Why Do You Get Hemorrhoids, and how can you find relief? At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the discomfort and concern associated with this common condition, offering expert-backed explanations and practical solutions to help you manage and prevent hemorrhoids, also known as piles. Delve into understanding the risk factors, explore various treatments, and discover how to maintain better anorectal health for long-term well-being, with insights into both internal and external hemorrhoid issues.
1. Understanding Hemorrhoids: An Overview
Hemorrhoids are a natural part of the human anatomy, acting as cushions of vascular tissue in the anal canal that help with bowel control. The problem arises when these cushions become inflamed, swollen, and symptomatic, leading to what we commonly refer to as hemorrhoids or piles. These swollen veins can cause discomfort, pain, itching, and bleeding, significantly impacting one’s quality of life. By the age of 50, approximately half the adult population experience hemorrhoid symptoms, making it a widespread concern.
1.1. What Are Hemorrhoids?
Everyone has hemorrhoidal tissue, which consists of blood vessels, support tissue, muscle fibers, and elastic fibers, located in the anal canal. These tissues help control bowel movements. Hemorrhoids are present when these tissues become swollen, inflamed, or displaced. This can be compared to varicose veins, where the veins become enlarged due to increased pressure and weakened walls.
1.2. Internal vs. External Hemorrhoids
There are two primary types of hemorrhoids, each with distinct characteristics:
-
Internal Hemorrhoids: Located inside the rectum, internal hemorrhoids are usually painless and may not be noticeable until they bleed. They are graded based on the degree of prolapse (protrusion from the anus):
- Grade I: Do not prolapse; simply enlarged blood vessels.
- Grade II: Prolapse during bowel movements but spontaneously reduce.
- Grade III: Prolapse and require manual reduction.
- Grade IV: Chronically prolapsed and cannot be manually reduced.
-
External Hemorrhoids: Found under the skin around the anus, external hemorrhoids are more likely to cause pain, itching, and discomfort, especially if a blood clot forms (thrombosed hemorrhoid).
Understanding the type of hemorrhoid is crucial for selecting the appropriate treatment. Internal hemorrhoids, for example, often require different management strategies compared to external ones.
1.3. Common Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Recognizing the symptoms of hemorrhoids is the first step towards seeking appropriate care. Common symptoms include:
- Rectal Bleeding: Bright red blood on toilet paper, in the toilet bowl, or on the stool.
- Itching: Persistent itching around the anus, often exacerbated by wiping.
- Pain: Discomfort or pain, particularly during bowel movements or when sitting.
- Swelling: Noticeable lumps or swelling around the anus.
- Prolapse: Protrusion of hemorrhoids through the anal canal.
- Fecal Leakage: Difficulty in keeping the anal area clean, leading to irritation.
The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the type and grade of hemorrhoid. While some individuals may experience mild discomfort, others may suffer from significant pain and disruption to their daily activities.
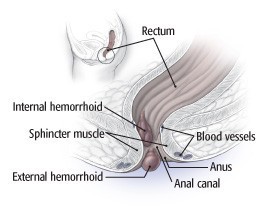 Illustration depicting internal and external hemorrhoids
Illustration depicting internal and external hemorrhoids
2. What Causes Hemorrhoids? Unveiling the Root Causes
Why do you get hemorrhoids? The development of hemorrhoids is often multifactorial, with several contributing factors that increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention and management.
2.1. Increased Pressure and Straining
Increased pressure in the lower rectum and anus is a primary cause of hemorrhoids. This pressure can result from:
- Straining During Bowel Movements: Chronic constipation or diarrhea can lead to excessive straining, which puts pressure on the veins.
- Prolonged Sitting on the Toilet: Spending extended periods on the toilet can also increase pressure on the anal veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to increased pressure in the abdominal and pelvic regions.
- Pregnancy: The growing uterus can press on the veins, and hormonal changes can weaken blood vessels, increasing the risk of hemorrhoids during pregnancy.
2.2. Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle habits can significantly impact the development of hemorrhoids:
- Low-Fiber Diet: A diet lacking in fiber can lead to constipation, increasing the likelihood of straining during bowel movements.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to poor bowel function and increased pressure in the rectal area.
- Poor Posture: Sitting for long periods with poor posture can restrict blood flow and increase pressure in the pelvic region.
2.3. Genetic Predisposition
Genetics can also play a role in the susceptibility to hemorrhoids. Individuals with a family history of hemorrhoids may be more prone to developing the condition. This could be due to inherited weaknesses in the walls of the blood vessels or other factors that increase the risk.
2.4. Age and Tissue Weakness
As we age, the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus can weaken. This can cause the veins to stretch and bulge more easily, leading to hemorrhoids. The natural aging process, coupled with other risk factors, can increase the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids later in life.
2.5. Anal Canal Tone
Recent studies suggest that individuals with hemorrhoids often have a higher resting anal canal tone, meaning the muscles in the anal canal are tighter than average. This increased tightness can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids, as it puts additional pressure on the veins during bowel movements.
3. Diagnosing Hemorrhoids: What to Expect
If you suspect you have hemorrhoids, seeking a proper diagnosis is crucial. A healthcare professional can confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of your symptoms. The diagnostic process typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, additional tests.
3.1. Medical History and Physical Exam
The initial step in diagnosing hemorrhoids involves a detailed discussion of your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors. Your doctor will ask about the nature of your symptoms, such as bleeding, pain, itching, and any factors that seem to worsen or relieve them. They will also inquire about your bowel habits, diet, and any family history of hemorrhoids or other gastrointestinal conditions.
A physical examination is then conducted to assess the anal area. This includes a visual inspection to identify external hemorrhoids or signs of prolapse. A digital rectal exam (DRE) may also be performed, where the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for any abnormalities, such as internal hemorrhoids or masses.
3.2. Anoscopy and Sigmoidoscopy
To further evaluate the condition, your doctor may perform an anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. These procedures involve inserting a small, lighted tube into the anus and rectum to visualize the area more clearly:
- Anoscopy: Uses an anoscope, a short, rigid tube, to examine the anal canal and lower rectum.
- Flexible Sigmoidoscopy: Involves a flexible tube with a camera to view the rectum and lower colon.
These procedures can help identify internal hemorrhoids, assess their grade, and rule out other potential causes of bleeding or discomfort, such as polyps or inflammation.
3.3. Colonoscopy
In certain cases, a colonoscopy may be recommended. This procedure involves inserting a long, flexible tube with a camera into the entire colon to examine it thoroughly. Colonoscopy is typically recommended for individuals with:
- Rectal bleeding, especially if they are over the age of 45.
- A family history of colorectal cancer.
- Changes in bowel habits.
Colonoscopy helps rule out more serious conditions, such as colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease, ensuring an accurate diagnosis.
4. Hemorrhoid Treatment: Finding Relief and Managing Symptoms
Once diagnosed, various treatment options are available to relieve symptoms and manage hemorrhoids. Treatment approaches range from simple home remedies to minimally invasive procedures and surgery, depending on the severity and type of hemorrhoids.
4.1. Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
For mild to moderate hemorrhoid symptoms, home remedies and lifestyle changes can provide significant relief:
- High-Fiber Diet: Increasing fiber intake softens stools, making them easier to pass and reducing straining. Aim for 25-30 grams of fiber per day through foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps keep stools soft and prevents constipation.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the anal area in warm water for 10-20 minutes several times a day can relieve itching, irritation, and muscle spasms.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories containing ingredients like hydrocortisone or witch hazel can reduce inflammation, itching, and pain.
- Avoid Straining: Try to avoid straining during bowel movements, and don’t spend too much time sitting on the toilet.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve bowel function and reduce pressure in the rectal area.
These measures are often effective in managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups.
4.2. Minimally Invasive Procedures
When home remedies are insufficient, minimally invasive procedures can provide more effective relief:
- Rubber Band Ligation: The most common procedure, where a small elastic band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid shrinks and falls off within a week.
- Sclerotherapy: Involves injecting a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink.
- Infrared Coagulation: Uses infrared light to create scar tissue, cutting off blood supply to the hemorrhoid.
- Laser Coagulation: Similar to infrared coagulation but uses laser energy.
These procedures are typically performed in a doctor’s office and have a relatively quick recovery time.
4.3. Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove hemorrhoids:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical removal of hemorrhoids. This is the most effective treatment for large or severe hemorrhoids but has a longer recovery time.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A procedure that uses a stapling device to reposition prolapsed hemorrhoids and reduce blood flow to the area.
Surgery is typically reserved for cases where other treatments have failed or when hemorrhoids are large and causing significant symptoms.
5. Preventing Hemorrhoids: Lifestyle Strategies
Prevention is key to avoiding the discomfort and complications associated with hemorrhoids. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce your risk:
5.1. Dietary Recommendations
A balanced diet rich in fiber is essential for preventing hemorrhoids:
- Include Fiber-Rich Foods: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your daily diet.
- Consider Fiber Supplements: If you struggle to get enough fiber from food alone, consider taking a fiber supplement like psyllium husk or methylcellulose.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit your intake of processed foods, which are often low in fiber and high in unhealthy fats.
5.2. Proper Bowel Habits
Developing healthy bowel habits can help prevent straining and reduce pressure on the anal veins:
- Go When You Need To: Don’t ignore the urge to have a bowel movement.
- Avoid Straining: Relax and breathe deeply during bowel movements.
- Limit Time on the Toilet: Avoid spending excessive time sitting on the toilet.
- Use a Footstool: Elevating your feet with a footstool can help align the colon and make bowel movements easier.
5.3. Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to hemorrhoid prevention:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity improves bowel function and reduces pressure in the rectal area.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: If you have a job that requires prolonged sitting, take regular breaks to stand up and move around.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Keep the anal area clean and dry to prevent irritation.
6. Understanding Hemorrhoids During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids due to hormonal changes and the pressure of the growing uterus on the pelvic veins. Managing hemorrhoids during pregnancy requires special consideration to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
6.1. Causes of Hemorrhoids in Pregnancy
Several factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy:
- Increased Pressure: The growing uterus puts pressure on the pelvic veins, making it harder for blood to return from the lower body.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy hormones can relax blood vessel walls, making them more prone to swelling.
- Constipation: Pregnancy can slow down digestion, leading to constipation and straining during bowel movements.
6.2. Safe Treatment Options for Pregnant Women
When treating hemorrhoids during pregnancy, it’s essential to choose safe and gentle options:
- Dietary Changes: Increase fiber intake and stay hydrated to prevent constipation.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking in warm water can relieve itching and discomfort.
- Topical Creams: Over-the-counter creams containing witch hazel or other safe ingredients can provide temporary relief.
- Avoid Straining: Use a footstool to elevate your feet during bowel movements and avoid straining.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before using any medications or undergoing any procedures during pregnancy.
6.3. Preventing Hemorrhoids During Pregnancy
Prevention is the best approach to managing hemorrhoids during pregnancy:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to prevent constipation.
- Eat a High-Fiber Diet: Include fiber-rich foods in your diet to promote regular bowel movements.
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercises like walking or swimming can improve circulation and prevent constipation.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Take breaks to move around and relieve pressure on the pelvic veins.
7. Debunking Myths About Hemorrhoids
There are several misconceptions about hemorrhoids. Understanding the truth can help you make informed decisions about prevention and treatment.
7.1. Common Misconceptions
- Myth: Hemorrhoids are always painful.
- Fact: Internal hemorrhoids are often painless, especially in the early stages.
- Myth: Hemorrhoids are caused by poor hygiene.
- Fact: Hemorrhoids are primarily caused by increased pressure and straining, not poor hygiene.
- Myth: Spicy foods cause hemorrhoids.
- Fact: Spicy foods can irritate existing hemorrhoids but do not cause them.
- Myth: Hemorrhoids always require surgery.
- Fact: Most hemorrhoids can be managed with home remedies and minimally invasive procedures.
7.2. The Truth About Hemorrhoids
- Hemorrhoids are common: Many people experience hemorrhoids at some point in their lives.
- Hemorrhoids are treatable: Various treatment options are available to relieve symptoms and manage the condition.
- Prevention is possible: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can reduce your risk of developing hemorrhoids.
8. Complications of Untreated Hemorrhoids
While hemorrhoids are rarely dangerous, leaving them untreated can lead to complications that affect your quality of life. Recognizing these potential issues can motivate you to seek timely medical attention.
8.1. Anemia
Chronic bleeding from hemorrhoids can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells. Symptoms of anemia include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and pale skin. Severe anemia may require iron supplements or, in rare cases, blood transfusions.
8.2. Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
A thrombosed hemorrhoid occurs when a blood clot forms inside an external hemorrhoid. This can cause sudden, severe pain, swelling, and inflammation. While thrombosed hemorrhoids are not life-threatening, they can be extremely painful and may require medical intervention to remove the clot and relieve symptoms.
8.3. Strangulated Hemorrhoids
If an internal hemorrhoid prolapses and becomes trapped outside the anus, it can become strangulated. This means the blood supply to the hemorrhoid is cut off, leading to tissue damage and severe pain. Strangulated hemorrhoids require prompt medical treatment to restore blood flow and prevent further complications.
8.4. Infection
Although rare, untreated hemorrhoids can become infected. Signs of infection include increased pain, swelling, redness, and pus drainage. Infections require antibiotics and, in some cases, drainage of the infected area.
9. When to See a Doctor for Hemorrhoids
While many cases of hemorrhoids can be managed with home remedies, it’s essential to know when to seek medical attention. Consulting a healthcare provider can help ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
9.1. Warning Signs and Symptoms
See a doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Severe Rectal Pain: Intense pain that doesn’t improve with home remedies.
- Excessive Bleeding: Heavy or persistent rectal bleeding.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Signs of anemia due to blood loss.
- Fever: A fever accompanied by rectal pain or swelling.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: A significant change in bowel habits, such as persistent diarrhea or constipation.
- Lump or Mass: A new or growing lump or mass in the anal area.
9.2. Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of hemorrhoids can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. A doctor can determine the type and severity of your hemorrhoids and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
9.3. Ruling Out Other Conditions
Rectal bleeding and other symptoms of hemorrhoids can also be signs of more serious conditions, such as colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease. A doctor can perform tests to rule out these conditions and ensure an accurate diagnosis.
10. Expert Insights on Hemorrhoid Management
To provide a comprehensive understanding of hemorrhoid management, we’ve gathered insights from medical experts in the field.
10.1. Howard E. LeWine, MD
Dr. Howard E. LeWine, Chief Medical Editor at Harvard Health Publishing and a practicing internist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, emphasizes the importance of lifestyle modifications in managing hemorrhoids. He recommends a high-fiber diet, regular exercise, and avoiding prolonged sitting on the toilet.
10.2. Other Expert Recommendations
- American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons: Recommends prompt medical evaluation for rectal bleeding to rule out other potential causes.
- Mayo Clinic: Advises using over-the-counter creams and suppositories for temporary relief of itching and pain.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): Highlights the importance of staying hydrated to prevent constipation.
11. Addressing Common Concerns About Hemorrhoids
Many individuals have questions and concerns about hemorrhoids. Addressing these common issues can provide reassurance and empower you to take control of your health.
11.1. Are Hemorrhoids Contagious?
Hemorrhoids are not contagious. They are caused by increased pressure and straining, not by a virus or bacteria.
11.2. Can Hemorrhoids Turn into Cancer?
Hemorrhoids do not turn into cancer. However, symptoms of hemorrhoids, such as rectal bleeding, can also be signs of colorectal cancer. It’s essential to see a doctor for any rectal bleeding to rule out other potential causes.
11.3. How Long Do Hemorrhoids Last?
The duration of hemorrhoid symptoms can vary. Mild hemorrhoids may resolve on their own with home remedies within a few days or weeks. More severe hemorrhoids may require medical treatment and can take longer to heal.
11.4. Can Hemorrhoids Be Prevented?
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce your risk of developing hemorrhoids. These habits include eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding straining during bowel movements, and exercising regularly.
12. Real-Life Experiences: Hemorrhoid Success Stories
Hearing from others who have successfully managed hemorrhoids can provide hope and inspiration. Here are a few real-life success stories:
12.1. Sarah’s Story
Sarah, a 35-year-old office worker, developed hemorrhoids during her pregnancy. She experienced rectal bleeding and discomfort, which made it difficult to sit for long periods. After consulting with her doctor, she made dietary changes, started taking sitz baths, and used over-the-counter creams. Within a few weeks, her symptoms improved significantly, and she was able to manage her hemorrhoids throughout her pregnancy.
12.2. John’s Story
John, a 50-year-old truck driver, had been struggling with chronic constipation and hemorrhoids for years. He tried various home remedies with little success. Eventually, he decided to see a gastroenterologist who recommended rubber band ligation. After a few sessions, his hemorrhoids were completely resolved, and he was able to live pain-free.
12.3. Maria’s Story
Maria, a 60-year-old retiree, had a family history of hemorrhoids and developed severe symptoms over time. She underwent a hemorrhoidectomy, which provided lasting relief. Although the recovery was challenging, she was grateful to have a definitive solution to her hemorrhoid problems.
13. Innovative Approaches to Hemorrhoid Treatment
Medical advancements have led to innovative approaches in treating hemorrhoids. These new methods aim to provide more effective and less invasive solutions.
13.1. Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization (THD)
THD is a minimally invasive procedure that uses Doppler technology to locate and ligate (tie off) the arteries that supply blood to the hemorrhoids. This reduces blood flow to the hemorrhoids, causing them to shrink and resolve. THD is less painful than traditional hemorrhoidectomy and has a quicker recovery time.
13.2. Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP)
LHP uses laser energy to shrink the hemorrhoid tissue. The laser is applied directly to the hemorrhoid, causing it to coagulate and reduce in size. LHP is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office with local anesthesia.
13.3. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
RFA uses radiofrequency energy to generate heat and destroy the hemorrhoid tissue. The procedure is performed using a probe inserted into the hemorrhoid, delivering targeted energy to the affected area. RFA is minimally invasive and has a low risk of complications.
14. Maintaining Long-Term Anorectal Health
Adopting a holistic approach to anorectal health can help prevent hemorrhoids and other related conditions. This involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and regular medical check-ups.
14.1. Regular Check-Ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your anorectal health and address any concerns. Early detection and treatment of hemorrhoids and other conditions can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
14.2. Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to digestive issues and exacerbate hemorrhoid symptoms. Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, to promote overall well-being.
14.3. Pelvic Floor Exercises
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can improve bowel control and reduce pressure on the anal veins. Perform Kegel exercises regularly to maintain pelvic floor health.
15. Navigating Hemorrhoid Care with WHY.EDU.VN
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand that finding reliable information and expert guidance can be challenging. That’s why we’re committed to providing you with accurate, trustworthy, and easy-to-understand resources on hemorrhoids and other health topics.
15.1. Comprehensive Information
Our website offers a wealth of information on hemorrhoids, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. We strive to provide you with the most up-to-date and evidence-based information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
15.2. Expert Advice
Our team of healthcare professionals and medical writers is dedicated to providing expert advice and guidance on managing hemorrhoids. We collaborate with leading experts in the field to ensure that our content is accurate and reliable.
15.3. Community Support
We offer a supportive community where you can connect with others who are experiencing hemorrhoids. Share your experiences, ask questions, and find encouragement from people who understand what you’re going through.
FAQ: Addressing Your Burning Questions About Hemorrhoids
Here are some frequently asked questions about hemorrhoids:
- What are the early signs of hemorrhoids?
Early signs include rectal itching, discomfort, and small amounts of blood on toilet paper. - Can hemorrhoids go away on their own?
Mild hemorrhoids may resolve on their own with home remedies. - Are there any foods I should avoid if I have hemorrhoids?
Avoid processed foods, spicy foods, and alcohol, as they can irritate hemorrhoids. - How can I relieve itching caused by hemorrhoids?
Sitz baths, witch hazel wipes, and over-the-counter creams can help relieve itching. - Is it safe to use over-the-counter hemorrhoid creams during pregnancy?
Consult with your doctor before using any medications during pregnancy. - What is the recovery time after a hemorrhoidectomy?
The recovery time can range from several weeks to a few months. - Can I exercise if I have hemorrhoids?
Yes, but avoid activities that put pressure on the anal area, such as heavy lifting. - How often should I take a sitz bath?
Take a sitz bath for 10-20 minutes several times a day. - What are the long-term effects of untreated hemorrhoids?
Untreated hemorrhoids can lead to anemia, thrombosed hemorrhoids, and strangulated hemorrhoids. - Are there any alternative treatments for hemorrhoids?
Some people find relief with acupuncture, herbal remedies, and other alternative treatments, but consult with your doctor before trying them.
Conclusion: Empowering You to Take Control of Your Anorectal Health
Understanding why you get hemorrhoids is the first step toward managing and preventing this common condition. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, seeking prompt medical attention when needed, and staying informed about the latest treatment options, you can take control of your anorectal health and improve your quality of life.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we’re here to support you on your journey to better health. Visit our website at WHY.EDU.VN to explore our comprehensive resources, connect with our community, and ask questions to our team of experts. Whether you’re looking for information on home remedies, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical options, we have the answers you need.
Do you have more questions or need personalized advice? Contact us today:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let us help you find the answers and solutions you’re looking for. At why.edu.vn, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and support you need to live a healthier, happier life.