Are you experiencing immediate bowel movements after consuming eggs and wondering “Why Do Eggs Make Me Poop Instantly”? This comprehensive guide from WHY.EDU.VN explores the potential reasons behind this phenomenon, ranging from common food sensitivities to more complex digestive issues. We aim to provide clear, actionable information to help you understand and manage your body’s reaction to eggs, offering solutions and insights for a healthier digestive system. Delve into the science behind food intolerances and discover how to optimize your gut health with our expert advice and practical tips, including dietary adjustments and professional guidance.
1. Understanding the Immediate Digestive Response to Eggs
The question, “Why do eggs make me poop instantly?”, suggests a rapid digestive process, and it’s essential to understand why this happens. Eggs, while nutritious, can trigger immediate bowel movements in some individuals due to several reasons. These include food sensitivities, intolerances, or even specific components within eggs that stimulate the gastrointestinal tract. Understanding these underlying causes is the first step toward finding relief and managing your digestive health effectively.
1.1. Defining the Term: “Instant Poop” After Eating Eggs
“Instant poop” refers to experiencing a bowel movement shortly after consuming eggs, usually within minutes to a couple of hours. This rapid response suggests that eggs are acting as a trigger for your digestive system, prompting it to eliminate waste quickly. While occasional rapid bowel movements might not be a cause for concern, consistent occurrences after eating eggs warrant further investigation.
1.2. Initial Considerations: Is It Normal?
While individual digestive systems vary, experiencing “instant poop” consistently after consuming eggs is not typically considered normal. A healthy digestive process usually involves a longer transit time, allowing for proper nutrient absorption. If eggs are consistently causing immediate bowel movements, it signals a potential issue that requires attention. Understanding the causes behind this response is crucial for maintaining digestive health.
2. Common Causes: Why Eggs Might Trigger Immediate Bowel Movements
Several factors can contribute to eggs causing immediate bowel movements. These include egg intolerance or allergy, high fat content in eggs, potential for salmonella contamination, and individual digestive sensitivities. Let’s explore each of these possibilities in detail.
2.1. Egg Intolerance vs. Egg Allergy: Understanding the Difference
Egg intolerance and egg allergy are distinct conditions, though both can cause digestive upset. An egg allergy involves the immune system reacting to egg proteins, triggering symptoms like hives, swelling, or even anaphylaxis. Egg intolerance, on the other hand, does not involve the immune system. Instead, it’s a digestive issue where the body has difficulty breaking down certain components in eggs, leading to symptoms like gas, bloating, and diarrhea.
| Feature | Egg Allergy | Egg Intolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Immune System | Involves immune system response | Does not involve immune system |
| Symptoms | Hives, swelling, anaphylaxis | Gas, bloating, diarrhea |
| Onset of Symptoms | Rapid, often immediate | Slower, may take hours to develop |
| Severity | Can be life-threatening | Generally not life-threatening |
| Diagnostic Tests | Skin prick test, blood test (IgE antibodies) | Elimination diet, food sensitivity testing |
2.2. The Role of Fat Content in Eggs
Eggs are relatively high in fat, particularly in the yolk. Fat can stimulate the gastrocolic reflex, a physiological response that increases colon motility and triggers the urge to defecate. For individuals with sensitive digestive systems, this effect can be more pronounced, leading to immediate bowel movements after consuming eggs.
2.3. Could It Be Salmonella Contamination?
Although less common, salmonella contamination in eggs can cause rapid and severe gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. Salmonella infection typically occurs from consuming raw or undercooked eggs. If you suspect salmonella contamination, seek medical attention immediately. Proper food handling and cooking practices can minimize the risk of salmonella.
2.4. Individual Sensitivities and Digestive System Differences
Each person’s digestive system is unique, and sensitivities to certain foods vary widely. Some individuals may have inherently more sensitive digestive tracts that react strongly to eggs, regardless of allergies or intolerances. Factors like gut microbiome composition, enzyme production, and overall digestive health play a role in how your body processes eggs.
3. Exploring Egg Allergy in Detail
Egg allergy is a common food allergy, particularly among children, but it can persist into adulthood. Understanding the types of egg proteins that cause allergic reactions, the symptoms of an egg allergy, and how to get a proper diagnosis is crucial for managing this condition.
3.1. Types of Egg Proteins That Cause Allergic Reactions
Egg allergies are typically triggered by proteins found in egg whites, though some individuals may also be allergic to egg yolk proteins. The primary allergenic proteins in egg whites include ovalbumin, ovotransferrin, ovomucoid, and lysozyme. These proteins can cause an immune response in sensitive individuals, leading to allergic reactions.
3.2. Common Symptoms of an Egg Allergy
Symptoms of an egg allergy can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Skin reactions (hives, eczema, rash)
- Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain)
- Respiratory symptoms (wheezing, coughing, difficulty breathing)
- Cardiovascular symptoms (dizziness, lightheadedness)
- Anaphylaxis (a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction)
If you experience any of these symptoms after eating eggs, consult an allergist for testing and diagnosis.
3.3. Diagnosing an Egg Allergy: Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing an egg allergy typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Common tests include:
- Skin Prick Test: A small amount of egg protein is placed on the skin, and the area is pricked to see if a reaction occurs.
- Blood Test (IgE Antibody Test): Measures the levels of specific IgE antibodies in the blood that are produced in response to egg proteins.
- Oral Food Challenge: Under medical supervision, small amounts of egg are ingested to monitor for any allergic reactions.
These tests help determine whether an egg allergy is present and guide appropriate management strategies.
4. Investigating Egg Intolerance
Egg intolerance, unlike an allergy, does not involve the immune system. Instead, it’s a digestive issue where the body struggles to break down certain components in eggs. Understanding the specific compounds causing intolerance, the associated symptoms, and how to diagnose it is essential for managing this condition effectively.
4.1. Specific Compounds in Eggs That May Cause Intolerance
Certain compounds in eggs, such as proteins and fats, can be difficult for some individuals to digest, leading to intolerance. Additionally, sulfur compounds found in eggs may contribute to digestive issues in sensitive individuals. These compounds can cause inflammation and irritation in the digestive tract, resulting in symptoms like gas, bloating, and diarrhea.
4.2. Common Symptoms of Egg Intolerance
Symptoms of egg intolerance typically involve gastrointestinal distress and may include:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Nausea
- Heartburn
These symptoms can vary in severity and may occur hours after consuming eggs, making it challenging to identify the trigger without proper testing and observation.
4.3. Diagnosing Egg Intolerance: Methods and Approaches
Diagnosing egg intolerance can be more challenging than diagnosing an egg allergy since there are no specific tests for intolerance. Common methods include:
- Elimination Diet: Removing eggs from your diet for a period of time and then reintroducing them to see if symptoms return.
- Food Sensitivity Testing: Various tests claim to identify food sensitivities, but their accuracy and reliability are debated. Consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing such tests.
- Symptom Tracking: Keeping a detailed food diary to track your symptoms and identify patterns related to egg consumption.
By carefully monitoring your body’s response to eggs and consulting with a healthcare provider, you can determine if you have an egg intolerance and develop a suitable management plan.
5. Other Potential Culprits: Ruling Out Other Causes
Sometimes, the reason why eggs make you poop instantly may not be directly related to the eggs themselves, but rather to other factors influencing your digestive system. Exploring these potential culprits is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
5.1. Dietary Factors: High-Fat Meals and Fiber Intake
High-fat meals, including those containing eggs, can stimulate the gastrocolic reflex, leading to increased colon motility and bowel movements. Similarly, diets lacking in fiber can contribute to irregular bowel movements. Fiber helps regulate digestion and promotes healthy bowel function. Ensure you have a balanced diet with sufficient fiber intake.
5.2. Underlying Digestive Conditions: IBS, IBD, and More
Underlying digestive conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) can increase sensitivity to certain foods, including eggs. These conditions can cause chronic inflammation and altered gut function, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and urgency. If you suspect an underlying digestive condition, consult a gastroenterologist for evaluation and treatment.
5.3. Medications and Supplements: Impact on Digestion
Certain medications and supplements can impact digestion and bowel movements. Antibiotics, for example, can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to diarrhea. Similarly, some supplements may have a laxative effect. Review your current medications and supplements with your healthcare provider to determine if they could be contributing to your symptoms.
6. Strategies for Managing Immediate Bowel Movements After Eating Eggs
Managing immediate bowel movements after eating eggs involves a combination of dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medical interventions. By implementing these strategies, you can improve your digestive health and reduce the frequency and severity of your symptoms.
6.1. Dietary Adjustments: Eliminating or Reducing Egg Consumption
The most straightforward approach to managing symptoms triggered by eggs is to eliminate or reduce their consumption. If you have an egg allergy, strict avoidance is necessary. For those with egg intolerance, reducing portion sizes or limiting egg consumption to certain meals may be sufficient. Monitor your symptoms carefully to determine the level of egg consumption that you can tolerate.
6.2. Alternative Protein Sources: Ensuring Nutritional Needs Are Met
When reducing or eliminating eggs from your diet, it’s crucial to find alternative protein sources to ensure you meet your nutritional needs. Excellent alternatives include:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, fish)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Nuts and seeds
- Dairy products (if tolerated)
Consult with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to create a balanced meal plan that meets your protein requirements.
6.3. Lifestyle Changes: Hydration, Exercise, and Stress Management
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact digestive health. Staying well-hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can all improve bowel function and reduce symptoms. Dehydration can lead to constipation, while exercise promotes gut motility. Stress can exacerbate digestive issues, so practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can be beneficial.
7. Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Doctor
While dietary and lifestyle changes can often manage immediate bowel movements after eating eggs, certain situations warrant seeking professional medical advice. Understanding when to consult a doctor is essential for addressing underlying issues and preventing complications.
7.1. Recognizing Warning Signs: Severe Symptoms and Red Flags
Pay attention to severe symptoms or red flags that may indicate a more serious underlying condition. These include:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent diarrhea or constipation
- Symptoms of anaphylaxis (difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, dizziness)
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
7.2. Consulting an Allergist: Testing and Diagnosis
If you suspect an egg allergy, consult an allergist for testing and diagnosis. An allergist can perform skin prick tests, blood tests, or oral food challenges to determine if you have an egg allergy and provide guidance on managing the condition.
7.3. Gastroenterologist Referral: Addressing Underlying Digestive Issues
If you suspect an underlying digestive condition like IBS or IBD, your primary care physician may refer you to a gastroenterologist. A gastroenterologist can perform diagnostic tests like colonoscopies or endoscopies to evaluate your digestive tract and recommend appropriate treatment.
8. Debunking Myths and Misconceptions About Eggs and Digestion
Many myths and misconceptions surround eggs and digestion. Separating fact from fiction is crucial for understanding how eggs affect your body and making informed decisions about your diet.
8.1. Common Myths About Egg Allergies and Intolerances
- Myth: Egg allergies are always lifelong.
- Fact: Many children outgrow egg allergies by adolescence.
- Myth: Egg intolerance is the same as lactose intolerance.
- Fact: Egg intolerance involves difficulty digesting egg proteins, while lactose intolerance involves difficulty digesting lactose, a sugar found in dairy products.
- Myth: You can build up a tolerance to eggs by gradually eating more of them.
- Fact: This is not recommended, especially if you have an egg allergy, as it can lead to severe allergic reactions.
8.2. The Truth About Egg Substitutes and Their Digestive Impact
Egg substitutes can be a useful alternative for those with egg allergies or intolerances, but it’s essential to understand their digestive impact. Some egg substitutes may contain ingredients that can cause digestive issues in sensitive individuals. Read labels carefully and choose substitutes that are well-tolerated.
8.3. Eggs and Cholesterol: Separating Fact from Fiction
For years, eggs have been associated with high cholesterol levels, leading some to believe they are bad for digestion. However, current research indicates that dietary cholesterol has less impact on blood cholesterol levels than previously thought. While eggs do contain cholesterol, they are also a good source of protein and essential nutrients. Moderation is key, and individuals with specific health conditions should consult their healthcare provider for personalized advice.
9. Latest Research and Developments in Understanding Egg Allergies and Intolerances
The understanding of egg allergies and intolerances is constantly evolving. Keeping up with the latest research and developments can help you stay informed and make the best decisions for your health.
9.1. Emerging Therapies for Egg Allergies: Oral Immunotherapy and More
Emerging therapies for egg allergies, such as oral immunotherapy (OIT), show promise in desensitizing individuals to egg proteins. OIT involves gradually increasing the dose of egg protein consumed over time to build tolerance. While OIT can be effective, it also carries risks and should be performed under the supervision of an allergist.
9.2. The Role of Gut Microbiome in Food Sensitivities
The gut microbiome plays a significant role in food sensitivities and intolerances. Imbalances in gut bacteria can contribute to inflammation and impaired digestion, making individuals more susceptible to food sensitivities. Research is ongoing to explore how modulating the gut microbiome through diet, probiotics, or fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) can improve food tolerance.
9.3. Advances in Diagnostic Testing for Food Intolerances
Advances in diagnostic testing for food intolerances are continuously being developed. While many tests on the market lack scientific validation, researchers are working on more accurate and reliable methods to identify food sensitivities. These tests may involve analyzing biomarkers in the blood or stool to assess gut function and immune responses to specific foods.
10. Practical Tips for Cooking and Baking Without Eggs
For individuals with egg allergies or intolerances, cooking and baking without eggs can be challenging but entirely possible. Numerous substitutes and techniques can help you create delicious and nutritious meals without eggs.
10.1. Egg Substitutes for Baking: Applesauce, Flaxseed, and More
Several substitutes can replace eggs in baking recipes:
- Applesauce: Adds moisture and sweetness. Use ¼ cup of unsweetened applesauce per egg.
- Flaxseed Meal: Mix 1 tablespoon of flaxseed meal with 3 tablespoons of water and let it sit for 5 minutes to create a binding agent.
- Mashed Banana: Provides moisture and sweetness. Use ½ mashed banana per egg.
- Commercial Egg Replacers: Available in powder form and can be used according to package instructions.
10.2. Egg-Free Recipes: Meal Ideas and Inspiration
Explore egg-free recipes for meal ideas and inspiration. Many dishes can be easily adapted to exclude eggs without sacrificing flavor or texture. Examples include:
- Pancakes made with applesauce or mashed banana
- Casseroles bound with breadcrumbs or cheese
- Cakes and cookies made with flaxseed meal or commercial egg replacers
10.3. Reading Labels: Identifying Hidden Eggs in Processed Foods
Reading labels carefully is crucial for avoiding eggs in processed foods. Eggs can be hidden under various names, including:
- Albumin
- Globulin
- Lysozyme
- Ovalbumin
- Ovovitellin
Be vigilant and choose products that are clearly labeled as egg-free.
11. Navigating Social Situations and Eating Out With Egg Allergies or Intolerances
Navigating social situations and eating out with egg allergies or intolerances requires careful planning and communication. By being proactive and informed, you can enjoy meals with friends and family without compromising your health.
11.1. Communicating Your Dietary Needs: Tips for Restaurants and Gatherings
When eating out, inform your server about your egg allergy or intolerance and ask about the ingredients in each dish. Be specific about hidden sources of eggs, such as sauces or dressings. At social gatherings, offer to bring a dish that you know is safe for you to eat and share with others.
11.2. Planning Ahead: Researching Menus and Preparing Safe Snacks
Before dining out, research the restaurant’s menu online to identify egg-free options. Call ahead to confirm that the restaurant can accommodate your dietary needs. When attending social events, bring safe snacks to ensure you have something to eat if egg-free options are limited.
11.3. Advocating for Yourself: Ensuring Your Needs Are Met
Advocate for yourself and ensure that your dietary needs are met. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or request modifications to dishes to avoid eggs. If you feel uncomfortable or unsure about the safety of a meal, it’s best to err on the side of caution and choose an alternative.
12. Addressing Psychological and Emotional Impact of Food Sensitivities
Food sensitivities, including egg allergies and intolerances, can have a significant psychological and emotional impact. Dealing with dietary restrictions, managing symptoms, and navigating social situations can be stressful and isolating.
12.1. The Stress and Anxiety of Managing Dietary Restrictions
Managing dietary restrictions can be stressful and anxiety-provoking. Constantly worrying about food choices, reading labels, and communicating your needs can take a toll on your mental well-being. Practicing stress management techniques and seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can help alleviate these feelings.
12.2. Coping Strategies: Mindfulness, Support Groups, and Therapy
Coping strategies can help you manage the psychological and emotional impact of food sensitivities:
- Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness can help you stay present and reduce anxiety related to food choices.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and validation. Sharing experiences and tips with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly helpful.
- Therapy: Working with a therapist can help you develop coping mechanisms and address underlying emotional issues related to food sensitivities.
12.3. Building a Positive Relationship With Food: Focus on What You Can Eat
Focus on building a positive relationship with food by exploring new recipes and enjoying the foods you can eat. Emphasize the abundance of nutritious and delicious egg-free options available and celebrate the joy of cooking and eating.
13. Expert Opinions: Insights From Doctors and Nutritionists
To provide a comprehensive understanding of why eggs might make you poop instantly, let’s consider insights from medical professionals and nutritionists.
13.1. Doctor’s Perspective: Diagnosing and Treating Digestive Issues Related to Eggs
Doctors emphasize the importance of accurate diagnosis through appropriate testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests for allergies. They also highlight the role of a detailed medical history and symptom tracking to identify intolerances. Treatment typically involves dietary modifications, symptom management, and addressing any underlying digestive conditions.
13.2. Nutritionist’s Advice: Meal Planning and Nutritional Balance Without Eggs
Nutritionists recommend focusing on balanced meal plans that provide adequate protein and essential nutrients without relying on eggs. They advise incorporating a variety of protein sources, such as lean meats, legumes, nuts, and seeds, and ensuring sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals through a diverse diet.
13.3. Combining Medical and Nutritional Approaches for Optimal Digestive Health
Combining medical and nutritional approaches is essential for optimal digestive health. Medical professionals can diagnose and treat underlying conditions, while nutritionists can provide guidance on dietary modifications and nutritional balance. Working collaboratively can help individuals manage symptoms, improve digestive function, and enhance their overall well-being.
14. Looking Ahead: Future Research and Potential Solutions
The field of food allergies and intolerances is continually evolving, with ongoing research exploring new diagnostic methods, treatments, and management strategies.
14.1. Promising Areas of Research: Novel Therapies and Diagnostic Tools
Promising areas of research include novel therapies for food allergies, such as epicutaneous immunotherapy (EPIT) and modified food proteins. Researchers are also developing more accurate and reliable diagnostic tools for food intolerances, which may involve analyzing biomarkers in the gut or assessing immune responses to specific foods.
14.2. Potential Solutions for Improved Egg Tolerance: Probiotics and Enzyme Supplements
Potential solutions for improving egg tolerance may involve the use of probiotics and enzyme supplements. Probiotics can help balance the gut microbiome and improve digestive function, while enzyme supplements can aid in the breakdown of egg proteins and reduce symptoms of intolerance.
14.3. The Future of Food Sensitivity Management: Personalized Approaches and Technological Advances
The future of food sensitivity management lies in personalized approaches and technological advances. By tailoring dietary recommendations and treatments to individual needs and utilizing innovative technologies, healthcare professionals can help individuals manage their symptoms, improve their digestive health, and enhance their quality of life.
15. WHY.EDU.VN: Your Resource for Understanding and Managing Food Sensitivities
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of living with food sensitivities and are committed to providing you with reliable, evidence-based information to help you manage your health. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to navigate the complexities of food sensitivities and improve your overall well-being.
15.1. Comprehensive Articles and Resources on Food Allergies and Intolerances
WHY.EDU.VN offers a wealth of comprehensive articles and resources on food allergies and intolerances. Whether you’re looking for information on specific conditions, dietary management strategies, or coping tips, you’ll find valuable insights and practical advice on our website.
15.2. Expert Q&A: Get Your Questions Answered by Professionals
Have questions about food sensitivities that you can’t find answers to? Our expert Q&A section allows you to submit your questions to healthcare professionals and receive personalized guidance. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of food sensitivities and make informed decisions about your health.
15.3. Community Forum: Connect With Others and Share Your Experiences
Connect with others who understand what you’re going through in our community forum. Share your experiences, ask questions, and find support from fellow individuals living with food sensitivities. Together, we can create a supportive and empowering community.
In conclusion, experiencing immediate bowel movements after eating eggs can be attributed to several factors, including egg allergies, intolerances, high fat content, or underlying digestive conditions. By understanding these potential causes and implementing appropriate management strategies, you can improve your digestive health and enhance your quality of life. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About Eggs and Digestion
Here are some frequently asked questions about eggs and digestion to help you better understand the topic.
-
Why do eggs sometimes give me diarrhea?
Eggs can cause diarrhea due to intolerance, allergy, or high fat content stimulating the digestive system. -
Can eggs trigger IBS symptoms?
Yes, eggs can trigger IBS symptoms in sensitive individuals due to their fat content and potential to cause inflammation. -
Are egg yolks harder to digest than egg whites?
Egg yolks are higher in fat, which can make them more challenging to digest for some individuals compared to egg whites. -
How can I tell if I have an egg intolerance or an egg allergy?
An allergist can diagnose an egg allergy through skin prick tests or blood tests. Egg intolerance is typically identified through an elimination diet and symptom tracking. -
What are some egg-free breakfast options?
Egg-free breakfast options include oatmeal, yogurt, smoothies, toast with avocado, and breakfast burritos with beans and vegetables. -
Can I eat eggs if they are cooked in baked goods?
Some individuals with egg allergies or intolerances may tolerate eggs in baked goods due to the altered protein structure from cooking, but it’s best to consult with an allergist or healthcare provider. -
Are there any medications that can help with egg intolerance symptoms?
Over-the-counter medications like antacids or anti-diarrheals can help manage symptoms, but they do not address the underlying intolerance. -
How long does it take for egg allergy symptoms to appear?
Egg allergy symptoms typically appear within minutes to a few hours after consuming eggs. -
Can stress worsen my reaction to eggs?
Yes, stress can worsen digestive symptoms and increase sensitivity to certain foods, including eggs. -
What should I do if I accidentally eat eggs and have a reaction?
If you experience mild symptoms, take an antihistamine. For severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, use an epinephrine auto-injector and seek immediate medical attention.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into why eggs might make you poop instantly and how to manage this condition effectively. Remember, your digestive health is essential, and taking proactive steps to understand and address your body’s responses to food is crucial for your overall well-being.
If you have more questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHY.EDU.VN. We are here to support you on your journey to better health.
WHY.EDU.VN – Your Trusted Source for Health and Wellness Information
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: why.edu.vn
This image shows a close-up of a fried egg, highlighting the yolk and egg white, representing the food that is causing the digestive issues being discussed.
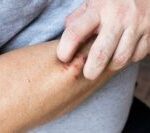
This image illustrates various allergic symptoms such as skin rash, swelling, and hives, which are important to recognize in the context of understanding egg allergies.
This diagram shows common symptoms of food intolerance, including bloating, gas, and abdominal pain, providing a visual guide to these often misunderstood reactions.