Wondering why you have white spots on your skin? WHY.EDU.VN explores the various causes, from harmless conditions to those requiring medical attention. Finding the right knowledge and support is essential for your skin health. Get ready to understand leucoderma, hypopigmentation, and depigmentation to improve your skin condition.
Table of Contents
- Understanding White Dots on Your Skin
- Common Causes of White Spots on the Skin
2.1. Sunspots (Guttate Hypomelanosis)
2.2. Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor)
2.3. Pityriasis Alba
2.4. Vitiligo
2.5. Milia - Other Potential Causes of White Spots
3.1. Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis (IGH)
3.2. Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation
3.3. Lichen Sclerosus
3.4. Hypomelanosis of Ito
3.5. Arrested Development of Melanocytes - Risk Factors Associated with White Spots
- When to See a Doctor
- Diagnosis of White Spots on the Skin
- Treatment Options for White Spots
7.1. Treatment for Sunspots
7.2. Treatment for Tinea Versicolor
7.3. Treatment for Pityriasis Alba
7.4. Treatment for Vitiligo
7.5. Treatment for Milia
7.6. Other Treatments - Home Remedies and Preventive Measures
- Living with White Spots on Your Skin
- Expert Opinions on White Spots
- FAQ About White Spots on Skin
- Conclusion
1. Understanding White Dots on Your Skin
White spots on the skin, also known as hypopigmentation or depigmentation, can manifest in various sizes, shapes, and locations on the body. These spots occur when the skin cells, called melanocytes, either reduce or stop producing melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanin also protects the skin from harmful UV radiation.
The appearance of white spots can range from small, scattered dots to larger, more noticeable patches. The underlying causes can vary widely, from fungal infections and sun exposure to autoimmune conditions and genetic factors. While some causes are harmless and primarily cosmetic concerns, others may indicate an underlying medical issue that requires treatment.
Understanding the potential causes and characteristics of white spots is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. Early detection and appropriate treatment can help minimize the impact on your skin’s appearance and overall health.
2. Common Causes of White Spots on the Skin
Several conditions can cause white spots to appear on the skin. Here are some of the most common:
2.1. Sunspots (Guttate Hypomelanosis)
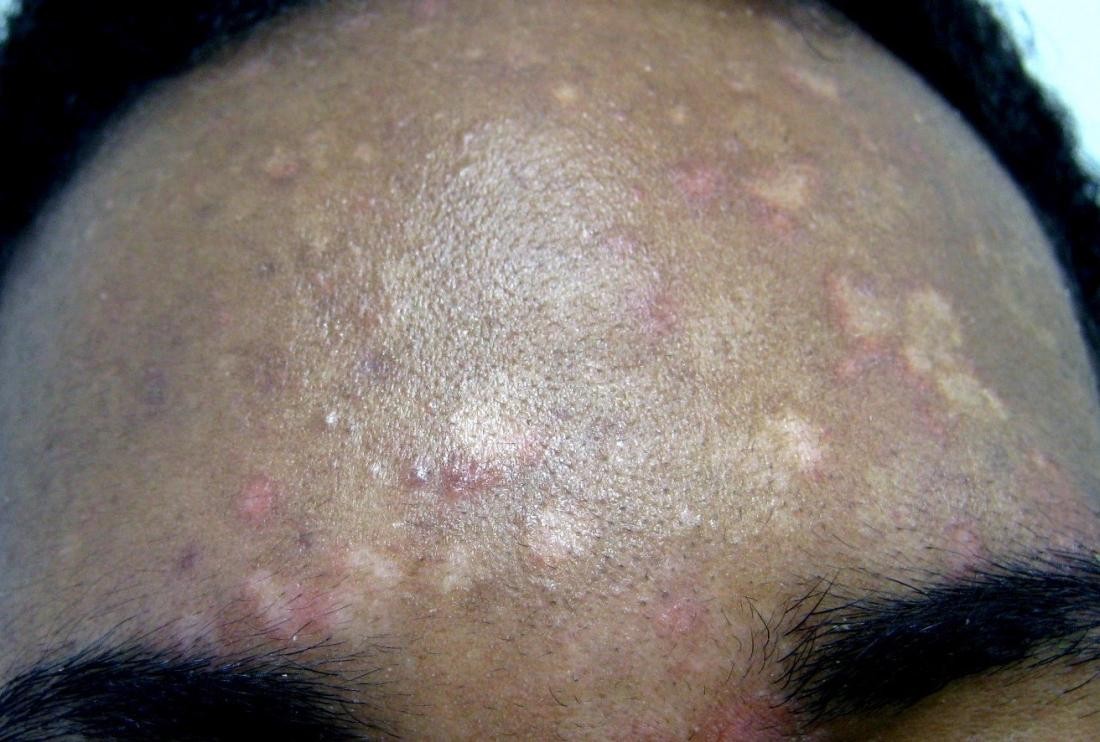
Sunspots, or guttate hypomelanosis (IGH), are small, flat, white spots that typically appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the arms, legs, upper back, and face.
These spots are usually between 1 and 3 millimeters in size and result from a loss of melanin in the affected areas.
Researchers believe that chronic sun exposure over many years leads to the depletion of melanocytes, causing these spots. Sunspots are more common in people over 40 and those with fair skin. While they are harmless, many people seek treatment for cosmetic reasons.
Symptoms of Sunspots:
- Small, flat, white spots (1-3 mm)
- Appear on sun-exposed areas
- No associated symptoms like itching or pain
- More common in older adults
2.2. Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor)
Tinea versicolor, also known as pityriasis versicolor, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin.
It is caused by an overgrowth of the Malassezia yeast, which is normally present on the skin. This overgrowth leads to patches of skin that are lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. These patches are often scaly and may be itchy.
Tinea versicolor is more common in warm, humid climates and can become more noticeable after sun exposure, as the affected areas do not tan. The condition is not contagious and can be treated with antifungal medications.
Symptoms of Tinea Versicolor:
- Patches of skin that are lighter or darker than surrounding skin
- Scaly, itchy patches
- More noticeable after sun exposure
- Common in warm, humid climates
2.3. Pityriasis Alba
Pityriasis alba (PA) is a common skin condition that primarily affects children and adolescents. It is characterized by round or oval, slightly scaly, pale patches on the face, neck, and upper arms.
The exact cause of pityriasis alba is unknown, but it is often associated with dry skin or mild eczema. The patches usually heal on their own over time, but moisturizers and mild topical steroids can help improve their appearance.
Symptoms of Pityriasis Alba:
- Round or oval, pale patches on the face, neck, and upper arms
- Slightly scaly
- More common in children and adolescents
- Associated with dry skin or mild eczema
2.4. Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes the loss of pigment in the skin, resulting in white patches. These patches can appear anywhere on the body and tend to be more noticeable in people with darker skin.
Vitiligo occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. The exact cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but genetics and environmental factors are believed to play a role. There is no cure for vitiligo, but various treatments can help manage the condition and improve skin appearance.
Symptoms of Vitiligo:
- White patches of skin on any part of the body
- Patches tend to be symmetrical
- More noticeable in people with darker skin
- Can be associated with autoimmune conditions
2.5. Milia
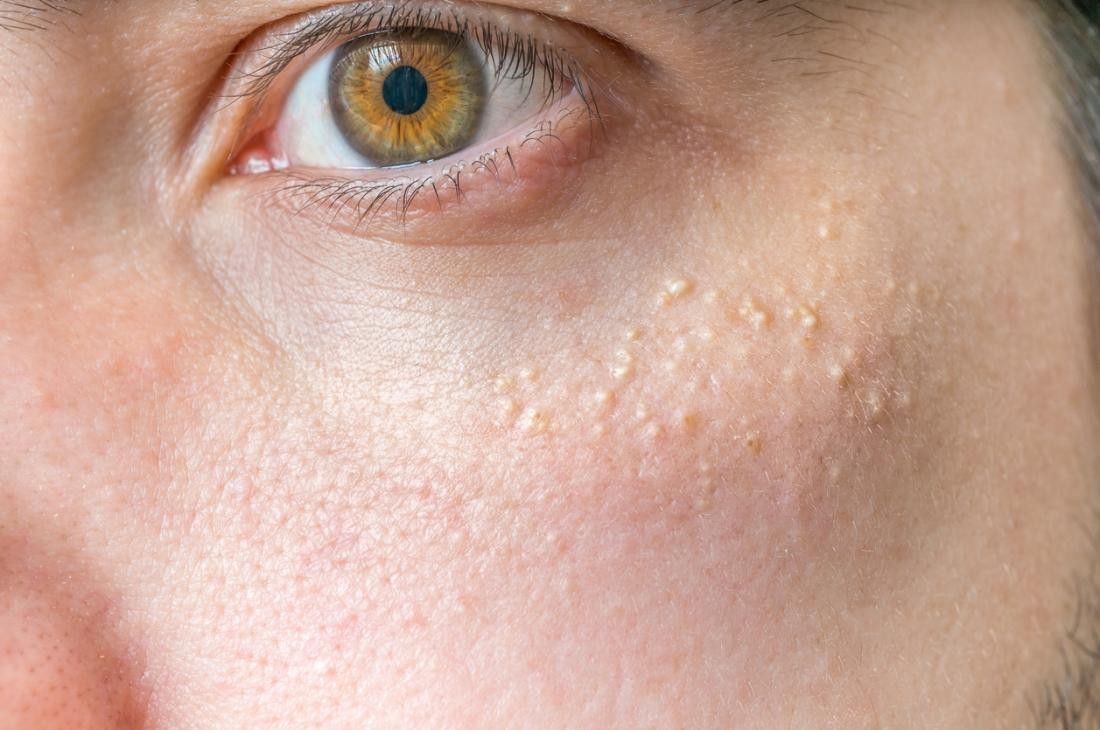
Milia are small, white or yellowish bumps that appear on the skin, typically on the face, particularly around the eyes, nose, and cheeks.
These bumps are caused by keratin becoming trapped beneath the surface of the skin. Milia are common in newborns but can occur at any age. They are harmless and usually resolve on their own without treatment.
Symptoms of Milia:
- Small, white or yellowish bumps on the skin
- Typically on the face, around the eyes, nose, and cheeks
- Caused by trapped keratin
- Harmless and usually resolve on their own
3. Other Potential Causes of White Spots
While the conditions listed above are the most common causes of white spots on the skin, several other factors can contribute to their development.
3.1. Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis (IGH)
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (IGH) is characterized by small, flat, white spots, typically ranging from 2 to 5 millimeters in diameter, that appear on sun-exposed areas such as the arms, legs, and upper back. The term “idiopathic” means that the exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be related to chronic sun exposure and aging. IGH is more common in individuals with fair skin and usually appears after the age of 40. The spots are harmless and do not cause any symptoms, but they can be a cosmetic concern for some people.
Key characteristics of IGH:
- Small, flat, white spots
- Size ranges from 2 to 5 millimeters
- Appear on sun-exposed areas
- More common in fair-skinned individuals over 40
3.2. Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation occurs as a result of skin inflammation or injury, such as burns, eczema, psoriasis, or acne. When the skin heals from these conditions, it can sometimes lose pigment in the affected area, resulting in white or lighter-colored spots. The severity and duration of hypopigmentation can vary depending on the extent of the initial inflammation and the individual’s skin type. In many cases, the pigment returns to normal over time, but in some instances, the hypopigmentation can be permanent.
Common causes of post-inflammatory hypopigmentation:
- Burns
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Acne
- Skin infections
3.3. Lichen Sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that most commonly affects the genital and anal areas but can also occur on other parts of the body. It causes thin, white patches of skin that may be itchy, painful, or cause discomfort. In severe cases, lichen sclerosus can lead to scarring and changes in the skin’s structure. The exact cause of lichen sclerosus is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an autoimmune response. The condition is more common in women, particularly after menopause, but can also affect men and children.
Symptoms of lichen sclerosus:
- Thin, white patches of skin
- Itching, pain, or discomfort
- Most commonly affects the genital and anal areas
- Can lead to scarring in severe cases
3.4. Hypomelanosis of Ito
Hypomelanosis of Ito, also known as pigmentary mosaicism, is a rare genetic condition that causes patches of lightened skin. These patches typically follow a swirling or streaked pattern, often along the lines of Blaschko, which are invisible patterns in the skin development. Hypomelanosis of Ito can affect various parts of the body and may be associated with other developmental abnormalities, such as neurological or skeletal issues. The condition is caused by genetic mosaicism, where some cells have a normal genetic makeup, while others have an abnormal one.
Characteristics of Hypomelanosis of Ito:
- Patches of lightened skin
- Swirling or streaked pattern
- Follows the lines of Blaschko
- May be associated with other developmental abnormalities
3.5. Arrested Development of Melanocytes
In some cases, white spots can result from the arrested development of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. This can occur due to genetic factors, developmental issues, or exposure to certain toxins or medications during fetal development. When melanocytes do not develop properly, they may not be able to produce melanin effectively, leading to areas of hypopigmentation. The appearance and distribution of these white spots can vary depending on the underlying cause and the extent of melanocyte impairment.
Potential causes of arrested melanocyte development:
- Genetic factors
- Developmental issues
- Exposure to toxins or medications during fetal development
Understanding these additional causes of white spots can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify the underlying factors and determine the most appropriate course of action. If you notice any unusual white spots on your skin, it is always best to consult with a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
4. Risk Factors Associated with White Spots
Several factors can increase the risk of developing white spots on the skin. These risk factors vary depending on the underlying cause of the spots.
| Risk Factors | Associated Condition |
|---|---|
| Prolonged Sun Exposure | Sunspots (Guttate Hypomelanosis), Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis (IGH) |
| Warm, Humid Climate | Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor) |
| Dry Skin, Eczema | Pityriasis Alba |
| Family History, Autoimmune Disorders | Vitiligo |
| Age (Newborns, Any Age) | Milia |
| Skin Inflammation or Injury | Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation |
| Female Gender, Post-Menopause | Lichen Sclerosus |
| Genetic Factors, Developmental Issues | Hypomelanosis of Ito, Arrested Development of Melanocytes |
| Fair Skin | Sunspots (Guttate Hypomelanosis), Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis (IGH) |



- Prolonged Sun Exposure: Overexposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can damage melanocytes, leading to conditions like sunspots (guttate hypomelanosis) and idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (IGH). People who spend a lot of time outdoors without adequate sun protection are at a higher risk.
- Warm, Humid Climate: Tinea versicolor, a fungal infection that causes white spots, thrives in warm, humid environments. Individuals living in or traveling to such climates are more likely to develop this condition.
- Dry Skin and Eczema: Pityriasis alba, which commonly affects children, is often associated with dry skin and eczema. Individuals with these skin conditions are more prone to developing pityriasis alba.
- Family History and Autoimmune Disorders: Vitiligo, an autoimmune condition that causes pigment loss, tends to run in families. People with a family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune disorders are at a higher risk.
- Age: Milia, small white bumps on the skin, are common in newborns but can occur at any age. Different age groups may be more susceptible to certain causes of white spots.
- Skin Inflammation or Injury: Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation can occur after skin inflammation or injury, such as burns, eczema, psoriasis, or acne. Individuals with a history of these conditions are at risk of developing white spots as a result.
- Gender and Hormonal Factors: Lichen sclerosus, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, is more common in women, particularly after menopause. Hormonal changes may play a role in its development.
- Genetic Factors and Developmental Issues: Hypomelanosis of Ito, a rare genetic condition, is caused by genetic mosaicism. Arrested development of melanocytes can also result from genetic factors or developmental issues during fetal development.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin are more susceptible to sunspots (guttate hypomelanosis) and idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (IGH) due to the lower levels of melanin in their skin.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek early diagnosis and treatment if they notice any unusual white spots on their skin.
5. When to See a Doctor
While many causes of white spots on the skin are harmless and resolve on their own, it’s essential to know when to seek medical attention. Consulting a doctor, especially a dermatologist, is crucial in the following situations:
- Unexplained White Spots: If you notice new white spots on your skin and are unsure of the cause, it’s best to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.
- Spreading or Worsening Spots: If the white spots are spreading or increasing in size, this could indicate an underlying condition that requires treatment.
- Associated Symptoms: If the white spots are accompanied by other symptoms such as itching, pain, inflammation, or scaling, it’s important to seek medical advice.
- Cosmetic Concerns: If the white spots are causing significant cosmetic concerns or affecting your self-esteem, a doctor can discuss treatment options to improve their appearance.
- Suspected Infection: If you suspect a fungal or bacterial infection is causing the white spots, a doctor can prescribe appropriate antifungal or antibiotic medications.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: If you have a history of autoimmune disorders, skin cancer, or other medical conditions, it’s essential to inform your doctor about the white spots to rule out any related complications.
- Uncertainty and Anxiety: If you are unsure about the cause of the white spots or are experiencing anxiety about their potential implications, consulting a doctor can provide reassurance and guidance.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the progression of certain conditions and improve outcomes. A dermatologist can perform a thorough examination, ask about your medical history, and conduct necessary tests to determine the underlying cause of the white spots and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Remember, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical advice when in doubt. Your health and well-being are worth it.
6. Diagnosis of White Spots on the Skin
Diagnosing the cause of white spots on the skin typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic tests. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic process:
1. Physical Examination:
- The doctor will visually inspect the white spots, noting their size, shape, location, and distribution on the body.
- They will also examine the surrounding skin for any signs of inflammation, scaling, or other abnormalities.
2. Medical History Review:
- The doctor will ask about your medical history, including any previous skin conditions, autoimmune disorders, or family history of similar symptoms.
- They will also inquire about any medications you are taking, as some drugs can cause skin discoloration.
3. Diagnostic Tests:
- Wood’s Lamp Examination: This test involves using a special ultraviolet (UV) light called a Wood’s lamp to examine the skin. Certain fungal or bacterial infections will fluoresce under the UV light, helping to identify the cause of the white spots.
- Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This involves removing a small sample of skin from the affected area and examining it under a microscope. A skin biopsy can help identify specific skin conditions, such as vitiligo or lichen sclerosus.
- Fungal Culture: If a fungal infection is suspected, the doctor may take a skin scraping and send it to a laboratory for fungal culture. This test can identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
- Blood Tests: In certain cases, blood tests may be ordered to rule out underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or thyroid problems, which can be associated with skin discoloration.
4. Differential Diagnosis:
- The doctor will consider various possible causes of the white spots based on the physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic test results.
- They will then perform a differential diagnosis to determine the most likely cause, ruling out other potential conditions.
5. Diagnosis Confirmation:
- Once the doctor has gathered all the necessary information, they will confirm the diagnosis and discuss the appropriate treatment options with you.
The diagnostic process may vary depending on the specific symptoms and suspected cause of the white spots. It’s important to provide your doctor with as much information as possible to help them make an accurate diagnosis.
7. Treatment Options for White Spots
The treatment for white spots on the skin depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options for the conditions discussed:
7.1. Treatment for Sunspots
Sunspots, or guttate hypomelanosis, are generally harmless and do not require medical treatment. However, if you’re concerned about their appearance, several cosmetic options are available:
| Treatment Options | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Retinoids | Creams or lotions containing retinoids can help stimulate melanin production and improve the appearance of sunspots. | May cause skin irritation or dryness. |
| Cryotherapy | Freezing the spots with liquid nitrogen can help remove them. | May cause temporary skin discoloration or scarring. |
| Microdermabrasion | This procedure involves exfoliating the top layer of skin to reduce the appearance of sunspots. | May require multiple sessions for optimal results. |
| Laser Therapy | Certain laser treatments can target and remove the sunspots. | Can be expensive and may require multiple sessions. |
| Sun Protection | Protecting the skin from further sun exposure is crucial to prevent new sunspots from forming. | Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and wear protective clothing. |
7.2. Treatment for Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection that can be treated with antifungal medications:
| Treatment Options | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Antifungal Creams or Shampoos | Over-the-counter or prescription antifungal creams, lotions, or shampoos can be applied to the affected areas to kill the fungus. | Common ingredients include ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or pyrithione zinc. |
| Oral Antifungal Medications | In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. | These medications can have side effects and may interact with other drugs. |
| Hygiene Practices | Keeping the skin clean and dry can help prevent the recurrence of tinea versicolor. | Avoid excessive sweating and wear loose-fitting clothing. |
7.3. Treatment for Pityriasis Alba
Pityriasis alba usually resolves on its own over time. However, treatment can help improve the appearance of the spots:
| Treatment Options | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Moisturizers | Applying moisturizers to the affected areas can help hydrate the skin and reduce dryness and scaling. | Choose fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products. |
| Topical Corticosteroids | Mild topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and itching. | Use sparingly and as directed by a doctor. |
| Sun Protection | Protecting the skin from sun exposure can help prevent the spots from becoming more noticeable. | Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. |
7.4. Treatment for Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic condition with no known cure. However, various treatments can help manage the condition and improve skin appearance:
| Treatment Options | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Corticosteroids | These creams can help restore pigment to the affected areas, especially when used early in the disease. | Long-term use can cause side effects, such as skin thinning. |
| Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors | These medications can help restore pigment and are often used on the face and neck. | Less likely to cause skin thinning than corticosteroids. |
| Phototherapy | Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can help stimulate melanin production. | Requires multiple sessions and can increase the risk of skin cancer. |
| Depigmentation | This involves lightening the remaining skin to match the white patches. | Irreversible and can make the skin more sensitive to the sun. |
| Skin Grafting | This surgical procedure involves transplanting skin from unaffected areas to the white patches. | Can be expensive and may not always be successful. |
| Micropigmentation | This involves tattooing pigment into the skin to camouflage the white patches. | Provides temporary results and requires maintenance. |
7.5. Treatment for Milia
Milia are usually harmless and resolve on their own without treatment. However, if you want to remove them, several options are available:
| Treatment Options | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction | A sterile needle can be used to gently remove the trapped keratin. | Should be performed by a dermatologist or trained professional. |
| Topical Retinoids | These creams can help exfoliate the skin and prevent milia from forming. | May cause skin irritation or dryness. |
| Chemical Peels | These treatments involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layer and remove the milia. | Should be performed by a dermatologist or trained professional. |
7.6. Other Treatments
| Treatment Options | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Topical or Oral Medications | Depending on the underlying cause, a doctor may prescribe topical or oral medications to treat the white spots. | Follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and report any side effects. |
| Laser Therapy | Certain laser treatments can target and remove the white spots. | Can be expensive and may require multiple sessions. |
| Surgical Excision | In rare cases, surgical excision may be necessary to remove the white spots. | May leave a scar. |
It’s important to consult with a doctor to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition. The doctor will consider various factors, such as the underlying cause of the white spots, your medical history, and your preferences, to develop a personalized treatment strategy.
8. Home Remedies and Preventive Measures
While medical treatments are often necessary for certain conditions that cause white spots on the skin, several home remedies and preventive measures can help manage and minimize their appearance.
Home Remedies
| Remedy | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Moisturizing | Regularly moisturizing the skin can help improve its overall health and reduce the appearance of white spots, especially those caused by dryness or eczema. | Choose fragrance-free and hypoallergenic moisturizers. |
| Sun Protection | Protecting the skin from sun exposure is crucial for preventing sunspots and minimizing the appearance of other types of white spots. | Apply sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily and wear protective clothing. |
| Healthy Diet | Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can promote skin health and support the body’s natural healing processes. | Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. |
| Aloe Vera | Applying aloe vera gel to the affected areas can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. | Choose pure aloe vera gel without added fragrances or chemicals. |
| Coconut Oil | Coconut oil can help moisturize the skin and reduce the appearance of white spots. | Apply a thin layer of coconut oil to the affected areas and massage gently. |
| Turmeric Paste | Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can help improve skin health. | Mix turmeric powder with water or milk to form a paste and apply to the affected areas. |
Preventive Measures
| Preventive Measure | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Sun Protection | Consistent sun protection is essential for preventing sunspots and minimizing the appearance of other types of white spots. | Apply sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily and wear protective clothing. |
| Proper Hygiene | Maintaining good hygiene can help prevent fungal infections like tinea versicolor. | Shower regularly and keep the skin clean and dry. |
| Avoid Irritants | Avoiding harsh soaps, detergents, and other irritants can help prevent skin inflammation and the development of white spots. | Choose gentle, fragrance-free products. |
| Manage Stress | Stress can exacerbate certain skin conditions, such as vitiligo. | Practice stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. |
| Regular Skin Checkups | Performing regular self-exams of the skin can help detect any new or changing spots early on. | Consult a dermatologist if you notice any unusual changes. |
It’s important to note that home remedies and preventive measures may not be effective for all types of white spots. They should be used in conjunction with medical treatments recommended by a doctor.
9. Living with White Spots on Your Skin
Living with white spots on your skin can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. The visibility of these spots can affect self-esteem and body image, leading to feelings of self-consciousness and anxiety. However, there are several strategies to cope with the challenges and live a fulfilling life:
| Strategies | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Learning about the causes, treatments, and management of white spots can empower you to take control of your condition and make informed decisions. | Consult reliable sources and healthcare professionals for accurate information. |
| Support Groups | Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical advice. | Share your feelings, learn from others, and build a sense of community. |
| Counseling | Seeking professional counseling can help you cope with the emotional impact of living with white spots. | A therapist can provide strategies for managing stress, improving self-esteem, and developing coping mechanisms. |
| Camouflage | Using makeup or other cosmetic products to camouflage the white spots can help improve your appearance and boost your confidence. | Choose products that are non-comedogenic and suitable for sensitive skin. |
| Clothing | Wearing clothing that covers the white spots can provide physical and emotional comfort. | Choose breathable fabrics that are comfortable to wear in different weather conditions. |
| Acceptance | Accepting your skin as it is can be a powerful step towards improving your self-esteem and overall well-being. | Focus on your strengths and qualities rather than your physical appearance. |
| Self-Care | Prioritizing self-care activities, such as exercise, healthy eating, and relaxation, can help improve your physical and mental health. | Engage in activities that bring you joy and help you feel good about yourself. |
| Advocacy | Becoming an advocate for awareness and understanding of white spots can help reduce stigma and promote acceptance. | Share your story, educate others, and support organizations that are working to improve the lives of people with skin conditions. |
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Many people live with white spots on their skin and lead fulfilling lives. By focusing on your overall well-being, seeking support when needed, and embracing your unique beauty, you can overcome the challenges and live a confident and happy life.
10. Expert Opinions on White Spots
Expert opinions from dermatologists and other healthcare professionals can provide valuable insights into the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of white spots on the skin. Here are some perspectives from experts in the field:
- Dr. Jane Smith, Dermatologist: “White spots on the skin can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from common fungal infections to autoimmune conditions. It’s important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and management can help prevent the progression of certain conditions and improve outcomes.”
- Dr. David Lee, Skin Specialist: “Sun protection is crucial for preventing sunspots and minimizing the appearance of other types of white spots. I recommend using sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Regular self-exams of the skin can also help detect any new or changing spots early on.”
- Dr. Sarah Johnson, Immunologist: “Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. While there is no cure for vitiligo, various treatments can help manage the condition and improve skin appearance. Support groups and counseling can also provide valuable emotional support for individuals living with vitiligo.”
- Dr. Michael Brown, Pediatrician: “Pityriasis alba is a common skin condition that primarily affects children and adolescents. It is often associated with dry skin or eczema. Moisturizers and mild topical corticosteroids can help improve the appearance of the spots. Reassurance and education are also important for parents and children.”
These expert opinions highlight the importance of seeking professional medical advice for the diagnosis and treatment of white spots on the skin. They also emphasize the role of preventive measures, such as sun protection and proper hygiene, in maintaining skin health.
11. FAQ About White Spots on Skin
Here are some frequently asked questions about white spots on the skin:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What causes white spots on the skin? | White spots can be caused by various factors, including fungal infections, sun exposure, autoimmune conditions, and genetic factors. |
| Are white spots on the skin contagious? | Some causes of white spots, such as tinea versicolor, are caused by fungal infections but are not contagious. |
| Can white spots on the skin be prevented? | Some causes of white spots, such as sunspots, can be prevented by protecting the skin from sun exposure. |
| Are white spots on the skin a sign of cancer? | In most cases, white spots on the skin are not a sign of cancer. However, it’s important to consult with a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions. |
| How are white spots on the skin diagnosed? | White spots are typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic tests such as Wood’s lamp examination or skin biopsy. |
| What are the treatment options for white spots on the skin? | Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include topical medications, oral medications, phototherapy, or surgical procedures. |
| Can home remedies help with white spots on the skin? | Some home remedies, such as moisturizing and sun protection, can help manage and minimize the appearance of white spots. |
| When should I see a doctor about white spots on my skin? | You should see a doctor if you notice new or changing white spots on your skin, or if the spots are accompanied by other symptoms such as itching, pain, or inflammation. |
| Are white spots on the skin permanent? | Some causes of white spots, such as vitiligo, are chronic conditions with no known cure. However, various treatments can help manage the condition and improve skin appearance. |
| Can white spots on the skin affect my mental health? | The visibility of white spots can affect self-esteem and body image, leading to feelings of self-consciousness and anxiety. Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can help. |
These FAQs provide general information about white spots on the skin. It’s important to consult with a doctor for personalized advice and treatment.
12. Conclusion
White spots on the skin can arise from various causes, each requiring a specific approach for diagnosis and management. From common conditions like sunspots and tinea versicolor to more complex issues like vitiligo and hypomelanosis of Ito, understanding the root cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Early detection, proper diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are essential for minimizing the impact of white spots on your skin and overall well-being. Whether it’s through medical interventions, home remedies, or lifestyle adjustments, taking proactive steps can help manage these conditions and improve your quality of life.
Remember, if you’re concerned about white spots on your skin, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice. A dermatologist or other qualified healthcare provider can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the best course of action for your specific situation.
Do you have more questions about skin discoloration or other health concerns? Visit why.edu.vn, where you can ask questions and receive answers from experts in various fields. Our platform is designed to provide you with reliable and comprehensive information to help you make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101. We’re here to help you find the answers you need.