Why Do We Get Wax In Ears? This is a common question, and at WHY.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide a comprehensive answer. Earwax, or cerumen, is a natural and essential substance that protects the ear canal, trapping dirt and preventing infections. This guide will explore the reasons behind earwax production, the problems associated with its buildup, and how to maintain healthy ears. We’ll also touch upon ear hygiene, cerumen impaction, and safe ear cleaning practices.
1. Understanding the Purpose of Earwax Production
Why Our Ears Produce Wax: The Cerumen Story
Earwax, scientifically known as cerumen, is a yellowish waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. Its primary function is to protect the ear canal from dust, debris, microorganisms, and insects. The glands in the outer ear canal produce this substance, which also lubricates the ear canal to prevent it from drying out and becoming itchy.
Earwax is a natural part of your body’s defense system. It cleans, lubricates, and protects the ear canal by trapping dirt and slowing the growth of bacteria. Without earwax, your ears would be more susceptible to infections and irritation.
Alt Text: A young woman experiencing ear pain due to impacted earwax, highlighting the discomfort and need for ear care.
The Composition of Earwax: What Makes It So Protective?
Earwax isn’t just a simple wax; it’s a complex mixture of substances that contribute to its protective qualities. The composition typically includes:
- Secretions from ceruminous and sebaceous glands: These glands produce the oily and waxy components of earwax.
- Dead skin cells: As the skin inside the ear canal naturally sheds, these cells become incorporated into the earwax.
- Hair: Tiny hairs in the ear canal also get trapped in the wax, adding to its ability to capture debris.
The combination of these elements creates a sticky barrier that traps foreign particles, preventing them from reaching the eardrum. The antibacterial and antifungal properties of earwax further protect the ear canal from infections.
Types of Earwax: Wet vs. Dry Cerumen
There are two main types of earwax: wet and dry. The type you have is determined by your genes. Wet earwax is dominant and is more common in people of African and European descent, while dry earwax is more common in Asian populations.
- Wet Earwax: This type is sticky and yellowish-brown in color. It contains a higher concentration of lipids and is more effective at trapping moisture and debris.
- Dry Earwax: This type is flaky and grayish-white. It contains less lipid content and is less sticky compared to wet earwax.
The type of earwax you have doesn’t necessarily affect its function, but it can influence how easily it moves out of the ear canal. Individuals with dry earwax may experience impaction more frequently, as it doesn’t naturally migrate out of the ear as easily as wet earwax.
2. Common Causes of Earwax Buildup
Overproduction: When Glands Work Overtime
In some individuals, the glands in the ear canal may produce more earwax than necessary. This overproduction can lead to buildup, especially if the natural mechanisms for earwax removal are not functioning optimally. Factors that can contribute to overproduction include:
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to producing more earwax.
- Age: As we age, the glands in the ear canal can become more active, leading to increased earwax production.
- Environment: Exposure to dusty or dirty environments can stimulate the glands to produce more earwax as a protective response.
If you suspect overproduction is the cause of your earwax buildup, consult with a healthcare professional. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate management strategies.
Improper Cleaning: The Q-Tip Myth
One of the most common causes of earwax buildup is improper cleaning methods, particularly the use of cotton swabs (Q-tips). While it may seem counterintuitive, using cotton swabs to clean your ears can actually push the earwax further into the ear canal, leading to impaction.
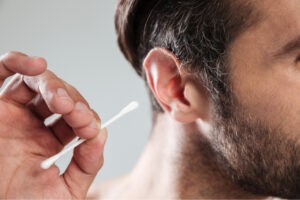 A person using a cotton swab to clean their ear, illustrating the common but risky practice.
A person using a cotton swab to clean their ear, illustrating the common but risky practice.
Alt Text: An individual using a cotton swab near the ear, highlighting the potential for pushing earwax further into the canal.
When you insert a cotton swab into your ear, it can disrupt the natural migration of earwax out of the ear canal. Instead of removing the wax, you’re likely compacting it against the eardrum, which can lead to discomfort, hearing loss, and even infection.
Ear Canal Obstructions: Hearing Aids and Earplugs
Frequent use of hearing aids, earplugs, or earbuds can also contribute to earwax buildup. These devices can block the natural movement of earwax out of the ear canal, causing it to accumulate over time.
- Hearing Aids: These devices sit inside the ear canal and can prevent the natural expulsion of earwax.
- Earplugs: Regular use of earplugs, especially those that fit tightly, can have a similar effect, leading to wax impaction.
- Earbuds: Like hearing aids and earplugs, earbuds can obstruct the ear canal and interfere with the natural removal of earwax.
If you use these devices regularly, it’s essential to have your ears checked periodically by a healthcare professional to ensure that earwax is not building up to problematic levels.
Anatomical Factors: Narrow or Irregular Ear Canals
Some individuals have naturally narrow or irregularly shaped ear canals, which can make it more difficult for earwax to migrate out on its own. This anatomical variation can predispose them to earwax buildup and impaction.
- Narrow Ear Canals: A smaller ear canal provides less space for earwax to move freely, increasing the likelihood of impaction.
- Irregularly Shaped Ear Canals: Twists and turns in the ear canal can create pockets where earwax can accumulate, making it harder for the wax to be naturally expelled.
If you have a narrow or irregular ear canal, you may need to take extra precautions to prevent earwax buildup. Regular check-ups with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can help manage this condition effectively.
3. Symptoms and Effects of Earwax Impaction
Recognizing the Signs: Common Symptoms of Blockage
Earwax impaction can manifest in a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to more severe issues. Recognizing these signs early can help you seek timely intervention and prevent further complications. Common symptoms include:
- Hearing Loss: One of the most noticeable symptoms of earwax impaction is a gradual decrease in hearing ability.
- Earache: A feeling of pain or discomfort in the ear can indicate that earwax is pressing against the eardrum.
- Tinnitus: This condition involves hearing ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ear, even when there is no external noise.
- Fullness or Pressure: A sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear can be a sign that earwax is blocking the ear canal.
- Itching: Excessive earwax can sometimes cause itching in the ear canal.
- Dizziness: In some cases, earwax impaction can lead to dizziness or vertigo.
- Cough: Rarely, impacted earwax can stimulate the vagus nerve, leading to a reflex cough.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Impact on Hearing: Temporary Hearing Loss
Earwax impaction can lead to temporary hearing loss. When earwax blocks the ear canal, it prevents sound waves from reaching the eardrum effectively. This can result in muffled hearing or difficulty hearing faint sounds.
The degree of hearing loss can vary depending on the extent of the impaction. In mild cases, hearing may only be slightly affected. However, in more severe cases, the hearing loss can be significant and impact daily activities.
Potential for Infection: Otitis Externa
In some cases, earwax impaction can create an environment that promotes bacterial or fungal growth, leading to an infection of the outer ear canal, known as otitis externa or swimmer’s ear. This condition can cause:
- Pain: Intense ear pain, especially when touching or moving the ear.
- Redness: Inflammation and redness of the ear canal.
- Swelling: Swelling of the ear canal, which can further block hearing.
- Discharge: Drainage of pus or fluid from the ear.
If you suspect you have an ear infection, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can diagnose the infection and prescribe appropriate treatment, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications.
Additional Complications: Tinnitus and Vertigo
Besides hearing loss and infection, earwax impaction can also lead to other complications, such as tinnitus and vertigo.
- Tinnitus: The pressure from impacted earwax can irritate the nerves in the ear, leading to the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds.
- Vertigo: In some cases, earwax impaction can affect the inner ear and disrupt balance, causing vertigo or dizziness.
These complications can significantly impact your quality of life, making it essential to address earwax impaction promptly.
4. Safe and Effective Methods for Earwax Removal
Professional Removal: When to See a Doctor
While some earwax can be safely removed at home, there are situations where professional removal by a healthcare provider is necessary. You should seek professional help if:
- You have a history of ear problems, such as ear infections or eardrum perforations.
- You have diabetes or a compromised immune system.
- You experience severe pain, bleeding, or drainage from the ear.
- Home remedies are not effective or cause further irritation.
A healthcare professional can use specialized tools and techniques to safely remove impacted earwax without causing damage to the ear canal or eardrum.
Home Remedies: Safe Methods and Precautions
If you don’t have any contraindications for home removal, you can try some safe and effective methods to soften and remove earwax. However, it’s crucial to follow these precautions:
- Never insert sharp or pointy objects into the ear canal.
- Do not irrigate your ear if you have a perforated eardrum or a history of ear surgery.
- If you experience pain, bleeding, or dizziness, stop immediately and seek medical attention.
Here are some safe home remedies:
- Mineral Oil: Applying a few drops of mineral oil into the ear canal can help soften the earwax, making it easier to come out on its own.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Diluted hydrogen peroxide (3% solution) can also be used to soften earwax.
- Over-the-Counter Ear Drops: Several over-the-counter ear drops are available that contain ingredients like carbamide peroxide, which help break up earwax.
Follow the instructions on the product label and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Ear Irrigation: The Bulb Syringe Technique
Ear irrigation, or ear syringing, is a method of flushing out earwax using water or a saline solution. This technique should be performed with caution and is not recommended for individuals with certain ear conditions.
To perform ear irrigation safely:
- Use a bulb syringe and lukewarm water.
- Tilt your head to the side and gently squirt the water into your ear canal.
- Allow the water to drain out, along with the softened earwax.
- Dry your ear thoroughly with a clean towel.
Avoid using too much pressure when irrigating your ear, as this can damage the eardrum.
5. Preventing Future Earwax Buildup
Routine Ear Hygiene: Best Practices for Clean Ears
Maintaining good ear hygiene is essential for preventing earwax buildup. However, it’s important to avoid over-cleaning, as this can disrupt the natural balance of the ear canal.
Here are some best practices for ear hygiene:
- Avoid using cotton swabs. Instead, gently clean the outer ear with a damp cloth.
- If you use hearing aids, earplugs, or earbuds, clean them regularly to prevent the buildup of bacteria and debris.
- Consider using earwax-softening drops periodically to help keep the earwax moving out of the ear canal.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Diet and Environmental Factors
Certain lifestyle adjustments can also help prevent earwax buildup. These include:
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep the earwax soft and prevent it from becoming dry and impacted.
- Avoiding Dusty Environments: If you work or live in a dusty environment, consider wearing earplugs to protect your ears.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce earwax production. Foods high in omega-3 include fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Regular Check-ups: Monitoring Ear Health
Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help monitor your ear health and identify any potential problems early on. If you are prone to earwax buildup or have a history of ear problems, consider scheduling regular ear cleanings with an ENT specialist.
6. Debunking Common Myths About Earwax
Myth: Earwax is Dirty
One of the most common misconceptions about earwax is that it is a sign of poor hygiene. In reality, earwax is a natural and essential substance that plays a vital role in protecting the ear canal. It’s not dirt; it’s a protective secretion.
Myth: You Need to Clean Your Ears Daily
Daily ear cleaning is not necessary and can actually be harmful. Over-cleaning can strip the ear canal of its natural oils, leading to dryness, irritation, and an increased risk of infection.
Myth: Cotton Swabs are the Best Way to Clean Your Ears
As mentioned earlier, cotton swabs can actually push earwax further into the ear canal, leading to impaction. They are not an effective or safe way to clean your ears.
Myth: Ear Candling is an Effective Removal Method
Ear candling is a practice that involves inserting a hollow candle into the ear canal and lighting it, with the belief that the heat will draw out earwax. However, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim, and it can be dangerous, potentially causing burns or eardrum damage.
7. The Role of Diet and Hydration in Earwax Management
Hydration: Keeping Earwax Soft
Staying properly hydrated is crucial for maintaining the consistency of earwax. When you’re dehydrated, your body produces thicker secretions, including earwax, which can lead to impaction. Drinking plenty of water helps keep the earwax soft and pliable, making it easier to move out of the ear canal naturally.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Impact on Earwax Production
While not as direct as hydration, certain nutritional deficiencies can indirectly impact earwax production. For example, deficiencies in essential fatty acids, such as omega-3s, can lead to dry, flaky skin, which can contribute to dry earwax. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is important for overall ear health.
Foods to Avoid: Those That May Increase Earwax
There is limited scientific evidence to suggest that specific foods directly increase earwax production. However, some anecdotal evidence suggests that certain foods may contribute to inflammation or increased mucus production, which could potentially affect earwax. These foods include:
- Dairy Products: Some people believe that dairy products can increase mucus production, leading to more earwax.
- Processed Foods: High levels of sugar and unhealthy fats in processed foods can contribute to inflammation, which may affect earwax consistency.
Diet and Supplements: Supporting Healthy Earwax Production
While there’s no magic diet for earwax management, a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support overall ear health. Consider incorporating these foods and supplements into your diet:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s can help maintain healthy skin and reduce inflammation.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that supports immune function and can help prevent ear infections.
- Zinc: Important for immune function and skin health, zinc can be found in foods like oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds.
8. Earwax in Children: Special Considerations
Differences in Pediatric Earwax: What to Expect
Earwax in children is similar in composition and function to that in adults, but there are some key differences to be aware of. Children’s ear canals are smaller and more delicate, making them more susceptible to earwax impaction. Additionally, children may be more prone to putting foreign objects in their ears, which can exacerbate the problem.
Safe Cleaning Practices for Children’s Ears
When it comes to cleaning children’s ears, less is more. Avoid using cotton swabs, as they can easily push earwax further into the ear canal. Instead, gently clean the outer ear with a damp cloth. If you suspect your child has earwax impaction, consult with a pediatrician or ENT specialist.
When to Seek Professional Help for Children
It’s especially important to seek professional help for earwax impaction in children if they experience:
- Hearing loss
- Ear pain
- Excessive ear pulling or scratching
- Fever
- Irritability
These symptoms could indicate an ear infection or other underlying problem that requires medical attention.
Preventing Earwax Buildup in Children
To prevent earwax buildup in children:
- Avoid over-cleaning their ears.
- Teach them not to insert foreign objects into their ears.
- Schedule regular check-ups with a pediatrician or ENT specialist.
9. Advanced Treatments for Severe Impaction
Manual Removal Techniques: Curettes and Suction
In cases of severe earwax impaction, healthcare professionals may use manual removal techniques, such as curettes or suction devices. Curettes are small, spoon-shaped instruments used to gently scoop out the earwax. Suction devices use gentle suction to remove the earwax. These techniques require specialized training and should only be performed by a qualified healthcare provider.
Cerumenolytics: Prescription-Strength Ear Drops
For stubborn earwax impaction, a doctor may prescribe cerumenolytics, which are prescription-strength ear drops that contain ingredients like triethanolamine polypeptide oleate-condensate. These drops are more effective at breaking up earwax than over-the-counter options.
Micro-Suction: A Minimally Invasive Option
Micro-suction is a minimally invasive technique that uses a microscope and a small suction device to remove earwax. This method allows the healthcare provider to visualize the ear canal clearly, reducing the risk of injury. Micro-suction is often used for individuals with a history of ear problems or those who cannot tolerate other removal methods.
When Surgery is Necessary: Rare Cases
In very rare cases, surgery may be necessary to remove impacted earwax. This is usually only considered if other treatments have failed and the impaction is causing severe complications.
10. Seeking Expert Advice and Ongoing Support
The Importance of Consulting with Professionals
Navigating the complexities of earwax management can be challenging. Consulting with healthcare professionals, such as audiologists or ENT specialists, is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. These experts can assess your specific situation, recommend the most appropriate removal methods, and provide guidance on preventing future buildup.
Leveraging Online Resources: Reliable Information Sources
In today’s digital age, numerous online resources offer information about earwax management. However, it’s crucial to rely on reputable sources, such as medical websites, professional organizations, and academic journals. Avoid relying on anecdotal advice or unverified claims.
The Value of Peer Support: Sharing Experiences
Connecting with others who have experienced earwax impaction can provide valuable support and insights. Online forums and support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, asking questions, and learning from others.
How WHY.EDU.VN Can Help You Find Answers
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of accessing reliable and expert-backed information. Our platform is dedicated to providing comprehensive answers to your health questions, including those related to earwax management. Our team of experts is committed to delivering accurate, up-to-date, and easy-to-understand information to empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Whether you’re seeking information on earwax removal methods, preventive strategies, or when to seek professional help, WHY.EDU.VN is your trusted source.
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: WHY.EDU.VN
FAQ: Your Questions About Earwax Answered
1. Is earwax a sign of poor hygiene?
No, earwax is a natural and necessary substance that protects the ear canal. Its presence doesn’t indicate poor hygiene.
2. How often should I clean my ears?
You generally don’t need to clean your ears regularly. The ears are self-cleaning, and excessive cleaning can cause irritation or impaction.
3. Can I use cotton swabs to remove earwax?
It’s best to avoid using cotton swabs, as they can push earwax further into the ear canal.
4. What are the symptoms of earwax impaction?
Symptoms include hearing loss, earache, tinnitus, fullness in the ear, and dizziness.
5. Can earwax impaction cause an ear infection?
Yes, earwax impaction can create an environment that promotes bacterial or fungal growth, potentially leading to an ear infection.
6. What is the best way to remove earwax at home?
Safe home remedies include using mineral oil, hydrogen peroxide, or over-the-counter ear drops to soften the earwax.
7. When should I see a doctor for earwax removal?
You should see a doctor if you have a history of ear problems, experience severe pain or bleeding, or if home remedies are ineffective.
8. What is ear irrigation?
Ear irrigation is a method of flushing out earwax using water or a saline solution. It should be performed with caution and is not recommended for individuals with certain ear conditions.
9. How can I prevent earwax buildup?
Preventive measures include avoiding over-cleaning your ears, staying hydrated, and making lifestyle adjustments to minimize exposure to dusty environments.
10. Is ear candling safe and effective?
No, ear candling is not considered a safe or effective method for earwax removal and can potentially cause harm.
Experiencing earwax buildup and looking for reliable solutions? Don’t let uncertainty affect your ear health. Visit why.edu.vn today and ask our experts your specific questions. Get the personalized advice you need to keep your ears healthy and clear. Your hearing matters to us!