Why Do I Have seasons? This question explores the fundamental science behind Earth’s yearly cycle of spring, summer, autumn, and winter, impacting daily life. At WHY.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive explanations and expert insights into the causes and effects of seasonal changes, providing clear, reliable answers to your questions. Delve into the earth’s axial tilt, solar radiation, and climatological shifts.
1. Earth’s Tilt: The Prime Reason Why Do I Have Seasons
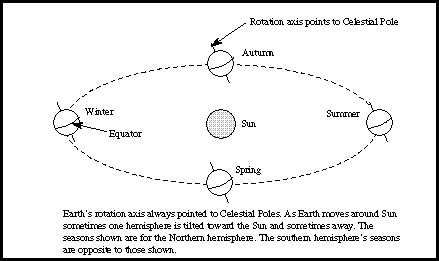
The primary reason why do I have distinct seasons is the Earth’s axial tilt of approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of direct sunlight throughout the year as the planet orbits the Sun.
1.1. Axial Tilt Explained
The Earth’s axis isn’t perpendicular to its orbital plane around the Sun. Instead, it’s tilted at an angle. This tilt is the single most important factor in why do I have seasonal changes.
1.2. How Tilt Affects Sunlight Distribution
During the Northern Hemisphere’s summer, the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun. This results in longer days and more direct sunlight. Conversely, during the Northern Hemisphere’s winter, the North Pole is tilted away from the Sun, leading to shorter days and less intense sunlight. The Southern Hemisphere experiences the opposite effect.
1.3. Seasonal Opposites
Because of Earth’s tilt, when the Northern Hemisphere experiences summer, the Southern Hemisphere experiences winter. This alternating pattern is a direct consequence of the angle at which sunlight strikes different parts of the Earth.
2. Orbit and Seasons: Understanding the Yearly Journey for Why Do I Have Seasons
While the Earth’s tilt is the primary factor, the Earth’s elliptical orbit around the Sun also plays a role, though a smaller one, in why do I have seasons.
2.1. Elliptical Orbit Basics
The Earth’s orbit isn’t a perfect circle but an ellipse. This means the distance between the Earth and the Sun varies throughout the year.
2.2. Perihelion and Aphelion
The Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in early January and farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in early July. However, this distance variation has a minimal impact on seasons. The tilt of the Earth’s axis is the dominant influence.
2.3. Impact on Seasonal Intensity
Although the elliptical orbit doesn’t cause seasons, it can influence their intensity. For example, the Southern Hemisphere’s summers are slightly warmer because they occur when the Earth is closer to the Sun.
3. Solstices and Equinoxes: Defining Seasonal Markers Explaining Why Do I Have Seasons
Solstices and equinoxes are key astronomical events that mark the transitions between seasons, impacting why do I have certain weather patterns at specific times of the year.
3.1. Summer Solstice
The summer solstice (around June 21 in the Northern Hemisphere) marks the day with the longest period of daylight. The North Pole is tilted most directly towards the Sun.
3.2. Winter Solstice
The winter solstice (around December 21 in the Northern Hemisphere) is the day with the shortest period of daylight. The North Pole is tilted farthest away from the Sun.
3.3. Equinoxes (Spring and Fall)
The equinoxes (around March 20 and September 22) occur when the Earth’s axis is neither tilted towards nor away from the Sun. This results in nearly equal day and night lengths all over the world.
4. Sunlight Angle and Intensity: The Key to Seasonal Temperatures in Understanding Why Do I Have Seasons
The angle at which sunlight strikes the Earth’s surface significantly affects the intensity of solar radiation, which in turn influences temperatures and explains why do I have warmer or cooler seasons.
4.1. Direct vs. Indirect Sunlight
When sunlight hits the Earth at a direct angle (close to 90 degrees), the energy is concentrated over a smaller area, resulting in higher temperatures. When sunlight hits at an indirect angle, the energy is spread over a larger area, leading to lower temperatures.
4.2. Atmospheric Absorption
Sunlight also travels through the atmosphere, where some of it is absorbed by gases, aerosols, and clouds. Direct sunlight passes through less atmosphere than indirect sunlight, so more energy reaches the surface.
4.3. Seasonal Temperature Differences
During summer, the hemisphere tilted towards the Sun receives more direct sunlight, leading to higher temperatures. During winter, the hemisphere tilted away from the Sun receives more indirect sunlight, resulting in lower temperatures.
5. Hemispheric Differences: Why Do I Have Different Seasons in Different Places?
The Northern and Southern Hemispheres experience opposite seasons due to the Earth’s axial tilt, providing an essential piece to the puzzle of why do I have different weather at different times of the year.
5.1. Opposite Seasonal Cycles
When it’s summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it’s winter in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. This reciprocal relationship is a direct consequence of the Earth’s tilt.
5.2. Impact on Agriculture and Ecosystems
The different seasonal cycles have significant impacts on agriculture, ecosystems, and human activities in each hemisphere. Planting seasons, animal migration patterns, and weather-related events are all influenced by these seasonal differences.
5.3. Cultural and Societal Adaptations
Societies in different hemispheres have adapted their lifestyles, customs, and celebrations to align with their respective seasons. Festivals, holidays, and traditional practices often reflect the changing seasons.
6. Latitude and Seasonal Variation: Explaining Why Do I Have Different Seasonal Changes
Latitude, or the distance from the equator, affects the degree of seasonal variation experienced in different regions, providing context for why do I have milder or more extreme seasons depending on location.
6.1. Equatorial Regions
Regions near the equator experience relatively little seasonal variation. The angle of sunlight remains fairly constant throughout the year, leading to consistent temperatures and day lengths.
6.2. Mid-Latitude Regions
Mid-latitude regions (between the tropics and the polar circles) experience the most distinct seasons. These areas have significant variations in temperature and day length throughout the year.
6.3. Polar Regions
Polar regions experience extreme seasonal variations. During summer, they have continuous daylight, while during winter, they have continuous darkness. Temperatures also vary dramatically between seasons.
7. Climate Zones and Seasons: Understanding Seasonal Variations across Different Zones in Exploring Why Do I Have Seasons
Different climate zones around the world exhibit distinct seasonal patterns influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, and proximity to oceans. This helps explain why do I have diverse weather experiences across the globe.
7.1. Tropical Climates
Tropical climates are characterized by warm temperatures year-round with distinct wet and dry seasons. Seasonal variations are primarily related to rainfall rather than temperature.
7.2. Temperate Climates
Temperate climates have four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter. These regions experience significant variations in temperature and precipitation throughout the year.
7.3. Polar Climates
Polar climates are characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. These regions have extreme seasonal variations in temperature and daylight.
8. Ocean Currents and Seasons: Influences of Oceans on Seasonal Weather Patterns Giving Insight to Why Do I Have Seasons
Ocean currents play a crucial role in moderating temperatures and influencing weather patterns, which in turn affects seasonal changes in coastal regions. This sheds light on why do I have milder or more extreme seasons near oceans.
8.1. Warm and Cold Currents
Warm ocean currents transport heat from the equator towards the poles, while cold ocean currents transport cold water from the poles towards the equator. These currents can significantly influence the temperature of nearby landmasses.
8.2. Coastal Climate Moderation
Coastal regions near warm ocean currents tend to have milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas. Conversely, coastal regions near cold ocean currents may experience cooler temperatures year-round.
8.3. Impact on Precipitation
Ocean currents also affect precipitation patterns. Warm currents can lead to increased evaporation and rainfall, while cold currents can create drier conditions.
9. Altitude and Seasons: Understanding How Elevation Impacts Seasonal Weather Patterns, Contributing to the Answer of Why Do I Have Seasons
Altitude affects temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to distinct seasonal variations in mountainous regions. Understanding this helps explain why do I have different seasonal experiences in highlands.
9.1. Temperature Decrease with Altitude
Temperature generally decreases with increasing altitude. This means that higher elevations tend to have cooler temperatures year-round.
9.2. Mountainous Seasonal Variations
Mountainous regions often experience shorter growing seasons and more extreme temperature fluctuations compared to lower elevations. Snowfall is also more common in mountainous areas during winter.
9.3. Influence on Ecosystems
Altitude-related seasonal variations have a significant impact on ecosystems. Different plant and animal species are adapted to specific altitudinal zones with varying temperature and precipitation patterns.
10. El Niño and La Niña: The Impact of These Phenomena on Seasonal Weather That Further Explains Why Do I Have Seasons
El Niño and La Niña are climate patterns in the Pacific Ocean that can significantly influence weather patterns and seasonal variations around the world. This knowledge is critical to grasping why do I have unpredictable or unusual seasons.
10.1. El Niño Explained
El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. This can lead to changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, affecting weather in many regions.
10.2. La Niña Explained
La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. This can also lead to changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, with effects that are often opposite to those of El Niño.
10.3. Global Weather Impacts
El Niño and La Niña can influence temperature and precipitation patterns in various regions around the world. They can also affect the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes.
11. Human Impact on Seasons: The Effects of Global Warming Giving Additional Layers of Understanding to Why Do I Have Seasons
Human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases, are altering the Earth’s climate and affecting seasonal patterns around the world. This is a crucial consideration to truly understanding why do I have shifting or erratic seasons.
11.1. Climate Change Overview
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature and weather patterns. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to a warming planet.
11.2. Altered Seasonal Patterns
Climate change is causing shifts in seasonal patterns, including earlier spring blooms, later autumn frosts, and changes in the timing and intensity of precipitation events.
11.3. Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is also contributing to an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms. These events can have devastating impacts on ecosystems, agriculture, and human societies.
12. Predicting Seasons: The Role of Meteorology and Climate Models That Assist in Answering Why Do I Have Seasons
Meteorologists and climate scientists use various tools and models to predict seasonal weather patterns and understand the factors that influence them. This gives foresight to why do I have certain expectations for upcoming seasons.
12.1. Weather Forecasting Techniques
Weather forecasting involves using observational data, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, to predict short-term weather conditions.
12.2. Climate Modeling
Climate models are complex computer simulations that use mathematical equations to represent the Earth’s climate system. These models can be used to predict long-term climate trends and seasonal variations.
12.3. Importance of Data Collection
Accurate and comprehensive data collection is essential for both weather forecasting and climate modeling. Scientists rely on data from weather stations, satellites, and other sources to monitor and understand the Earth’s climate system.
13. Adapting to Seasonal Changes: Strategies for Living Through the Seasons That Connects to The Question of Why Do I Have Seasons
Understanding seasonal changes is crucial for adapting human activities and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events. This reveals practical implications of why do I have seasonal awareness.
13.1. Agricultural Practices
Farmers use seasonal forecasts to plan planting and harvesting schedules and to manage irrigation and pest control.
13.2. Public Health Measures
Public health officials use seasonal forecasts to prepare for seasonal health risks, such as heatwaves, cold snaps, and outbreaks of infectious diseases.
13.3. Infrastructure Planning
Engineers and urban planners use seasonal forecasts to design and maintain infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, such as floods, storms, and heatwaves.
14. Seasonal Celebrations and Traditions: Cultural Significance Of Seasons That Adds Cultural Context to Why Do I Have Seasons
Seasons have played a significant role in shaping human cultures and traditions around the world. Many festivals, holidays, and customs are associated with the changing seasons. Understanding this offers cultural context to why do I have seasonal experiences.
14.1. Harvest Festivals
Harvest festivals are celebrated in many cultures to mark the end of the growing season and to give thanks for a bountiful harvest.
14.2. Winter Solstice Celebrations
Winter solstice celebrations are held to mark the shortest day of the year and to celebrate the return of light and warmth.
14.3. Spring Festivals
Spring festivals are celebrated to mark the beginning of the growing season and to celebrate the rebirth of nature.
15. The Future of Seasons: Climate Change Projections That Predict Changes to Understanding Why Do I Have Seasons
Climate change is projected to continue altering seasonal patterns in the coming decades, with significant implications for ecosystems, agriculture, and human societies. This gives a forward-looking perspective to why do I have concerns about future seasons.
15.1. Temperature Increases
Global average temperatures are projected to continue rising, leading to warmer summers and milder winters in many regions.
15.2. Precipitation Changes
Changes in precipitation patterns are also expected, with some regions becoming wetter and others becoming drier.
15.3. Extreme Weather Events
The frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms, are projected to increase.
16. Educational Resources for Understanding Seasons: Tools and Platforms To Help Explore Why Do I Have Seasons
Various educational resources are available to help people learn more about seasons, including books, websites, museums, and educational programs. These options help deepen the understanding of why do I have certain seasonal knowledge.
16.1. Books and Articles
Numerous books and articles explain the science behind seasons and explore the cultural and historical significance of seasonal celebrations.
16.2. Websites and Online Resources
Many websites offer educational resources about seasons, including interactive simulations, videos, and lesson plans.
16.3. Museums and Science Centers
Museums and science centers often have exhibits about seasons and climate, providing hands-on learning experiences for people of all ages.
17. Citizen Science and Seasonal Monitoring: Getting Involved to Understand Why Do I Have Seasons
Citizen science projects allow people to contribute to scientific research by collecting and analyzing data about seasonal phenomena. This allows individuals to directly contribute to understanding why do I have certain scientific findings about seasons.
17.1. Phenology Projects
Phenology is the study of the timing of seasonal events in plants and animals, such as leafing, flowering, and migration. Citizen scientists can participate in phenology projects by recording observations of these events.
17.2. Weather Observation Networks
Citizen scientists can also participate in weather observation networks by collecting and reporting data about temperature, precipitation, and other weather conditions.
17.3. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Citizen scientists can contribute to data analysis and interpretation by helping to identify trends and patterns in seasonal data.
18. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): How Seasons Impact Mental Health and Understanding Why Do I Have Seasons
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that is related to changes in seasons. Understanding SAD helps in grasping the wide-ranging impacts of why do I have seasonal changes.
18.1. SAD Symptoms
SAD symptoms can include fatigue, low energy, sadness, difficulty concentrating, and changes in appetite and sleep patterns.
18.2. Causes of SAD
SAD is thought to be caused by changes in brain chemistry due to reduced exposure to sunlight during the winter months.
18.3. Treatment Options
Treatment options for SAD include light therapy, medication, and psychotherapy.
19. Seasonal Allergies: Understanding Seasonal Allergies Related to Changing Seasons that Connects to The Understanding of Why Do I Have Seasons
Seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever, are allergic reactions that occur during specific times of the year, typically in the spring, summer, or fall. This helps connect the environmental science of why do I have seasons to personal health.
19.1. Common Allergens
Common allergens include pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds.
19.2. Allergy Symptoms
Allergy symptoms can include sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and congestion.
19.3. Management Strategies
Management strategies for seasonal allergies include avoiding allergens, taking antihistamines, and using nasal sprays.
20. Space Weather and Seasons: Exploring How Solar Activity Impacts Earth’s Seasons, Providing Another Perspective for Why Do I Have Seasons
Space weather refers to the conditions in space that can affect the Earth’s atmosphere and magnetosphere. Solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can influence seasonal weather patterns. This introduces the cosmic dimension of why do I have earthly seasons.
20.1. Solar Flares and CMEs
Solar flares are sudden bursts of energy from the Sun’s surface, while coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona.
20.2. Geomagnetic Storms
When solar flares and CMEs reach the Earth, they can cause geomagnetic storms, which can disrupt radio communications, damage satellites, and cause power outages.
20.3. Influence on Weather Patterns
Some studies suggest that solar activity can influence weather patterns on Earth, although the mechanisms are not fully understood.
21. Seasonal Eating: Connecting Food and Seasons for a Healthier Lifestyle That Gives a Dietary Angle to Why Do I Have Seasons
Seasonal eating involves consuming foods that are naturally available during specific times of the year. This encourages a holistic approach to why do I have seasonal considerations.
21.1. Benefits of Seasonal Eating
Benefits of seasonal eating include fresher and more flavorful produce, lower food costs, and reduced environmental impact.
21.2. Seasonal Produce Guide
A seasonal produce guide can help people identify which fruits and vegetables are in season in their region.
21.3. Recipes and Meal Planning
Recipes and meal planning tips can help people incorporate seasonal ingredients into their diet.
22. Seasonal Travel: Planning Trips Based on Seasons and Climate That Enhances the Exploration of Why Do I Have Seasons
Seasonal travel involves planning trips based on the seasons and climate in different regions of the world. This gives a practical and experiential aspect to understanding why do I have different seasonal opportunities.
22.1. Best Times to Visit Different Regions
The best time to visit different regions depends on the desired weather conditions and activities. For example, the best time to visit tropical regions is often during the dry season, while the best time to visit ski resorts is during the winter.
22.2. Packing Tips for Seasonal Travel
Packing tips for seasonal travel include bringing appropriate clothing and gear for the expected weather conditions.
22.3. Seasonal Travel Destinations
Popular seasonal travel destinations include ski resorts, beaches, national parks, and cultural festivals.
23. Seasonal Gardening: Adapting Gardening Practices to Seasonal Change That Encourages Practical Application to Why Do I Have Seasons
Seasonal gardening involves adapting gardening practices to the changing seasons. This gives a hands-on, practical approach to why do I have seasonal awareness.
23.1. Spring Gardening
Spring gardening tasks include planting seeds, transplanting seedlings, and preparing garden beds.
23.2. Summer Gardening
Summer gardening tasks include watering, weeding, and harvesting crops.
23.3. Fall Gardening
Fall gardening tasks include harvesting crops, planting cover crops, and preparing garden beds for winter.
23.4. Winter Gardening
Winter gardening tasks may include protecting plants from frost, planning for the next growing season, and starting seeds indoors.
24. Seasonal Home Maintenance: Preparing Homes for Changing Seasons Connecting the Question of Why Do I Have Seasons to Home Care
Seasonal home maintenance involves preparing homes for the changing seasons. This ties the understanding of why do I have seasons to tangible actions.
24.1. Spring Home Maintenance
Spring home maintenance tasks include cleaning gutters, inspecting roofs, and checking for leaks.
24.2. Summer Home Maintenance
Summer home maintenance tasks include checking air conditioners, sealing windows, and repairing decks.
24.3. Fall Home Maintenance
Fall home maintenance tasks include raking leaves, winterizing plumbing, and inspecting heating systems.
24.4. Winter Home Maintenance
Winter home maintenance tasks include shoveling snow, preventing ice dams, and maintaining heating systems.
25. Astronomy and Seasons: Observing The Sky in Different Seasons That Introduces Astronomical Perspective to Why Do I Have Seasons
Observing the night sky is a great way to connect with the seasons. Different constellations and celestial events are visible at different times of the year. This links the fundamental question of why do I have seasons to celestial observations.
25.1. Spring Constellations
Spring constellations include Leo, Virgo, and Ursa Major.
25.2. Summer Constellations
Summer constellations include Sagittarius, Scorpius, and Cygnus.
25.3. Fall Constellations
Fall constellations include Pegasus, Andromeda, and Pisces.
25.4. Winter Constellations
Winter constellations include Orion, Taurus, and Gemini.
 Earth's Tilt Causes Seasons
Earth's Tilt Causes Seasons
Understanding why do I have seasons is fundamental to understanding the world around us. From the Earth’s axial tilt to the effects of climate change, many factors influence the changing seasons. By exploring these factors, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the importance of adapting to seasonal changes.
Still curious about the intricate dance of our planet and its seasons? Do you have burning questions about how these cycles affect your daily life? Don’t let your curiosity fade! Visit WHY.EDU.VN today, your ultimate hub for in-depth answers and expert insights. Our team of specialists is ready to tackle your questions and provide the knowledge you seek. Explore the science of seasons with us. Your quest for knowledge begins at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101. Visit us at why.edu.vn for more insights.
FAQ About Earth’s Seasons
Here are some frequently asked questions about Earth’s seasons:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What causes the seasons? | The tilt of the Earth’s axis is the primary cause of the seasons. |
| Why are seasons different in each hemisphere? | Because the Earth’s tilt causes the Northern and Southern Hemispheres to receive different amounts of direct sunlight at different times of the year. |
| What are solstices and equinoxes? | Solstices mark the days with the longest and shortest periods of daylight, while equinoxes mark the days when day and night are of equal length. |
| How does latitude affect seasonal variation? | Regions near the equator experience little seasonal variation, while mid-latitude regions experience distinct seasons, and polar regions experience extreme variations. |
| Do ocean currents affect seasons? | Yes, ocean currents can moderate temperatures and influence precipitation patterns, affecting seasonal changes in coastal regions. |
| How does altitude affect seasons? | Altitude affects temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to distinct seasonal variations in mountainous regions. |
| What are El Niño and La Niña? | El Niño and La Niña are climate patterns in the Pacific Ocean that can significantly influence weather patterns and seasonal variations around the world. |
| How does climate change affect seasons? | Climate change is altering seasonal patterns, leading to earlier spring blooms, later autumn frosts, and changes in the timing and intensity of precipitation events. |
| What is Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)? | SAD is a type of depression related to changes in seasons, typically occurring during the winter months. |
| How can I adapt to seasonal changes? | Strategies for adapting to seasonal changes include adjusting agricultural practices, taking public health measures, and planning infrastructure improvements. |