Why Did John Hancock Sign So Big on the Declaration of Independence? This question explores the historical context, motivations, and legacy of John Hancock’s prominent signature, a symbol of American patriotism and defiance. At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into this iconic act, offering insights into the man behind the signature and the historical significance of his bold declaration, providing the answers you need. This exploration uncovers the details behind this bold act, examines the signature’s lasting impact, and explores the symbolism behind this important historical document.
1. Understanding the Historical Context of the Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, a cornerstone of American history, wasn’t just a document; it was a bold declaration of freedom. To grasp why John Hancock’s signature became such a standout feature, we first need to understand the climate in which it was created.
1.1. The Road to Independence
The mid-1770s were turbulent times. Tensions between Great Britain and its American colonies had been simmering for years, escalating due to a series of unpopular acts imposed by the British government. Colonists felt their rights were being trampled, and the cry for “no taxation without representation” echoed throughout the land. Key events that fueled the revolution include:
- The Stamp Act (1765): Imposed a direct tax on printed materials in the colonies, sparking widespread protests.
- The Boston Massacre (1770): British soldiers fired on a group of colonists, further inflaming anti-British sentiment.
- The Tea Act (1773) and Boston Tea Party: The Tea Act, designed to benefit the British East India Company, led to the Boston Tea Party, where colonists dumped tea into Boston Harbor.
- The Intolerable Acts (1774): Passed by the British Parliament in response to the Boston Tea Party, these acts further restricted colonial freedoms and autonomy.
These events culminated in the meeting of the Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia in 1775. The Congress initially sought reconciliation with Britain, but as conflict escalated, the sentiment shifted towards independence.
1.2. The Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress served as the governing body of the American colonies during the Revolutionary War. Composed of delegates from each of the thirteen colonies, it was responsible for:
- Raising a Continental Army: Recognizing the need for a unified military force, the Congress established the Continental Army and appointed George Washington as its commander-in-chief.
- Managing the War Effort: The Congress oversaw the procurement of supplies, the recruitment of soldiers, and the coordination of military strategies.
- Seeking Foreign Allies: Recognizing the importance of foreign support, the Congress dispatched diplomats to seek recognition and assistance from European powers.
Within this Congress, figures like John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, and Benjamin Franklin debated fiercely on the future of the colonies. The decision to declare independence was not taken lightly.
1.3. Drafting the Declaration
A committee of five, including Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Roger Sherman, and Robert Livingston, was tasked with drafting a document that would articulate the reasons for separation from Great Britain. Thomas Jefferson was primarily responsible for writing the first draft. The document asserted:
- Natural Rights: It proclaimed that all men are created equal and endowed with certain unalienable rights, including life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
- Grievances Against the King: It listed a long series of grievances against King George III, accusing him of tyranny and violations of colonial rights.
- Declaration of Independence: It formally declared that the thirteen American colonies were free and independent states, absolved from all allegiance to the British Crown.
After several revisions, the Declaration of Independence was presented to the Continental Congress on June 28, 1776. On July 2, 1776, the Congress voted in favor of independence. Two days later, on July 4, 1776, the Declaration of Independence was officially adopted.
2. John Hancock: More Than Just a Signature
To understand why John Hancock’s signature on the Declaration of Independence is so prominent, it is helpful to know who he was.
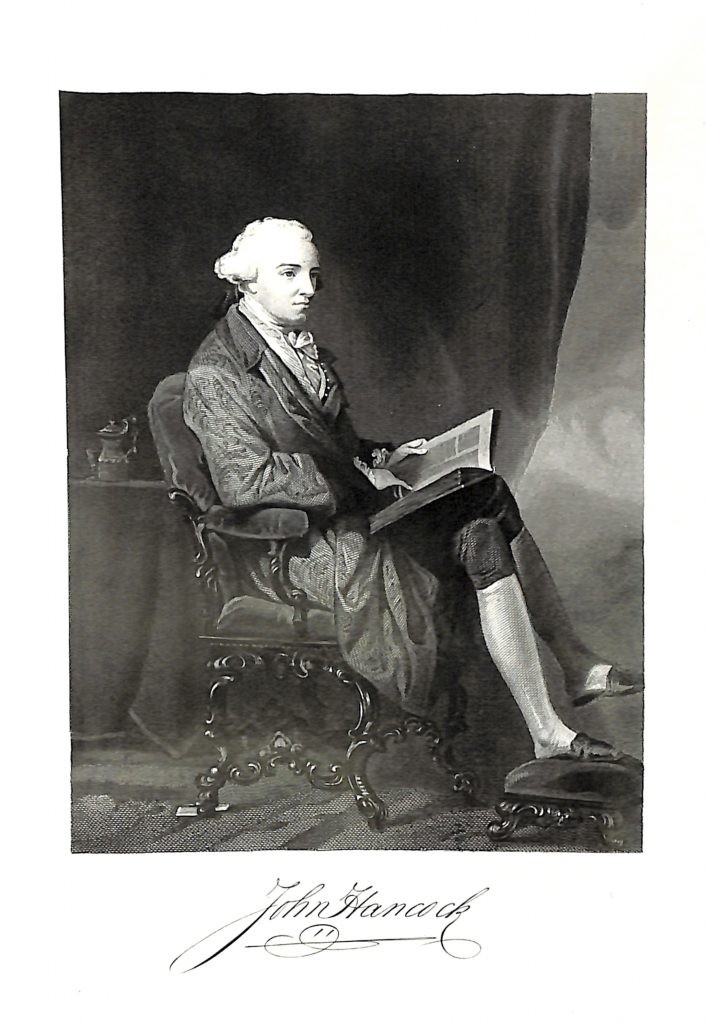
2.1. A Wealthy Merchant and Patriot
Born in Braintree, Massachusetts, in 1737, John Hancock was a prominent figure in colonial America. He inherited a thriving mercantile business from his uncle, which made him one of the wealthiest men in the colonies.
Hancock’s wealth and social standing afforded him considerable influence, which he used to champion the cause of American independence. He became a vocal critic of British policies, using his financial resources to support the burgeoning revolutionary movement.
2.2. President of the Continental Congress
John Hancock’s leadership skills and commitment to the revolutionary cause led to his election as President of the Second Continental Congress in 1775. In this role, he presided over the debates and decisions that would shape the future of the United States. His responsibilities included:
- Facilitating Deliberations: Hancock skillfully guided the Continental Congress through intense debates on issues ranging from military strategy to diplomatic negotiations.
- Maintaining Order: As President, Hancock was responsible for maintaining order and decorum during congressional sessions, ensuring that all delegates had the opportunity to express their views.
- Representing the Congress: Hancock served as the public face of the Continental Congress, representing the body in its dealings with other governments and organizations.
His position made him a key figure in the movement for independence, putting him directly in the crosshairs of the British government.
2.3. A Target of the Crown
As tensions escalated, Hancock became a marked man. His involvement in the revolutionary movement made him a target of the British Crown, and his actions were closely monitored. He was accused of smuggling and sedition, and his property was often subject to search and seizure.
Despite the risks, Hancock remained steadfast in his commitment to the American cause. He used his wealth and influence to support the Continental Army, providing critical resources and supplies.
His defiance of British authority made him a symbol of resistance and a hero to many colonists.
3. Analyzing the Signature: Size and Symbolism
John Hancock’s large signature on the Declaration of Independence is not just a historical fact; it’s a symbol laden with meaning. Let’s break down the elements that make it so iconic.
3.1. The Sheer Size of the Signature
Hancock’s signature is considerably larger than those of the other delegates. This isn’t just a quirk of handwriting; it was a deliberate act that has sparked much speculation and interpretation over the years. The size of the signature made it impossible to ignore and conveyed the importance he gave to the document.
3.2. Defiance and Boldness
One common interpretation is that the large signature was an act of defiance against King George III. The story, though likely apocryphal, suggests that Hancock wanted to ensure that the King could read his name without spectacles, a bold challenge to British authority. This interpretation aligns with Hancock’s reputation as a firebrand and a staunch advocate for American rights.
The act of signing the Declaration of Independence was an act of treason, punishable by death. By signing his name so prominently, Hancock was making a clear statement that he was willing to risk his life for the cause of independence.
3.3. A Symbol of Unity
Beyond personal defiance, the signature can also be seen as a symbol of unity and resolve. As President of the Continental Congress, Hancock was responsible for ensuring that the colonies presented a united front against British aggression. His prominent signature signaled to both the British and the American people that the colonies were united in their determination to secure their independence.
3.4. Personal Pride and Legacy
There is also a more straightforward explanation: Hancock was simply proud of his role in this historic event. He likely recognized that the Declaration of Independence would be a defining moment in American history, and he wanted to ensure that his name would be forever associated with it.
Whatever the motivation, the large signature has undoubtedly contributed to John Hancock’s enduring legacy. It has made him one of the most recognizable figures of the American Revolution, and it has solidified his place in the pantheon of American heroes.
4. Debunking Myths and Legends
Over time, John Hancock’s signature has become the stuff of legend. But how much of what we know is fact, and how much is fiction?
4.1. The Spectacles Anecdote
One of the most famous stories surrounding Hancock’s signature is the anecdote about King George III needing spectacles to read it. As mentioned earlier, the story goes that Hancock signed his name so large so that the King could easily see it as a sign of defiance. While this story is widely circulated, there is no historical evidence to support it.
The likely origin of the story is the desire to create a memorable and inspiring narrative around the signing of the Declaration of Independence. The story has become a part of American folklore, and it continues to be told and retold to this day.
4.2. Bounties on Hancock’s Head
Another myth is that the British government had placed a bounty on John Hancock’s head. While it’s true that Hancock was a wanted man, there is no record of a specific reward being offered for his capture. This myth likely arose from the fact that Hancock was a prominent leader of the revolutionary movement and a vocal critic of British policies.
It is also possible that the myth was created to further demonize the British government and to rally support for the American cause. Whatever the origin, the myth of the bounty on Hancock’s head has become a part of the larger narrative of the American Revolution.
4.3. Hancock’s Intentions
While we can speculate about Hancock’s intentions, the truth is that we don’t know for sure why he signed his name so large. It’s likely that a combination of factors played a role, including defiance, pride, and a desire to make a statement. Regardless of the specific motivation, the signature has become a powerful symbol of American independence and a testament to Hancock’s enduring legacy.
5. The Signature’s Enduring Legacy
John Hancock’s signature has transcended its historical origins and become a cultural icon, deeply embedded in the American consciousness.
5.1. A Synonym for Signature
Today, the phrase “put your John Hancock on it” is a common idiom for signing one’s name. This speaks to the signature’s ubiquity and its association with the act of formal agreement. This usage highlights the signature’s lasting impact on the English language and its connection to the concept of personal responsibility and commitment.
5.2. Patriotism and American Identity
The signature has become a symbol of American patriotism and defiance, representing the courage and determination of the Founding Fathers. It evokes a sense of national pride and reminds Americans of the sacrifices made to secure their independence. It is often used in patriotic imagery and rhetoric, serving as a visual shorthand for the ideals of freedom and self-government.
5.3. Cultural References
John Hancock’s signature frequently appears in popular culture, from movies and television shows to books and advertisements. These references often play on the signature’s size and its association with American independence. It has become a familiar and recognizable symbol that resonates with audiences of all ages.
6. Why This Matters Today
Understanding the story behind John Hancock’s signature offers more than just a history lesson; it provides valuable insights into the principles and values that underpin American society.
6.1. Remembering the Foundations of Freedom
In an era of political division and social unrest, it’s crucial to remember the foundations upon which the United States was built. The Declaration of Independence, with Hancock’s bold signature, reminds us of the importance of freedom, equality, and self-governance. It encourages us to reflect on the challenges faced by the Founding Fathers and the sacrifices they made to secure these principles.
6.2. The Power of Individual Action
Hancock’s story demonstrates the power of individual action in shaping the course of history. His commitment to the American cause, his willingness to defy British authority, and his leadership within the Continental Congress all contributed to the success of the American Revolution. It inspires us to take action in our own communities and to stand up for the values we believe in.
6.3. Questioning Authority
The story behind the signature encourages critical thinking and questioning authority. It challenges us to examine the narratives we are told and to seek out the truth for ourselves. It reminds us that progress and change often come from those who are willing to challenge the status quo and to advocate for a better future.
7. Expert Opinions on Hancock’s Signature
To provide a comprehensive understanding of why John Hancock signed so big, let’s consider perspectives from historians and handwriting experts.
7.1. Historians’ Perspectives
Historians offer various interpretations of Hancock’s prominent signature, often considering the historical context and Hancock’s personal motivations.
- David McCullough: The esteemed historian, known for his biographies of American leaders, might emphasize Hancock’s role as a wealthy merchant who risked his fortune and reputation for the cause of independence. His signature, in this view, becomes a symbol of that commitment.
- Pauline Maier: A specialist in early American history, Maier could argue that Hancock’s signature was a deliberate act of political theater. As President of the Continental Congress, he aimed to project confidence and unity, and the bold signature served that purpose.
7.2. Handwriting Analysis
Handwriting analysts, also known as graphologists, study handwriting to infer personality traits and behavioral patterns. While graphology is not universally accepted as a science, it offers intriguing insights into Hancock’s character.
- Large Size: Graphologists might interpret the large size of the signature as indicative of extroversion, confidence, and a desire for recognition. It suggests that Hancock was comfortable in the spotlight and sought to make a lasting impression.
- Bold Strokes: The bold strokes could be seen as a sign of determination, assertiveness, and a willingness to take risks. It aligns with Hancock’s reputation as a bold and decisive leader.
- Flamboyant Style: The flamboyant style of the signature might reflect a sense of theatricality and a desire to stand out from the crowd. It suggests that Hancock enjoyed being the center of attention and was not afraid to express himself.
7.3. Contrasting Views
It’s important to note that not all experts agree on the interpretation of Hancock’s signature. Some historians may dismiss the notion that it was a deliberate act of defiance, arguing that it was simply a reflection of Hancock’s natural handwriting style. Similarly, some graphologists may caution against drawing definitive conclusions based solely on a single signature.
By considering multiple perspectives, we can gain a more nuanced understanding of the motivations and symbolism behind John Hancock’s iconic signature.
8. Contemporary Interpretations and Relevance
John Hancock’s signature remains a relevant symbol in modern discussions about freedom, identity, and political expression.
8.1. Modern Political Symbolism
In contemporary political discourse, Hancock’s signature is often invoked to represent ideals of American liberty and self-determination. It appears in political cartoons, posters, and online memes, symbolizing resistance against perceived tyranny or government overreach. The signature serves as a reminder of the nation’s founding principles and the importance of civic engagement.
8.2. Corporate Branding and Marketing
Businesses sometimes use imagery inspired by Hancock’s signature to convey messages of authenticity, patriotism, and quality. Brands seeking to align themselves with American values may incorporate elements of the signature into their logos or advertising campaigns. This strategy aims to evoke a sense of trust and nostalgia, appealing to consumers who appreciate heritage and tradition.
8.3. Artistic and Creative Inspirations
Artists and designers continue to draw inspiration from Hancock’s signature, incorporating it into paintings, sculptures, and graphic designs. The signature’s bold and distinctive style makes it a visually compelling element, suitable for a wide range of creative applications. It serves as a reminder of the historical context while allowing for contemporary interpretations and artistic expression.
9. Summary Table: Key Facts About John Hancock’s Signature
| Fact | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Size | John Hancock’s signature is notably larger than the signatures of other delegates on the Declaration of Independence. | Conveys importance, defiance, and a desire for recognition. |
| Location | It is the first and most prominent signature on the document. | Establishes Hancock’s leadership role as President of the Continental Congress. |
| Anecdotes | The story about King George needing spectacles to read Hancock’s signature is widely circulated but likely apocryphal. | Adds to the legend and reinforces the image of Hancock as a defiant patriot. |
| Modern Idiom | The phrase “put your John Hancock on it” is a common idiom for signing one’s name. | Demonstrates the signature’s cultural ubiquity and its association with formal agreement. |
| Symbolism | It symbolizes American patriotism, defiance, and the courage of the Founding Fathers. | Evokes national pride and reminds Americans of the sacrifices made to secure their independence. |
| Handwriting Analysis | Graphologists suggest the signature reflects extroversion, confidence, determination, and a desire to stand out. | Provides insights into Hancock’s personality traits and motivations. |
| Relevance Today | The signature remains a potent symbol in modern political discourse, corporate branding, and artistic creations. | Connects historical ideals of liberty with contemporary expressions of freedom and identity. |
| Historical Context | Signed on August 2, 1776, nearly a month after the Declaration was formally adopted. | Highlights the deliberate and momentous nature of the signing. |
| Hancock’s Role as Target of the Crown | Hancock was a wealthy merchant and prominent figure, making him a target for British authorities. | Emphasizes the risks and sacrifices involved in declaring independence. |
| Misconceptions | Despite popular belief, there’s no solid evidence of a bounty on Hancock’s head by the British. | Clarifies historical accuracy versus embellished narratives. |
| Other Interpretations | Apart from defiance, some historians suggest it might have been a personal statement or a reflection of his status. | Adds nuance to understanding the complex motivations behind his act. |
| Appearance in Popular Culture | Hancock’s signature frequently appears in movies, TV shows, books, and advertisements. | Reinforces its iconic status and cultural recognition. |
| Continued Influence | Continues to influence contemporary discussions about freedom, identity, and political expression. | Shows how historical symbols can remain relevant and adaptable in modern contexts. |
| Signature Style | Characterized by bold strokes and flamboyant style. | Highlights his sense of drama and self-assuredness. |
| Inspiration for Creatives | Serves as a source of inspiration for artists and designers. | Shows the aesthetic and enduring appeal of Hancock’s signature beyond its historical meaning. |


10. FAQ: Unraveling the Mysteries of Hancock’s Signature
Let’s address some frequently asked questions related to John Hancock and his famous signature:
10.1. Was John Hancock the First to Sign the Declaration of Independence?
Yes, as the President of the Continental Congress, John Hancock was the first to sign the Declaration of Independence on August 2, 1776. His prominent signature was placed in the center, making it the most visible.
10.2. Why Did It Take So Long to Sign the Declaration?
The Declaration of Independence was adopted on July 4, 1776, but the formal signing didn’t occur until August 2, 1776. This delay allowed time for an official engrossed (written in a clear, large hand) copy to be prepared and for all delegates to be present.
10.3. Did All the Delegates Sign on August 2nd?
No, not all delegates signed on August 2nd. Some were absent, and others signed later. In fact, some delegates never signed the Declaration.
10.4. What Pen Did John Hancock Use?
The exact type of pen John Hancock used is not definitively known. Quill pens were the standard writing instrument during that time, made from bird feathers and dipped in ink.
10.5. Where Is the Original Declaration of Independence Housed?
The original Declaration of Independence is housed at the National Archives Museum in Washington, D.C. It is displayed in a specially designed case to protect it from light and environmental damage.
10.6. How Has the Declaration Been Preserved Over Time?
The Declaration has undergone several preservation efforts. In the 19th century, it was improperly stored, causing fading. Today, it is kept in a climate-controlled, sealed case with special lighting to minimize deterioration.
10.7. What Were the Risks of Signing the Declaration?
Signing the Declaration of Independence was an act of treason against the British Crown, punishable by death. The signatories risked their lives, fortunes, and reputations.
10.8. How Did Hancock’s Signature Influence Others?
Hancock’s bold signature served as an inspiration to other delegates, encouraging them to stand firm in their commitment to independence. It also sent a clear message to the British government of the colonies’ resolve.
10.9. Why Is Hancock’s Signature Larger Than Others?
While there are various theories, the most popular is that Hancock signed his name so large as a sign of defiance, ensuring that King George III could read it without his spectacles. Another theory suggests it was a display of his status as President of the Continental Congress.
10.10. Has Hancock’s Signature Been Used in Modern Advertising?
Yes, Hancock’s signature has been used in various modern advertisements to evoke a sense of history, patriotism, and authenticity. It adds a touch of heritage to brands seeking to align themselves with American values.
Do you have more questions about John Hancock, the Declaration of Independence, or any other historical topic? Visit WHY.EDU.VN, where our experts are ready to provide you with accurate, insightful answers. We are located at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Your quest for knowledge starts at why.edu.vn.
