Why Are Russian And Ukraine Fighting is a question on the minds of many, as the conflict has far-reaching global implications; explore the complexities of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, addressing the key factors driving this ongoing dispute and providing expert insights, only on WHY.EDU.VN. Delve into the historical context, geopolitical strategies, and humanitarian consequences of this crisis.
1. Historical Context of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
The Russia-Ukraine conflict didn’t erupt overnight; it’s deeply rooted in a complex history that spans centuries, with periods of cooperation, conflict, and shifting alliances. Understanding this historical context is crucial to grasping the underlying tensions and motivations driving the current crisis.
1.1. Early History and Cultural Ties
The shared history of Russia and Ukraine dates back to the medieval period, with the emergence of the East Slavic civilization centered in Kyiv. This civilization, known as Kyivan Rus’, laid the foundation for both modern Ukrainian and Russian identities, sharing a common language, culture, and religion.
- 9th-13th Centuries: Kyivan Rus’ flourishes as a major political and cultural center in Eastern Europe.
- 988: Prince Vladimir the Great of Kyiv adopts Christianity as the state religion, a pivotal moment that shaped the religious landscape of both Ukraine and Russia.
- 13th Century: The Mongol invasion leads to the decline of Kyivan Rus’, and the territory is divided among various regional powers.
1.2. Periods of Polish and Russian Influence
Over the centuries, Ukrainian lands were contested and divided between various empires, including Poland, Lithuania, and Russia. This period saw the emergence of a distinct Ukrainian identity, language, and culture, despite being under foreign rule.
- 14th-18th Centuries: Ukrainian territories are divided between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia.
- 1654: The Treaty of Pereyaslav leads to a partial integration of Ukrainian lands into the Russian Tsardom.
- 18th Century: The Russian Empire gradually absorbs most of Ukrainian territory, suppressing Ukrainian language and culture.
1.3. The Rise of Ukrainian Nationalism
The 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the rise of Ukrainian nationalism, as Ukrainians sought to assert their national identity and gain independence from foreign rule. This period saw the emergence of Ukrainian political movements and cultural organizations that advocated for greater autonomy and self-determination.
- 19th Century: Ukrainian intellectuals and writers begin to promote Ukrainian language and culture, fostering a sense of national identity.
- Early 20th Century: Ukrainian political parties and organizations emerge, advocating for greater autonomy within the Russian Empire.
1.4. The Soviet Era and Ukrainian Independence
The collapse of the Russian Empire in 1917 led to a brief period of Ukrainian independence, but this was short-lived as Ukraine became a battleground in the Russian Civil War. Eventually, most of Ukraine was incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic.
- 1917-1922: Ukraine experiences a period of revolution and civil war, with various factions vying for control.
- 1922: The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic is established as part of the Soviet Union.
- 1932-1933: The Holodomor, a man-made famine, devastates Ukraine, resulting in millions of deaths.
- 1986: The Chernobyl disaster highlights the environmental and human costs of Soviet policies in Ukraine.
- 1991: Ukraine declares independence following the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Areas of Control in Eastern Ukraine: A visual representation of the shifting territorial control, highlighting the contested regions and the dynamics of the conflict.
1.5. Post-Soviet Relations
Following Ukraine’s independence in 1991, relations with Russia were initially cooperative, but tensions gradually increased due to issues such as energy supplies, the status of the Russian-speaking population in Ukraine, and geopolitical orientation.
- 1990s: Ukraine and Russia maintain generally cooperative relations, but disagreements arise over issues such as the Black Sea Fleet and energy supplies.
- 2004: The Orange Revolution in Ukraine, which overturned a rigged presidential election, strained relations with Russia.
- 2008: Russia’s war with Georgia raised concerns in Ukraine about Russia’s willingness to use military force in the region.
- 2010: Viktor Yanukovych, a pro-Russian politician, is elected president of Ukraine, leading to closer ties with Russia.
2. Key Events Leading to the Current Conflict
Several key events have significantly escalated tensions between Russia and Ukraine, culminating in the current armed conflict. These events reveal the complex interplay of political, economic, and security factors that have fueled the crisis.
2.1. The Euromaidan Revolution (2013-2014)
The Euromaidan Revolution, also known as the Revolution of Dignity, was a series of protests and civil unrest in Ukraine that began in November 2013 in response to President Viktor Yanukovych’s decision to suspend preparations for the implementation of an association agreement with the European Union and instead seek closer economic ties with Russia.
- November 2013: Protests erupt in Kyiv after President Yanukovych rejects the EU Association Agreement.
- February 2014: Yanukovych is ousted from power following violent clashes between protesters and security forces.
- Aftermath: The Euromaidan Revolution led to a pro-Western government in Ukraine and a sharp deterioration in relations with Russia.
2.2. The Annexation of Crimea (2014)
In March 2014, following the Euromaidan Revolution, Russia annexed Crimea, a Ukrainian territory with a majority-Russian population, after a disputed referendum. This action was widely condemned by the international community as a violation of international law and Ukrainian sovereignty.
- March 2014: Russian forces occupy Crimea, and a referendum is held on the peninsula’s status.
- Result: The referendum results, widely disputed, showed a majority in favor of joining Russia.
- International Response: The annexation of Crimea was condemned by the United States, the European Union, and other countries, which imposed sanctions on Russia.
2.3. The War in Donbas (2014-Present)
Following the annexation of Crimea, pro-Russian separatists in eastern Ukraine, with alleged support from Russia, launched an armed insurgency against the Ukrainian government. This conflict, known as the War in Donbas, has resulted in thousands of deaths and widespread destruction.
- April 2014: Pro-Russian separatists seize government buildings in eastern Ukrainian cities and declare independence.
- Ongoing Conflict: The war in Donbas has continued for several years, despite several ceasefire agreements.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The conflict has caused a severe humanitarian crisis, with millions of people displaced and in need of assistance.
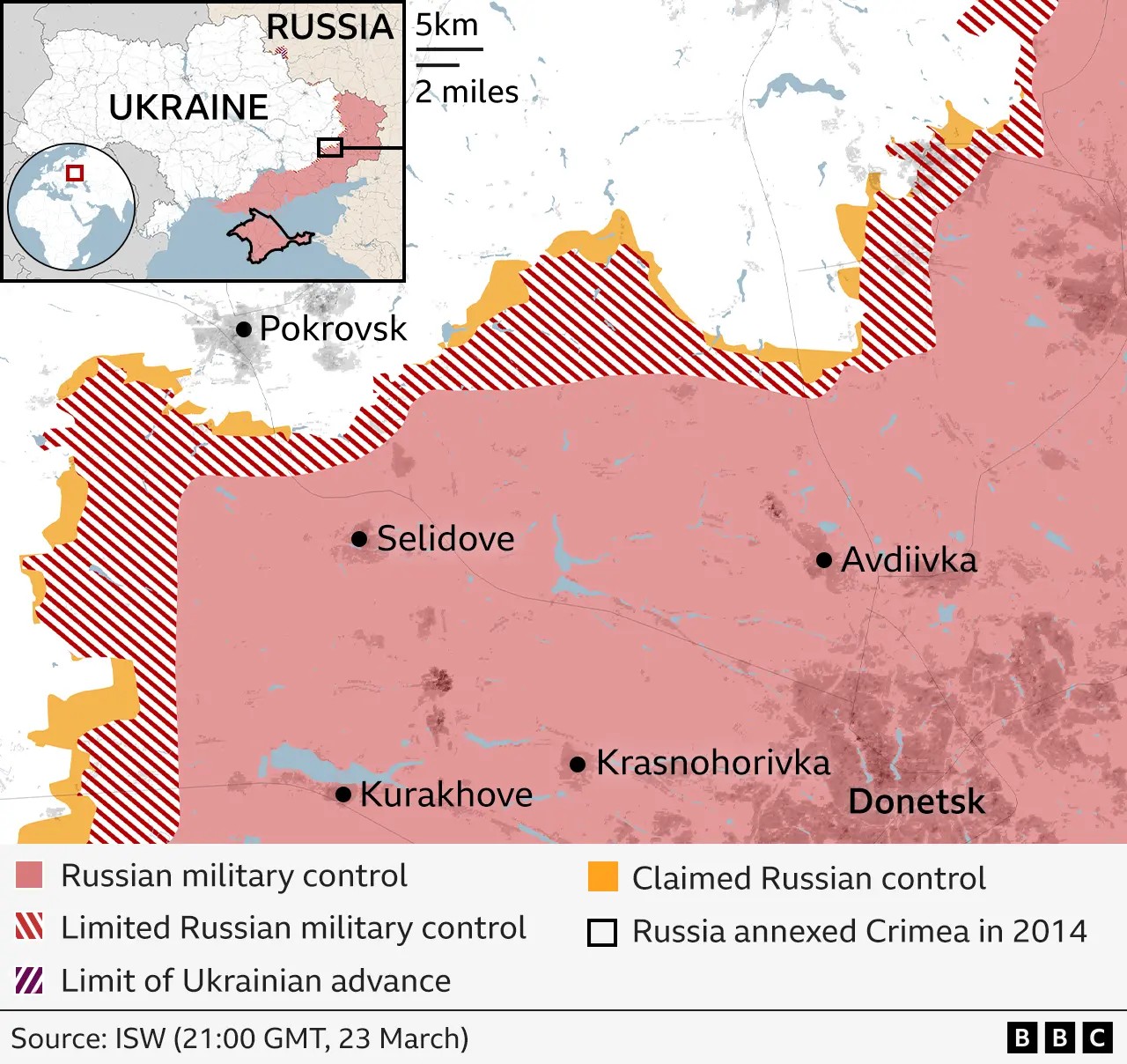
Donetsk Region Control: A detailed view of the Donetsk region, indicating the extent of Russian military control and the strategic importance of the area in the ongoing conflict.
2.4. Escalation of Tensions (2021-2022)
In late 2021 and early 2022, tensions between Russia and Ukraine escalated significantly, with Russia amassing troops along the Ukrainian border. Despite repeated denials, Russia eventually launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
- Late 2021: Russia begins to build up its military presence along the Ukrainian border.
- February 2022: Russia launches a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, marking a major escalation of the conflict.
- International Response: The international community has responded with condemnation, sanctions, and military assistance to Ukraine.
3. Motivations Behind Russia’s Actions
Understanding the motivations behind Russia’s actions is crucial for comprehending the conflict’s dynamics and potential pathways to resolution. Various factors, including geopolitical strategy, historical narratives, and domestic politics, have shaped Russia’s policies toward Ukraine.
3.1. Geopolitical Considerations
Russia views Ukraine as a strategically important country, both geographically and politically. Maintaining influence over Ukraine is seen as vital for Russia’s security and its role as a major power in the region.
- Buffer Zone: Russia considers Ukraine as a buffer zone between itself and NATO, seeking to prevent further expansion of the alliance eastward.
- Black Sea: Ukraine’s coastline on the Black Sea is strategically important for Russia’s naval power and access to the Mediterranean.
- Energy Transit: Ukraine is a key transit country for Russian gas exports to Europe, giving Russia leverage over European energy security.
3.2. Historical Narratives and Identity
Russia’s historical narratives play a significant role in shaping its views on Ukraine. Russia often portrays Ukraine as an integral part of Russian civilization and denies the legitimacy of Ukrainian national identity.
- Shared History: Russia emphasizes the shared history and cultural ties between Russia and Ukraine, portraying Ukrainians as “brotherly people.”
- “Russkiy Mir”: The concept of “Russkiy Mir” (Russian World) promotes the idea of a common Russian civilization that includes Ukraine and other countries with Russian-speaking populations.
- Denial of Ukrainian Identity: Some Russian politicians and intellectuals deny the existence of a distinct Ukrainian identity, viewing Ukrainians as simply Russians.
3.3. Domestic Political Factors
Domestic political factors also influence Russia’s actions toward Ukraine. The conflict can be used to rally domestic support, divert attention from internal problems, and consolidate President Putin’s power.
- Nationalism: The conflict can be used to appeal to Russian nationalism and patriotism, boosting support for the government.
- Diverting Attention: The conflict can divert attention from domestic problems, such as economic stagnation and corruption.
- Consolidating Power: The conflict can be used to justify authoritarian measures and suppress dissent, consolidating President Putin’s power.
Belgorod Border Advances: This map illustrates the advances along the border near Belgorod, highlighting the strategic locations and the intensity of the conflict in this area.
4. The Role of External Actors
The Russia-Ukraine conflict is not solely a bilateral issue; it involves various external actors with their own interests and agendas. The involvement of these actors has significantly shaped the conflict’s dynamics and potential outcomes.
4.1. The United States
The United States has been a strong supporter of Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity, providing military and financial assistance to the country. The U.S. also views the conflict as a challenge to the international rules-based order and a threat to European security.
- Military Aid: The U.S. has provided Ukraine with significant military aid, including weapons, equipment, and training.
- Financial Assistance: The U.S. has provided Ukraine with billions of dollars in financial assistance to support its economy and government.
- Diplomatic Support: The U.S. has been a vocal advocate for Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity, condemning Russia’s actions and working with allies to impose sanctions.
4.2. The European Union
The European Union has also been a strong supporter of Ukraine, providing economic and political assistance to the country. The EU views the conflict as a threat to its own security and stability and has imposed sanctions on Russia in response to its actions.
- Economic Assistance: The EU has provided Ukraine with significant economic assistance to support its economy and reforms.
- Political Support: The EU has offered Ukraine closer political ties, including an association agreement and visa-free travel for Ukrainian citizens.
- Sanctions: The EU has imposed sanctions on Russia, targeting individuals, companies, and sectors of the Russian economy.
4.3. NATO
NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, has increased its military presence in Eastern Europe in response to the conflict, seeking to reassure its members and deter further Russian aggression. However, NATO has ruled out direct military intervention in Ukraine, as Ukraine is not a member of the alliance.
- Increased Military Presence: NATO has increased its military presence in Eastern Europe, deploying additional troops, ships, and aircraft to the region.
- Reassurance Measures: NATO has taken steps to reassure its members, conducting military exercises and increasing its readiness to respond to any threats.
- No Direct Intervention: NATO has ruled out direct military intervention in Ukraine, but has provided support to the country through other means.
5. Humanitarian Consequences of the Conflict
The Russia-Ukraine conflict has had devastating humanitarian consequences, resulting in widespread displacement, casualties, and suffering. The conflict has also exacerbated existing social and economic problems in Ukraine.
5.1. Displacement and Refugee Crisis
The conflict has caused a massive displacement of people, with millions of Ukrainians fleeing their homes to seek safety in other parts of the country or in neighboring countries. This has created a major refugee crisis, with many countries struggling to cope with the influx of refugees.
- Internal Displacement: Millions of Ukrainians have been internally displaced, fleeing their homes in the east and south of the country to seek safety in the west.
- Refugees: Millions of Ukrainians have fled to neighboring countries, such as Poland, Romania, and Moldova, seeking refuge from the conflict.
- Humanitarian Assistance: International organizations and governments are providing humanitarian assistance to displaced people and refugees, including food, shelter, medical care, and other essential services.
5.2. Casualties and Human Rights Abuses
The conflict has resulted in thousands of casualties, including both military personnel and civilians. There have also been reports of human rights abuses, including war crimes, committed by both sides of the conflict.
- Civilian Casualties: The conflict has resulted in a large number of civilian casualties, with many people killed or injured by shelling, airstrikes, and other forms of violence.
- Human Rights Abuses: There have been reports of human rights abuses committed by both sides of the conflict, including extrajudicial killings, torture, and arbitrary detention.
- International Investigations: International organizations and governments are investigating alleged war crimes and human rights abuses committed during the conflict.
5.3. Economic and Social Impacts
The conflict has had a significant impact on the Ukrainian economy, disrupting trade, damaging infrastructure, and causing widespread unemployment. The conflict has also exacerbated existing social problems, such as poverty, inequality, and corruption.
- Economic Disruption: The conflict has disrupted trade, damaged infrastructure, and caused widespread unemployment, leading to a sharp decline in the Ukrainian economy.
- Social Problems: The conflict has exacerbated existing social problems, such as poverty, inequality, and corruption, making it more difficult for Ukrainians to meet their basic needs.
- Reconstruction Efforts: International organizations and governments are providing assistance to Ukraine to help rebuild its economy and infrastructure.
Kursk Region Regained Control: This map illustrates how Russia has regained control in the Kursk region following a Ukrainian offensive, highlighting the strategic shifts and territorial changes.
6. Potential Pathways to Resolution
Finding a resolution to the Russia-Ukraine conflict is a complex and challenging task, but several potential pathways could lead to a peaceful settlement. These pathways involve a combination of diplomacy, negotiations, and international pressure.
6.1. Diplomatic Negotiations
Diplomatic negotiations between Russia and Ukraine, with the involvement of international mediators, are essential for finding a peaceful resolution to the conflict. These negotiations could address issues such as territorial disputes, security guarantees, and the status of the Russian-speaking population in Ukraine.
- Direct Talks: Direct talks between Russian and Ukrainian officials are necessary to address the core issues of the conflict.
- International Mediation: International mediators, such as the United Nations, the European Union, or individual countries, can play a role in facilitating negotiations and helping to find common ground.
- Comprehensive Agreement: The goal of negotiations should be to reach a comprehensive agreement that addresses all of the key issues in the conflict and provides a framework for long-term peace and stability.
6.2. Ceasefire and De-escalation
A ceasefire and de-escalation of the conflict are crucial steps toward creating a more conducive environment for negotiations. This would involve both sides ceasing hostilities, withdrawing troops from the front lines, and implementing confidence-building measures.
- Ceasefire Agreement: A ceasefire agreement would commit both sides to cease all hostilities and refrain from using force.
- Troop Withdrawal: Troop withdrawal would involve both sides withdrawing their forces from the front lines and establishing a demilitarized zone.
- Confidence-Building Measures: Confidence-building measures, such as prisoner exchanges and joint patrols, can help to reduce tensions and build trust between the two sides.
6.3. International Pressure and Sanctions
International pressure and sanctions can be used to encourage Russia to change its behavior and comply with international law. This would involve maintaining existing sanctions, imposing new sanctions if necessary, and working with allies to isolate Russia diplomatically.
- Maintaining Sanctions: Maintaining existing sanctions on Russia can help to weaken its economy and limit its ability to finance the conflict.
- Imposing New Sanctions: Imposing new sanctions on Russia can increase the pressure on the country to change its behavior.
- Diplomatic Isolation: Working with allies to isolate Russia diplomatically can send a strong message that its actions are unacceptable.
7. The Future of Russia-Ukraine Relations
The future of Russia-Ukraine relations is uncertain, but it is likely to be shaped by the outcome of the current conflict and the broader geopolitical context. Several possible scenarios could unfold, ranging from continued conflict to eventual reconciliation.
7.1. Continued Conflict
One possible scenario is that the conflict continues for the foreseeable future, with neither side able to achieve a decisive victory. This could lead to a protracted war of attrition, with ongoing violence, instability, and humanitarian suffering.
- Stalemate: The conflict could reach a stalemate, with neither side able to make significant gains on the battlefield.
- Proxy War: The conflict could become a proxy war between Russia and the West, with both sides providing support to their respective allies.
- Regional Instability: The conflict could destabilize the entire region, leading to increased tensions and conflicts in other countries.
7.2. Frozen Conflict
Another possible scenario is that the conflict becomes a frozen conflict, with a ceasefire agreement but no resolution to the underlying issues. This could lead to a long-term situation of instability and uncertainty, with the potential for renewed conflict at any time.
- No Resolution: The underlying issues of the conflict, such as territorial disputes and security guarantees, remain unresolved.
- Instability: The situation remains unstable, with the potential for renewed conflict at any time.
- Limited Cooperation: There is limited cooperation between Russia and Ukraine, with ongoing tensions and mistrust.
7.3. Eventual Reconciliation
A more optimistic scenario is that Russia and Ukraine eventually find a way to reconcile and build a more peaceful and cooperative relationship. This would require both sides to address the underlying issues of the conflict, build trust, and find common ground.
- Addressing Underlying Issues: Both sides address the underlying issues of the conflict, such as territorial disputes and security guarantees.
- Building Trust: Both sides take steps to build trust, such as implementing confidence-building measures and engaging in cultural exchange.
- Finding Common Ground: Both sides find common ground on issues of mutual interest, such as trade, energy, and environmental protection.
Sudzha Region Control: A before-and-after view of the Sudzha region, illustrating the shift in control from Ukraine in August 2024 to Russia in March 2025, highlighting the dynamics of territorial gains and losses.
8. Expert Opinions on the Conflict
To provide a comprehensive understanding of the conflict, it is important to consider the opinions of experts from various fields, including political science, international relations, and military analysis. These experts offer valuable insights into the causes, dynamics, and potential outcomes of the conflict.
8.1. Political Science Perspective
Political scientists emphasize the role of power politics, geopolitical competition, and national interests in shaping the conflict. They argue that Russia’s actions are motivated by a desire to maintain its influence in the region and prevent further encroachment by the West.
8.2. International Relations Perspective
Experts in international relations focus on the role of international law, norms, and institutions in the conflict. They argue that Russia’s actions violate international law and undermine the international rules-based order.
8.3. Military Analysis Perspective
Military analysts assess the military capabilities of both sides, the strategic importance of the contested territories, and the potential for escalation. They provide insights into the military dynamics of the conflict and the potential for future developments.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Russia-Ukraine conflict, providing concise answers to common queries:
Q1: What are the main causes of the Russia-Ukraine conflict?
The main causes include historical tensions, geopolitical competition, and Russia’s desire to maintain influence over Ukraine.
Q2: What is the current status of the conflict?
The conflict is ongoing, with active fighting in eastern and southern Ukraine.
Q3: What is the role of NATO in the conflict?
NATO has increased its military presence in Eastern Europe but has ruled out direct military intervention in Ukraine.
Q4: What are the humanitarian consequences of the conflict?
The conflict has resulted in widespread displacement, casualties, and human rights abuses.
Q5: What are the potential pathways to resolution?
Potential pathways include diplomatic negotiations, a ceasefire and de-escalation, and international pressure and sanctions.
Q6: What is the future of Russia-Ukraine relations?
The future is uncertain, with possible scenarios ranging from continued conflict to eventual reconciliation.
Q7: How has the conflict impacted the global economy?
The conflict has disrupted global supply chains, increased energy prices, and contributed to inflation.
Q8: What is the role of the United Nations in the conflict?
The United Nations has been involved in humanitarian assistance, monitoring human rights, and attempting to mediate a peaceful resolution.
Q9: What is the significance of Crimea in the conflict?
Crimea was annexed by Russia in 2014 and remains a point of contention between Russia and Ukraine.
Q10: How can individuals support humanitarian efforts in Ukraine?
Individuals can support humanitarian efforts by donating to reputable organizations providing assistance to Ukrainians affected by the conflict.
10. Stay Informed with WHY.EDU.VN
The Russia-Ukraine conflict is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications. Staying informed about the latest developments and understanding the underlying causes and dynamics of the conflict is crucial for making sense of this crisis.
WHY.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with accurate, reliable, and up-to-date information on the Russia-Ukraine conflict, as well as expert analysis and insights from leading experts in the field. We strive to present a balanced and objective view of the conflict, taking into account the perspectives of all sides.
We encourage you to explore our website, WHY.EDU.VN, to learn more about the Russia-Ukraine conflict and other important global issues. You can find in-depth articles, analysis, and multimedia resources that will help you stay informed and engaged.
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about a particular aspect of the conflict, please don’t hesitate to contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States or via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Our team of experts is always available to provide you with the information and insights you need. Visit our website WHY.EDU.VN.
Are you seeking clarity on a specific topic or eager to expand your knowledge? Don’t hesitate! Visit why.edu.vn today and pose your questions to our team of experts. Let us be your guide in navigating the complexities of our world.