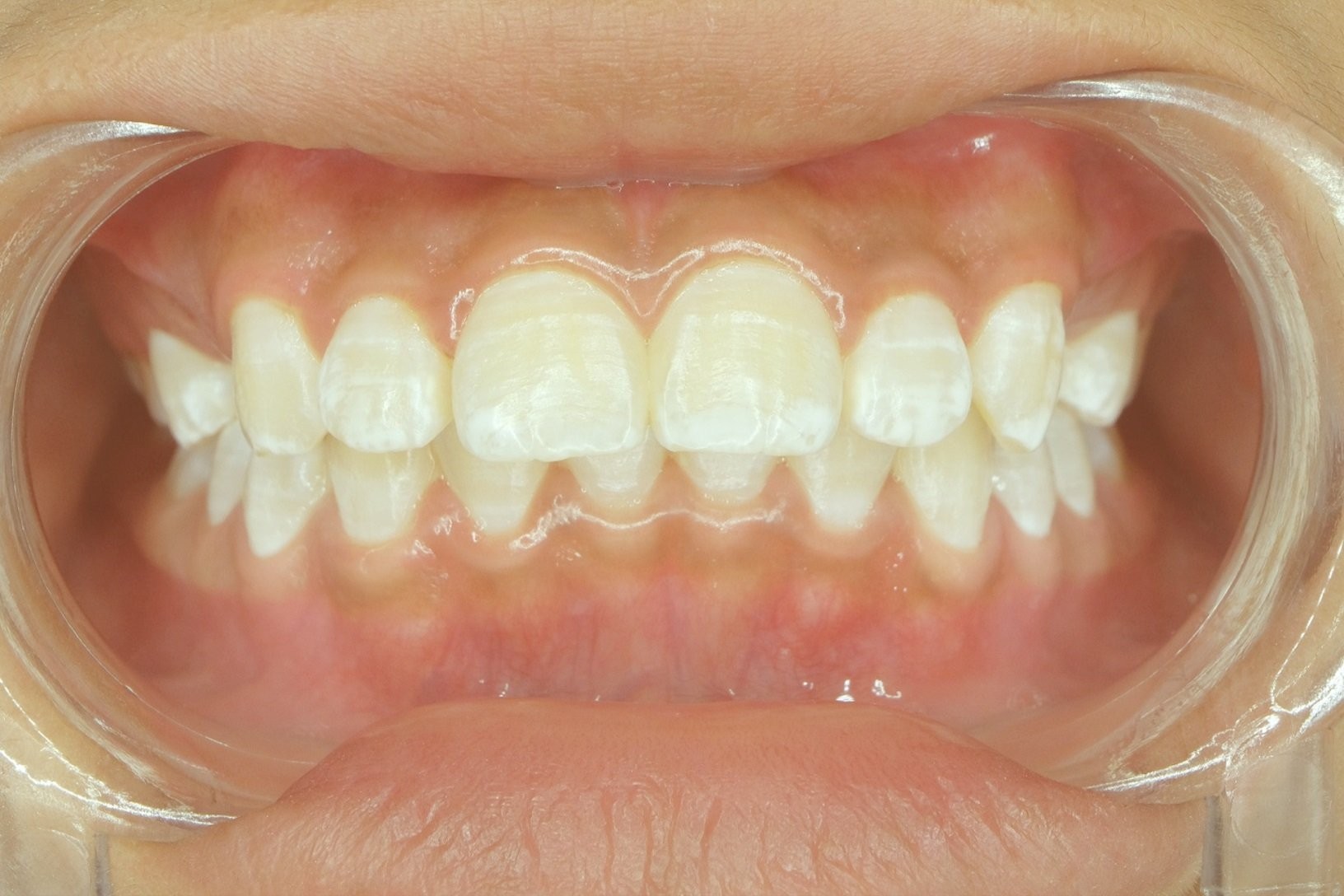
White spots on your teeth can be concerning, even if you maintain a good oral hygiene routine. While brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups are crucial, various factors can still lead to these unsightly marks. Understanding the underlying causes of white spots is essential for effective treatment and preventing future oral health issues.
Common Causes of White Spots on Teeth
Several factors contribute to the development of white spots on teeth, ranging from dietary habits to underlying medical conditions.
1. Demineralization and Early Tooth Decay
Demineralization occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to mineral loss. This process often manifests as white spots, signaling the early stages of tooth decay. These spots are often chalky in appearance and may be more susceptible to further decay.
2. Enamel Hypoplasia (Turner’s Tooth)
Enamel hypoplasia is a developmental defect characterized by thin or improperly formed enamel. This condition can result from various factors, including:
- Nutritional deficiencies during tooth development
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy
- Premature birth
- High fever during childhood illnesses
Turner’s tooth can present as white spots or pits on the tooth surface, making teeth more vulnerable to sensitivity and decay.
3. Fluorosis
While fluoride is beneficial for strengthening teeth, excessive exposure during tooth development can lead to fluorosis. This condition causes white spots or streaks on the enamel. Common sources of excess fluoride include:
- Drinking water with high fluoride levels
- Swallowing toothpaste
- Fluoride supplements
Treatment Options for White Spots
Treatment for white spots depends on the underlying cause.
Demineralization:
- Improved oral hygiene: Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and daily flossing are crucial.
- Professional fluoride treatments: Your dentist may recommend fluoride gels or varnishes to remineralize the enamel.
- Dental fillings: If decay has progressed, fillings may be necessary to restore the tooth structure.
Enamel Hypoplasia:
- Monitoring: If the spots are not causing decay or sensitivity, monitoring may be sufficient.
- Cosmetic treatments: Teeth whitening or dental veneers can improve the appearance of the spots if they are a cosmetic concern.
Fluorosis:
- Reduced fluoride intake: Switching to bottled water or using a fluoride-free toothpaste can help prevent further discoloration.
- Cosmetic dentistry: In severe cases, treatments like teeth whitening, veneers, or crowns can address the discoloration.
Preventing White Spots on Teeth
Preventing white spots involves addressing the underlying causes:
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks: These contribute to demineralization.
- Rinse with water after eating or drinking: This helps neutralize acids in the mouth.
- Use the appropriate amount of fluoride: Children should use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste and be supervised while brushing.
- Regular dental checkups: Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing and treating white spots.
Conclusion
White spots on your teeth can have various causes, but understanding the underlying reasons allows for appropriate treatment and prevention. By practicing good oral hygiene, limiting sugary and acidic foods, and seeking regular dental care, you can minimize your risk of developing white spots and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile. Consult with your dentist to determine the cause of your white spots and develop a personalized treatment plan.