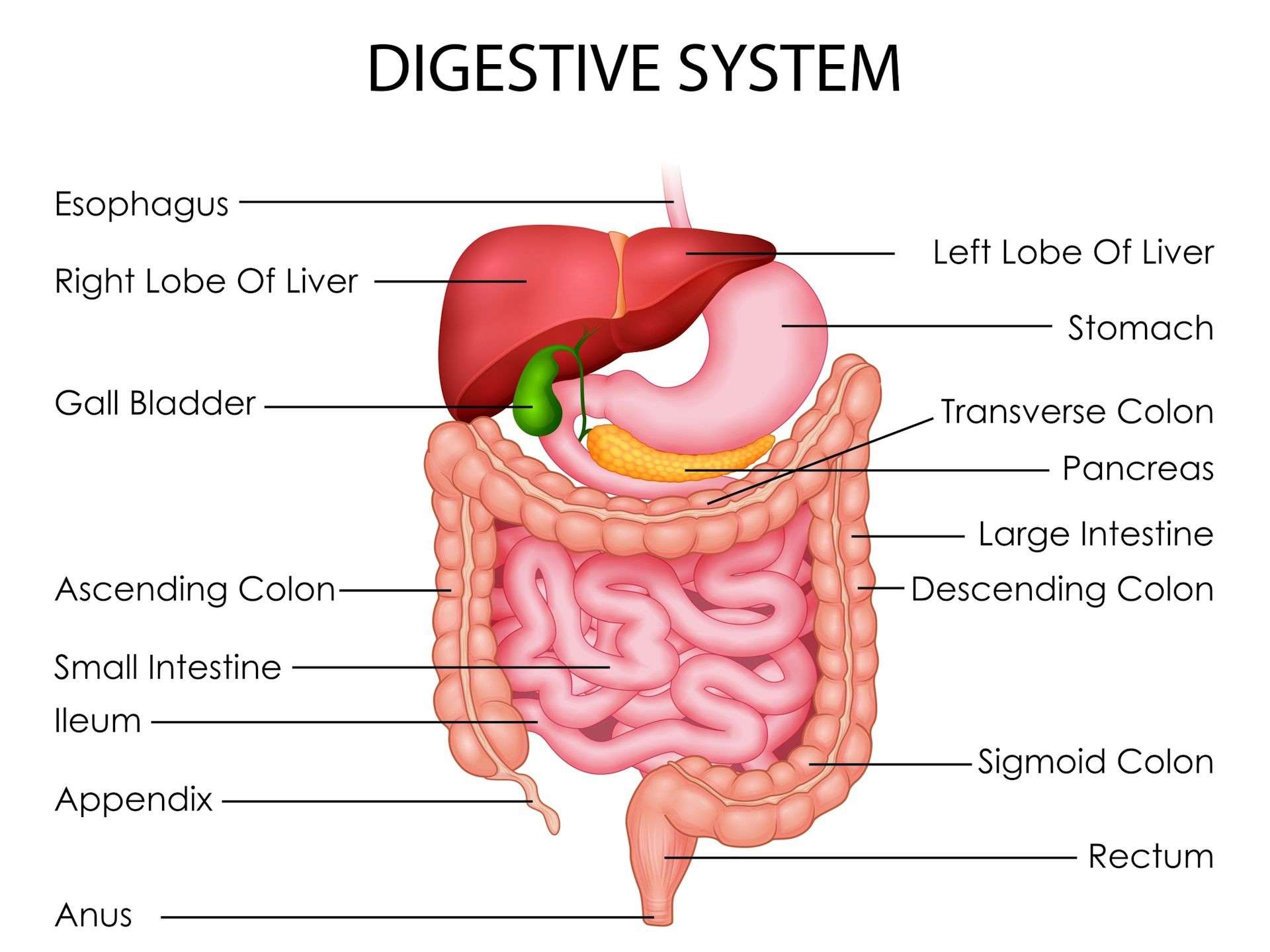
Why Do I Poop Every Morning? Discover the science behind morning bowel movements, factors influencing your digestive rhythm, and tips for regularity. At WHY.EDU.VN, we explore the fascinating interplay between your body clock, diet, and gut health, providing insights into why many people experience bowel movements shortly after waking. Understand your gastrocolic reflex, circadian rhythm, and learn about potential remedies for digestive inconsistencies, as well as common digestive triggers.
1. The Science Behind Morning Bowel Movements: Why It Happens
The question “Why do I poop every morning?” is surprisingly common, and the answer involves a combination of biological processes. Our bodies are finely tuned machines, and the timing of our bowel movements is no exception. Several key factors contribute to this morning phenomenon:
- Circadian Rhythm: Our bodies operate on a 24-hour internal clock known as the circadian rhythm. This clock regulates various bodily functions, including digestion.
- Gastrocolic Reflex: This reflex is triggered when food enters the stomach, stimulating the colon to contract and move waste. This reflex is often strongest in the morning.
- Overnight Digestion: While we sleep, our digestive system continues to process food. By morning, waste is ready to be eliminated.
- Breakfast: Eating breakfast further stimulates the gastrocolic reflex, prompting a bowel movement.
2. Circadian Rhythm and Digestion: The Body Clock’s Role
The circadian rhythm plays a crucial role in regulating our digestive system. During sleep, digestive activity slows down, allowing the body to focus on repair and restoration. However, as we approach morning, our internal clock signals the digestive system to ramp up activity.
- Minimal Nighttime Activity: The muscular contractions in our colon are minimal at night. This is why we don’t typically feel the urge to poop while sleeping.
- Increased Morning Activity: As we wake up, our colon contractions become more active, preparing the body for waste elimination.
- Mass Movements: These powerful contractions push stool toward the rectum, preparing for a bowel movement. They are more frequent in the morning.
3. The Gastrocolic Reflex: How Eating Triggers Bowel Movements
The gastrocolic reflex is a physiological response that stimulates colon contractions when food enters the stomach. This reflex is particularly strong in the morning, contributing to the urge to poop after breakfast.
- Stomach Stretching: When we eat or drink, our stomach stretches, triggering the gastrocolic reflex.
- Colon Stimulation: This reflex stimulates the colon to contract forcefully, moving waste toward the rectum.
- Morning Peak: The gastrocolic reflex is typically strongest in the morning, making breakfast a potent trigger for bowel movements.
4. Breakfast and Bowel Movements: The Morning Connection
Breakfast is often a significant trigger for bowel movements due to its impact on the gastrocolic reflex. Eating and drinking in the morning kickstarts the digestive system, prompting waste elimination.
- Food and Drink: The act of consuming food and beverages stimulates the gastrocolic reflex.
- Colon Contractions: The colon responds by contracting, moving stool toward the rectum.
- Regularity: For many, this morning routine establishes a pattern of regular bowel movements.
5. Coffee’s Role: A Stimulant for Bowel Activity
For many, a morning cup of coffee is an essential part of their routine, and it can also stimulate bowel movements. Coffee contains compounds that can increase colon contractions and promote waste elimination.
- Stimulant Effect: Coffee stimulates contractions in the sigmoid colon (the last part of the colon before the rectum) and the rectum itself.
- Muscle Contractions: This stimulation leads to increased muscle contractions in the digestive tract.
- Diuretic: Coffee also has a diuretic effect, which can contribute to softer stools and easier bowel movements.
6. Normal Bowel Movement Frequency: What’s Considered Regular?
While morning bowel movements are common, what’s considered “normal” can vary significantly from person to person. Understanding the range of normal bowel movement frequency can help alleviate concerns about regularity.
- Wide Range: Most people poop between three times a day and three times a week.
- Individual Variation: Bowel habits can vary based on diet, lifestyle, and individual physiology.
- Consistency: More important than frequency is the consistency and ease of bowel movements.
7. Factors Influencing Bowel Habits: Beyond the Morning Routine
Several factors beyond the morning routine can influence bowel habits. Understanding these factors can help you identify potential causes of changes in your regularity.
- Diet: Fiber intake, hydration, and food sensitivities can all impact bowel movements.
- Lifestyle: Physical activity, stress levels, and sleep patterns can influence digestive health.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect bowel habits, causing either constipation or diarrhea.
- Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can impact bowel regularity.
8. Is Irregularity a Concern? Knowing When to Seek Help
Occasional irregularity is usually not a cause for concern. However, persistent changes in bowel habits or the presence of other symptoms may warrant medical attention.
- Change in Regularity: If you experience a significant change in your bowel habits that lasts for more than a few weeks, consult a doctor.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, blood in stool, or unexplained weight loss should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Underlying Conditions: Persistent bowel irregularities can sometimes indicate an underlying medical condition.
9. Training Your Bowels: Tips for Establishing Regularity
While you can’t completely control your bowel movements, you can take steps to encourage regularity. Lifestyle and dietary changes can help promote healthy bowel habits.
- Consistent Schedule: Try to establish a consistent daily routine, including regular meal times and sleep patterns.
- Toilet Time: Dedicate a specific time each day for using the toilet, preferably after breakfast.
- Proper Posture: Ensure a comfortable and relaxed posture while on the toilet.
- Respond to Urges: Don’t ignore the urge to defecate, as this can lead to constipation.
10. Diet and Bowel Health: The Importance of Fiber and Hydration
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bowel habits. Fiber and hydration are particularly important for promoting regularity.
- Fiber Intake: Fiber adds bulk to stool, making it easier to pass. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps keep stool soft and prevents constipation.
- Probiotics: Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, can promote a healthy gut microbiome.
11. Exercise and Bowel Movements: Staying Active for Digestive Health
Regular physical activity can stimulate bowel movements and improve overall digestive health. Exercise helps to increase blood flow to the digestive system and promote muscle contractions in the colon.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, running, and swimming can stimulate bowel movements.
- Abdominal Exercises: Core-strengthening exercises can improve muscle tone in the abdominal region, aiding in digestion.
- Consistent Routine: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
12. Stress and Digestion: The Gut-Brain Connection
Stress can significantly impact digestion and bowel habits. The gut-brain connection is a complex network that allows for communication between the digestive system and the brain.
- Stress Hormones: When stressed, the body releases hormones that can disrupt digestive processes.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Stress can exacerbate symptoms of IBS, leading to irregular bowel movements.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help manage stress and improve digestion.
13. Common Digestive Problems: Constipation, Diarrhea, and IBS
Several common digestive problems can affect bowel habits. Understanding these conditions can help you identify potential causes of irregularity.
- Constipation: Characterized by infrequent bowel movements and difficulty passing stool.
- Diarrhea: Characterized by frequent, loose, and watery stools.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic digestive disorder that can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.
14. When to See a Doctor: Red Flags and Warning Signs
While occasional bowel irregularities are usually not a cause for concern, certain signs and symptoms warrant medical attention.
- Blood in Stool: This can indicate bleeding in the digestive tract and should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Persistent Abdominal Pain: Ongoing abdominal pain or cramping can be a sign of an underlying digestive issue.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without a known cause should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
- Changes in Stool Color or Shape: Changes in stool color or shape, especially if persistent, can indicate a digestive problem.
15. The Impact of Medication: How Drugs Affect Bowel Habits
Certain medications can affect bowel habits, either causing constipation or diarrhea. Understanding the potential side effects of medications can help you manage your bowel movements.
- Opioids: These pain medications can slow down bowel movements and cause constipation.
- Antibiotics: These medications can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to diarrhea.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressants can cause either constipation or diarrhea as a side effect.
- Iron Supplements: Iron supplements can cause constipation in some individuals.
16. Probiotics and Gut Health: Balancing Your Microbiome
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can improve gut health and promote regular bowel movements. They can help restore balance to the gut microbiome, which can be disrupted by factors like antibiotics and stress.
- Sources of Probiotics: Probiotics can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in supplement form.
- Benefits of Probiotics: Probiotics can help improve digestion, reduce bloating, and promote regular bowel movements.
- Choosing a Probiotic Supplement: When choosing a probiotic supplement, look for strains that have been clinically proven to be effective.
17. The Role of Hydration: Staying Properly Hydrated for Bowel Regularity
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining healthy bowel movements. Water helps to soften stool and makes it easier to pass.
- Daily Water Intake: Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Fluid-Rich Foods: Consume fluid-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and soups to stay hydrated.
- Avoid Dehydration: Limit consumption of beverages that can lead to dehydration, such as alcohol and caffeine.
18. Fiber Supplements: When to Consider Adding Them to Your Diet
Fiber supplements can be a helpful addition to your diet if you struggle to get enough fiber from food alone. They can help add bulk to stool and promote regular bowel movements.
- Types of Fiber Supplements: Common types of fiber supplements include psyllium husk, methylcellulose, and wheat dextrin.
- Benefits of Fiber Supplements: Fiber supplements can help relieve constipation, improve bowel regularity, and lower cholesterol levels.
- Starting Slowly: When starting a fiber supplement, begin with a low dose and gradually increase it to avoid digestive discomfort.
19. Natural Remedies for Constipation: Gentle Solutions for Relief
Several natural remedies can help relieve constipation and promote regular bowel movements. These remedies are often gentler than over-the-counter medications.
- Prune Juice: Prune juice is a natural laxative that can help soften stool and stimulate bowel movements.
- Warm Lemon Water: Drinking warm lemon water in the morning can stimulate the digestive system and promote bowel regularity.
- Castor Oil: Castor oil is a strong laxative that should be used with caution.
20. Understanding the Bristol Stool Chart: A Visual Guide to Stool Consistency
The Bristol Stool Chart is a visual tool that can help you assess the consistency of your stool. It categorizes stool into seven types, ranging from hard and lumpy to watery.
- Types of Stool: The chart categorizes stool based on its shape and consistency, providing a helpful guide for understanding your bowel health.
- Assessing Your Stool: Use the chart to assess the consistency of your stool and identify any potential irregularities.
- Discussing Concerns with Your Doctor: If you have concerns about your stool consistency, discuss them with your doctor.
21. The Importance of a Healthy Gut Microbiome: Bacteria and Bowel Habits
The gut microbiome is a complex community of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion and bowel regularity.
- Beneficial Bacteria: Beneficial bacteria help break down food, absorb nutrients, and protect against harmful pathogens.
- Factors Affecting the Microbiome: Factors like diet, antibiotics, and stress can impact the balance of gut bacteria.
- Supporting the Microbiome: Consume a diet rich in fiber and probiotics to support a healthy gut microbiome.
22. Identifying Food Sensitivities: How They Impact Digestion
Food sensitivities can contribute to digestive problems and irregular bowel movements. Identifying and eliminating trigger foods can help improve digestion.
- Common Food Sensitivities: Common food sensitivities include lactose, gluten, and certain additives.
- Symptoms of Food Sensitivities: Symptoms can include bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Elimination Diet: An elimination diet can help you identify potential food sensitivities by systematically removing and reintroducing foods.
23. Addressing Bloating and Gas: Minimizing Digestive Discomfort
Bloating and gas are common digestive symptoms that can be caused by various factors. Understanding the causes and implementing strategies to minimize these symptoms can improve your overall comfort.
- Causes of Bloating and Gas: Common causes include eating too quickly, consuming gas-producing foods, and having an imbalance of gut bacteria.
- Strategies for Minimizing Bloating and Gas: Eat slowly, avoid gas-producing foods, and consider taking a digestive enzyme supplement.
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Over-the-counter remedies like simethicone can help relieve gas and bloating.
24. Traveling and Bowel Movements: Maintaining Regularity on the Go
Traveling can disrupt your regular bowel habits due to changes in diet, routine, and stress levels. Implementing strategies to maintain regularity while traveling can help prevent digestive discomfort.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water while traveling to prevent dehydration and constipation.
- Eat Fiber-Rich Foods: Pack snacks that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole-grain crackers.
- Maintain a Routine: Try to maintain a consistent sleep schedule and meal times while traveling.
- Consider Probiotics: Taking a probiotic supplement can help support gut health and prevent digestive issues while traveling.
25. The Importance of Chewing Your Food Properly: Improving Digestion from the Start
Chewing your food thoroughly is an often-overlooked aspect of digestion. Proper chewing can improve nutrient absorption and reduce digestive discomfort.
- Breaking Down Food: Chewing helps break down food into smaller particles, making it easier for the digestive system to process.
- Saliva Production: Chewing stimulates saliva production, which contains enzymes that begin the digestion process.
- Reducing Digestive Discomfort: Proper chewing can reduce bloating, gas, and indigestion.
26. Digestive Enzymes: Enhancing Nutrient Absorption
Digestive enzymes are proteins that help break down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Supplementing with digestive enzymes can improve nutrient absorption and reduce digestive discomfort.
- Types of Digestive Enzymes: Common digestive enzymes include amylase (breaks down carbohydrates), protease (breaks down proteins), and lipase (breaks down fats).
- Benefits of Digestive Enzymes: Digestive enzymes can help improve nutrient absorption, reduce bloating, and alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders.
- When to Consider Digestive Enzymes: Consider taking digestive enzymes if you experience symptoms like bloating, gas, or indigestion after meals.
27. Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Strategies for Relief
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic digestive disorder that can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements. While there is no cure for IBS, several strategies can help manage symptoms.
- Dietary Changes: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods can help reduce IBS symptoms.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation and yoga can help manage stress and alleviate IBS symptoms.
- Medications: Medications like antispasmodics and laxatives can help relieve specific IBS symptoms.
- Probiotics: Probiotics can help balance the gut microbiome and improve IBS symptoms.
28. The Connection Between Sleep and Bowel Movements: Prioritizing Rest
Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and can also impact bowel movements. Prioritizing sleep can help regulate your digestive system and promote regular bowel habits.
- Circadian Rhythm: Sleep helps regulate the circadian rhythm, which influences digestive processes.
- Stress Reduction: Getting enough sleep can help reduce stress levels, which can improve digestion.
- Consistency: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate bowel movements.
29. Gut-Directed Hypnotherapy: A Mind-Body Approach to Digestive Health
Gut-directed hypnotherapy is a mind-body technique that can help improve digestive health and alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders like IBS.
- How It Works: Gut-directed hypnotherapy involves using hypnosis to target the digestive system and promote relaxation and healing.
- Benefits: Studies have shown that gut-directed hypnotherapy can effectively reduce symptoms of IBS, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
- Finding a Practitioner: Look for a qualified hypnotherapist who specializes in gut-directed hypnotherapy.
30. The Importance of Regular Check-Ups: Monitoring Your Digestive Health
Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential for monitoring your digestive health and identifying any potential problems early on.
- Screening Tests: Your doctor may recommend screening tests like colonoscopies to detect colorectal cancer and other digestive issues.
- Discussing Concerns: Use your check-ups as an opportunity to discuss any concerns you have about your bowel habits or digestive health.
- Preventative Measures: Your doctor can provide guidance on preventative measures to maintain good digestive health, such as diet and lifestyle changes.
In conclusion, the question “Why do I poop every morning?” has a multifaceted answer rooted in our body’s natural rhythms and digestive processes. By understanding these factors and adopting healthy habits, you can promote regular bowel movements and improve your overall digestive health.
Do you have more questions about your bowel habits or digestive health? Visit WHY.EDU.VN at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Our team of experts is here to provide you with detailed, easy-to-understand answers and connect you with the knowledge you need. Explore a world of answers at why.edu.vn, where curiosity meets expertise. Don’t just wonder, discover today!
FAQ: Common Questions About Bowel Habits
-
Is it normal to poop every day?
- Yes, it is normal to poop every day, but bowel habits vary widely. Anywhere from three times a day to three times a week is considered within the normal range.
-
What causes constipation?
- Constipation can be caused by dehydration, low fiber intake, lack of physical activity, certain medications, and medical conditions.
-
What causes diarrhea?
- Diarrhea can be caused by infections, food sensitivities, medications, and digestive disorders.
-
How can I improve my bowel regularity?
- You can improve your bowel regularity by staying hydrated, eating a high-fiber diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
-
What are the symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
- Symptoms of IBS include abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
-
When should I see a doctor about my bowel habits?
- See a doctor if you experience significant changes in your bowel habits, blood in stool, persistent abdominal pain, or unexplained weight loss.
-
Can stress affect my bowel movements?
- Yes, stress can affect bowel movements by disrupting the digestive process and exacerbating symptoms of digestive disorders.
-
What are probiotics and how can they help my gut health?
- Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can improve gut health by balancing the gut microbiome, aiding digestion, and reducing bloating.
-
How does fiber help with bowel regularity?
- Fiber adds bulk to stool, making it easier to pass and promoting regular bowel movements.
-
Can certain foods cause bloating and gas?
- Yes, certain foods like beans, broccoli, and carbonated beverages can cause bloating and gas.