Why aren’t my messages sending? If you’re grappling with messaging issues on your iPhone, Android or other device, WHY.EDU.VN offers comprehensive troubleshooting steps to get you back on track. This guide delves into common causes like network connectivity, incorrect settings, and device-specific problems, providing effective solutions for seamless communication. Explore the nuances of SMS, MMS, RCS, and iMessage, along with expert tips for resolving delivery failures and optimizing your messaging experience.
1. Identifying the Root Cause: Why Aren’t My Messages Sending?
The frustration of unsent messages is universal. Several factors can contribute to this problem, ranging from simple connectivity issues to more complex software glitches. Before diving into solutions, let’s pinpoint the potential culprits:
-
Network Issues: A weak or unstable internet connection is a primary suspect.
-
Service Outages: Carrier-related outages can temporarily disrupt messaging services.
-
Incorrect Settings: Misconfigured settings on your device can prevent messages from being sent.
-
App-Specific Problems: Glitches within the messaging app itself may be the cause.
-
Device-Related Issues: Sometimes, the problem lies within the device’s hardware or software.
1.1 Network Connectivity: The Foundation of Messaging
A stable network connection is crucial for sending messages, especially for data-dependent services like iMessage, WhatsApp, and RCS.
Troubleshooting Steps
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Check Wi-Fi | Ensure you’re connected to a stable Wi-Fi network. Try restarting your router or connecting to a different network. |
| Cellular Data | Verify that cellular data is enabled and that you have sufficient data allowance. |
| Airplane Mode | Make sure Airplane Mode is turned off. This mode disables all wireless communications, including cellular and Wi-Fi. |
| Network Reset | Reset your network settings to default. This can resolve issues caused by incorrect configurations. |
| Speed Test | Run a speed test to check your internet speed. If the speed is significantly lower than expected, contact your internet provider. |
| Signal Strength | Check your cellular signal strength. A weak signal can prevent messages from sending. |
1.2 Service Disruptions: When the Carrier is the Culprit
Sometimes, the issue isn’t on your end. Carrier-related service outages can temporarily disrupt messaging services, preventing you from sending or receiving messages.
How to Check for Outages
-
Carrier’s Website: Visit your carrier’s official website to check for any reported outages in your area.
-
Social Media: Monitor your carrier’s social media accounts (e.g., Twitter, Facebook) for real-time updates.
-
Down Detector: Use websites like Down Detector to see if other users are reporting issues with your carrier’s services.
-
Contact Support: Call your carrier’s customer support line to inquire about potential outages.
1.3 Configuration Errors: Diving into Device Settings
Incorrect settings on your device can interfere with messaging functionality. This could involve iMessage settings on iPhones, SMS settings on Android devices, or network configurations.
Common Settings to Check
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| iMessage (iOS) | Ensure iMessage is enabled and correctly configured. Check your registered phone number and Apple ID. |
| SMS Center Number | Verify the SMS center number is correctly configured in your device’s settings. Contact your carrier for the correct number. |
| Preferred Network Type | Select the appropriate network type (e.g., 4G, 5G) based on your carrier’s support and coverage in your area. |
| Roaming Settings | If you’re traveling, ensure data roaming is enabled if required by your plan. |
| APN Settings | Access Point Name (APN) settings define how your device connects to the carrier’s network. Ensure these settings are correctly configured. |
| Date and Time | Incorrect date and time settings can interfere with network connections and message delivery. Enable automatic date and time synchronization. |
1.4 Application Glitches: When the App Misbehaves
Sometimes, the problem lies within the messaging app itself. App glitches, bugs, or outdated versions can prevent messages from sending.
Troubleshooting Steps
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Restart the App | Force-close the messaging app and reopen it. This can resolve minor glitches. |
| Clear App Cache | Clear the app’s cache to remove temporary files that may be causing issues. |
| Update the App | Ensure you have the latest version of the messaging app. Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements. |
| Reinstall the App | Uninstall and reinstall the app to resolve more persistent issues. |
| Try Another App | If the issue persists, try using a different messaging app to see if the problem is specific to the original app. |
1.5 Device-Specific Issues: Digging Deeper
In some cases, the problem might be related to your device’s hardware or software. This could involve outdated operating systems, storage issues, or more complex hardware malfunctions.
Potential Device-Related Problems
-
Outdated OS: Ensure your device is running the latest version of its operating system (iOS, Android, etc.).
-
Storage Issues: Insufficient storage space can prevent messages from being sent or received.
-
Hardware Malfunctions: In rare cases, hardware issues with the device’s modem or antenna can cause messaging problems.
-
Software Conflicts: Conflicts between different apps or system processes can interfere with messaging functionality.
2. Deciphering Error Messages: Understanding the Clues
Error messages are your allies in troubleshooting. They provide valuable insights into why your messages aren’t sending. Here’s a breakdown of common error messages and their implications:
-
“Message Not Delivered”: This generic error indicates that the message failed to reach the recipient.
-
“Waiting for Activation”: This message typically appears when iMessage or FaceTime is not properly activated on your device.
-
“SMS Not Sent”: This error indicates that the SMS message failed to send, usually due to network issues or incorrect settings.
-
“Invalid Destination Address”: This error means that the phone number or email address you’re trying to send the message to is not valid.
-
“No Service”: This error indicates that your device is not connected to a cellular network, preventing you from sending SMS or MMS messages.
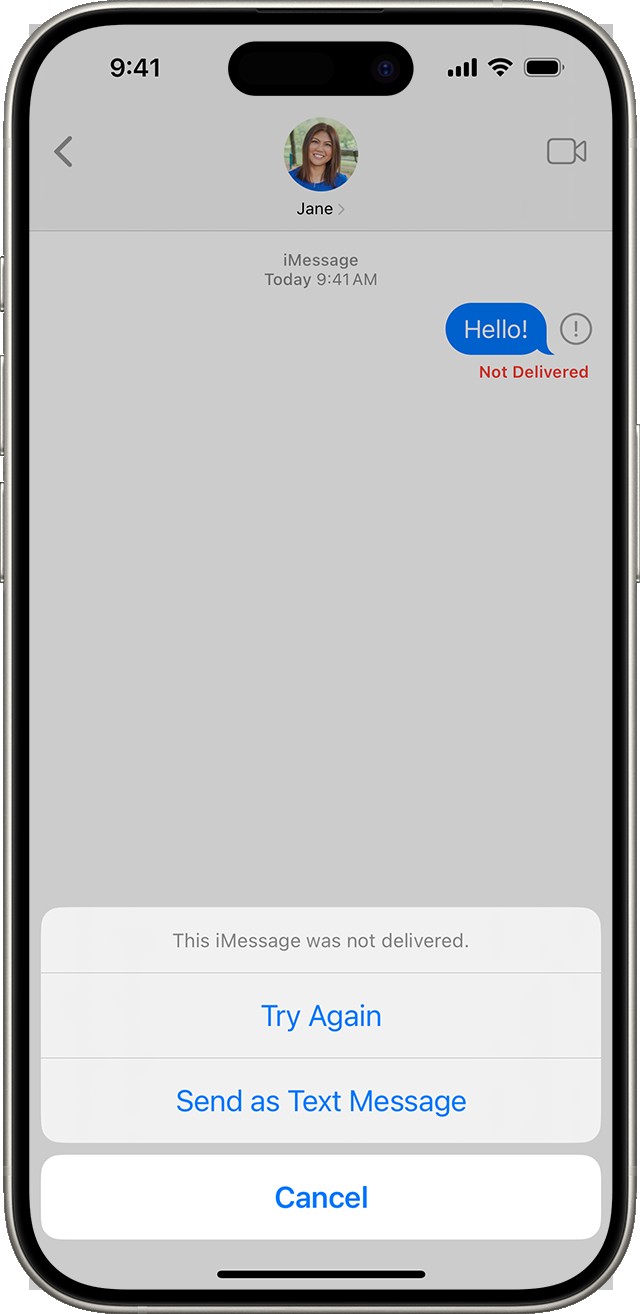
2.1 The Red Exclamation Point: A Universal Symbol of Failure
The red exclamation point is a common sight when messages fail to send, particularly on iPhones using iMessage. This icon indicates a delivery failure and prompts you to take action.
Actions to Take When You See the Red Exclamation Point
- Check Network Connection: Verify that you have a stable internet connection, either through Wi-Fi or cellular data.
- Tap “Try Again”: Tap the red exclamation point and select “Try Again” to resend the message.
- “Send as Text Message”: If resending fails, tap the red exclamation point again and choose “Send as Text Message” to send the message via SMS.
- Contact Recipient: If all else fails, contact the recipient through another means (e.g., phone call, email) to ensure they received the message.
2.2 Decoding “Waiting for Activation”: Resolving iMessage Issues
The “Waiting for Activation” message can be particularly frustrating, as it often appears when you’re trying to set up iMessage on a new device or after a software update. This message indicates that iMessage is not properly activated on your device, preventing you from sending or receiving iMessages.
Steps to Resolve “Waiting for Activation”
- Check Internet Connection: Ensure your device is connected to a stable Wi-Fi or cellular data network.
- Verify Apple ID: Make sure you’re signed in to your Apple ID in the Settings app.
- Date and Time Settings: Set your device’s date and time settings to “Automatic.”
- Toggle iMessage Off and On: In the Settings app, go to Messages and toggle iMessage off and then back on.
- Restart Your Device: Restart your iPhone or iPad to refresh the system and resolve any temporary glitches.
- Contact Apple Support: If the issue persists, contact Apple Support for further assistance.
2.3 Understanding SMS Failures: Addressing Text Message Issues
SMS (Short Message Service) is the foundation of text messaging, allowing you to send and receive messages over the cellular network. When SMS messages fail to send, it’s usually due to network issues, incorrect settings, or problems with the recipient’s device or carrier.
Troubleshooting SMS Sending Issues
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| SMS Not Sent | Network issues, incorrect SMS center number, recipient’s device is off or out of coverage. | Check network connection, verify SMS center number, contact recipient through another means. |
| Invalid Destination Address | Incorrect phone number, recipient’s number is no longer in service, country code is missing or incorrect. | Double-check the phone number, confirm the number is still active, ensure the correct country code is included. |
| Message Blocking | Recipient has blocked your number, carrier is blocking your messages due to suspected spam. | Contact the recipient to unblock your number, contact your carrier to investigate potential message blocking. |
| Insufficient Credit | Prepaid account has insufficient credit to send SMS messages. | Top up your prepaid account to ensure you have sufficient credit. |
3. The iMessage Ecosystem: Navigating Apple’s Messaging Service
iMessage is Apple’s proprietary messaging service, offering features like end-to-end encryption, read receipts, and high-quality image and video sharing. However, iMessage can also be a source of frustration when it doesn’t work as expected.
3.1 Blue vs. Green Bubbles: Understanding iMessage Status
The color of the message bubble in the Messages app provides valuable information about the type of message being sent.
-
Blue Bubbles: Indicate iMessages, which are sent over Wi-Fi or cellular data to other Apple devices.
-
Green Bubbles: Indicate SMS/MMS messages, which are sent over the cellular network and require a text messaging plan.
If your messages are consistently appearing as green bubbles when sending to other iPhone users, it could indicate a problem with iMessage activation or connectivity.
3.2 Troubleshooting iMessage Activation Issues
iMessage activation issues can prevent you from sending or receiving iMessages, causing your messages to be sent as SMS instead.
Common Causes of iMessage Activation Issues
- Incorrect Apple ID: Ensure you’re signed in to the correct Apple ID in the Settings app.
- Network Connectivity: A weak or unstable internet connection can prevent iMessage from activating.
- Date and Time Settings: Incorrect date and time settings can interfere with iMessage activation.
- Software Glitches: Temporary software glitches can sometimes prevent iMessage from activating properly.
3.3 Addressing iMessage Delivery Failures
Even when iMessage is activated correctly, messages can still fail to deliver due to various reasons.
Potential Causes of iMessage Delivery Failures
- Recipient’s Device is Offline: If the recipient’s device is turned off or not connected to the internet, the iMessage may not be delivered.
- Recipient’s iMessage is Disabled: If the recipient has disabled iMessage on their device, your messages will be sent as SMS instead.
- Network Issues: Network problems on either your end or the recipient’s end can prevent iMessages from being delivered.
- iMessage Server Issues: In rare cases, issues with Apple’s iMessage servers can cause delivery failures.
4. The Android Messaging Landscape: SMS, MMS, and RCS
Android devices offer a variety of messaging options, including SMS, MMS, and RCS (Rich Communication Services). Understanding these different technologies is crucial for troubleshooting messaging issues on Android.
4.1 SMS vs. MMS: Understanding the Differences
SMS (Short Message Service) and MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) are two distinct messaging technologies used on Android devices.
| Feature | SMS | MMS |
|---|---|---|
| Message Type | Text-based messages | Multimedia messages (images, videos, audio) |
| Message Size | Limited to 160 characters | Larger message size limits |
| Network | Cellular network | Cellular network or Wi-Fi |
| Cost | Typically lower cost | Typically higher cost |
4.2 Embracing RCS: The Future of Android Messaging
RCS (Rich Communication Services) is the next-generation messaging protocol for Android, offering features similar to iMessage, such as read receipts, typing indicators, and high-quality media sharing.
Benefits of RCS Messaging
- Enhanced Features: RCS offers a richer messaging experience with features like read receipts, typing indicators, and group chats.
- High-Quality Media: RCS allows you to send and receive high-resolution images and videos.
- Improved Security: RCS supports end-to-end encryption, providing enhanced security for your messages.
- Universal Compatibility: RCS is designed to be a universal messaging standard, working across different Android devices and carriers.
4.3 Troubleshooting Android Messaging Issues
Android messaging issues can stem from various sources, including network problems, incorrect settings, and app-specific glitches.
Common Android Messaging Problems and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| SMS Not Sending | Network issues, incorrect SMS center number, recipient’s device is off or out of coverage. | Check network connection, verify SMS center number, contact recipient through another means. |
| MMS Not Sending | Network issues, incorrect APN settings, message size exceeds carrier limits. | Check network connection, verify APN settings, compress the media file or send a lower-quality version. |
| RCS Not Working | RCS is not enabled on your device, carrier does not support RCS, network issues. | Enable RCS in the Messages app settings, contact your carrier to confirm RCS support, check network connection. |
| Messages Not Receiving | Network issues, message blocking, insufficient storage space, outdated messaging app. | Check network connection, verify that you haven’t blocked the sender, free up storage space, update the messaging app. |
5. Beyond the Basics: Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If you’ve tried the basic troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing messaging issues, it’s time to delve into more advanced techniques.
5.1 Resetting Network Settings: A Clean Slate
Resetting your network settings can resolve issues caused by incorrect configurations or corrupted data. This process will erase all saved Wi-Fi passwords, VPN settings, and cellular configurations, so be sure to have this information readily available before proceeding.
How to Reset Network Settings
- iOS: Go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Reset > Reset Network Settings.
- Android: The process may vary depending on your device manufacturer, but typically it can be found under Settings > General management > Reset > Reset network settings.
5.2 Clearing App Cache and Data: A Fresh Start
Clearing the cache and data of your messaging app can resolve issues caused by temporary files or corrupted data. This will remove all saved messages, settings, and preferences, so be sure to back up any important data before proceeding.
How to Clear App Cache and Data
- iOS: Since iOS doesn’t allow you to directly clear app cache, you’ll need to uninstall and reinstall the app.
- Android: Go to Settings > Apps > [Your Messaging App] > Storage > Clear Cache and Clear Data.
5.3 Checking for Software Updates: Keeping Your Device Current
Outdated software can cause various issues, including messaging problems. Ensure your device is running the latest version of its operating system (iOS, Android, etc.) to benefit from bug fixes, performance improvements, and security updates.
How to Check for Software Updates
- iOS: Go to Settings > General > Software Update.
- Android: Go to Settings > Software update or System update.
6. Carrier-Specific Solutions: Addressing Network-Related Issues
Sometimes, the problem lies with your carrier’s network or services. In such cases, contacting your carrier’s customer support line is the best course of action.
6.1 Verifying SMS Center Number: Ensuring Correct Configuration
The SMS center number is a crucial setting that allows your device to send SMS messages. An incorrect SMS center number can prevent you from sending text messages.
How to Verify the SMS Center Number
- Contact Your Carrier: The most reliable way to obtain the correct SMS center number is to contact your carrier’s customer support line.
- Online Resources: Some websites and forums may list SMS center numbers for different carriers, but it’s always best to confirm the information with your carrier directly.
6.2 Checking APN Settings: Configuring Data Connectivity
APN (Access Point Name) settings define how your device connects to your carrier’s cellular data network. Incorrect APN settings can prevent you from sending MMS messages or using data-dependent messaging services like RCS.
How to Check APN Settings
- Contact Your Carrier: The most accurate way to obtain the correct APN settings is to contact your carrier’s customer support line.
- Online Resources: Some websites and forums may list APN settings for different carriers, but it’s crucial to verify the information with your carrier directly.
6.3 Reporting Service Outages: Contributing to Resolution
If you suspect a service outage is affecting your messaging services, report it to your carrier. This helps them identify and resolve the issue more quickly.
How to Report a Service Outage
- Carrier’s Website: Visit your carrier’s official website and look for a section to report service outages.
- Social Media: Contact your carrier through their social media channels (e.g., Twitter, Facebook).
- Customer Support: Call your carrier’s customer support line and report the outage.
7. When to Seek Professional Help: Identifying Hardware Issues
If you’ve exhausted all troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing messaging issues, it’s possible that your device has a hardware problem. In such cases, seeking professional help from a qualified technician is the best course of action.
7.1 Identifying Potential Hardware Problems
Hardware problems can manifest in various ways, including:
- Inability to Connect to Cellular Network: If your device consistently fails to connect to the cellular network, it could indicate a problem with the modem or antenna.
- Weak Signal Strength: Consistently weak signal strength, even in areas with good coverage, could suggest a hardware issue.
- Intermittent Connectivity: If your device frequently loses connection to the cellular network or Wi-Fi, it could be a sign of a hardware problem.
- Physical Damage: Visible physical damage to your device, such as a cracked screen or bent frame, could affect its messaging capabilities.
7.2 Finding a Qualified Technician
When seeking professional help, it’s crucial to find a qualified technician who has experience repairing your specific device model.
Tips for Finding a Qualified Technician
- Authorized Service Centers: Look for authorized service centers that are certified by your device manufacturer (e.g., Apple, Samsung).
- Read Reviews: Check online reviews and ratings to gauge the technician’s reputation and expertise.
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations.
- Inquire About Experience: Ask the technician about their experience repairing your specific device model.
8. Proactive Measures: Preventing Messaging Issues in the Future
While troubleshooting is essential, preventing messaging issues in the first place is even better. Here are some proactive measures you can take to minimize the risk of encountering messaging problems:
- Keep Your Device Updated: Regularly update your device’s operating system and apps to benefit from bug fixes, performance improvements, and security updates.
- Manage Storage Space: Keep your device’s storage space under control by deleting unnecessary files and apps.
- Monitor Network Connectivity: Pay attention to your network connection and ensure you have a stable signal strength.
- Avoid Unreliable Apps: Be cautious when installing apps from untrusted sources, as they may contain malware or interfere with your device’s functionality.
- Back Up Your Data: Regularly back up your data to prevent data loss in case of device malfunction or software issues.
8.1 Optimizing Your Messaging App Settings
Taking the time to optimize your messaging app settings can significantly improve your messaging experience and prevent potential issues.
Key Messaging App Settings to Configure
- Notification Preferences: Customize your notification preferences to receive alerts for important messages while minimizing distractions.
- Privacy Settings: Adjust your privacy settings to control who can see your online status, read receipts, and profile information.
- Storage Management: Configure your app’s storage management settings to automatically delete old messages and attachments, freeing up storage space.
- Backup and Restore: Enable backup and restore features to protect your messages in case of device loss or software issues.
8.2 Maintaining a Clean Device: Preventing Software Conflicts
Software conflicts can interfere with messaging functionality. Maintaining a clean device by regularly removing unnecessary files and apps can help prevent such conflicts.
Tips for Maintaining a Clean Device
- Uninstall Unused Apps: Regularly uninstall apps that you no longer use.
- Delete Unnecessary Files: Delete unnecessary photos, videos, and documents.
- Clear Browser Cache: Clear your browser’s cache and cookies to remove temporary files.
- Use a Cleaning App: Consider using a reputable cleaning app to remove junk files and optimize your device’s performance.
9. Expert Insights: Understanding Messaging Protocols
To truly understand why your messages aren’t sending, it’s helpful to have a basic understanding of the different messaging protocols involved.
9.1 The Role of SMS, MMS, RCS, and iMessage
Each messaging protocol has its own strengths and limitations.
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| SMS | Short Message Service: The basic text messaging protocol that allows you to send and receive text messages over the cellular network. |
| MMS | Multimedia Messaging Service: An extension of SMS that allows you to send and receive multimedia messages, such as images, videos, and audio files. |
| RCS | Rich Communication Services: The next-generation messaging protocol for Android, offering features similar to iMessage, such as read receipts, typing indicators, and encryption. |
| iMessage | Apple’s proprietary messaging service that allows you to send and receive messages over Wi-Fi or cellular data to other Apple devices. |
9.2 How Messaging Protocols Interact
Understanding how these protocols interact can help you diagnose messaging issues. For example, if you’re trying to send an image to an Android user from an iPhone, the message will be sent as MMS instead of iMessage.
10. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Messaging
There are many misconceptions about messaging that can lead to confusion and frustration. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones:
- “iMessage Only Works With iPhones”: While iMessage is primarily designed for Apple devices, it can also be used on Macs and iPads.
- “SMS is Always Free”: SMS messages are not always free. Depending on your carrier plan, you may be charged for each SMS message you send or receive.
- “RCS is Available on All Android Devices”: While RCS is the future of Android messaging, it’s not yet available on all Android devices.
- “Blocking a Number Prevents All Communication”: Blocking a number prevents phone calls and text messages, but it doesn’t necessarily prevent communication through other apps or platforms.
10.1 Separating Fact from Fiction: Common Messaging Myths
It’s crucial to separate fact from fiction when it comes to messaging. Relying on misinformation can lead to incorrect troubleshooting steps and unnecessary frustration.
Common Messaging Myths Debunked
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| “More bars of signal means faster data.” | Signal strength indicates the strength of the cellular signal, but it doesn’t necessarily correlate with data speed. Network congestion and other factors can also affect data speed. |
| “Closing apps saves battery life.” | Closing apps doesn’t always save battery life. In some cases, it can actually drain more battery, as the app needs to be reloaded each time you open it. |
| “Clearing cache improves performance.” | Clearing cache can improve performance in some cases, but it can also have a negative impact if it removes important data that the app needs to function properly. |
| “Using Wi-Fi is always faster than data.” | Wi-Fi is not always faster than data. The speed of your Wi-Fi connection depends on various factors, such as the router’s capabilities, network congestion, and the distance from the router. |
If you’re tired of unreliable answers and endless searching, visit WHY.EDU.VN today! Our platform connects you with experts who can provide accurate, detailed solutions to all your questions. Whether it’s a tech issue, a complex academic problem, or just a burning curiosity, WHY.EDU.VN is your trusted source for knowledge. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States or via Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101. Start exploring at why.edu.vn and experience the power of verified answers!
 Smartphone displaying message failure
Smartphone displaying message failure
FAQ: Addressing Common Messaging Questions
1. Why are my messages sending as SMS instead of iMessage?
This usually happens when the recipient doesn’t have iMessage enabled, or when there’s a problem with your internet connection or iMessage activation.
2. How do I fix the “Waiting for Activation” error on iMessage?
Ensure you have a stable internet connection, verify your Apple ID, set your date and time to “Automatic,” toggle iMessage off and on, and restart your device.
3. What is RCS messaging, and how is it different from SMS?
RCS (Rich Communication Services) is the next-generation messaging protocol for Android, offering features like read receipts, typing indicators, and high-quality media sharing, unlike the basic text-only SMS.
4. How do I enable RCS messaging on my Android phone?
Open the Messages app, tap the three dots in the upper right corner, go to Settings > Chat features, and toggle “Enable chat features” on.
5. Why can’t I send pictures via text message on my Android phone?
This could be due to network issues, incorrect APN settings, or message size limits imposed by your carrier.
6. How do I check my SMS center number on my iPhone or Android phone?
The SMS center number is typically configured automatically by your carrier. Contact your carrier’s customer support line for assistance.
7. What should I do if I can’t receive text messages on my phone?
Check your network connection, verify that you haven’t blocked the sender, free up storage space, and update your messaging app.
8. How do I block unwanted text messages on my iPhone or Android phone?
On iPhone, open the message, tap the contact icon, tap “info,” and then tap “Block this Caller.” On Android, open the message, tap the three dots in the upper right corner, and then tap “Block number.”
9. Why are my group messages not working on my iPhone or Android phone?
This could be due to network issues, incorrect group messaging settings, or problems with the participants’ devices.
10. How do I troubleshoot messaging issues when traveling internationally?
Ensure data roaming is enabled if required by your plan, verify your APN settings, and contact your carrier if you experience any issues.