Why Did Bob Marley Die? Bob Marley’s death at the young age of 36 was due to acral lentiginous melanoma, a rare and aggressive form of skin cancer. This article from WHY.EDU.VN will explore the specifics of his illness, its progression, and the broader implications for skin cancer awareness, especially among people of color, offering insights into early detection and treatment. Melanoma awareness and skin cancer education are crucial for prevention.
1. Bob Marley’s Diagnosis: Acral Lentiginous Melanoma (ALM)
Bob Marley, the reggae icon, received a diagnosis of acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM). This diagnosis came after he noticed a dark spot underneath his toenail, which he initially dismissed as a soccer injury. Acral lentiginous melanoma is a unique type of skin cancer that requires specific understanding.
1.1. What is Acral Lentiginous Melanoma?
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is a subtype of melanoma that arises on the palms, soles, or nail beds. Unlike other forms of melanoma primarily linked to UV radiation exposure, ALM’s causes are less clear and may involve genetic factors. Its name derives from “acral,” referring to the extremities, and “lentiginous,” describing its freckled appearance. It is essential to understand this distinct form of melanoma for effective diagnosis and treatment.
1.2. How ALM Differs from Other Melanomas
The typical melanomas are usually linked to ultraviolet (UV) radiation coming from the sun, or from tanning beds. However, ALM develops on areas that aren’t exposed to the sun, such as under the nails, on the soles of the feet, or palms of the hands; this type of melanoma is frequently caused by genetic factors. This difference in causation highlights the importance of checking even sun-protected areas for unusual skin changes. Recognizing these differences is crucial for early detection.
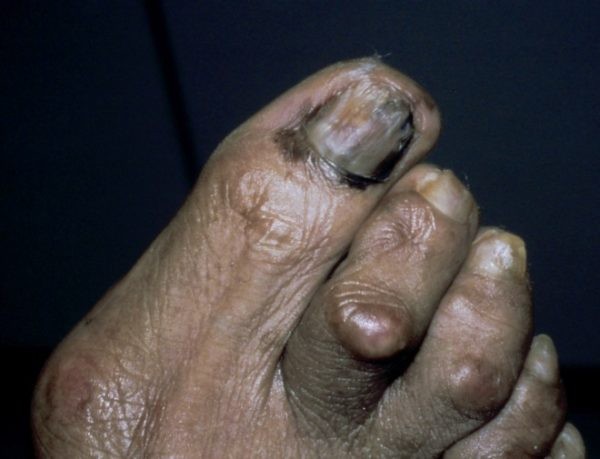 Acral lentiginous melanoma example (not a photo of Bob Marley)
Acral lentiginous melanoma example (not a photo of Bob Marley)
1.3. ALM in People of Color
While acral lentiginous melanoma is rare overall, it is the most common form of melanoma found in people of color. This is a crucial point because melanoma is often thought of as a “white person’s disease,” leading to delayed diagnosis in other populations. It is important to consider that this can be caused by several factors, including a lack of awareness and access to healthcare.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Lack of Awareness | Melanoma is often perceived as a condition primarily affecting individuals with fair skin, leading to reduced vigilance among people of color. |
| Delayed Diagnosis | Due to lower awareness and potential misdiagnosis, melanoma in people of color is often detected at later stages, resulting in poorer outcomes. |
| Genetic Predisposition | ALM’s development on non-sun-exposed areas suggests a potential genetic component, making it more prevalent among certain ethnic groups. |
| Access to Healthcare | Disparities in healthcare access can result in fewer regular skin examinations and delayed medical attention, contributing to delayed diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. |
| Cultural and Societal Factors | Cultural beliefs and societal norms may influence attitudes toward healthcare, leading to delayed medical intervention for skin abnormalities. |
2. Bob Marley’s Treatment Choices and Their Consequences
Following his diagnosis, Bob Marley was advised to undergo surgical removal of his toe, a procedure known as amputation. He refused this treatment and instead opted for excisional surgery. This involved removing the nail bed and cancerous tissue. This section will address how his decision influenced the progression of his illness.
2.1. The Recommended Treatment: Amputation
The recommended treatment for ALM, especially in advanced stages, is often amputation. This aggressive approach aims to prevent the cancer from spreading further into the body. Doctors recommended this course of action to Bob Marley.
2.2. Marley’s Alternative: Excisional Surgery
Instead of amputation, Marley chose excisional surgery. While this procedure can be effective in early-stage melanomas, it may not be sufficient for ALM, which tends to be more aggressive. Choosing this option had a substantial impact on his prognosis.
2.3. The Spread of Melanoma
Unfortunately, after the excisional surgery, the melanoma metastasized, spreading to other areas of his body. This included his brain, liver, and lungs. This metastasis proved fatal and directly led to his death. This illustrates the aggressive nature of ALM and the challenges in treating it effectively.
3. The Importance of Early Detection and Awareness
Bob Marley’s case underscores the importance of early detection and awareness of skin cancer, particularly ALM. Had his cancer been detected and treated earlier, the outcome might have been different. This section will emphasize the importance of early detection and awareness.
3.1. Checking Your Skin: What to Look For
Regular self-exams are crucial for detecting skin cancer early. It is essential to check your skin carefully from head to toe every month, paying close attention to areas that don’t get much sunlight. Look for anything new, changing, or unusual. This includes spots under the nails, on the palms of the hands, and the soles of the feet.
3.2. The “ABCDE” of Melanoma
The “ABCDE” rule is a helpful guide for identifying potentially cancerous moles:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges of the mole are irregular, notched, or blurred.
- Color: The mole has uneven colors, with shades of black, brown, and tan.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about 1/4 inch) in diameter.
- Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
3.3. Seeking Professional Help
If you notice any suspicious changes on your skin, it is crucial to seek professional help immediately. A dermatologist can perform a thorough skin exam and determine whether a biopsy is necessary. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of survival.
4. Disparities in Melanoma Outcomes
The survival rate for melanoma varies among different racial and ethnic groups. Black people with melanoma have a lower five-year survival rate compared to white people. This disparity is often due to later diagnosis, as melanoma in people of color is frequently detected at more advanced stages. This section will explore the disparities in melanoma outcomes.
4.1. Factors Contributing to Disparities
Several factors contribute to disparities in melanoma outcomes:
- Lack of Awareness: Melanoma is often perceived as a “white person’s disease,” leading to reduced vigilance among people of color.
- Delayed Diagnosis: Due to lower awareness and potential misdiagnosis, melanoma in people of color is often detected at later stages.
- Access to Healthcare: Disparities in healthcare access can result in fewer regular skin examinations and delayed medical attention.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic factors may increase the risk of melanoma in specific populations.
4.2. Improving Outcomes for People of Color
Addressing disparities in melanoma outcomes requires a multifaceted approach:
- Raising Awareness: Increasing awareness of melanoma risk among people of color through targeted education campaigns.
- Promoting Early Detection: Encouraging regular self-exams and professional skin screenings for early detection.
- Improving Access to Healthcare: Ensuring equitable access to dermatological care for all populations.
- Addressing Cultural Barriers: Overcoming cultural beliefs and societal norms that may delay medical intervention.
4.3. The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in improving melanoma outcomes for people of color. They must be aware of the unique presentation of melanoma in different skin types and be proactive in screening and educating their patients.
5. The #LoveYourSkin Campaign
In memory of Bob Marley, The Skin Cancer Foundation launched the #LoveYourSkin campaign to raise awareness about the dangers of skin cancer, particularly in people of color. This campaign focuses on skin cancer education, early detection, and sun protection. This section will present the #LoveYourSkin campaign.
5.1. Campaign Goals
The goals of the #LoveYourSkin campaign include:
- Increasing awareness of skin cancer risk in people of color.
- Promoting early detection through regular self-exams and professional screenings.
- Encouraging sun protection practices, such as wearing sunscreen and protective clothing.
- Providing resources and information about skin cancer prevention and treatment.
5.2. How to Get Involved
You can get involved in the #LoveYourSkin campaign by:
- Following The Skin Cancer Foundation on social media.
- Sharing posts, facts, and graphics to help spread the word.
- Using the hashtag #LoveYourSkinProtectYourSkin and tagging @SkinCancerOrg.
- Donating to support skin cancer research and education.
5.3. The Power of Collective Action
Together, we can help one another, share the facts, and the love. Because loving your skin means protecting your skin. By raising awareness and promoting early detection, we can save lives and reduce the burden of skin cancer.
6. Understanding Melanoma: Facts and Statistics
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that can be deadly if not detected and treated early. It is important to understand the facts and statistics about melanoma to protect yourself and your loved ones. This section will delve deeper into the facts and statistics about melanoma.
6.1. Incidence Rates
The incidence rate of melanoma has been increasing over the past few decades. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, it is estimated that one in 36 white people will develop melanoma in their lifetime, compared to one in 1,000 Black people and one in 167 Hispanic people. However, melanoma is often diagnosed at a later stage in people of color, leading to poorer outcomes.
6.2. Survival Rates
The five-year survival rate for melanoma is high when detected early. The American Cancer Society states that the five-year survival rate for localized melanoma is around 99%. However, the survival rate decreases significantly when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. This section will address the survival rate.
6.3. Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase your chances of developing melanoma:
- UV Radiation Exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the most significant risk factor.
- Moles: Having many moles or unusual moles (dysplastic nevi) can increase your risk.
- Family History: A family history of melanoma increases your risk.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, freckles, and light hair have a higher risk.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to skin cancer.
| Risk Factor | Description | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| UV Radiation Exposure | Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. | Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, avoid tanning beds. |
| Moles | Having many moles or unusual moles (dysplastic nevi). | Monitor moles for changes, consult a dermatologist for suspicious moles. |
| Family History | A family history of melanoma increases your risk. | Inform your doctor, undergo regular skin screenings. |
| Fair Skin | People with fair skin, freckles, and light hair have a higher risk. | Take extra precautions in the sun, use sunscreen, wear protective clothing. |
| Weakened Immune System | People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to skin cancer. | Follow medical advice, take care of your immune system. |
7. Bob Marley’s Legacy: A Reminder
Bob Marley’s legacy extends far beyond his music. His untimely death serves as a reminder that anyone can develop melanoma, regardless of age, skin tone, or lifestyle. His story underscores the importance of early detection, awareness, and proactive skin care. This section will talk about Bob Marley’s legacy.
7.1. Spreading the Message
By sharing Bob Marley’s story, we can help spread the message about the importance of skin cancer prevention and early detection. We can encourage others to take care of their skin and seek professional help if they notice any suspicious changes.
7.2. Honoring His Memory
In honor of Bob Marley’s memory, let us commit to raising awareness about skin cancer and promoting early detection. By doing so, we can help save lives and prevent others from suffering the same tragic fate.
7.3. Encouraging Proactive Skin Care
Bob Marley’s experience highlights the necessity of adopting a proactive approach to skin care. This involves routine self-examinations, awareness of melanoma risk factors, and seeking timely medical advice for any concerning skin changes. By integrating these practices into our lives, we can enhance our chances of detecting melanoma early and improving treatment outcomes.
8. Common Misconceptions About Melanoma
There are several common misconceptions about melanoma that can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Addressing these misconceptions is essential for promoting early detection and improving outcomes. This section will discuss common misconceptions.
8.1. “Melanoma Only Affects White People”
One of the most pervasive misconceptions is that melanoma only affects white people. While it is true that melanoma is more common in white people, people of color can also develop melanoma, and it is often diagnosed at a later stage, leading to poorer outcomes.
8.2. “You Only Need to Worry About Moles”
Another misconception is that you only need to worry about moles. While moles are a common site for melanoma to develop, melanoma can also appear as a new spot or growth on the skin. It is important to check your entire body for any new, changing, or unusual spots.
8.3. “Sunscreen Is Only Necessary on Sunny Days”
Many people believe that sunscreen is only necessary on sunny days. However, UV radiation can penetrate clouds, so it is important to wear sunscreen even on cloudy days. It is also important to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and to reapply it every two hours.
| Misconception | Fact |
|---|---|
| Melanoma only affects white people | Melanoma can affect people of all skin colors, and is often diagnosed later in people of color. |
| You only need to worry about moles | Melanoma can appear as a new spot or growth on the skin, not just from existing moles. |
| Sunscreen is only necessary on sunny days | UV radiation can penetrate clouds, making sunscreen necessary even on cloudy days. |
| Tanning beds are safer than the sun | Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation that increases the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. |
| Early detection isn’t that important | Early detection is crucial for successful melanoma treatment, with a five-year survival rate of 99% when detected early, versus significantly lower rates later on. |
9. Innovations in Melanoma Treatment
The field of melanoma treatment is constantly evolving, with new innovations offering hope for improved outcomes. This section will highlight some of the latest advancements in melanoma treatment.
9.1. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. It has shown remarkable success in treating advanced melanoma, with some patients experiencing long-term remission.
9.2. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy involves using drugs that specifically target cancer cells. This type of treatment can be effective for melanomas with certain genetic mutations.
9.3. Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that test new treatments for melanoma. Participating in a clinical trial can provide access to cutting-edge therapies and help advance the field of melanoma treatment.
10. Seeking More Answers and Expert Advice at WHY.EDU.VN
Navigating complex health information can be overwhelming, but WHY.EDU.VN is here to help. Our platform is designed to provide clear, reliable answers to your questions and connect you with experts in various fields. Whether you’re seeking deeper insights into melanoma or have other pressing questions, WHY.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources and expert guidance.
10.1. How WHY.EDU.VN Can Help
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding accurate and trustworthy information. Our platform offers:
- Detailed Answers: Comprehensive explanations of complex topics, including melanoma, its causes, and treatments.
- Expert Insights: Access to professionals who can provide in-depth knowledge and personalized advice.
- Reliable Resources: Information sourced from reputable organizations and experts in the field.
- Community Support: A platform for asking questions, sharing experiences, and connecting with others.
10.2. Take the Next Step
Don’t let unanswered questions linger. Visit WHY.EDU.VN today to explore our resources and get the expert answers you need.
10.3. Contact Us
Have a specific question or need further assistance? Reach out to us:
- Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
- Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Let WHY.EDU.VN be your trusted source for knowledge and guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What exactly is acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM)?
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is a rare type of skin cancer that develops on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, or under the nails. It’s different from other melanomas that are mainly caused by sun exposure.
2. Is ALM more common in people of color?
Yes, while ALM is rare overall, it is the most common type of melanoma found in people of color. This is why it’s crucial for everyone to be aware of this type of skin cancer.
3. What were Bob Marley’s treatment options for ALM?
Bob Marley was advised to have his toe amputated to stop the cancer from spreading. He chose to have excisional surgery instead, which involved removing the nail bed and cancerous tissue.
4. Why is early detection so important for melanoma?
Early detection of melanoma is vital because it significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. When melanoma is found early, it’s usually easier to treat and less likely to spread.
5. What are the key signs to look for when checking my skin for melanoma?
When checking your skin, look for the “ABCDE” signs: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter (larger than 6mm), and Evolving (changing in size, shape, or color). Also, be aware of any new, unusual spots.
6. How often should I check my skin for signs of melanoma?
It’s recommended to check your skin once a month. Pay close attention to areas that don’t get much sun exposure, like the soles of your feet and under your nails.
7. Can melanoma be prevented?
While not all melanomas can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by protecting your skin from excessive sun exposure. Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and avoid tanning beds.
8. What should I do if I find a suspicious spot on my skin?
If you find a spot on your skin that concerns you, see a dermatologist right away. They can assess the spot and determine if a biopsy is needed.
9. How is melanoma treated?
Melanoma treatment varies depending on the stage of the cancer. It may include surgery, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
10. Where can I find more reliable information about melanoma?
For more reliable information about melanoma, you can visit the websites of reputable organizations like The Skin Cancer Foundation, the American Academy of Dermatology, and the American Cancer Society, or visit why.edu.vn.
By understanding the facts about melanoma and taking proactive steps to protect your skin, you can reduce your risk and help save lives.