Why Do I Get Nosebleeds frequently? Discover the common causes of epistaxis and effective treatment options, and find relief with expert guidance at WHY.EDU.VN. Learn about nasal saline sprays, humidifiers, and other remedies to manage nosebleeds, ensuring a healthier quality of life and prevent recurrent bleeding. Explore key factors such as Kiesselbach’s plexus, environmental triggers, and underlying health conditions, supported by expert insights and practical tips.
1. Understanding Nosebleeds: An Overview
Nosebleeds, medically termed epistaxis, are a common occurrence, affecting a significant portion of the population. While most nosebleeds are isolated incidents that resolve on their own, some individuals experience frequent episodes, impacting their daily lives. According to David A. Gudis, MD, associate professor of otolaryngology/head & neck surgery at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians & Surgeons, recurrent nosebleeds warrant medical attention to determine the underlying cause and prevent potential complications. These frequent episodes can be disruptive, hindering a normal and healthy quality of life, emphasizing the importance of effective management and treatment.
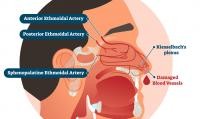
2. The Anatomy Behind Nosebleeds: Kiesselbach’s Plexus
Most nosebleeds originate from Kiesselbach’s plexus, an area in the front of the nasal septum where several arterial branches converge. This region is rich in blood vessels, which are essential for maintaining the health of the sinuses. However, the dense network of blood vessels also makes it susceptible to bleeding, contributing to frequent nosebleeds. The superficial location of these vessels means they are easily affected by minor trauma, dry air, or inflammation, making this area a common source of epistaxis.
3. Common Causes of Nosebleeds in Adults
In adults, turbulent airflow inside the nose, often due to a deviated nasal septum, can lead to nosebleeds. This airflow can cause trauma to the mucous membrane covering Kiesselbach’s plexus, resulting in recurrent bleeding. Cold, dry air is another significant trigger, as it dries out the nasal passages, making them more prone to cracking and bleeding. Additionally, certain medications, such as aspirin and anticoagulants, can impair blood clotting, increasing the likelihood of nosebleeds. Addressing these factors through proper humidification and medication management can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of nosebleeds.
4. Digital Trauma: The Culprit in Children’s Nosebleeds
For children, a common cause of nosebleeds is “digital trauma,” which refers to nose-picking. The Kiesselbach’s plexus is easily accessible to children’s fingers, making it vulnerable to injury. This frequent poking and prodding can traumatize the region, leading to recurrent nosebleeds. Educating children about the risks of nose-picking and encouraging alternative habits can help prevent these episodes. Parents and caregivers can also consider using saline sprays to keep the nasal passages moist, reducing the urge to pick the nose.
5. When to See an ENT Specialist for Nosebleeds
If nosebleeds become very frequent, troublesome, upsetting, or interfere with daily activities, it’s crucial to consult an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. An ENT specialist can conduct a thorough examination to rule out underlying conditions such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), a genetic disorder causing abnormal blood vessel formation. According to Gudis, HHT can cause severe nosebleeds, sometimes resulting in significant blood loss. Additionally, tumors, both benign and malignant, in the nose or sinuses can also contribute to frequent nosebleeds, necessitating prompt medical evaluation.
6. Recognizing Severe Nosebleeds: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
It’s essential to differentiate between minor and severe nosebleeds to determine when immediate medical attention is required. If a nosebleed soaks a few tissues or paper towels and stops on its own, it’s generally not considered severe. However, Gudis advises that if the nosebleed could fill a cup with blood or if it’s a continuous, unstoppable leak, urgent medical care is necessary. Such severe nosebleeds can lead to significant blood loss, potentially resulting in airway obstruction or life-threatening emergencies. Prompt intervention can prevent serious complications and ensure patient safety.
7. Effective Home Remedies for Managing Nosebleeds
For frequent nosebleeds without concerning symptoms, several home remedies can be effective. Topical moisturizing agents, such as nasal saline gel sprays or a small amount of petroleum jelly applied to the front of the nose, can protect the nasal lining and minimize bleeding. Humidifiers, especially in the bedroom or office, help prevent dry air from irritating the nasal passages. Maintaining a moist environment and protecting the nasal lining can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of nosebleeds.
8. Debunking Myths: Copper Pennies and Nosebleeds
One common home remedy involves placing a copper penny on the forehead or nose during a nosebleed. However, there’s no scientific evidence to support its effectiveness. While cold compresses can constrict blood vessels and potentially slow down bleeding, the primary benefit comes from the cold temperature rather than the copper itself. Relying on proven methods, such as direct pressure and nasal moisturization, is more likely to provide effective relief.
9. Silver Nitrate Cauterization: A Medical Solution for Persistent Nosebleeds
For more troublesome cases, silver nitrate cauterization, performed in a doctor’s office, can effectively stop nosebleeds. Silver nitrate causes sclerosis of blood vessels, reducing blood flow and minimizing the likelihood of future bleeding. The procedure is quick and simple, although it may cause temporary discomfort. According to Gudis, the stinging sensation usually lasts only five to ten minutes, with rare cases of prolonged pain manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers. This treatment doesn’t affect the sense of smell and is a reliable option for managing persistent epistaxis.
10. Understanding Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is a genetic condition that leads to the formation of abnormal blood vessels throughout the body. One of the most common and noticeable symptoms of HHT is frequent and severe nosebleeds. Unlike typical nosebleeds that can be easily managed, those associated with HHT often involve significant blood loss and can occur spontaneously.
Key Characteristics of HHT-Related Nosebleeds:
- Severity: Patients may lose a substantial amount of blood, even from simple activities.
- Frequency: Nosebleeds can occur regularly, sometimes multiple times a day.
- Spontaneity: Bleeding may start without any apparent cause or trigger.
Diagnosis and Management:
Diagnosing HHT involves a clinical evaluation, including a review of family history and physical examination. Genetic testing can also confirm the diagnosis. Management of HHT-related nosebleeds focuses on minimizing bleeding episodes and addressing the underlying vascular abnormalities.
Treatment Options Include:
- Topical Treatments: Saline sprays and ointments to keep the nasal passages moist.
- Cauterization: Using heat or chemicals to seal off bleeding vessels.
- Laser Therapy: Targeting and closing abnormal blood vessels with laser energy.
- Medications: Drugs that promote blood clotting or reduce blood vessel growth.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment:
Early detection and management of HHT are crucial to prevent complications and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Individuals with frequent, severe nosebleeds should seek evaluation by a healthcare professional to determine if HHT is a potential cause.
11. The Role of Medications and Supplements in Nosebleeds
Certain medications and supplements can increase the risk of nosebleeds. Anticoagulants like warfarin, antiplatelet drugs like aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can interfere with blood clotting, making it easier for nosebleeds to occur. Supplements like vitamin E, ginkgo biloba, and garlic can also have blood-thinning effects. If you experience frequent nosebleeds while taking these medications or supplements, consult your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments to minimize the risk of bleeding. It’s essential to balance the benefits of these medications with the potential risk of nosebleeds.
12. Environmental Factors Contributing to Nosebleeds
Environmental conditions play a significant role in triggering nosebleeds. Dry air, common during winter months or in arid climates, can dry out the nasal passages, leading to cracking and bleeding. Exposure to irritants like smoke, pollution, and chemical fumes can also inflame the nasal lining, increasing the risk of nosebleeds. Using a humidifier, avoiding irritants, and applying nasal saline sprays can help maintain nasal moisture and reduce the likelihood of nosebleeds. Understanding and managing these environmental factors can significantly improve nasal health.
13. Nasal Sprays and Their Impact on Nosebleeds
Nasal sprays, both medicated and saline, can influence the occurrence of nosebleeds. Decongestant nasal sprays, used to relieve nasal congestion, can dry out the nasal passages and cause irritation, leading to nosebleeds. It’s crucial to use these sprays sparingly and follow the recommended dosage. Saline nasal sprays, on the other hand, help moisturize the nasal passages and prevent dryness, reducing the risk of nosebleeds. Regular use of saline sprays can be particularly beneficial in dry environments or for individuals prone to nosebleeds. Choosing the right nasal spray and using it correctly is essential for maintaining nasal health.
14. Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Nosebleeds
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can help prevent nosebleeds. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water keeps the nasal passages moist. Avoiding nose-picking and vigorous nose-blowing reduces the risk of trauma to the nasal lining. Quitting smoking minimizes irritation and inflammation of the nasal passages. Using a humidifier, especially during dry seasons, maintains optimal nasal moisture. These simple adjustments can significantly decrease the frequency and severity of nosebleeds. Consistent adherence to these lifestyle changes can lead to long-term improvements in nasal health.
15. Dietary Considerations for Managing Nosebleeds
Diet plays a role in managing nosebleeds by supporting overall health and blood vessel integrity. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and berries, strengthen blood vessels and promote healing. Vitamin K, found in leafy green vegetables, is essential for blood clotting. Iron-rich foods, like lean meats and beans, help maintain healthy blood levels. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and spicy foods can reduce nasal irritation. A balanced diet that includes these nutrients supports nasal health and minimizes the risk of nosebleeds. Consulting a nutritionist or healthcare provider can provide personalized dietary recommendations.
16. Homeopathic Remedies for Nosebleeds: What the Research Says
Homeopathic remedies for nosebleeds are a topic of interest, but scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited. Some individuals report benefits from homeopathic treatments like Arnica, which is believed to reduce bleeding and inflammation. However, these claims are largely based on anecdotal evidence rather than rigorous scientific studies. It’s essential to approach homeopathic remedies with caution and consult a healthcare professional before using them as a primary treatment for nosebleeds. Mainstream medical treatments, such as saline sprays and cauterization, have a stronger evidence base and are generally recommended for managing nosebleeds.
17. Nosebleeds During Pregnancy: Causes and Management
Nosebleeds are more common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume. Elevated estrogen levels can cause the blood vessels in the nasal passages to dilate, making them more prone to bleeding. Increased blood volume puts additional pressure on these vessels. Simple home remedies, such as using a humidifier and applying saline nasal sprays, can often manage nosebleeds during pregnancy. If nosebleeds are frequent or severe, consult a healthcare provider to rule out underlying conditions and ensure proper management. Pregnancy-related nosebleeds are usually temporary and resolve after delivery.
18. The Connection Between Allergies and Nosebleeds
Allergies can contribute to nosebleeds by causing inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages. Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, leads to nasal congestion, sneezing, and itching, which can damage the delicate lining of the nose. Frequent nose-blowing and nose-picking, common responses to allergy symptoms, further increase the risk of nosebleeds. Managing allergies with antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and allergen avoidance can reduce nasal inflammation and prevent nosebleeds. Consulting an allergist can help identify triggers and develop an effective management plan.
19. Sinus Infections and Their Link to Nosebleeds
Sinus infections, or sinusitis, can also lead to nosebleeds due to inflammation and increased pressure in the nasal passages. The infection causes swelling and irritation of the sinus lining, making it more prone to bleeding. Frequent nose-blowing and nasal congestion associated with sinus infections can exacerbate the problem. Treating the sinus infection with antibiotics, decongestants, and nasal saline rinses can reduce inflammation and prevent nosebleeds. Seeking medical attention for persistent sinus infections is essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
20. Trauma and Injuries Causing Nosebleeds
Trauma and injuries to the nose are common causes of nosebleeds. A blow to the face, nasal fractures, and even vigorous nose-blowing can damage the blood vessels in the nasal passages, leading to bleeding. In cases of significant trauma, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention to rule out more serious injuries. Minor nosebleeds from trauma can usually be managed with direct pressure and ice packs. Protecting the nose during sports and other activities can prevent traumatic nosebleeds.
21. High Blood Pressure and Its Effect on Nosebleeds
High blood pressure, or hypertension, has long been thought to be a significant cause of nosebleeds. The prevailing theory was that elevated blood pressure could cause the delicate blood vessels in the nose to rupture more easily. However, recent studies have challenged this traditional view. While high blood pressure isn’t typically the direct cause of most nosebleeds, it can make them more severe and prolonged.
How High Blood Pressure Affects Nosebleeds:
- Prolonged Bleeding: High blood pressure can interfere with the body’s natural ability to stop bleeding, leading to nosebleeds that last longer and are more difficult to control.
- Increased Severity: Although it may not initiate a nosebleed, hypertension can exacerbate the bleeding once it starts, making it more profuse.
Managing High Blood Pressure and Nosebleeds:
- Regular Monitoring: Individuals with high blood pressure should monitor their blood pressure regularly and work with their healthcare provider to keep it within a healthy range.
- Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed blood pressure medications as directed is crucial for preventing complications, including severe nosebleeds.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly can help manage blood pressure.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you have high blood pressure and experience frequent or severe nosebleeds, seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare provider can assess your condition and recommend appropriate treatment strategies.
22. Less Common Causes of Nosebleeds
While the above causes are the most common, there are some less frequent reasons for nosebleeds that individuals should be aware of. These include:
- Tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors in the nasal passages can cause nosebleeds. If you experience persistent, unexplained nosebleeds, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like nasal congestion or facial pain, consult a healthcare provider.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Conditions such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease can impair the body’s ability to form blood clots, leading to frequent and prolonged nosebleeds.
- Structural Abnormalities: Deviations in the nasal septum or other structural issues in the nose can increase the risk of nosebleeds by causing turbulent airflow and irritation.
- Chemical Irritants: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those found in cleaning products or industrial settings, can irritate the nasal lining and cause bleeding.
- Foreign Objects: Particularly in children, inserting foreign objects into the nose can cause trauma and bleeding.
Importance of Thorough Evaluation:
If you experience frequent or severe nosebleeds, it’s essential to undergo a thorough medical evaluation to identify any underlying causes. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life.
23. Nosebleeds in the Elderly: Unique Considerations
Nosebleeds are more common in older adults due to several factors related to aging. The nasal passages tend to become drier and more fragile with age, making them more susceptible to bleeding. Additionally, many elderly individuals take medications like aspirin or anticoagulants, which increase the risk of nosebleeds.
Unique Considerations for Elderly Individuals:
- Medication Management: Review medications with a healthcare provider to assess the risk of bleeding and adjust dosages if necessary.
- Hydration: Encourage adequate fluid intake to prevent nasal dryness.
- Humidification: Use a humidifier in the bedroom to maintain optimal humidity levels.
- Gentle Nasal Care: Avoid vigorous nose-blowing and use saline nasal sprays to keep the nasal passages moist.
Importance of Medical Evaluation:
Frequent or severe nosebleeds in the elderly should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out underlying conditions such as high blood pressure or blood clotting disorders. Prompt management can prevent complications and improve the overall health of older adults.
24. First Aid for Nosebleeds: Step-by-Step Guide
Knowing how to properly manage a nosebleed can help prevent complications and provide relief. Here’s a step-by-step guide for first aid:
- Stay Calm: Panicking can elevate blood pressure and worsen the bleeding.
- Sit Upright and Lean Forward: This position helps prevent swallowing blood and reduces pressure in the nasal vessels.
- Pinch Your Nose: Use your thumb and index finger to firmly pinch the soft part of your nose, just below the bony bridge.
- Maintain Pressure: Hold the pressure continuously for 10-15 minutes. Avoid releasing the pressure to check if the bleeding has stopped, as this can disrupt clot formation.
- Apply Ice: Applying an ice pack to the bridge of your nose can help constrict blood vessels and slow down the bleeding.
- Swallow Any Blood: If blood accumulates in your mouth, spit it out to avoid nausea.
- Check for Continued Bleeding: After 10-15 minutes, release the pressure and check if the bleeding has stopped. If it continues, repeat the process for another 10-15 minutes.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- The nosebleed lasts longer than 20 minutes despite applying pressure.
- The bleeding is severe or profuse.
- You have difficulty breathing.
- The nosebleed is the result of a significant injury.
- You have other symptoms, such as dizziness or weakness.
25. Understanding Anterior vs. Posterior Nosebleeds
Nosebleeds are generally classified into two main types: anterior and posterior. Understanding the differences between these types can help in managing and seeking appropriate medical care.
Anterior Nosebleeds:
- Location: These are the most common type and occur in the front part of the nose, typically from Kiesselbach’s plexus.
- Severity: Usually less severe and easier to manage.
- Cause: Often caused by dry air, nose-picking, or minor trauma.
- Management: Can usually be stopped with simple first aid measures, such as applying pressure to the nose.
Posterior Nosebleeds:
- Location: These occur deeper in the nose, typically in the back part of the nasal cavity.
- Severity: More severe and often require medical intervention.
- Cause: Often associated with high blood pressure, blood clotting disorders, or structural abnormalities.
- Management: Typically require medical attention, such as packing the nose or cauterization.
Key Differences in Management:
Anterior nosebleeds can often be managed at home with simple first aid measures. However, posterior nosebleeds usually require medical intervention due to their severity and location.
26. Advanced Medical Treatments for Severe Nosebleeds
When conservative treatments and first aid measures are insufficient, advanced medical treatments may be necessary to manage severe or recurrent nosebleeds. These treatments include:
- Nasal Packing: This involves inserting gauze or inflatable sponges into the nasal cavity to apply pressure and stop the bleeding.
- Cauterization: Using heat (electrocautery) or chemicals (silver nitrate) to seal off bleeding vessels.
- Endoscopic Procedures: Using an endoscope to visualize and treat bleeding vessels in the nasal cavity.
- Ligation: Surgically tying off the blood vessels that supply the bleeding area.
- Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure to block the blood vessels that feed the bleeding site.
Choosing the Right Treatment:
The choice of treatment depends on the severity and cause of the nosebleed, as well as the patient’s overall health. A healthcare provider can assess the condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment strategy.
27. Nosebleeds and Air Quality: What You Need to Know
Air quality plays a significant role in nasal health and the occurrence of nosebleeds. Poor air quality, whether due to pollution, smoke, or dry conditions, can irritate and dry out the nasal passages, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Impact of Air Quality:
- Pollution: Exposure to pollutants can inflame the nasal lining and make it more prone to bleeding.
- Smoke: Smoke, whether from cigarettes or environmental sources, can irritate and dry out the nasal passages.
- Dry Air: Low humidity levels, common during winter months or in arid climates, can cause the nasal passages to crack and bleed.
Protecting Your Nasal Health:
- Use a Humidifier: Maintain optimal humidity levels in your home to prevent nasal dryness.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimize exposure to smoke, pollution, and chemical fumes.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep the nasal passages moist.
- Use Saline Nasal Sprays: Regular use of saline sprays can help moisturize and protect the nasal lining.
Air Quality and Public Health:
Public health initiatives aimed at improving air quality can have a positive impact on nasal health and reduce the occurrence of nosebleeds.
28. Genetic Factors Influencing Nosebleeds
Genetic factors can play a significant role in predisposing individuals to nosebleeds. Certain genetic conditions, such as Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), directly affect blood vessel formation and increase the risk of frequent and severe nosebleeds.
Genetic Predisposition:
- HHT: This genetic disorder causes abnormal blood vessel formation, leading to frequent nosebleeds and other vascular abnormalities.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Genetic conditions that impair blood clotting can also increase the risk of nosebleeds.
- Structural Abnormalities: Inherited structural issues in the nose, such as a deviated septum, can contribute to nosebleeds.
Family History:
Individuals with a family history of frequent nosebleeds or related conditions may be at higher risk. Genetic testing can help identify specific genetic factors that may be contributing to the problem.
Genetic Counseling:
Genetic counseling can provide valuable information and support for individuals with a family history of nosebleeds or genetic conditions that increase the risk.
29. Complementary Therapies for Nosebleed Prevention
In addition to conventional medical treatments, some individuals explore complementary therapies for preventing nosebleeds. These therapies include:
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, such as yarrow and nettle, are believed to have blood-clotting properties that may help prevent nosebleeds. However, scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited.
- Acupuncture: Some individuals report benefits from acupuncture in reducing the frequency of nosebleeds. Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate healing.
- Yoga and Meditation: Stress reduction techniques, such as yoga and meditation, may help prevent nosebleeds by lowering blood pressure and reducing nasal congestion.
Important Considerations:
It’s essential to approach complementary therapies with caution and consult a healthcare provider before using them as a primary treatment for nosebleeds. These therapies may not be appropriate for everyone and may interact with other medications or treatments.
30. Expert Q&A: Common Questions About Nosebleeds Answered
To provide further clarity, here are answers to some frequently asked questions about nosebleeds:
Q: Is it normal to get nosebleeds frequently?
A: Occasional nosebleeds are common, but frequent nosebleeds should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Q: What should I do if my nosebleed won’t stop?
A: Apply continuous pressure to your nose for 10-15 minutes. If the bleeding continues, seek medical attention.
Q: Can certain foods cause nosebleeds?
A: Spicy foods and alcohol may irritate the nasal passages and increase the risk of nosebleeds in some individuals.
Q: Are nosebleeds more common in certain age groups?
A: Nosebleeds are common in children and older adults due to various factors related to age.
Q: Can I use a nasal spray to stop a nosebleed?
A: Decongestant nasal sprays can help constrict blood vessels and slow down the bleeding, but they should be used sparingly.
Q: Should I see a doctor for a child’s nosebleed?
A: If a child has frequent or severe nosebleeds, consult a pediatrician or ENT specialist.
Q: Can nosebleeds be a sign of a serious health problem?
A: In some cases, nosebleeds can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as high blood pressure or a blood clotting disorder.
Q: How can I prevent nosebleeds during the winter?
A: Use a humidifier, stay hydrated, and apply saline nasal sprays to prevent nasal dryness.
Q: Can allergies cause nosebleeds?
A: Yes, allergies can cause inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages, increasing the risk of nosebleeds.
Q: What is the best way to moisturize my nasal passages?
A: Use saline nasal sprays or apply a small amount of petroleum jelly to the front of your nose.
FAQ: Addressing Your Concerns About Nosebleeds
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the most common cause of nosebleeds? | Dry air is a frequent culprit, causing the nasal passages to become brittle and crack. |
| Are nosebleeds more common in winter? | Yes, the cold, dry air of winter can significantly increase the incidence of nosebleeds. |
| Can allergies lead to nosebleeds? | Allergies can inflame and irritate the nasal lining, making it more susceptible to bleeding. |
| Is high blood pressure a common cause? | While not always the direct cause, high blood pressure can prolong and worsen nosebleeds. |
| What should I do immediately during a nosebleed? | Sit upright, lean forward, and pinch your nose firmly for 10-15 minutes to apply direct pressure. |
| When should I seek medical attention? | If the nosebleed lasts longer than 20 minutes despite applying pressure, or if it’s severe, seek medical help. |
| Can medications cause nosebleeds? | Yes, blood-thinning medications like aspirin and warfarin can increase the risk. |
| Are nosebleeds in children common? | Yes, children frequently experience nosebleeds, often due to nose-picking or minor injuries. |
| What role does humidity play? | Low humidity dries out the nasal passages, increasing the risk of nosebleeds. Using a humidifier can help. |
| Can nosebleeds indicate a serious condition? | Although most nosebleeds are harmless, recurrent or severe cases may signal an underlying health issue. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to rule out any potential concerns. Remember, WHY.EDU.VN is here to provide reliable information. |

Navigating the world of nosebleeds can be overwhelming, but with the right information, you can manage and prevent these occurrences effectively. At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding accurate and trustworthy answers to your health questions. Our platform is dedicated to providing you with expert insights and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
Do you have more questions about nosebleeds or other health concerns? Don’t hesitate to reach out to our team of experts at WHY.EDU.VN. We’re here to provide you with the answers you need. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Visit our website, why.edu.vn, to explore a wealth of knowledge and connect with our community. Let us help you find the answers you’re looking for.