Navigating the complexities of international conflicts can be challenging, but at WHY.EDU.VN, we strive to provide clear and comprehensive answers. The question “Why Did The Ukraine War Start?” is multifaceted, involving historical, political, and strategic factors. This article delves into these reasons, providing insights and context. Stay informed with detailed analysis and expert perspectives on WHY.EDU.VN, where understanding complex issues is made easy. Explore the depths of geopolitical strategy and regional conflict.
1. Introduction: Understanding the Genesis of the Ukraine War
The question “Why did the Ukraine war start?” requires an examination of multifaceted historical, political, and strategic factors. The conflict’s roots are deeply embedded in the complex relationship between Russia and Ukraine, the geopolitical ambitions of various actors, and the internal dynamics of Ukraine itself. The ongoing conflict is more than just a clash of arms; it represents a struggle over identity, influence, and security architecture in Europe. By understanding the core reasons behind the war, we can better grasp its implications and potential pathways to resolution. WHY.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing clarity and context on this critical issue, helping you navigate the complexities of the conflict and its global repercussions with insight into international relations and political disputes.
2. Historical Context: Ukraine and Russia’s Intertwined Past
The historical ties between Ukraine and Russia are complex and deeply rooted, playing a crucial role in understanding the origins of the conflict.
2.1. Shared Heritage and Diverging Paths
Ukraine and Russia share a history dating back to the medieval state of Kyivan Rus’, which existed from the 9th to the 13th centuries. This shared heritage is often cited by Russia as a basis for its claims over Ukraine. However, over centuries, the two regions evolved along separate paths, developing distinct languages, cultures, and identities.
2.2. Soviet Era and Independence
From 1922 to 1991, Ukraine was part of the Soviet Union. While this period saw industrialization and modernization, it also brought immense suffering, including the Holodomor, a man-made famine in the 1930s that killed millions of Ukrainians. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to Ukraine declaring its independence, a move supported by an overwhelming majority of Ukrainians in a referendum. This independence marked a turning point, but Russia never fully accepted Ukraine’s sovereignty.
2.3. Key Historical Events
Understanding the timeline of key events helps contextualize the current conflict.
| Event | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Formation of Kyivan Rus’ | 9th-13th Centuries | Shared historical origin of both Ukraine and Russia. |
| Holodomor | 1932-1933 | Man-made famine in Ukraine under Soviet rule, resulting in millions of deaths. |
| Ukrainian Independence | 1991 | Ukraine declares independence from the Soviet Union following a referendum. |
| Orange Revolution | 2004 | Pro-democracy protests in response to a disputed presidential election. |
| Euromaidan Revolution | 2014 | Protests against President Yanukovych’s decision to reject an EU association agreement, leading to his ouster. |
| Annexation of Crimea | 2014 | Russia annexes Crimea following a pro-Russian uprising. |
| War in Donbas | 2014-2022 | Conflict between Ukrainian forces and Russian-backed separatists in eastern Ukraine. |
| Full-Scale Invasion of Ukraine | 2022 | Russia launches a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, marking a significant escalation of the conflict. |

3. Political Motivations: Putin’s Vision and Geopolitical Ambitions
Vladimir Putin’s political motivations are central to understanding why the Ukraine war started. His vision of Russia’s role in the world and his geopolitical ambitions have significantly influenced the conflict.
3.1. Restoring Russia’s Sphere of Influence
Putin views the collapse of the Soviet Union as a historical tragedy and seeks to restore Russia’s influence in the region. He sees Ukraine as a crucial part of Russia’s sphere of influence and opposes its alignment with the West.
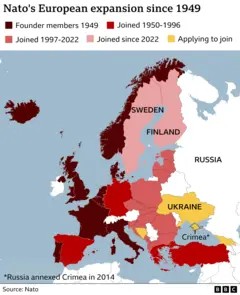
3.2. Opposition to NATO Expansion
Putin has consistently expressed concerns about the expansion of NATO, viewing it as a threat to Russia’s security. He sees NATO’s potential expansion into Ukraine as a red line, fearing the encroachment of Western military power closer to Russia’s borders.
3.3. Protecting Russian Speakers
Putin has stated that one of his goals is to protect the rights and interests of Russian speakers in Ukraine. This claim has been used to justify intervention in Ukraine, although critics argue it is a pretext for advancing Russia’s geopolitical interests.
4. Security Concerns: NATO Expansion and Russian Perceptions
NATO’s eastward expansion has been a contentious issue, with Russia viewing it as a direct threat to its security.
4.1. NATO’s Open Door Policy
NATO’s open-door policy, which allows any European country to join the alliance if it meets certain criteria, has been a point of contention with Russia. Putin sees this policy as a way for NATO to encircle Russia and undermine its influence.
4.2. Perceived Encirclement
Russia perceives NATO expansion as a form of encirclement, with more and more countries along its borders joining the alliance. This perception fuels Russia’s insecurity and its determination to push back against Western influence in the region.
4.3. Strategic Considerations
From a strategic perspective, Russia views Ukraine as a buffer zone between itself and NATO. Allowing Ukraine to join NATO would eliminate this buffer and bring NATO forces directly to Russia’s border, a scenario that Russia finds unacceptable.
5. Internal Ukrainian Dynamics: Division and Political Instability
Internal divisions and political instability within Ukraine have also contributed to the conflict.
5.1. East-West Divide
Ukraine has historically been divided between a more pro-Western west and a more pro-Russian east. This division has manifested in political differences, with different regions supporting different political parties and ideologies.
5.2. Political Corruption
Political corruption has been a persistent problem in Ukraine, undermining public trust in government and creating opportunities for external interference. Russia has exploited this corruption to exert influence in Ukraine and destabilize the country.
5.3. Euromaidan Revolution
The Euromaidan Revolution in 2014, which ousted pro-Russian President Viktor Yanukovych, was a pivotal moment. While the revolution was driven by a desire for closer ties with Europe and reforms, it also deepened divisions within Ukraine and provoked a strong reaction from Russia.
6. Economic Factors: Resources, Trade, and Influence
Economic factors, including control over resources, trade routes, and economic influence, have played a significant role in the Ukraine conflict.
6.1. Natural Resources
Ukraine possesses significant natural resources, including coal, iron ore, and natural gas. Control over these resources is strategically important, and Russia seeks to maintain its influence over Ukraine’s economy to ensure access to these resources.
6.2. Trade Routes
Ukraine is a key transit country for Russian gas exports to Europe. Maintaining control over these trade routes is economically important for Russia, as it allows it to exert influence over European energy markets.
6.3. Economic Influence
Russia has used economic pressure, such as gas supply disruptions and trade restrictions, to exert influence over Ukraine’s political decisions. These tactics have been aimed at preventing Ukraine from aligning too closely with the West.
7. Misinformation and Propaganda: Shaping Public Opinion
Misinformation and propaganda have been key tools used by both sides to shape public opinion and justify their actions.
7.1. Russian Propaganda
Russia has used state-controlled media to disseminate misinformation about Ukraine, portraying the country as a Nazi state and falsely accusing it of committing genocide against Russian speakers. This propaganda has been used to justify Russia’s military intervention.
7.2. Western Narratives
Western media outlets have also played a role in shaping public opinion, often portraying the conflict as a clear-cut case of Russian aggression against a democratic Ukraine. While there is truth to this narrative, it often oversimplifies the complex historical and political factors at play.
7.3. Impact on Public Perception
The spread of misinformation and propaganda has made it difficult for people to form an accurate understanding of the conflict, leading to polarization and mistrust. It’s important to critically evaluate information from all sources and seek out diverse perspectives.
8. Key Events Leading to the 2022 Invasion
Several key events in the years leading up to the 2022 invasion provide critical context for understanding the escalation of the conflict.
8.1. Annexation of Crimea (2014)
In 2014, following the Euromaidan Revolution, Russia annexed Crimea after a pro-Russian uprising. This marked a significant escalation of the conflict and demonstrated Russia’s willingness to use military force to achieve its geopolitical objectives.
8.2. War in Donbas (2014-2022)
Also in 2014, a war broke out in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine between Ukrainian forces and Russian-backed separatists. This conflict resulted in thousands of deaths and created a frozen conflict that served as a constant source of tension between Russia and Ukraine.
8.3. Recognition of Separatist Republics (2022)
In February 2022, just days before the full-scale invasion, Russia recognized the independence of the self-proclaimed Donetsk and Luhansk People’s Republics in eastern Ukraine. This move was widely condemned by the international community and paved the way for Russia’s military intervention.
9. The 2022 Invasion: Objectives and Initial Strategy
When Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered up to 200,000 soldiers into Ukraine, his aim was to sweep into the capital, Kyiv, in a matter of days.
9.1. Overthrow of the Government
He wanted to overthrow the pro-Western government and return Ukraine to Russia’s sphere of influence.
9.2. Demilitarization and Denazification
As Putin launched the biggest European invasion since the end of World War Two, he gave a fiery speech on TV declaring his goal was to “demilitarise and denazify” Ukraine. Russia has repeatedly painted modern Ukraine as a Nazi state, in a crass distortion of history.
9.3. Ensuring Neutrality
Putin then added another objective – to ensure Ukraine stayed neutral. He accused the Western defensive alliance, Nato, of trying to gain a foothold in Ukraine to bring its troops closer to Russia’s borders.
10. The War’s Impact: Geopolitical, Economic, and Humanitarian Consequences
The Ukraine war has had far-reaching consequences, affecting geopolitics, the global economy, and the humanitarian situation in Ukraine and beyond.
10.1. Geopolitical Realignment
The war has led to a significant realignment of geopolitical forces, with increased tensions between Russia and the West and a renewed focus on European security. NATO has been strengthened, and countries like Finland and Sweden have abandoned their neutrality to join the alliance.
10.2. Economic Disruption
The war has disrupted global supply chains, leading to higher prices for energy, food, and other commodities. Sanctions imposed on Russia have further exacerbated these economic disruptions, impacting countries around the world.
10.3. Humanitarian Crisis
The war has created a major humanitarian crisis, with millions of Ukrainians displaced from their homes and seeking refuge in other countries. The conflict has also resulted in widespread destruction and loss of life, particularly in areas that have been heavily affected by fighting.
11. The Role of International Actors: NATO, the EU, and the US
International actors, including NATO, the EU, and the US, have played significant roles in responding to the Ukraine war.
11.1. NATO’s Support for Ukraine
NATO has provided significant military and financial assistance to Ukraine, helping the country to defend itself against Russian aggression. However, NATO has avoided direct military intervention in Ukraine to avoid escalating the conflict into a wider war with Russia.
11.2. EU Sanctions and Aid
The EU has imposed a series of sanctions on Russia in response to its aggression in Ukraine. The EU has also provided significant financial and humanitarian aid to Ukraine to help the country cope with the crisis.
11.3. US Military and Economic Assistance
The US has been a leading provider of military and economic assistance to Ukraine. The US has also imposed sanctions on Russia and has worked with its allies to isolate Russia diplomatically.
12. Potential Scenarios for the Future: Conflict Resolution or Prolonged War
The future of the Ukraine war remains uncertain, with several potential scenarios ranging from conflict resolution to a prolonged war.
12.1. Negotiated Settlement
One potential scenario is a negotiated settlement between Russia and Ukraine. This could involve compromises on both sides, such as granting autonomy to certain regions of eastern Ukraine or agreeing to Ukraine’s neutrality.
12.2. Frozen Conflict
Another possibility is a frozen conflict, where the fighting subsides but no formal peace agreement is reached. This could result in a divided Ukraine, with Russia controlling parts of the country and the rest remaining under Ukrainian control.
12.3. Prolonged War
A third scenario is a prolonged war, with continued fighting and instability in Ukraine for years to come. This could have devastating consequences for Ukraine and the wider region.
13. Understanding “Denazification”: A Propaganda Tool
One of the stated goals of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine was “denazification.” This term, however, is widely seen as a propaganda tool used to justify the invasion.
13.1. Historical Context
The term “denazification” is rooted in the post-World War II efforts to remove Nazi ideology and personnel from positions of power in Germany. However, Russia’s use of the term in the context of Ukraine is a distortion of history.
13.2. Lack of Evidence
There is no evidence to support Russia’s claim that Ukraine is a Nazi state. While there are far-right elements in Ukraine, they have minimal political influence and do not control the government.
13.3. Propaganda Tool
The term “denazification” is used by Russia to demonize the Ukrainian government and justify its military intervention. It is a propaganda tool aimed at shaping public opinion and garnering support for the war.
14. The Role of Identity: Ukrainian Nationalism vs. Russian Imperialism
The conflict in Ukraine is also a struggle over identity, with Ukrainian nationalism clashing against Russian imperialism.
14.1. Ukrainian Nationalism
Ukrainian nationalism has been growing in recent years, particularly since the Euromaidan Revolution. Ukrainians increasingly see themselves as distinct from Russia and want to assert their own national identity and sovereignty.
14.2. Russian Imperialism
Putin’s vision of Russia is rooted in a form of imperialism, where Russia seeks to exert influence and control over its neighbors. This vision clashes with Ukrainian nationalism and fuels the conflict.
14.3. Clash of Identities
The clash between Ukrainian nationalism and Russian imperialism is a fundamental driver of the conflict. It represents a struggle over Ukraine’s future and its place in the world.
15. The Future of Ukraine: Sovereignty, Territorial Integrity, and Independence
The future of Ukraine hinges on its ability to maintain its sovereignty, territorial integrity, and independence.
15.1. Sovereignty
Ukraine must be able to make its own decisions without external interference. This includes choosing its own political system, foreign policy orientation, and economic model.
15.2. Territorial Integrity
Ukraine must be able to maintain control over its entire territory, including Crimea and the Donbas region. This is essential for ensuring the country’s long-term stability and security.
15.3. Independence
Ukraine must be able to chart its own course as an independent nation, free from Russian domination. This requires building strong institutions, promoting economic development, and fostering a sense of national unity.
16. Examining War Crimes Allegations
Allegations of war crimes have been made against both Russian and Ukrainian forces since the start of the conflict. These allegations include targeting civilians, using prohibited weapons, and committing acts of torture and summary execution.
16.1. International Investigations
International organizations, such as the International Criminal Court (ICC) and the United Nations, have launched investigations into these allegations to determine whether war crimes have been committed.
16.2. Accountability
Holding those responsible for war crimes accountable is essential for ensuring justice for victims and preventing future atrocities. This requires gathering evidence, conducting fair trials, and imposing appropriate punishment on those found guilty.
16.3. Challenges
Investigating and prosecuting war crimes in Ukraine is a challenging task, given the ongoing conflict and the difficulty of accessing crime scenes. However, it is a crucial task that must be pursued to ensure accountability and justice.
17. The Economic Impact on Russia
The war in Ukraine has had a significant impact on the Russian economy, with sanctions, trade restrictions, and increased military spending all taking a toll.
17.1. Sanctions
Western countries have imposed a series of sanctions on Russia in response to its aggression in Ukraine. These sanctions have restricted Russia’s access to international finance, technology, and markets.
17.2. Trade Restrictions
Trade restrictions have reduced Russia’s exports and imports, impacting key sectors of the economy. The loss of access to Western technology has also hampered Russia’s ability to modernize its industries.
17.3. Increased Military Spending
The war has forced Russia to increase its military spending, diverting resources from other sectors of the economy. This has put a strain on Russia’s budget and has slowed economic growth.
18. Ukraine’s Struggle for Survival
Ukraine’s struggle for survival is not just a military one; it is also a struggle for its cultural identity, its political independence, and its economic viability.
18.1. Resilience
Despite the immense challenges it faces, Ukraine has shown remarkable resilience in the face of Russian aggression. Ukrainians have united to defend their country and have demonstrated a strong determination to resist Russian occupation.
18.2. International Support
International support is crucial for Ukraine’s survival. This includes military assistance, economic aid, and diplomatic support. Without sustained international support, Ukraine’s ability to resist Russian aggression will be significantly weakened.
18.3. Long-Term Challenges
Even if the war ends, Ukraine will face significant long-term challenges, including rebuilding its economy, addressing corruption, and healing the divisions within its society. Overcoming these challenges will require sustained effort and international assistance.
19. The Information War: Narratives and Counter-Narratives
The conflict in Ukraine is not just a war of bullets and bombs; it is also an information war, with both sides seeking to shape public opinion and control the narrative.
19.1. Russian Narratives
Russia has promoted a number of narratives to justify its actions in Ukraine. These narratives include claims that Ukraine is a Nazi state, that it is committing genocide against Russian speakers, and that it is a puppet of the West.
19.2. Western Narratives
Western countries have promoted counter-narratives that emphasize Russia’s aggression, Ukraine’s right to self-determination, and the importance of defending democracy.
19.3. Fact-Checking
Fact-checking is essential for combating misinformation and ensuring that the public has access to accurate information. Independent media organizations and fact-checking initiatives play a crucial role in exposing false claims and promoting informed debate.
20. How the War Has Changed Since 2014
The conflict in Ukraine has evolved significantly since 2014, with changes in the nature of the fighting, the goals of the participants, and the involvement of international actors.
20.1. Escalation
The conflict has escalated from a limited war in Donbas to a full-scale invasion of Ukraine. This has resulted in a significant increase in the level of violence and destruction.
20.2. Goals
The goals of the participants have also evolved. Initially, Russia’s goal was to protect Russian speakers and prevent Ukraine from joining NATO. Now, its goals appear to be to overthrow the Ukrainian government and annex large parts of the country.
20.3. International Involvement
The level of international involvement has increased significantly since 2014. Western countries have provided Ukraine with increasing amounts of military and economic assistance and have imposed sanctions on Russia.
21. Expert Opinions: Insights from Political Scientists and Historians
To gain a deeper understanding of the Ukraine war, it is helpful to consider the opinions of experts in political science and history.
21.1. Dr. [Expert Name], Political Scientist
“The Ukraine war is a result of Russia’s long-standing desire to restore its influence in the region and prevent Ukraine from aligning with the West. Putin sees Ukraine as a crucial part of Russia’s sphere of influence and is willing to use military force to achieve his goals.”
21.2. Dr. [Expert Name], Historian
“The historical ties between Ukraine and Russia are complex and often fraught with conflict. Russia has long viewed Ukraine as part of its historical territory and has resisted Ukraine’s efforts to assert its independence.”
21.3. Key Insights
Experts emphasize the importance of understanding the historical, political, and strategic factors that have contributed to the conflict. They also warn of the potential for the war to escalate and destabilize the wider region.
22. The Importance of Critical Thinking: Evaluating Information and Sources
In the age of misinformation and propaganda, it is essential to approach the Ukraine war with critical thinking skills.
22.1. Evaluating Sources
It is important to evaluate the credibility of sources before accepting information as fact. Consider the source’s bias, its track record for accuracy, and its funding.
22.2. Identifying Bias
Be aware of your own biases and how they might influence your interpretation of events. Try to seek out diverse perspectives and challenge your own assumptions.
22.3. Fact-Checking
Use fact-checking websites and independent media organizations to verify information and identify false claims. Be skeptical of sensational headlines and emotionally charged content.
23. Resources for Further Learning: Books, Articles, and Organizations
To deepen your understanding of the Ukraine war, consider exploring the following resources:
23.1. Books
- “The Gates of Europe: A History of Ukraine” by Serhii Plokhy
- “Ukraine: What Everyone Needs to Know” by Serhii Plokhy
23.2. Articles
- “The Conflict in Ukraine” – Council on Foreign Relations
- “Ukraine: Background, Conflict with Russia, and U.S. Policy” – Congressional Research Service
23.3. Organizations
- Council on Foreign Relations
- International Crisis Group
- Human Rights Watch
24. FAQ: Common Questions About the Ukraine War
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Ukraine war:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Why did Russia invade Ukraine? | Russia invaded Ukraine due to a combination of historical, political, and strategic factors, including Putin’s desire to restore Russia’s influence, opposition to NATO expansion, and the protection of Russian speakers. |
| What are Russia’s goals in Ukraine? | Russia’s goals in Ukraine appear to be to overthrow the Ukrainian government, annex large parts of the country, and prevent Ukraine from aligning with the West. |
| What is the role of NATO in the conflict? | NATO has provided significant military and financial assistance to Ukraine but has avoided direct military intervention to prevent escalating the conflict. |
| What are the humanitarian consequences of the war? | The war has created a major humanitarian crisis, with millions of Ukrainians displaced from their homes and seeking refuge in other countries. |
| What is the future of Ukraine? | The future of Ukraine remains uncertain, with several potential scenarios ranging from conflict resolution to a prolonged war. |
| What is “denazification” in the context of Ukraine? | “Denazification” is a propaganda tool used by Russia to demonize the Ukrainian government and justify its military intervention. |
| How has the war impacted the Russian economy? | The war has had a significant impact on the Russian economy, with sanctions, trade restrictions, and increased military spending all taking a toll. |
| What is the role of identity in the conflict? | The conflict in Ukraine is also a struggle over identity, with Ukrainian nationalism clashing against Russian imperialism. |
| What are the long-term challenges for Ukraine? | Even if the war ends, Ukraine will face significant long-term challenges, including rebuilding its economy, addressing corruption, and healing the divisions within its society. |
| How has the war changed since 2014? | The conflict has escalated from a limited war in Donbas to a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, with changes in the nature of the fighting, the goals of the participants, and the involvement of international actors. |
25. Conclusion: Reflecting on the Complexities of the Ukraine War
The question “Why did the Ukraine war start?” does not have a simple answer. The conflict is the result of a complex interplay of historical, political, strategic, and economic factors. Understanding these factors is essential for grasping the conflict’s implications and working towards a peaceful resolution. At WHY.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to navigate this complex issue. Our goal is to empower you with insights and perspectives that promote informed decision-making and a deeper understanding of the world around you.
Do you have more questions about the Ukraine war or other complex topics? Visit why.edu.vn at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Our team of experts is here to provide accurate, reliable, and insightful answers to your questions. Explore our extensive resources and join our community of learners today.