Why can’t I swallow pills? If you find yourself struggling with this common issue, you’re not alone. Many individuals experience difficulty swallowing pills, leading to frustration and potential health risks. At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into the reasons behind this challenge and offer practical strategies to make pill swallowing easier. Explore effective methods and expert advice to overcome this hurdle and maintain your medication routine and learn about swallowing difficulties.
1. Understanding the Difficulty: Why Can’t I Swallow Pills?
The simple act of swallowing a pill can be surprisingly challenging for many people. The reasons behind this difficulty vary, ranging from psychological factors to physical conditions. Understanding these causes is the first step toward finding effective solutions.
1.1. Psychological Factors
Mental and emotional states play a significant role in the ability to swallow pills. Anxiety, fear, and negative past experiences can create a psychological barrier that makes swallowing difficult.
- Anxiety and Fear: The fear of choking or gagging can trigger anxiety, tightening the throat muscles and hindering the swallowing process. This is a common issue, especially for those who have had unpleasant experiences with swallowing pills in the past.
- Negative Past Experiences: A previous choking incident or a particularly large pill can create a lasting aversion to swallowing pills. This can manifest as a conditioned response, where the mere sight of a pill triggers anxiety and difficulty.
- Pill Aversion: Some people develop a general aversion to pills, often due to their taste, texture, or association with illness. This aversion can make the act of swallowing pills a mentally challenging task.
1.2. Physical Factors
Physical conditions and anatomical issues can also contribute to difficulty swallowing pills. These factors may involve the throat, esophagus, or nervous system.
- Dysphagia: This medical condition refers to difficulty swallowing. It can result from various causes, including neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, or muscle weakness. Dysphagia can affect the ability to swallow both food and pills.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Saliva plays a crucial role in lubricating the mouth and throat, making it easier to swallow. Conditions or medications that reduce saliva production can lead to dry mouth, making it difficult for pills to slide down the throat.
- Esophageal Issues: Problems with the esophagus, such as strictures (narrowing), inflammation, or motility disorders, can impede the passage of pills. These issues can cause pills to get stuck or trigger discomfort during swallowing.
- Tonsil Size: Enlarged tonsils can narrow the passage in the throat, making it more difficult to swallow pills, especially larger ones. This is more common in children and young adults.
1.3. Medication-Related Factors
The characteristics of the pills themselves can also contribute to swallowing difficulties. Size, shape, and coating all play a role in how easily a pill goes down.
- Pill Size and Shape: Larger pills are generally more challenging to swallow than smaller ones. Similarly, irregularly shaped pills can be more difficult to manage in the mouth and throat.
- Pill Coating: Some pills have a smooth coating that makes them easier to swallow, while others have a rough or uneven surface that can cause them to stick in the throat.
- Taste: Pills with a bitter or unpleasant taste can trigger a gag reflex, making them harder to swallow.
2. Assessing the Problem: Identifying the Root Cause
Determining the underlying cause of your difficulty swallowing pills is essential for finding the right solution. A thorough assessment may involve consulting with healthcare professionals and considering various diagnostic tests.
2.1. Medical Consultation
Consulting with your primary care physician is a crucial first step. They can evaluate your medical history, perform a physical exam, and assess any underlying health conditions that may be contributing to the problem.
- Medical History Review: Your doctor will ask about your past medical conditions, medications, and any previous swallowing difficulties.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam may include assessing your oral cavity, throat, and neck to identify any structural abnormalities or signs of inflammation.
2.2. Specialist Referrals
Depending on the initial assessment, your doctor may refer you to specialists who can provide more in-depth evaluation and treatment.
- Otolaryngologist (ENT Specialist): An ENT specialist can examine your ears, nose, and throat to identify any structural issues or abnormalities that may be affecting your ability to swallow.
- Speech-Language Pathologist: A speech-language pathologist specializes in swallowing disorders. They can conduct a swallowing assessment and provide therapy to improve swallowing function.
- Gastroenterologist: A gastroenterologist can evaluate the esophagus and gastrointestinal tract to identify any motility disorders or structural issues that may be contributing to swallowing difficulties.
2.3. Diagnostic Tests
Various diagnostic tests can help identify the cause of swallowing difficulties. These tests may include imaging studies, endoscopic procedures, and swallowing assessments.
- Modified Barium Swallow Study (MBSS): This test involves swallowing liquids and solids mixed with barium, a contrast agent that makes them visible on X-rays. The X-rays allow the healthcare provider to observe the swallowing process and identify any abnormalities.
- Endoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the esophagus to visualize its lining and identify any structural issues or inflammation.
- Esophageal Manometry: This test measures the pressure and coordination of the muscles in the esophagus during swallowing. It can help identify motility disorders that may be contributing to swallowing difficulties.
3. Practical Techniques: How to Swallow Pills More Easily
Once you have a better understanding of the reasons behind your difficulty swallowing pills, you can try various practical techniques to make the process easier. These methods focus on improving the mechanics of swallowing and reducing anxiety.
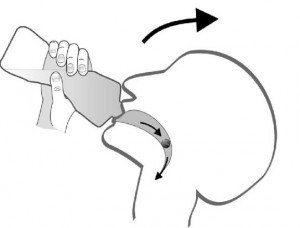
3.1. The Pop-Bottle Method
This technique is designed for swallowing tablets and involves using a plastic bottle to create a sucking motion that aids in swallowing.
- Prepare the Bottle: Fill a plastic water or soda bottle with water.
- Position the Tablet: Place the tablet on your tongue.
- Seal the Bottle: Close your lips tightly around the bottle opening, ensuring a good seal.
- Suck and Swallow: Take a drink, using a sucking motion to draw the water and pill into your throat. Maintain contact between the bottle and your lips and avoid letting air enter the bottle.
The pop-bottle method helps direct the pill towards the throat while minimizing the risk of it getting stuck.
3.2. The Lean-Forward Method
This technique is specifically designed for swallowing capsules and involves tilting your head forward to facilitate the passage of the capsule down the throat.
- Position the Capsule: Place the capsule on your tongue.
- Take a Sip: Take a sip of water but do not swallow yet.
- Tilt Your Chin: Tilt your chin towards your chest, bending your head forward.
- Swallow: Swallow the capsule and water while keeping your head bent forward.
The lean-forward method helps align the throat and esophagus, making it easier for the capsule to slide down.
3.3. Other Helpful Techniques
In addition to the pop-bottle and lean-forward methods, several other techniques can help make swallowing pills easier.
- The “Chin Tuck” Method: Similar to the lean-forward method, this technique involves tucking your chin towards your chest while swallowing. This helps protect the airway and directs the pill towards the esophagus.
- The “Head Rotation” Method: This technique involves turning your head to one side while swallowing. It can be helpful for individuals with weakness on one side of the throat.
- The “Supraglottic Swallow” Method: This technique involves taking a deep breath, holding it, swallowing, and then coughing. It helps clear any residue from the throat and prevent aspiration.
3.4. Modifying the Pill
Sometimes, modifying the pill itself can make it easier to swallow. However, it’s essential to consult with your pharmacist or doctor before making any changes to your medication.
- Crushing Pills: Crushing pills into a powder and mixing them with food or liquid can make them easier to swallow. However, some medications should not be crushed, as this can affect their effectiveness or cause adverse effects.
- Splitting Pills: Splitting pills into smaller pieces can also make them easier to swallow. However, some medications should not be split, as this can affect their dosage or release mechanism.
- Using a Pill Cutter: A pill cutter can help you split pills accurately and safely.
3.5. Changing the Formulation
If you consistently have difficulty swallowing pills, talk to your doctor about alternative formulations of your medication.
- Liquid Medications: Liquid medications are often easier to swallow than pills. They are available for many common medications.
- Chewable Tablets: Chewable tablets are another option for individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills. They can be chewed and swallowed like food.
- Transdermal Patches: Transdermal patches deliver medication through the skin and bypass the need for swallowing altogether.
- Sublingual Tablets: Sublingual tablets are placed under the tongue and dissolve, allowing the medication to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
4. Addressing Psychological Barriers
Psychological factors can significantly impact your ability to swallow pills. Addressing these barriers is crucial for overcoming your difficulty and maintaining your medication routine.
4.1. Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can help reduce anxiety and tension, making it easier to swallow pills.
- Deep Breathing: Deep breathing exercises can help calm your nerves and relax your throat muscles.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in your body to reduce overall tension.
- Meditation: Meditation can help focus your mind and reduce anxiety.
- Visualization: Visualizing yourself swallowing pills successfully can help build confidence and reduce fear.
4.2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a type of therapy that helps you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It can be effective in addressing pill aversion and anxiety related to swallowing.
- Identifying Negative Thoughts: CBT helps you identify negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to your difficulty swallowing pills.
- Challenging Negative Thoughts: CBT teaches you how to challenge and reframe these negative thoughts, replacing them with more positive and realistic ones.
- Behavioral Techniques: CBT incorporates behavioral techniques, such as exposure therapy, to gradually desensitize you to the act of swallowing pills.
4.3. Seeking Support
Talking to a therapist or counselor can provide emotional support and guidance in overcoming your difficulty swallowing pills. Support groups can also be helpful, allowing you to connect with others who share similar challenges.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain lifestyle adjustments can also make it easier to swallow pills. These adjustments focus on maintaining oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and optimizing your posture.
5.1. Oral Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall health and can also help improve your ability to swallow pills.
- Brush Your Teeth Regularly: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day helps remove plaque and bacteria that can contribute to oral health problems.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth, preventing gum disease.
- Use Mouthwash: Using mouthwash can help kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
5.2. Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining adequate saliva production, which is essential for swallowing.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Avoid Dehydrating Beverages: Limit your intake of caffeine and alcohol, as they can dehydrate you.
- Use a Humidifier: Using a humidifier can help keep your mouth and throat moist.
5.3. Posture
Maintaining proper posture while swallowing can also make it easier for pills to go down.
- Sit Upright: Sit upright with your back straight and your head slightly tilted forward.
- Avoid Lying Down: Avoid lying down while swallowing pills, as this can make it more difficult for them to pass through the throat.
6. When to Seek Professional Help
While many cases of difficulty swallowing pills can be managed with self-help techniques, it’s essential to seek professional help if you experience certain symptoms or if your difficulty persists.
6.1. Warning Signs
Seek medical attention if you experience any of the following warning signs:
- Frequent Choking or Gagging: Frequent choking or gagging while swallowing can indicate a more serious underlying problem.
- Pain or Discomfort: Pain or discomfort while swallowing can be a sign of inflammation or structural abnormalities.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of an underlying medical condition that is affecting your ability to eat and swallow.
- Recurring Pneumonia: Recurring pneumonia can be a sign of aspiration, where food or liquid enters the lungs.
- Voice Changes: Changes in your voice, such as hoarseness or a raspy voice, can be a sign of a swallowing disorder.
6.2. Professional Evaluation
If you experience any of these warning signs, your doctor may recommend a professional evaluation by a specialist. This evaluation may include diagnostic tests to identify the cause of your swallowing difficulties.
7. Expert Opinions and Research
Research and expert opinions provide valuable insights into the causes and treatments for difficulty swallowing pills.
7.1. Studies and Findings
Several studies have investigated the prevalence and causes of difficulty swallowing pills. These studies have shown that it is a common problem that can affect people of all ages.
- A study published in the Annals of Family Medicine found that using the pop-bottle and lean-forward methods significantly improved the ability to swallow pills in individuals with difficulty swallowing.
- Research has also shown that psychological factors, such as anxiety and fear, play a significant role in difficulty swallowing pills.
- Studies have identified various physical conditions, such as dysphagia and dry mouth, as contributing factors to swallowing difficulties.
7.2. Expert Recommendations
Experts recommend a multifaceted approach to managing difficulty swallowing pills, including:
- Identifying and addressing underlying psychological factors.
- Using practical techniques to improve the mechanics of swallowing.
- Modifying the pill or changing the formulation, when appropriate.
- Seeking professional help when necessary.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why do I have trouble swallowing pills but not food?
A: This could be due to the size and shape of the pill, psychological factors like anxiety related to taking medication, or a mild form of dysphagia that only affects pill swallowing.
Q2: Is it safe to crush my pills to make them easier to swallow?
A: Not all pills can be crushed safely. Some medications are time-released or enteric-coated, and crushing them can affect their efficacy or cause side effects. Always consult with your pharmacist or doctor before crushing any medication.
Q3: Can dry mouth cause difficulty swallowing pills?
A: Yes, dry mouth (xerostomia) reduces saliva production, which is essential for lubricating the mouth and throat, making it harder to swallow pills.
Q4: What is dysphagia, and how does it affect pill swallowing?
A: Dysphagia is a medical condition characterized by difficulty swallowing. It can result from various causes, including neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, or muscle weakness, making it difficult to swallow both food and pills.
Q5: Are there alternative forms of medication available if I can’t swallow pills?
A: Yes, many medications are available in alternative forms, such as liquids, chewable tablets, transdermal patches, and sublingual tablets. Talk to your doctor about these options.
Q6: Can anxiety make it harder to swallow pills?
A: Yes, anxiety and fear can tighten the throat muscles and hinder the swallowing process, making it more difficult to swallow pills.
Q7: What is the pop-bottle method for swallowing pills?
A: The pop-bottle method involves filling a plastic bottle with water, placing the tablet on your tongue, sealing your lips around the bottle opening, and using a sucking motion to swallow the water and pill.
Q8: What is the lean-forward method for swallowing pills?
A: The lean-forward method involves placing the capsule on your tongue, taking a sip of water, tilting your chin towards your chest, and swallowing the capsule and water while keeping your head bent forward.
Q9: When should I see a doctor about my difficulty swallowing pills?
A: Seek medical attention if you experience frequent choking or gagging, pain or discomfort while swallowing, unexplained weight loss, recurring pneumonia, or voice changes.
Q10: Where can I find more information and support for difficulty swallowing pills?
A: You can find more information and support at WHY.EDU.VN, where experts provide detailed answers and guidance on various health-related topics. Additionally, consider consulting with healthcare professionals and support groups for personalized assistance.
9. Resources and Support
Navigating the challenges of difficulty swallowing pills can be easier with the right resources and support.
- WHY.EDU.VN: At WHY.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing accurate and reliable information to help you understand and overcome your health challenges. Our website offers a wealth of articles, expert advice, and community support to empower you on your health journey. Visit us at WHY.EDU.VN to explore our resources and connect with our community.
- Healthcare Professionals: Consulting with healthcare professionals, such as doctors, pharmacists, and speech-language pathologists, is crucial for personalized guidance and treatment.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and connect you with others who share similar challenges.
10. Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Pill-Swallowing Difficulties
Dealing with difficulty swallowing pills can be frustrating, but understanding the causes and implementing effective techniques can help you overcome this challenge. From psychological factors to physical conditions, addressing the root cause is essential for finding the right solution. By exploring practical techniques, lifestyle adjustments, and professional support, you can take control of your pill-swallowing difficulties and maintain your medication routine.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Many people experience difficulty swallowing pills, and there are resources available to help you. At WHY.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing the information and support you need to navigate your health challenges with confidence.
Do you have questions about why you can’t swallow pills or need expert advice? Visit why.edu.vn today and connect with our community of experts. Our team is here to provide you with the answers and support you need to overcome your health challenges.
Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Your health is our priority, and we’re here to help you every step of the way.