Why Do Leds Flicker? Understanding this phenomenon, along with related lighting issues and flicker causes, is key to optimizing your lighting solutions. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide in-depth answers and expert insights into electrical engineering. This guide will explore LED flicker reasons, power supply designs, and voltage fluctuations, equipping you with practical knowledge and expert advice.
1. Understanding LED Flicker: An Overview
LED flicker is the perceptible variation in light output from an LED lamp or bulb. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are semiconductor devices that produce light when an electric current passes through them. This process is highly efficient but also sensitive to voltage fluctuations and other electrical disturbances. LED flicker can manifest in different forms, including:
- Visible Flicker: Obvious, rapid changes in light intensity that are easily noticeable.
- Stroboscopic Effect: A less obvious flicker that becomes apparent when observing moving objects under LED lighting, causing them to appear jerky or discontinuous.
- Phantom Array Effect: Similar to the stroboscopic effect, but more related to how the brain processes intermittent light, leading to visual distortions.
Flickering LEDs can be more than just an annoyance; they can also lead to eye strain, headaches, and even trigger photosensitive epilepsy in susceptible individuals. Understanding the causes of LED flicker and how to mitigate them is essential for creating a comfortable and safe lighting environment.
2. The Technical Reasons Behind LED Flicker
To understand why LEDs flicker, it’s important to examine the technical factors that contribute to this issue. The primary reasons include the design of LED power supplies, voltage fluctuations, and other external electrical disturbances.
2.1. LED Power Supply Design
LED bulbs require a driver circuit to convert AC voltage from the mains supply to the DC voltage that LEDs need. The design and quality of this driver significantly impact the likelihood of flicker.
2.1.1. Simple Capacitor-Based Power Supplies
Many inexpensive LED bulbs use a simple capacitor-based power supply to reduce voltage and limit current. This design is cost-effective but has several drawbacks:
- Lack of Voltage Regulation: These power supplies do not provide consistent voltage regulation. Any fluctuations in the input voltage directly affect the current supplied to the LEDs, leading to brightness variations.
- Ripple Effect: After rectification, the DC voltage still contains a significant ripple component. A large capacitor can smooth out this ripple, but cheaper designs often use smaller capacitors to reduce costs. This results in more pronounced voltage fluctuations and, consequently, flicker.
2.1.2. Linear Regulators
Another common design uses linear regulators to provide a stable DC voltage. While linear regulators can offer better voltage regulation compared to capacitor-based supplies, they have their limitations:
- Heat Dissipation: Linear regulators dissipate excess energy as heat. In a sealed LED bulb, this heat can build up and reduce the lifespan of both the regulator and the LEDs.
- Efficiency: Linear regulators are less efficient than switching regulators, meaning more energy is wasted as heat rather than being converted into light.
2.1.3. Switching Power Supplies
High-quality LED bulbs often use switching power supplies, which are more complex but offer several advantages:
- Stable Voltage Output: Switching power supplies use feedback mechanisms to maintain a consistent voltage output, even when the input voltage fluctuates.
- Higher Efficiency: They are more efficient than linear regulators, reducing heat generation and improving overall energy efficiency.
- Flicker Reduction: Well-designed switching power supplies can significantly reduce or eliminate flicker.
2.2. Voltage Fluctuations
Voltage fluctuations in the electrical grid can also cause LEDs to flicker. These fluctuations can originate from various sources:
- Switching of Heavy Loads: When large appliances like HVAC systems, refrigerators, or water heaters switch on or off, they can cause temporary voltage drops in the electrical circuit.
- Electrical Noise: Noise injected into the power lines from other devices can disrupt the stable operation of LED drivers.
- Grid Instability: In some areas, the electrical grid may be inherently unstable, with frequent voltage variations.
2.3. PWM Dimming
Some LED lighting systems use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to control the brightness of the LEDs. While PWM is an effective dimming technique, it can also cause flicker if not implemented correctly:
- Low PWM Frequency: If the PWM frequency is too low, the on-off cycling of the LEDs becomes noticeable as flicker.
- Incompatible Dimmers: Using dimmers that are not designed for LED lighting can lead to compatibility issues and flicker.
3. Common Causes of LED Flickering
Identifying the specific cause of LED flickering is crucial for implementing the right solution. Here are some of the most common reasons why LEDs might flicker:
3.1. Loose Connections
A loose electrical connection is one of the simplest yet most frequent causes of LED flicker. This can occur at various points in the circuit:
- Bulb Socket: The LED bulb may not be screwed in tightly enough, resulting in an intermittent connection.
- Wiring Connections: Wires in the light fixture or electrical panel may be loose or corroded, disrupting the flow of electricity.
- Switch Connections: The connections at the light switch could be loose, causing the circuit to break and reconnect sporadically.
3.2. Incompatible Dimmers
Using a dimmer switch that is not compatible with LED bulbs can cause flickering. Traditional dimmers are designed for incandescent bulbs, which have different electrical characteristics than LEDs:
- Minimum Load Requirements: Incandescent dimmers often require a minimum load to function correctly. A single LED bulb may not draw enough power to meet this requirement, leading to flicker or erratic dimming behavior.
- Triac-Based Dimmers: These dimmers use a triac to control the current flow. However, triacs can cause flickering with LEDs due to their switching characteristics.
3.3. Voltage Fluctuations
As mentioned earlier, voltage fluctuations in the electrical grid can cause LEDs to flicker. These fluctuations can be caused by:
- Large Appliances: The operation of large appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines can cause voltage dips.
- Wiring Issues: Overloaded circuits or faulty wiring can exacerbate voltage fluctuations.
- External Factors: Problems with the utility grid or nearby industrial equipment can also affect voltage stability.
3.4. Faulty LED Bulb
In some cases, the LED bulb itself may be defective. This could be due to:
- Component Failure: Internal components in the LED driver circuit may fail, leading to inconsistent performance.
- Manufacturing Defects: Manufacturing defects can cause premature failure or flickering.
3.5. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby electronic devices can disrupt the operation of LED drivers and cause flickering. Sources of EMI include:
- Motors and Generators: These devices can generate significant electromagnetic noise.
- Fluorescent Lights: Older fluorescent lights and their ballasts can produce EMI.
- Wireless Devices: Wireless routers, cell phones, and other devices can emit electromagnetic radiation that interferes with LED circuits.
3.6. Neutral Wiring Issues
A less common but potentially serious cause of LED flickering is a problem with the neutral wiring in the electrical system. This can occur when:
- Neutral Wire is Loose: A loose neutral wire can cause voltage imbalances and flickering.
- Shared Neutral Wire: Sharing a neutral wire between multiple circuits can overload the neutral and cause voltage fluctuations.
4. The Impact of LED Flicker on Health and Well-being
The flicker from LED lights is more than a mere annoyance; it can have significant impacts on health and well-being. It’s essential to recognize these effects to prioritize proper lighting solutions.
4.1. Eye Strain and Headaches
One of the most common complaints associated with LED flicker is eye strain. The constant, subtle changes in light intensity force the eyes to work harder to maintain focus, leading to fatigue and discomfort. Prolonged exposure to flickering lights can result in headaches, which may range from mild to severe.
4.2. Visual Discomfort and Fatigue
Flickering lights can cause visual discomfort, even if the flicker is not consciously perceived. This discomfort can manifest as a general sense of unease or a feeling that something is “off” with the lighting. Over time, this can lead to chronic fatigue and reduced productivity.
4.3. Photosensitive Epilepsy
For individuals with photosensitive epilepsy, flickering lights can trigger seizures. The rapid changes in light intensity can disrupt brain activity, leading to a loss of consciousness and convulsions. While this condition is relatively rare, it highlights the importance of minimizing flicker in lighting systems.
4.4. Reduced Visual Performance
Flickering lights can impair visual performance, making it more difficult to perform tasks that require sharp vision and concentration. This can be particularly problematic in workplaces, schools, and other environments where visual acuity is essential.
4.5. Psychological Effects
Some studies suggest that exposure to flickering lights can have psychological effects, such as increased irritability, anxiety, and even depression. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, it is clear that lighting can play a significant role in mood and overall well-being.
5. Practical Steps to Eliminate or Reduce LED Flicker
Addressing LED flicker involves a systematic approach to identify the cause and implement the appropriate solution. Here are practical steps you can take to eliminate or reduce flicker:
5.1. Check and Tighten Connections
Start by checking all electrical connections associated with the flickering LED:
- Inspect Bulb Sockets: Ensure the LED bulb is screwed in tightly. If the socket seems loose, try bending the center tab slightly upward to improve contact.
- Examine Wiring Connections: If you are comfortable working with electrical wiring, carefully inspect the connections in the light fixture and electrical panel. Make sure all wires are securely fastened and free from corrosion.
- Test Switch Connections: Check the connections at the light switch. If the switch feels loose or wobbly, it may need to be replaced.
5.2. Use Compatible Dimmers
If you are using a dimmer switch with your LED bulbs, make sure it is designed for LED compatibility:
- LED-Specific Dimmers: Replace traditional dimmers with LED-specific models that are designed to work with the electrical characteristics of LEDs.
- Check Minimum Load: Ensure that the LED bulbs meet the minimum load requirements of the dimmer switch. If necessary, use multiple LED bulbs to reach the minimum load.
- Test Compatibility: Consult the dimmer switch manufacturer’s compatibility list to ensure that the dimmer is compatible with your specific LED bulbs.
5.3. Replace Faulty Bulbs
If you suspect that an LED bulb is faulty, try replacing it with a new one:
- Test with Known Good Bulb: Use a known good LED bulb to test the fixture. If the new bulb does not flicker, the original bulb was likely the problem.
- Check Warranty: Many LED bulbs come with a warranty. If the bulb is still under warranty, contact the manufacturer for a replacement.
5.4. Invest in High-Quality LED Bulbs
Choosing high-quality LED bulbs can significantly reduce the risk of flicker:
- Look for Reputable Brands: Choose LED bulbs from reputable brands that are known for their quality and reliability.
- Check Specifications: Look for bulbs that are specifically designed to minimize flicker. Some manufacturers provide a flicker index or flicker percentage in the product specifications.
- Consider Switching Power Supplies: Opt for LED bulbs that use switching power supplies, as they provide more stable voltage output and reduce flicker.
5.5. Address Voltage Fluctuations
If voltage fluctuations are causing the flickering, consider the following steps:
- Balance Electrical Load: Distribute the electrical load evenly across different circuits to prevent overloading any single circuit.
- Use Voltage Stabilizers: Consider using voltage stabilizers or surge protectors to protect sensitive electronic devices from voltage fluctuations.
- Consult an Electrician: If voltage fluctuations are severe or persistent, consult a qualified electrician to inspect your electrical system and identify potential problems.
5.6. Shield Against Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
To mitigate EMI, take the following actions:
- Relocate Devices: Move EMI-generating devices away from LED lights.
- Use Shielded Cables: Use shielded cables for sensitive electronic equipment to reduce EMI emissions.
- Install EMI Filters: Install EMI filters on the power lines to reduce the amount of electromagnetic noise.
5.7. Check and Correct Neutral Wiring Issues
Neutral wiring problems can be complex and potentially dangerous. If you suspect a neutral wiring issue:
- Consult a Qualified Electrician: Hire a qualified electrician to inspect your electrical system and identify any neutral wiring problems.
- Correct Wiring Issues: Have the electrician correct any wiring issues, such as loose connections or shared neutral wires.
5.8. Increase PWM Frequency
If you are using PWM dimming, ensure that the PWM frequency is high enough to prevent flicker:
- Use High-Frequency Drivers: Use LED drivers that operate at a high PWM frequency (e.g., above 200 Hz).
- Adjust Dimming Settings: Adjust the dimming settings to optimize flicker performance. Some dimmers allow you to adjust the PWM frequency or dimming curve.
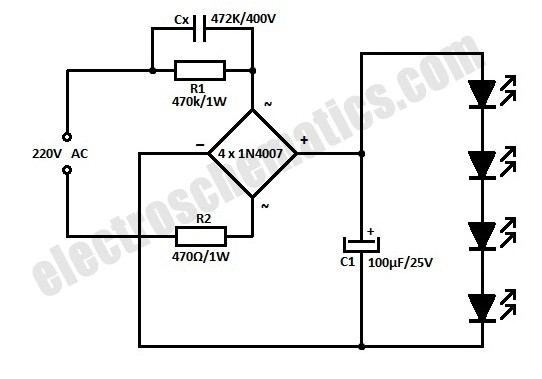 LED Power Supply Design
LED Power Supply Design
Diagram illustrating a simple LED power supply design, highlighting the rectifier, current-limiting element, and series of LEDs, crucial for understanding flicker causes.
6. LED Flicker Testing and Measurement
Quantifying LED flicker is essential for ensuring that lighting systems meet safety and performance standards. Several methods and metrics are used to measure flicker:
6.1. Flicker Frequency
Flicker frequency refers to the rate at which the light output of an LED fluctuates. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), which represents the number of cycles per second. High flicker frequencies are less likely to be perceived by the human eye.
6.2. Flicker Percentage
Flicker percentage, also known as the modulation depth, indicates the amount of light modulation relative to the average light output. It is calculated using the following formula:
Flicker Percentage = [(Max - Min) / (Max + Min)] * 100Where:
- Max is the maximum light output.
- Min is the minimum light output.
A lower flicker percentage indicates less flicker.
6.3. Flicker Index
The flicker index is a more sophisticated metric that takes into account the shape of the light output waveform. It ranges from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating no flicker and 1 indicating maximum flicker. The flicker index is calculated using the following formula:
Flicker Index = Area above average / Total areaThe flicker index provides a more accurate representation of flicker perception compared to flicker percentage.
6.4. Stroboscopic Effect Visibility Measure (SVM)
The SVM is a more recent metric developed to quantify the stroboscopic effect of lighting. It takes into account the frequency, amplitude, and waveform shape of the light output. An SVM value of 1 or less indicates that the stroboscopic effect is not likely to be noticeable.
6.5. Measurement Tools
Several tools are available for measuring LED flicker:
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes can be used to visualize the light output waveform and measure flicker frequency, flicker percentage, and flicker index.
- Light Meters with Flicker Measurement: Some light meters are equipped with flicker measurement capabilities. These meters can directly measure flicker percentage and flicker index.
- Specialized Flicker Analyzers: Specialized flicker analyzers are designed specifically for measuring flicker in lighting systems. These analyzers provide accurate and detailed flicker measurements.
- Smartphone Apps: While not as accurate as dedicated instruments, several smartphone apps can provide an approximate measure of flicker using the phone’s camera.
7. Regulations and Standards for LED Flicker
To ensure safety and minimize the negative impacts of LED flicker, several regulations and standards have been established:
7.1. IEEE Std 1789-2015
IEEE Std 1789-2015 is a recommended practice for modulating current in high-brightness LEDs for mitigating health risks. It provides guidelines for flicker frequency and flicker percentage to minimize potential health effects.
7.2. California Title 24
California Title 24 is a set of energy efficiency standards that include requirements for flicker in lighting systems. The standards specify maximum allowable flicker percentages for different types of lighting.
7.3. European Union Ecodesign Directive
The European Union Ecodesign Directive sets minimum performance requirements for lighting products, including limits on flicker. The directive aims to reduce energy consumption and minimize the environmental impact of lighting.
7.4. ENERGY STAR
ENERGY STAR is a voluntary labeling program that identifies energy-efficient products. ENERGY STAR certified LED bulbs must meet certain flicker requirements to ensure that they provide high-quality lighting.
8. Future Trends in LED Lighting and Flicker Reduction
The field of LED lighting is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development focused on improving performance and reducing flicker. Here are some future trends to watch:
8.1. Advanced Driver Designs
Manufacturers are developing more sophisticated LED driver designs that incorporate advanced features such as:
- Active Flicker Cancellation: Active flicker cancellation circuits use feedback mechanisms to detect and compensate for voltage fluctuations, further reducing flicker.
- High-Frequency PWM Dimming: Increasing the PWM frequency to several kilohertz can eliminate visible flicker and reduce the risk of stroboscopic effects.
- Digital Control: Digital control systems allow for precise control of the LED driver, enabling advanced dimming and flicker reduction algorithms.
8.2. Improved Component Quality
Using higher-quality components in LED bulbs can improve their reliability and reduce the risk of flicker:
- High-Quality Capacitors: Using capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) can reduce voltage ripple and improve flicker performance.
- Robust Integrated Circuits: Using robust integrated circuits in the LED driver can improve its stability and resistance to EMI.
8.3. Standardized Flicker Metrics
Efforts are underway to develop standardized flicker metrics that provide a more accurate and comprehensive assessment of flicker performance:
- International Standards: International organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) are working on developing standardized flicker metrics and testing procedures.
- Industry Collaboration: Industry stakeholders are collaborating to develop common flicker metrics that can be used by manufacturers, regulators, and consumers.
8.4. Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems offer the potential to further reduce flicker through advanced control and monitoring:
- Adaptive Lighting: Adaptive lighting systems can automatically adjust the light output based on ambient conditions and user preferences, reducing the need for dimming and minimizing flicker.
- Flicker Monitoring: Smart lighting systems can monitor flicker levels in real-time and alert users to potential problems.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Flicker Solutions
Examining real-world scenarios where LED flicker was addressed can provide valuable insights and practical solutions.
9.1. Case Study 1: Office Building Lighting Upgrade
Problem: An office building experienced widespread complaints of eye strain and headaches after upgrading to LED lighting. Employees reported that the lights seemed to flicker, causing discomfort and reduced productivity.
Solution: An investigation revealed that the LED bulbs used in the upgrade had low-quality power supplies and high flicker percentages. The building management replaced the bulbs with high-quality LED bulbs that met IEEE Std 1789-2015 recommendations for flicker.
Results: The new LED bulbs significantly reduced flicker, and employee complaints of eye strain and headaches decreased dramatically. Productivity also improved.
9.2. Case Study 2: School Classroom Lighting Retrofit
Problem: A school district retrofitted its classrooms with LED lighting to save energy. However, teachers reported that the lights were causing distraction and discomfort for students, particularly those with sensory sensitivities.
Solution: The school district conducted a flicker assessment and found that the LED bulbs had high flicker indices. They replaced the bulbs with flicker-free LED bulbs that met California Title 24 requirements.
Results: The new LED bulbs eliminated visible flicker, and teachers reported that students were more focused and engaged in classroom activities.
9.3. Case Study 3: Home Lighting Improvement
Problem: A homeowner experienced flickering LED lights in their living room. The flickering was particularly noticeable when using a dimmer switch.
Solution: The homeowner replaced the traditional dimmer switch with an LED-compatible dimmer switch. They also replaced the LED bulbs with high-quality bulbs from a reputable brand.
Results: The new dimmer switch and LED bulbs eliminated the flickering, providing smooth and consistent dimming performance.
10. Addressing Common Misconceptions About LED Flicker
Several misconceptions surround LED flicker, which can lead to confusion and ineffective solutions.
10.1. Misconception: All LEDs Flicker
Reality: Not all LEDs flicker. High-quality LED bulbs with well-designed power supplies produce minimal or no flicker. The likelihood of flicker depends on the quality of the LED bulb and the design of its driver circuit.
10.2. Misconception: Flicker is Only Visible
Reality: Flicker can be present even if it is not consciously perceived. Subconscious flicker can still cause eye strain, headaches, and other health problems.
10.3. Misconception: Dimmers Always Cause Flicker
Reality: Dimmers do not always cause flicker. When used with compatible LED bulbs and properly installed, LED-compatible dimmers can provide smooth and consistent dimming performance without flicker.
10.4. Misconception: Expensive LEDs Never Flicker
Reality: While expensive LEDs are more likely to have better power supplies and lower flicker, price alone is not a guarantee of flicker-free performance. It is essential to check the specifications and certifications of LED bulbs to ensure that they meet flicker requirements.
10.5. Misconception: Flicker is Only a Problem for People with Epilepsy
Reality: While flicker can trigger seizures in people with photosensitive epilepsy, it can also cause eye strain, headaches, and other health problems in the general population. Minimizing flicker is important for creating a comfortable and safe lighting environment for everyone.
11. Conclusion: Ensuring Flicker-Free LED Lighting
LED flicker is a common issue that can affect the quality of lighting and impact health and well-being. By understanding the causes of LED flicker and taking practical steps to eliminate or reduce it, you can create a more comfortable and safe lighting environment.
From checking connections and using compatible dimmers to investing in high-quality LED bulbs and addressing voltage fluctuations, there are many strategies you can implement to ensure flicker-free LED lighting. Remember to stay informed about the latest regulations and standards, and consider future trends in LED lighting technology.
By prioritizing flicker reduction, you can enjoy the energy-saving benefits of LED lighting without compromising your health and comfort. For deeper insights and expert solutions tailored to your needs, visit WHY.EDU.VN, where we address all your questions with precision and expertise.
Facing challenges finding reliable answers to your questions? Overwhelmed by information overload? At WHY.EDU.VN, we offer detailed, easy-to-understand explanations based on expert knowledge. Connect with specialists who provide direct answers, fostering a community of insightful discussions. Visit us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101, or explore our website at WHY.EDU.VN to ask your questions and discover a world of knowledge.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About LED Flicker
Here are some frequently asked questions about LED flicker:
-
What is LED flicker and why does it occur?
LED flicker is the perceptible variation in light output from an LED lamp or bulb, often due to poor power supply design, voltage fluctuations, or incompatible dimmers. -
Is LED flicker harmful to health?
Yes, LED flicker can cause eye strain, headaches, visual discomfort, and in rare cases, trigger photosensitive epilepsy. -
How can I tell if my LED lights are flickering?
You can visually inspect the lights for obvious flicker, use a smartphone app designed to detect flicker, or employ specialized measurement tools like oscilloscopes. -
What should I do if my LED lights are flickering?
Check and tighten connections, use compatible dimmers, replace faulty bulbs, invest in high-quality LED bulbs, and address voltage fluctuations. -
Are all LED dimmers the same?
No, traditional dimmers are designed for incandescent bulbs and may not work properly with LEDs. Use LED-specific dimmers for optimal performance. -
Can voltage fluctuations cause LED flicker?
Yes, voltage fluctuations from large appliances or grid instability can cause LEDs to flicker, especially those with simple power supplies. -
How do I choose high-quality, flicker-free LED bulbs?
Look for reputable brands, check specifications for low flicker percentage or index, and opt for bulbs with switching power supplies. -
What are the regulations and standards for LED flicker?
Standards include IEEE Std 1789-2015, California Title 24, the European Union Ecodesign Directive, and ENERGY STAR, which set limits on flicker. -
Is it possible to completely eliminate LED flicker?
Yes, by using high-quality LED bulbs with advanced driver designs and addressing electrical issues, you can significantly reduce or eliminate flicker. -
Where can I find more information and expert advice on LED lighting and flicker reduction?
Visit why.edu.vn for in-depth insights, expert solutions, and answers to all your questions about LED lighting.