Why did Russia declare war in Ukraine in 2022? This is a complex question with deep historical roots and far-reaching geopolitical implications. At WHY.EDU.VN, we provide clarity and understanding. Explore the reasons behind the Russia-Ukraine war, and gain insights into the motivations and strategic goals of both sides, including understanding the military conflict and geopolitical crisis. Delve into the causes of Russian aggression, the historical context, and the consequences of this war, plus discover insights into the geopolitical motivations behind the invasion.
1. Unveiling the Motivations: Why Russia Declared War
The declaration of war by Russia against Ukraine in 2022 was a culmination of various factors, historical grievances, and geopolitical ambitions. To truly understand the “why,” it’s crucial to dissect the multifaceted reasoning behind this decision.
1.1. Historical Ties and Putin’s Vision
President Vladimir Putin has repeatedly emphasized the historical connections between Russia and Ukraine, viewing them as inextricably linked. He has, on multiple occasions, stated that Ukrainians and Russians are “one people,” sharing a common history and culture dating back centuries. This perspective underpins his belief that Ukraine should remain within Russia’s sphere of influence, rather than aligning with the West.
In a lengthy essay published in 2021, Putin further elaborated on his views, arguing that modern Ukraine was an artificial construct created by Bolshevik leaders after the 1917 revolution. He criticized the Soviet Union’s policies for allegedly favoring Ukraine at the expense of Russia, thus laying the groundwork for his justification of military intervention.
Vladimir Putin has made repeated false allegations of genocide and Nazi taunts against Ukraine
1.2. Geopolitical Strategy: NATO Expansion
One of Russia’s primary security concerns is the eastward expansion of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Putin views NATO’s growing presence in Eastern Europe as a direct threat to Russia’s borders and strategic interests.
Putin has consistently argued that NATO’s expansion violates assurances given to Soviet leaders in the early 1990s that the alliance would not extend eastward. Although NATO denies making such commitments, Putin sees the inclusion of former Soviet bloc countries into the alliance as an encroachment on Russia’s traditional sphere of influence.
The prospect of Ukraine joining NATO is a red line for Putin. He believes that Ukraine’s membership in the alliance would allow NATO to position military forces and infrastructure directly on Russia’s border, significantly diminishing Russia’s strategic depth and ability to project power.
1.3. Protecting Russian Speakers: A Pretext for War?
Russia has often cited the need to protect Russian-speaking populations in Ukraine as a justification for its actions. Particularly in the eastern and southern regions of Ukraine, large numbers of people identify as Russian speakers, and Moscow claims that these individuals face discrimination and persecution from the Ukrainian government.
Following the 2014 Ukrainian revolution, Russia seized Crimea, citing the need to protect the predominantly Russian-speaking population from alleged threats posed by the new government in Kyiv. Similarly, Russia has supported separatist movements in the Donbas region, where Russian speakers form a significant portion of the population.
However, critics argue that the protection of Russian speakers is merely a pretext for Russia’s broader geopolitical goals. They contend that Russia exaggerates the extent of discrimination against Russian speakers in Ukraine to justify its military intervention and undermine Ukrainian sovereignty.
1.4. “Denazification” and Regime Change: A False Narrative
One of the most frequently cited reasons by Putin for the war was the “denazification” of Ukraine. This claim is based on the false assertion that the Ukrainian government is controlled by Nazis and that the country is overrun with far-right extremists.
In reality, far-right parties have minimal support in Ukraine, and the country’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, is Jewish and lost family members in the Holocaust. The “denazification” narrative is seen by many as a propaganda tool used to dehumanize Ukrainians and justify the invasion.
Another stated goal of Russia’s military operation was to overthrow the Ukrainian government and replace it with a pro-Russian regime. Russia initially attempted to seize Kyiv in the early days of the war, presumably to install a puppet government. However, these efforts were thwarted by the Ukrainian military and fierce resistance from the Ukrainian people.
1.5. Economic Interests: Resources and Trade
Economic considerations also played a role in Russia’s decision to invade Ukraine. Ukraine possesses significant natural resources, including coal, natural gas, and fertile agricultural land. Control over these resources would provide Russia with economic benefits and strengthen its position as a major energy supplier.
Ukraine is also a key transit country for Russian gas exports to Europe. By controlling Ukraine, Russia could ensure the uninterrupted flow of gas to its European customers and exert greater influence over the European energy market.
Moreover, Ukraine is an important trading partner for Russia, with significant economic ties in areas such as manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation. By bringing Ukraine back into its sphere of influence, Russia could enhance its economic power and create new opportunities for Russian businesses.
2. The Invasion Unfolds: Key Events and Strategic Failures
The invasion of Ukraine began on February 24, 2022, marking a significant escalation in the long-standing conflict between the two countries. Russia launched a multi-pronged assault, targeting key cities, military installations, and infrastructure across Ukraine.
2.1. Initial Objectives and Blitzkrieg Strategy
Russia’s initial objectives were to quickly seize control of Kyiv, overthrow the Ukrainian government, and install a pro-Russian regime. The Russian military employed a blitzkrieg strategy, relying on rapid advances by armored columns supported by air power.
However, the Russian offensive quickly bogged down in the face of fierce Ukrainian resistance. Ukrainian forces, armed with anti-tank weapons and bolstered by Western military aid, inflicted heavy losses on the Russian invaders.
2.2. Stiff Resistance and Shifting Strategies
The Ukrainian military’s unexpected resilience disrupted Russia’s plans for a swift victory. Russian forces encountered determined resistance in key cities such as Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Mariupol, where Ukrainian troops and civilian volunteers fought street by street to defend their homeland.
As the initial blitzkrieg failed, Russia shifted its strategy, focusing on consolidating its control over the Donbas region and establishing a land bridge to Crimea. Russian forces also intensified their bombardment of Ukrainian cities, causing widespread destruction and civilian casualties.
2.3. War Crimes and International Condemnation
Throughout the war, Russian forces have been accused of committing numerous war crimes, including the targeting of civilians, indiscriminate shelling of residential areas, and summary executions of prisoners of war. These allegations have been supported by evidence gathered by international organizations and human rights groups.
The war crimes committed by Russian forces have drawn widespread condemnation from the international community. The International Criminal Court (ICC) has opened an investigation into alleged war crimes, crimes against humanity, and genocide committed in Ukraine.
2.4. Current Status of the War: A Protracted Conflict
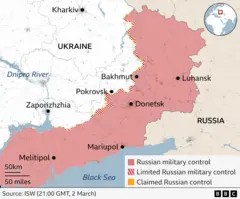
As of late 2024, the war in Ukraine remains a protracted conflict, with neither side achieving a decisive victory. The front lines have largely stabilized, with fighting concentrated in the Donbas region and along the southern coast of Ukraine.
Russia has consolidated its control over a significant portion of Ukrainian territory, including Crimea and parts of the Donbas region. However, Ukrainian forces have launched successful counter-offensives, reclaiming some territory and inflicting heavy losses on the Russian military.
The war has had a devastating impact on Ukraine, causing widespread destruction, displacement, and loss of life. The conflict has also had far-reaching consequences for the global economy, contributing to rising energy prices, food shortages, and supply chain disruptions.
2.5. Impact on Global Politics and Alliances
The Russia-Ukraine war has had a profound impact on global politics and alliances. The conflict has led to a renewed sense of unity among Western countries, with NATO members increasing their military spending and strengthening their collective defense capabilities.
The war has also accelerated the process of European integration, with the European Union granting Ukraine candidate status and providing substantial financial and military assistance. The conflict has also prompted Sweden and Finland to abandon their long-standing neutrality and apply for NATO membership.
However, the war has also exposed divisions within the international community. Some countries, particularly in the Global South, have been reluctant to condemn Russia’s actions or impose sanctions, citing concerns about the economic consequences of the conflict.
3. Examining the False Narratives: Debunking Russian Claims
Russia’s justification for the war in Ukraine has been built on a foundation of false narratives and propaganda. It’s essential to debunk these claims to understand the true nature of the conflict and the motivations behind Russia’s aggression.
3.1. The Myth of “Nazis” in Ukraine
One of the most pervasive and absurd claims made by Russia is that Ukraine is controlled by Nazis and that the war is aimed at “denazifying” the country. This assertion is patently false and unsupported by any credible evidence.
Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, is Jewish and lost family members in the Holocaust. Far-right parties have minimal support in Ukraine, failing to gain significant representation in parliament. The claim of “Nazis” in Ukraine is a blatant attempt to demonize the Ukrainian government and justify the invasion.
3.2. The “Genocide” Allegations: A Fabricated Crisis
Russia has also accused Ukraine of committing genocide against Russian speakers in the Donbas region. This allegation is baseless and has been rejected by international organizations and human rights groups.
While there has been conflict and violence in the Donbas region since 2014, there is no evidence to support the claim that Ukraine has deliberately targeted Russian speakers for extermination. The “genocide” narrative is a fabricated crisis designed to create a pretext for Russian intervention.
3.3. NATO Expansion as the Root Cause: A Misleading Argument
Russia argues that NATO expansion is the root cause of the war in Ukraine, claiming that the alliance’s eastward expansion poses an existential threat to Russia’s security. This argument is misleading and ignores the historical context of NATO expansion.
NATO is a defensive alliance that was created to protect its members from external aggression. The alliance has expanded eastward not through coercion or aggression, but through the voluntary decisions of sovereign nations to join the alliance in order to enhance their security.
The claim that NATO expansion is the root cause of the war ignores Russia’s own aggressive actions in the region, including its invasion of Georgia in 2008 and its annexation of Crimea in 2014. These actions demonstrate that Russia’s security concerns are not solely related to NATO expansion, but rather to its desire to maintain control over its neighbors and prevent them from aligning with the West.
3.4. Protecting Russian Speakers: A Smokescreen for Imperial Ambitions
Russia has consistently invoked the protection of Russian speakers in Ukraine as a justification for its actions. However, this claim is often used as a smokescreen for Russia’s imperial ambitions and its desire to undermine Ukrainian sovereignty.
While it is true that there are Russian speakers in Ukraine, there is no evidence to suggest that they face systematic discrimination or persecution. The Ukrainian government has taken steps to protect the rights of all its citizens, regardless of their language or ethnicity.
The claim that Russia is acting to protect Russian speakers in Ukraine is undermined by its own actions in the occupied territories, where it has suppressed Ukrainian language and culture and imposed its own political and cultural agenda.
3.5. The “Special Military Operation”: A War of Aggression
Russia initially described its invasion of Ukraine as a “special military operation” aimed at protecting civilians and “denazifying” the country. This characterization is a blatant attempt to downplay the true nature of the conflict, which is a full-scale war of aggression.
The Russian military has deliberately targeted civilians, bombed hospitals and schools, and committed numerous other war crimes. The “special military operation” narrative is a deceptive attempt to cover up the brutality and illegality of Russia’s actions.
4. The Human Cost: Casualties, Displacement, and Suffering
The war in Ukraine has had a devastating impact on the Ukrainian people, causing widespread casualties, displacement, and suffering. The human cost of the conflict is immense and will be felt for generations to come.
4.1. Civilian Casualties: A Tragic Toll
The war has resulted in a tragic loss of civilian life. The United Nations has confirmed that thousands of civilians have been killed in Ukraine, and the actual number is likely much higher.
Russian forces have deliberately targeted civilians, bombing residential areas, hospitals, and schools. The use of indiscriminate weapons, such as cluster munitions and thermobaric bombs, has caused horrific injuries and deaths.
The war has also disrupted access to essential services, such as healthcare, food, and water, further increasing the risk of civilian casualties.
4.2. Displacement: Millions Flee Their Homes
The war has forced millions of Ukrainians to flee their homes, seeking safety in other parts of the country or in neighboring countries. The United Nations estimates that more than 6 million Ukrainians have been internally displaced, while more than 8 million have fled to other countries as refugees.
The displacement crisis has created immense humanitarian challenges, as refugees and internally displaced persons struggle to find shelter, food, and medical care. Many have been separated from their families and have lost their homes and livelihoods.
4.3. Humanitarian Crisis: A Struggle for Survival
The war has created a severe humanitarian crisis in Ukraine, with millions of people in need of assistance. The conflict has disrupted supply chains, destroyed infrastructure, and limited access to essential services.
Many Ukrainians are struggling to find food, water, and medical care. The war has also increased the risk of disease outbreaks, as sanitation systems have been damaged and access to healthcare has been limited.
International organizations and aid agencies are working to provide humanitarian assistance to those in need, but the scale of the crisis is overwhelming.
4.4. Psychological Trauma: A Lasting Impact
The war has inflicted deep psychological trauma on the Ukrainian people. Many have witnessed horrific violence, lost loved ones, and been forced to flee their homes.
Children are particularly vulnerable to the psychological effects of war. They may experience nightmares, anxiety, and depression. The war has also disrupted their education and social development.
The psychological trauma of the war will have a lasting impact on the Ukrainian people, and it will take years of dedicated effort to address their mental health needs.
4.5. Long-Term Consequences: A Bleak Future
The war in Ukraine will have long-term consequences for the country and its people. The conflict has destroyed infrastructure, disrupted the economy, and displaced millions of people.
The war will also have a lasting impact on Ukraine’s political and social fabric. The conflict has exacerbated existing divisions and created new grievances.
Rebuilding Ukraine after the war will be a massive undertaking that will require international assistance and a commitment to long-term development.
5. The Geopolitical Fallout: Global Repercussions and Realignment
The Russia-Ukraine war has had far-reaching geopolitical consequences, reshaping global alliances, accelerating the energy transition, and raising concerns about the future of international order.
5.1. Strengthening of NATO: A Renewed Alliance
The war has led to a renewed sense of purpose and unity within NATO. The alliance has increased its military presence in Eastern Europe, strengthened its collective defense capabilities, and welcomed new members, such as Finland and Sweden.
The war has also prompted NATO members to increase their defense spending, reversing a trend of declining military budgets. The alliance is now more united and prepared to face potential threats from Russia.
5.2. Western Sanctions: Isolating Russia
Western countries have imposed unprecedented sanctions on Russia in response to its invasion of Ukraine. These sanctions target Russia’s financial sector, energy industry, and defense sector.
The sanctions have had a significant impact on the Russian economy, causing a sharp decline in GDP, rising inflation, and a depreciation of the ruble. The sanctions have also limited Russia’s access to international markets and technology.
While the sanctions have not yet forced Russia to end its war in Ukraine, they have significantly weakened its economy and limited its ability to project power abroad.
5.3. Energy Crisis: Accelerating the Transition
The war has triggered a global energy crisis, as Russia is a major supplier of oil and gas to Europe. The conflict has disrupted energy supplies and driven up prices, forcing countries to seek alternative sources of energy.
The energy crisis has accelerated the transition to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydrogen. Countries are now investing heavily in renewable energy infrastructure to reduce their dependence on Russian fossil fuels.
The war has also highlighted the vulnerability of Europe’s energy security and the need to diversify energy supplies.
5.4. Global Food Crisis: A Threat to Food Security
The war has contributed to a global food crisis, as Ukraine is a major exporter of grain and other agricultural products. The conflict has disrupted agricultural production and exports, leading to rising food prices and shortages in some parts of the world.
The food crisis has disproportionately affected developing countries, where many people are already struggling with food insecurity. The war has exacerbated existing inequalities and increased the risk of famine.
International organizations are working to address the food crisis, but the challenges are immense.
5.5. The Future of International Order: A World in Flux
The Russia-Ukraine war has raised fundamental questions about the future of international order. The conflict has demonstrated the limits of international law and the willingness of some countries to violate the sovereignty of others.
The war has also highlighted the growing competition between great powers and the potential for future conflicts. The world is now more multipolar and less predictable than it was before the war.
The future of international order will depend on the ability of countries to cooperate and uphold international law. The war in Ukraine has shown that this is not always the case, and that the world faces significant challenges in maintaining peace and security.
6. The Role of Information: Propaganda, Disinformation, and Truth
In the Russia-Ukraine war, information has become a crucial battleground. Both sides have engaged in propaganda and disinformation campaigns to influence public opinion and shape the narrative of the conflict.
6.1. Russian Propaganda: Distorting Reality
Russia has engaged in a sophisticated propaganda campaign to justify its war in Ukraine and undermine international support for Kyiv. Russian propaganda outlets have spread false narratives about the conflict, including claims that Ukraine is controlled by Nazis, that Russia is protecting Russian speakers from genocide, and that NATO expansion is the root cause of the war.
Russian propaganda has also sought to demonize Ukrainian leaders, portraying them as corrupt and incompetent. The goal of Russian propaganda is to distort reality and create confusion, making it difficult for people to understand the true nature of the conflict.
6.2. Ukrainian Information Warfare: Countering Disinformation
Ukraine has also engaged in information warfare, using social media and other platforms to counter Russian disinformation and rally international support for its cause. Ukrainian officials have been active on social media, sharing images and videos of the war and appealing to the world for help.
Ukrainian information warfare has been largely successful in countering Russian disinformation and shaping international public opinion. However, Ukraine faces a constant challenge in keeping up with the scale and sophistication of Russian propaganda efforts.
6.3. The Importance of Fact-Checking: Verifying Information
In the age of social media and instant communication, it is more important than ever to verify information before sharing it. The Russia-Ukraine war has demonstrated the dangers of spreading false or misleading information.
Fact-checking organizations play a crucial role in verifying information and debunking false narratives. These organizations use a variety of methods to assess the accuracy of claims, including consulting experts, examining evidence, and analyzing data.
By relying on fact-checked information, people can make informed decisions about the conflict and avoid being misled by propaganda or disinformation.
6.4. The Role of Social Media: Amplifying Voices and Spreading Disinformation
Social media has played a significant role in the Russia-Ukraine war, both amplifying voices and spreading disinformation. Social media platforms have allowed Ukrainians to share their stories with the world and have enabled international supporters to organize protests and raise funds for humanitarian aid.
However, social media has also been used to spread disinformation and propaganda. Russian-linked accounts have spread false narratives about the conflict, while Ukrainian-linked accounts have shared graphic images and videos of the war.
Social media platforms have a responsibility to combat disinformation and ensure that their platforms are not used to spread hate speech or incite violence.
6.5. The Power of Truth: Holding Russia Accountable
The Russia-Ukraine war has demonstrated the power of truth in holding aggressors accountable. By documenting war crimes, exposing false narratives, and sharing the stories of victims, the world can hold Russia accountable for its actions.
The truth is a powerful weapon that can be used to counter propaganda and disinformation. By supporting independent media, fact-checking organizations, and human rights groups, people can help to ensure that the truth prevails.
7. What Next for Ukraine and Russia? The Future of the Conflict
The future of the Russia-Ukraine war remains uncertain. The conflict could continue for months or even years, with neither side achieving a decisive victory. However, there are several possible scenarios that could play out in the coming months.
7.1. Protracted Conflict: A War of Attrition
The most likely scenario is that the war will continue as a protracted conflict, with neither side able to achieve a decisive breakthrough. The front lines will remain largely static, with fighting concentrated in the Donbas region and along the southern coast of Ukraine.
In this scenario, both sides will continue to suffer heavy casualties and economic losses. The war will have a devastating impact on Ukraine, causing widespread destruction, displacement, and suffering.
7.2. Russian Victory: A Pyrrhic Outcome
It is possible that Russia could achieve a military victory in Ukraine, capturing Kyiv and installing a pro-Russian regime. However, such a victory would likely be pyrrhic, as Russia would face a long and costly insurgency.
The Ukrainian people would never accept Russian rule, and they would continue to resist the occupation. Russia would also face international condemnation and sanctions, further isolating it from the world.
7.3. Negotiated Settlement: A Fragile Peace
It is possible that the war could end with a negotiated settlement, in which both sides agree to a ceasefire and a framework for resolving their disputes. However, such a settlement would likely be fragile and could easily collapse.
Any negotiated settlement would need to address the key issues that are driving the conflict, including the status of Crimea and the Donbas region, the future of NATO expansion, and the protection of Russian speakers in Ukraine.
7.4. Escalation: A Wider Conflict
There is a risk that the war could escalate, drawing in other countries and potentially leading to a wider conflict. This could happen if Russia were to attack a NATO member state or if NATO were to intervene directly in the conflict.
Escalation would have catastrophic consequences, potentially leading to a nuclear war. It is essential that all parties act with restraint and avoid taking steps that could escalate the conflict.
7.5. The Role of International Actors: Seeking a Resolution
International actors, such as the United Nations, the European Union, and the United States, have a crucial role to play in seeking a resolution to the conflict. These actors can use their diplomatic and economic leverage to pressure both sides to negotiate a peaceful settlement.
International actors can also provide humanitarian assistance to Ukraine and help to rebuild the country after the war. It is essential that the international community remains united in its support for Ukraine and its efforts to achieve a just and lasting peace.
FAQ: Understanding the Russia-Ukraine War
To further clarify the complexities surrounding the Russia-Ukraine war, here are some frequently asked questions:
- What were Russia’s stated goals at the beginning of the invasion? Russia claimed its goals were to “demilitarize” and “denazify” Ukraine, protect Russian speakers, and prevent Ukraine from joining NATO.
- How has NATO expansion factored into Russia’s grievances? Russia views NATO’s eastward expansion as a threat to its security, arguing it violates earlier assurances.
- What is the current state of the conflict? The conflict is now a protracted war of attrition, with the most intense fighting in the Donbas region.
- What war crimes have been alleged? Accusations include targeting civilians, indiscriminate shelling, and summary executions by Russian forces.
- What impact has the war had on global energy markets? The war has caused an energy crisis in Europe, leading to rising prices and a push for alternative energy sources.
- How many Ukrainians have been displaced by the conflict? Millions of Ukrainians have been internally displaced or have fled to other countries as refugees.
- What is the role of propaganda in the war? Both sides have engaged in propaganda and disinformation campaigns to influence public opinion.
- What are the potential long-term consequences for Ukraine? The long-term consequences include economic devastation, infrastructure damage, and psychological trauma.
- How has the war affected global alliances? The war has strengthened NATO and led to Western sanctions against Russia.
- What are the possible scenarios for the war’s resolution? Possible scenarios include a protracted conflict, a Russian victory, a negotiated settlement, or escalation to a wider conflict.
Do you have more questions about the Russia-Ukraine war? The conflict has caused widespread devastation, displacement, and geopolitical instability. Do you need reliable answers? At WHY.EDU.VN, our team of experts is ready to provide in-depth insights and clarify the complexities of this war. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States or via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. You can also visit our website at why.edu.vn to ask your questions and explore our extensive knowledge base. We are here to help you understand the world better.
Ukrainians sought shelter in underground shelters as Russian forces attacked on 24 February 2022