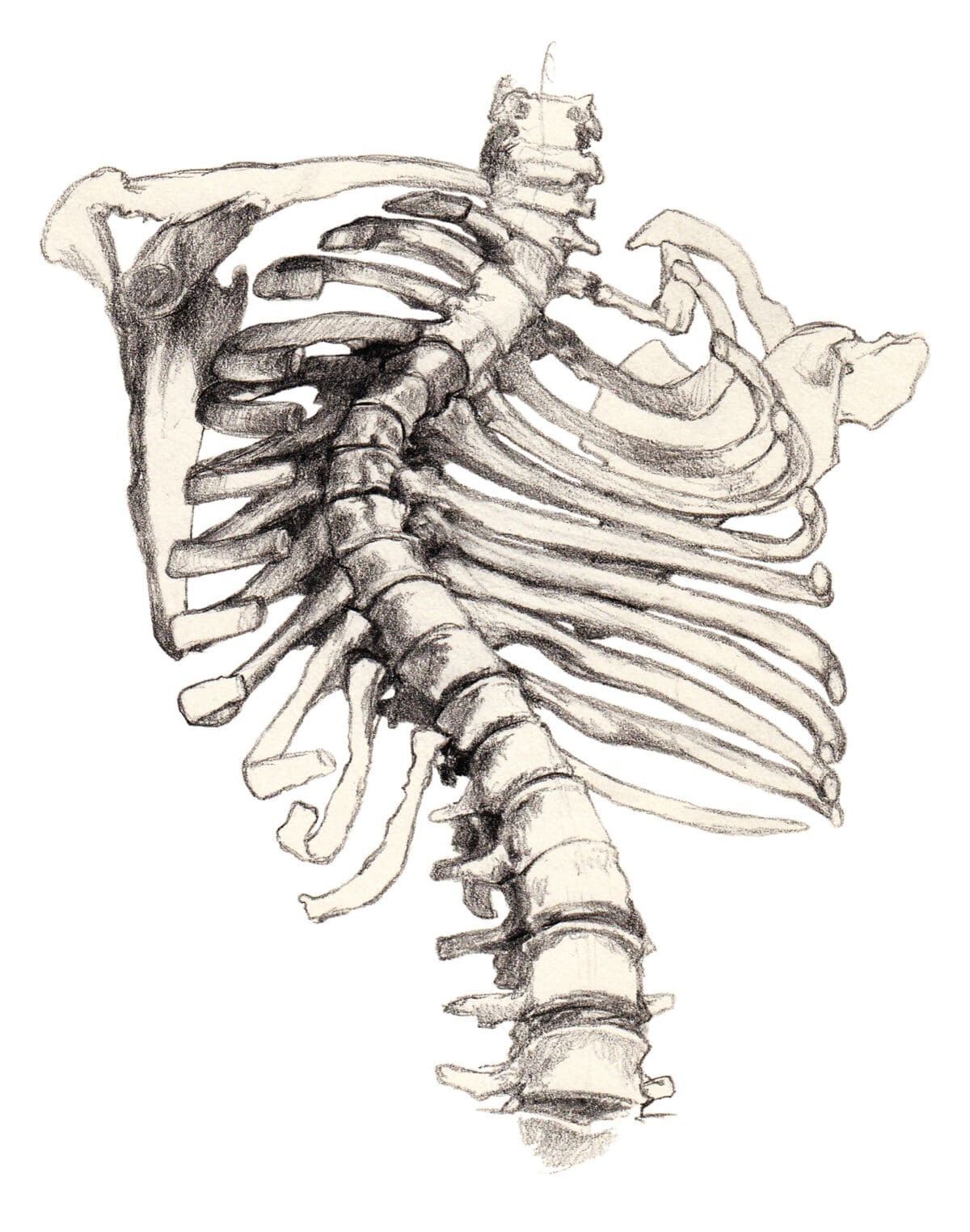 Cartoon drawwing of a rib cage and spine. The spine is curved from scoliosis.
Cartoon drawwing of a rib cage and spine. The spine is curved from scoliosis.
Image: Illustration depicting a rib cage and spine, highlighting the curvature associated with scoliosis, a condition that can contribute to breathing-related back pain.
2. Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature and Breathing Mechanics
Scoliosis refers to an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. While often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, scoliosis can also develop later in life. The severity of scoliosis varies greatly, ranging from mild curves to pronounced deformities.
In more severe cases, the spinal curvature can become so significant that it restricts the space within the chest cavity, compressing the lungs and other vital organs. This compression can directly impact lung capacity and function, making it uncomfortable and even difficult to breathe deeply. The restricted lung expansion can also put strain on the back muscles as they work harder to facilitate breathing, leading to back pain that worsens with inhalation.
Treatment for scoliosis is tailored to the individual and depends on factors like age, the degree of spinal curvature, and the presence of symptoms. Fortunately, chiropractic treatment has proven to be highly effective in managing scoliosis symptoms and improving spinal alignment in many cases, potentially easing breathing difficulties and associated back pain.
3. Soft Tissue Injuries: Inflammation and Respiratory Infections
Persistent coughing, often associated with conditions like a common cold, influenza, or COVID-19, can place considerable stress on the muscles and soft tissues of the chest and back. This repetitive strain from coughing can lead to muscle soreness and even contribute to back pain that becomes noticeable when breathing. This is especially relevant if the respiratory illness progresses to pneumonia, a lung infection characterized by prolonged and forceful coughing.
Furthermore, inflammation of the pleura, the lining surrounding the lungs (pleurisy), or inflammation of the cartilage in the rib cage (costochondritis) can both cause sharp chest pain that may radiate to the back and intensify with deep breaths. These inflammatory conditions irritate the tissues involved in breathing, making each inhalation painful.
If your back pain when breathing emerges following a respiratory illness, it’s advisable to consult your general practitioner to rule out any underlying infections or inflammatory conditions. However, if you haven’t been recently ill, inflammation might be stemming from a recent injury or trauma. In such instances, a qualified chiropractor can perform a comprehensive assessment, including X-rays if necessary, to diagnose the cause of your pain and recommend appropriate treatment options for any underlying musculoskeletal issues.
4. Obesity: Excess Weight and Musculoskeletal Strain
Carrying excess weight places additional strain on the entire musculoskeletal system, including muscles, bones, and ligaments. Over time, this extra burden can weaken muscles and lead to postural imbalances, forcing the body to work harder to perform everyday activities, including breathing.
When the body is burdened by excess weight, the respiratory muscles may have to work harder to expand the chest cavity, leading to fatigue and strain. This increased effort can manifest as back pain, particularly when taking deep breaths. The added weight can also compress the rib cage and abdomen, further restricting lung expansion and exacerbating breathing difficulties and related back pain.
The most effective long-term solution for obesity-related back pain is weight management. However, losing weight can be challenging when pain and discomfort limit physical activity. Fortunately, chiropractic care can play a supportive role. By addressing musculoskeletal imbalances and alleviating pain, chiropractic adjustments can improve range of motion and make exercise more comfortable and accessible. As your body becomes better able to move freely, weight loss efforts can become more sustainable and effective, ultimately reducing strain and back pain associated with breathing.
5. Heart Attack: A Critical Consideration
While less common, it’s crucial to be aware that back pain when breathing can, in rare cases, be a symptom of a heart attack, a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
It’s important to recognize that heart attack symptoms can differ between men and women. While chest discomfort remains the primary symptom for men, women are more likely to experience atypical symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, extreme fatigue, shortness of breath, and back pain.
If you are at risk of heart disease or heart attack, it’s vital to familiarize yourself with the full spectrum of potential symptoms for both men and women. If you experience sudden, unexplained back pain accompanied by any of these other symptoms, especially shortness of breath, chest discomfort, or nausea, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt action can be life-saving in the event of a heart attack.
6. Lung Problems: When to Suspect Respiratory Conditions
Although not a frequent cause of back pain when breathing, certain lung conditions, such as lung cancer and pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lung), can manifest as pain that worsens with breathing. These conditions can sometimes be subtle and challenging to detect in their early stages.
Lung cancer can cause chest and back pain as tumors grow and press on surrounding tissues. Pulmonary embolism, a blockage of blood flow to the lungs, can also trigger chest and back pain, along with shortness of breath and coughing.
It’s essential to be vigilant about any persistent or unexplained symptoms, including back pain that is linked to breathing. If you experience these symptoms, particularly if you have risk factors for lung disease, consult your doctor for a thorough evaluation to rule out any serious underlying respiratory conditions.
Chiropractic Care: A Path to Relief
Once serious conditions like heart attack or pulmonary issues have been excluded, many individuals with persistent or chronic back pain when breathing explore options like prescription medications or surgery. However, these approaches often focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying cause of the pain.
For back pain originating from musculoskeletal issues such as scoliosis, muscle strain, or soft tissue injuries, a holistic approach combining chiropractic adjustments and massage therapy can be highly beneficial. Chiropractic adjustments aim to restore proper spinal alignment and joint function, reducing nerve irritation and muscle tension that can contribute to back pain and breathing difficulties. Massage therapy complements chiropractic care by relaxing tight muscles, improving circulation, and promoting tissue healing.
If your back pain is related to a recent trauma, such as a car accident, seeking treatment within 14 days is crucial to ensure coverage under your PIP (Personal Injury Protection) insurance policy and to prevent potential long-term complications.
Regardless of the specific cause of your breathing-related back pain, Oviedo Chiropractic offers a drug-free and surgery-free approach to pain management. Chiropractic care can be safely integrated with other treatment plans, providing a natural and effective way to address musculoskeletal imbalances and alleviate your pain.
Back Pain with Breathing: A Signal to Listen To
Back pain that intensifies when you breathe isn’t always indicative of a severe medical emergency. However, it’s always a signal from your body that warrants attention and investigation. Fortunately, a wide range of treatment options are available, from chiropractic care and massage therapy to over-the-counter medications, physical therapy, natural remedies, and medical consultations.
At Oviedo Chiropractic, our mission is to enhance your daily comfort and well-being. Through chiropractic adjustments, therapeutic massage, and personalized exercise and stretching guidance, we are dedicated to helping you achieve a pain-free and more fulfilling life. Schedule an appointment with us today to discuss your concerns and explore your path towards lasting relief and improved health!